The optimal time to start a short IVF protocol is 2-3 days into the new monthly cycle. Its average duration is 28-30 days.
Taking drugs to ensure superovulation in a short protocol lasts approximately two weeks. The scheme assumes that within two weeks the patient will have several dominant follicles mature. Short stimulation regimens block the natural synthesis of FSH and LH. Then the doctor prescribes medications containing similar hormones, only of synthetic origin. As a result, after 15 days, 10-15 oocytes mature in the female genital organs. In the short protocol, a complete blockade of the hormone-synthesizing function of the gonads is not carried out.
The growth of follicles and endometrium is monitored by ultrasound scanning. Research is carried out every day. During short stimulation, the follicles should increase by 2 mm daily, and the thickness of the uterine mucosa by 1 mm. If for some reason the numbers fall below normal, the scheme is revised.
Differences between a short protocol and a long one
Short protocol
carried out against the background of the patient’s natural hormonal balance. IVF begins immediately with the prescription of medications that stimulate the maturation of several eggs at the same time. With a long protocol, reproductive specialists block the action of the body's natural hormones, achieving artificial menopause, and then prescribe drugs that stimulate ovarian function. As a result, the growth of follicles and the uterine mucosa becomes completely controlled, and doctors are able to synchronize these processes. The duration of a short IVF regimen is up to 30 days, long - 45.
The choice of IVF regimen is influenced by the patient’s age, the reasons for the impossibility of natural conception, the condition of the woman’s genital organs, as well as medical history. If a couple has a history of unsuccessful attempts, the doctor will likely recommend a short protocol.
Read more about the stages of in vitro fertilization in this material - note. altravita-ivf.ru
What awaits patients?
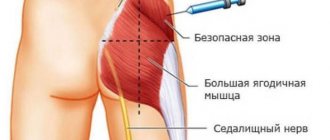
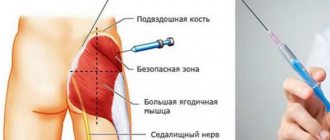
Stimulation of superovulation begins 2-5 days after the onset of menstruation (if a long protocol is chosen, it starts at the end of the cycle). The woman is prescribed gonadotropins, which must be administered subcutaneously. As a rule, injections are made into the fat fold on the abdomen with a syringe with a thin needle or a special pen. Gonadotropin is administered strictly at the same time. At the same time, estrogen is taken, which is necessary for the growth of the endometrium. Blood thinners and vitamins may also be prescribed. The growth of follicles is monitored by ultrasound every 3-4 days.
As soon as the reproductive specialist sees that the oocytes have matured, that is, they have grown to the desired size (the indicator is individual for each patient, but usually it is about 20-22 mm), an ovulation trigger is introduced. And exactly 36 hours later, follicle sampling is scheduled and seminal fluid is donated. A woman is given progesterone-containing drugs to support the second phase of the cycle.
The sampling takes place under general anesthesia and takes 15-30 minutes. Then the patient is given a couple of hours to rest in the ward and sent home. At this time, embryologists get down to business. They select mature eggs, combine them with sperm and monitor their development. If the embryos are weak, the transfer is scheduled on the third day after puncture. If strong - on the fifth or sixth. The remaining embryos are disposed of or frozen.
The transfer takes place without anesthesia, under ultrasound control. The embryo is transferred in a drop of liquid in which it developed. It is placed between the layers of the endometrium. This completes the IVF protocol. The couple just has to wait for the results of the hCG blood test. It is prescribed 12-14 days after embryo transfer.
Medicines used
The protocol uses the following groups of drugs:
- gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists - drugs compete with natural hormones and block the action of the pituitary gland - are prescribed from the first days of the protocol;
- ovulation stimulants - potentiate the maturation of several follicles in the ovaries at the same time;
- ovulation inducers - hCG - stimulate the ovulation process;
- Progesterone preparations - support the luteal phase of the cycle and promote implantation of the fertilized egg.
If the IVF regimen is successfully completed, progesterone is recommended to be taken throughout the first trimester.
Answers to popular questions
What is done after follicle puncture during IVF?
After 4-6 days, the woman undergoes an embryo implantation procedure. One or two viable blastocysts are transferred into the uterine cavity using a catheter. The effectiveness of IVF is assessed after 2 weeks using laboratory tests. After another 1-2 weeks, an ultrasound is performed to assess the location of the ovum and exclude ectopic pregnancy.
Is it possible to eat on the day of the puncture?
If the procedure is planned to be performed under general anesthesia, you should not eat food. The last meal should take place the night before.
Is it possible to perform a puncture without anesthesia?
The use of anesthesia is advisable, even if follicle puncture occurs during IVF in a natural cycle. In this case, it is necessary to obtain an aspirate from 2-3 follicles. The manipulation takes a few minutes and is accompanied by minor discomfort. The reason for refusing anesthesia may be the patient’s allergy to drugs.
At the SM-Clinic Reproductive Health Center, all types of procedures are performed as part of the IVF program in accordance with advanced protocols. Contact the Center's reproductive specialists to realize your dream of motherhood!
Indications and contraindications
The short protocol is indicated in the following cases:
- woman's age over 35 years;
- regular menstrual cycle;
- male factor infertility with preserved female fertility;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- an unsuccessful attempt in a long IVF protocol.
The condition required for entry into the short protocol program is sufficient ovarian reserve.
Contraindications to the protocol are endometriosis, fibroids, endometrial hyperplastic diseases, irregular menstrual cycle, lack of ovulation, depletion of ovarian reserve.
Preparation for the procedure
Lifestyle for both spouses
In order for the body to be ready for such a procedure as embryo transfer and the upcoming pregnancy, it is necessary to maintain a healthy lifestyle. The diet should be varied, rich in vitamins, proteins, containing a moderate amount of fats, as well as carbohydrates. No strict diets. When you need to donate blood for biochemical or hormonal studies, you can have breakfast only after drawing blood. It is recommended to take vitamin and mineral complexes intended for pregnant women. An alternative is to take folic acid, potassium iodide, and vitamin E in small doses a month before the start of the program. Avoid taking medications that are contraindicated during pregnancy. Smoking, even passive smoking, should be avoided. You should not drink more than two cups of coffee per day, and alcohol consumption should be kept to a minimum. Avoid hot baths, steam baths, saunas. Try to lead an active, mobile lifestyle. Try to ensure that the treatment has as little impact on your mood as possible. Avoid significant stress, as well as physical or psychological stress. After embryo transfer, the importance of a healthy lifestyle increases even more
Sexual contacts
The general nature of sexual activity during the in vitro fertilization procedure should not change. You can have sex with the same frequency as always. But you need to abstain from sexual intercourse for 3-4 days so that your husband can accumulate a sufficient amount of sperm. Also, the spouse should refrain from masturbation. Abstinence should continue for about seven days until the day of embryo transfer arrives. Sexual intercourse after embryo transfer should be avoided until pregnancy tests show that the embryo has been successfully implanted and the embryo is developing properly. Both spouses should try to avoid casual sex. Detected genital infections must be treated, so subsequent sexual intercourse should be carried out with a condom. When in vitro fertilization is performed, after embryo transfer, pain during sexual intercourse is possible due to enlarged ovaries.
Minimum preliminary examination
When you are indicated for an IVF procedure or embryo transfer, a number of studies can be done at your place of residence. Find out the required minimum examinations. Usually this is a spermogram of the spouse, a hormonal analysis, an image of the uterus, fallopian tubes, a blood test, and a vaginal smear analysis for the presence of infectious diseases. When you come to your initial appointment with a doctor, do not forget to take with you all the available results of previous examinations, extracts from medical records, etc. All this will be needed for the embryo implantation to be successful. Infections Before the procedure, it may be necessary to be examined for some infections that, after embryo transfer, pose a danger to the embryo and have a negative impact on its development, as well as on the pregnancy. These include, for example, herpes, cytomegalovirus, rubella, toxoplasmosis. These infections are widespread, but often occur hidden. The scope of diagnosis is determined by the attending physician.
Hormonal examination Often, infertility is accompanied by hormonal abnormalities. Their timely detection, as well as correction, can increase not only the likelihood of pregnancy after embryo transfer, but also the chances of its favorable course. Most hormones are tested from days 1 to 5 of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, the first visit should occur during this period. Blood is donated from a vein, usually in the morning, on an empty stomach.
Visit to an andrologist, sperm examination
Treatment of infertility with IVF involves a mandatory examination by an andrologist, including sperm testing. Before a sperm analysis, the spouse must follow some rules: abstain from sexual activity for 3 to 7 days (optimally 5), do not drink alcohol, do not take steam, no hot baths, do not urinate for two hours before visiting the doctor, eat only low-fat, non-spicy foods.
Planning visits to the doctor Treatment with IVF and embryo transfer takes place on an outpatient basis, but requires discipline and punctuality from patients. Before starting the program, plan your activities so that you do not have night shifts so that you can undergo ovulation stimulation (for 2-4 weeks), and then come for puncture and embryo transfer on the day of embryo implantation. The presence of the husband is required for a preliminary examination and sperm donation during follicle puncture. After the embryo transfer, you will be issued a sick leave certificate.
Agreements If you are planning to start treatment with IVF or other methods of assisted reproduction, which include ICSI, artificial insemination, fertilization with donor sperm, egg donation, surrogacy, then first decide with your doctor all the ethical and legal issues that concern you. For each type of treatment, a legal agreement is concluded with the clinic, which must be signed by both spouses.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the protocol include:
- good tolerance;
- can be used for any type of infertility;
- minimal number of complications, in particular ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome;
- no age restrictions;
- lower cost compared to a long protocol.
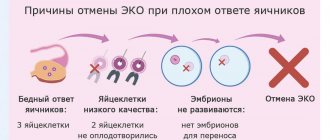
The short protocol has few disadvantages. The first is the relatively high probability of spontaneous ovulation. In this case, the circuit is interrupted. You can return to stimulation after a few months. Secondly, reproductive specialists are not always able to obtain a sufficient number of healthy eggs.
Postoperative period and recovery
Women undergoing oocyte retrieval should not worry. You should not be afraid of pain, since the maximum that is felt is the insertion of a catheter into a vein by the anesthesiologist. Recovery from anesthesia occurs over several hours, which the patient spends in the clinic. At this stage, you feel distracted attention, weakness, and slight dizziness. These disorders resolve quickly, so the patient usually goes home. It is recommended to be accompanied by relatives or friends, since anesthesia drugs are still present in the blood, and driving under their influence is prohibited.
Manipulations during egg retrieval are low-traumatic, so there is most often no serious pain in the postoperative period. There may be nagging pain when moving, small traces of blood on the underwear. Your doctor may prescribe painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs at first.
Complications after puncture are very rare. But still, if the patient feels severe pain in the lower abdomen, vestibular disorders, or excessive weakness, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. Most often these are symptoms of internal bleeding. Compliance with all the rules for this procedure reduces the likelihood of such a complication to very low.
After puncture, during the first few days, patients may experience ovarian hyperstimulation. This syndrome is accompanied by nausea, pain in the lower abdomen, and bloating. In some cases, the body reacts with vomiting, urinary retention, constipation or diarrhea. The presence of such symptoms should be reported to your doctor.
The patient is recommended to spend the first day after surgery lying down. It’s best to sleep, don’t do homework, don’t lift anything, or bend over too much.
Preparation
Preparation is no different from that for other types of IVF.
Before entering into the short protocol scheme, future parents undergo a comprehensive examination, which includes:
- consultation with an endocrinologist;
- study of fallopian tube patency (hysterosalpingography;
- blood test for group and Rh factor;
- general blood analysis;
- biochemical screening;
- general urine analysis;
- testing for HIV, viral hepatitis, syphilis;
- blood test for sex hormones, thyroid hormones;
- smears for pathological flora;
- cytological examination of scrapings from the cervix;
- examination for hidden infections - chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, herpes, cytomegalovirus;
- consultation with a therapist;
- fluorography;
- Breast ultrasound or mammography.
Before IVF, a man must undergo a spermogram, a urethral smear for pathological flora, a blood test for HIV, syphilis, viral hepatitis B and C. He also needs to be examined for infectious diseases of the reproductive system.
HCG injection during natural pregnancy
HCG during natural pregnancy can be prescribed in case of ovulation disorders and to support an already existing pregnancy. If ovulation is disrupted or absent (anovulation), pregnancy, accordingly, cannot occur. In the absence of maturation of full-fledged eggs in the ovaries, women stimulate ovulation with hormonal drugs. The goal of hormonal therapy is the formation in the female body of eggs that are capable of fertilization.
There are many hormonal drugs for ovarian stimulation, but you should not prescribe them yourself or on the advice of friends or relatives. The name, dosage of drugs and course duration are strictly prescribed by the attending physician. Otherwise, you may get a completely different result than you expected. Especially in cases where the cause of ovulation disorders has not been established.
Before prescribing hormonal therapy, a woman undergoes a hormone test.
Based on the blood results for thyroid hormones, male hormones (testosterone, dihydroepiandrosterone sulfate, androstenedione), prolactin, the issue of starting hormonal therapy is decided. If the level of these hormones is not normal, then stimulation of ovulation is postponed until they normalize. Perhaps, natural ovulation will be restored.
Also, to determine the causes of ovulation disorders, a woman is prescribed an ultrasound examination. The first ultrasound is performed on days 8-10 of the cycle with a duration of 28 days. Then ultrasound is done every 2-3 days. As a result of such a study, deviations in the process of egg maturation are revealed. And based on the results, treatment is prescribed, if necessary.
If the cause of anovulation is failure to open the follicle, then the woman is given an injection of hCG, which stimulates the ovulation process. After an HCG injection, ovulation occurs within 24-36 hours. Ovulation is confirmed by ultrasound. The couple can then engage in sexual intercourse to conceive a child. The frequency of sexual intercourse will depend on the man’s spermogram. If the indicators are normal, then it is enough to have sexual intercourse every other day. You can also do it every day, starting from the date of the hCG injection until the onset of pregnancy in this menstrual cycle.
Scheme of a short IVF protocol by day
The first stage of the protocol is stimulation of superovulation. It can be carried out with agonist hormones or antagonist hormones . On the second day of the menstrual cycle, a woman is prescribed medications that inhibit the gonadotropic function of the pituitary gland. WITH
From the third day, the actual stimulation of superovulation begins - the patient is injected with human menopausal gonadotropin, which contains two hormonal substances - LH and FSH. When the follicles reach a diameter of 18-20 mm, and the thickness of the uterine mucosa becomes more than 8 mm (11-16 days of the protocol), the woman is given an hCG injection . The injection must be given at a strictly prescribed time. It triggers the maturation of follicles. In addition, under the influence of human chorionic gonadotropin, the oocyte detaches from the follicular wall and floats freely in its fluid, so that the egg can be extracted.
One and a half days after the hCG injection, they proceed to the next stage of the protocol - puncture. The manipulation is performed on an outpatient basis in a small operating room. It is very important to follow the deadlines and do the puncture 36 hours after the hCG injection. Being late is fraught with spontaneous ovulation, while puncture too early risks getting immature eggs unsuitable for IVF.
So, what preparation is done before follicle puncture?
Despite the short duration of the procedure itself, it requires careful adherence to certain rules.
- During stimulation, you must try to lead a healthy lifestyle. This refers to the ban on smoking and alcohol, abuse of spicy and fatty foods. It is advisable to limit excessive physical activity.
- Try to avoid viral and infectious diseases, and prevent exacerbation of chronic processes, if any.
- Do not take medications without the knowledge of a fertility specialist.
- Food should be rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Avoid sexual activity 3-5 days before the puncture.
- With an accuracy of no more than 10-15 minutes, enter the so-called. trigger the final maturation of the follicles, trying not to lose a drop of solution. For this purpose, human chorionic gonadotropin is usually used (there are other options), which is administered 34-36 hours before the puncture. A trigger is prescribed when the majority of follicles reach 18mm in diameter. Strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions in the stimulation protocol, especially the time of trigger introduction, is one of the most important conditions for successful egg retrieval.
- If anesthesia is required, the puncture is performed on an empty stomach, so eating before the procedure is prohibited. The need for anesthesia (pain relief) is discussed on the day of the trigger appointment.
How is the follicle puncture procedure performed during IVF?
The day and time of puncture is determined by the reproductologist when prescribing a trigger. The start time of the manipulation is selected to the nearest minute and delay in starting the procedure is undesirable. On the day of the puncture, you need to be at the clinic 30-40 minutes before the start - in order to have time to fill out documents, change clothes and “settle in” at the day hospital, and have time to discuss the type of anesthesia with the anesthesiologist. In most cases, intravenous anesthesia is chosen, so you need to come to the puncture with an empty stomach. If there are few follicles (no more than 3), it is permissible to perform the operation without anesthesia.
The duration of the operation is from several minutes to half an hour and depends on the number of punctured follicles and technical difficulties (for example, related to the location of the ovary). The patient awakens in the operating room and is transferred to the day hospital. In case of successful collection (collection) of eggs, the spouse is invited to donate sperm.
Reasons for deviation of hCG from the norm
Very often, during IVF, several blastocysts are implanted into the body of the expectant mother at once. In this way, it is possible to increase the chances of implantation of at least one embryo into the uterine wall. In some cases, implantation of all blastocysts implanted in the uterus is observed, which leads to multiple pregnancies. In such a situation, during a blood test, the hormone content in the plasma is high.
Low hCG
If hCG slowly increases after IVF, this may indicate the following conditions:
- fetal freezing;
- threat of spontaneous abortion;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Tests are taken at least 2-3 times to determine the dynamics of increase or decrease in plasma hormone levels. If it is in a borderline state, the expectant mother is prescribed hormone injections. Maintaining hCG at normal levels reduces the risk of miscarriage.
A sharp decrease in hCG
After IVF, the likelihood of fetal death is high, so the level of gonadotropin in the blood is monitored until the 2nd trimester. A critical decrease in hCG levels is a good reason to seek help from a fertility specialist.
Important! To eliminate the possibility of high error in the results of the hCG test, it is recommended that tests be taken in the same laboratory.
Hormonal instability increases the risk of miscarriage or pathological intrauterine development of the fetus. If such a problem is detected, the woman is sent to the hospital for conservation. Artificially maintaining hormonal balance helps prevent miscarriage and normalize the course of pregnancy.