Ovulation formula
Knowing when ovulation occurs is important for resolving two issues: if a woman wants to get pregnant or if a woman chooses a calendar method of birth control. The fertile period—the period when fertilization can occur—lasts approximately six days: five days before ovulation and the day of ovulation. The highest probability of conception is within two days before and on the day of ovulation.
Calculating the day of ovulation mathematically makes sense if you have a very clear and stable menstrual cycle. The length of the first phase of the cycle varies. The second phase is more stable and lasts 14 days. Accordingly, to calculate the day of ovulation, you need to subtract 14 from the cycle length. In an ideal 28-day cycle, ovulation occurs exactly in the middle: 28-14 = 14. In a short cycle it will occur earlier: for example, with a cycle length of 24 days, ovulation will occur approximately on the 10th day. In the long one - later: 33-14 = 19. For women whose menstrual cycle fluctuates by several days, the formula becomes more complicated: you need to take into account the duration of both the shortest and longest cycle, and calculate the average. Still, the figure will only be approximate.
A woman can determine days favorable for conception if she pays attention to the changes that occur to her on certain days of the cycle. These changes are most noticeable in the lining of the uterus and cervix.
Drug stimulation of ovulation
In fertility clinics, for a successful pregnancy when using IVF, a procedure such as ovulation stimulation is prescribed. The procedure is quite serious and requires maximum attention from the clinic’s specialists and the woman herself. Therefore, expectant mothers need to know about the process of stimulating ovulation, indications and contraindications for it.
Indications for ovulation stimulation
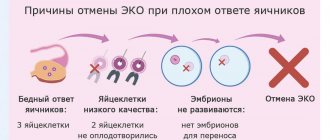
In some cases, the cause of infertility may be the absence of ovulation, irregular and rare ovulations, or impaired follicle maturation. This is mainly due to pathology of the endocrine organs and the hypothalamic-pituitary system, in particular. Primary ovarian failure also occurs, in which the level of FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) is increased, but for various reasons, follicles do not form in response to natural hormonal stimulation. With these pathologies, women are advised to stimulate ovulation using various drugs.
The stimulation procedure is also included in the in vitro fertilization protocol and is used to obtain eggs, which will subsequently be extracted for fertilization in the laboratory. However, in this case, this is only possible for women who, when stimulated, can form healthy follicles.
How is drug stimulation performed?
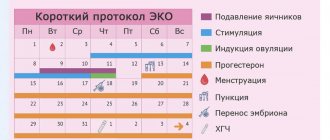
There are several schemes for stimulating ovulation, prescribed in different cases of infertility.
1. The first regimen involves taking direct gonadotropins. These drugs stimulate the production of hormones in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, which will subsequently enhance the functioning of the ovaries. Thus, stimulation of ovulation by Clostilbegit will ensure the maturation of the follicles necessary for fertilization. Usually this procedure is prescribed on the third or fifth day of the menstrual cycle. The drug is taken for five days, after which ultrasound monitoring of follicle maturation is carried out every two or three days.
When the follicles reach approximately 18-20 mm, the woman is prescribed Pregnil (human chorionic gonadotropin), which acts similarly to the LH hormone, that is, it promotes ovulation. In most cases, ovulation after Pregnil occurs within a day. If, after stimulating ovulation with Clostilbegit, fertilization is planned naturally, then full sexual intercourse is recommended within the next day from the moment of taking hCG. If a woman has been prescribed IVF, then mature follicles are selected for the subsequent stages of the procedure.
To increase the likelihood of implantation and maintaining pregnancy, the expectant mother is prescribed progesterone preparations from the 16th day of the menstrual cycle. It is worth noting that the entire process of stimulating ovulation with the help of Clostilbegit and its analogues (Clomiphene citrate, Clomid) must be carried out under constant ultrasound monitoring, which is performed at least once every two to three days.
2. In the second scheme, Follitropin (recombinant FSH) preparations are used instead of Clostilbegit to stimulate ovulation. These remedies are indicated when Clomiphene citrate (Clomid) is ineffective and does not give the expected results. Follitropin is prescribed on the second day of the menstrual cycle by injection and under mandatory ultrasound monitoring. By the beginning of the second week of the cycle, when the follicles have reached the required size, the woman is prescribed Pregnil, and is also recommended to have sexual intercourse after it. To consolidate the effect, it is recommended to take progesterone preparations from the 1st sixteenth day.
3. The third scheme for stimulating ovulation consists of a combination of Clostilbegit, taken from the third to fifth day for five days, and gonadotropins, used over the next five days. Further stages of stimulation are no different from the previous ones, and the entire procedure must also be carried out under ultrasound supervision.
After stimulating ovulation with Clostilbegit or gonadotropins, a day before the start of the next menstrual cycle or after a week of delay, you must take a pregnancy test and subsequently donate blood for hCG. It is also necessary to do an ultrasound examination to confirm pregnancy and monitor the condition of the ovum.
Contraindications
Drug stimulation has a fairly high probability of successful ovulation and subsequent pregnancy in the case of natural fertilization. However, this procedure has its side effects and contraindications.
It is not recommended to use ovulation stimulation after thirty-six years of age due to depletion of follicle reserves. It is also impossible to stimulate the ovaries in case of tubal obstruction, diseases of the uterus, inflammatory and infectious processes, pregnancy and lactation. It is not advisable to carry out the procedure if there is male factor infertility.
In addition, there is a limit on the number of stimulations of ovulation with Clostilbegit and other similar drugs (no more than six in a lifetime). This is due to the fact that the pool of follicles in the ovaries can quickly become depleted when using such drugs.
It is worth considering contraindications and side effects of drugs intended for stimulation. One of the most common side effects is ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, which is characterized by symptoms such as nausea, stool upset, decreased blood pressure, vomiting and others. There are also known cases of ectopic pregnancy that occurred after stimulation.
Drug stimulation of ovulation is a rather complex and dangerous procedure that must be carried out under the careful supervision of experienced specialists. At the Nalchik IVF Center, highly qualified reproductologists, embryologists and ultrasound doctors will perform stimulation with special attention and an individual approach to each woman. Thanks to their work and advanced technologies, the probability of pregnancy is quite high and comparable to leading European clinics. The center also helps older patients after thirty-six years old to see their long-awaited child.
Slime
The glands of the cervix produce mucus. It is usually thick: a real plug that closes the cervical canal and prevents infections from passing into the uterus. In such thick mucus, sperm quickly lose mobility and it is difficult for them to ascend into the uterine cavity. But the main (dominant) follicle growing in the ovary, from which the egg will be released, produces the hormone estradiol. The more estradiol, the more cervical mucus becomes and the thinner it is. On the eve of ovulation, it becomes stretchable, like egg white. For some women, this sticky clear discharge in the middle of the cycle is very noticeable. For some - a few days before ovulation, for others - only on the day of ovulation itself. It's individual.
Methodology
First, an ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the follicular apparatus. When using a long regimen, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists are started in advance. In all other cases, from about the 2-3rd day, gonadotropins are introduced, which promote the growth of several follicles at once. At the same time, GnRH agonists or antagonists are used to block premature ovulation. When the follicles are 18-20 mm in size, an ovulation trigger is introduced. They contribute to the separation of the egg-bearing tubercle, containing the female reproductive cell, from the wall of the follicle.
Approximately 34-36 hours later, an ovarian puncture is performed to obtain follicles. In laboratory conditions, eggs are aspirated from the follicle and fertilized with sperm, the embryo is incubated and then implanted into the uterine cavity. After the puncture, the woman begins taking progesterone medications.
Pain
Ovulation may be indicated by pain in the lower abdomen on days of the cycle that are not associated with menstrual bleeding. The pain can be in the lower abdomen in the center or on the right/left - depending on which ovary the dominant follicle matures in. The pain is often nagging in nature. It may be accompanied by slight bloating or a feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen. At first the pain is minor, but over the course of a couple of days it may intensify. These pains are associated with an increase in the level of biologically active substances in a woman’s body before ovulation - prostaglandins. Prostaglandins dissolve the follicle wall and ovarian tissue so that the egg can be released into the abdominal cavity, and from there enter the fallopian tube. A “side effect” of prostaglandins is pain. Just like a change in the nature of cervical mucus, pain associated with ovulation can occur only on the day of ovulation itself or be noted on the eve of ovulation and even a day or two after it.
Indications for injection
Ask your gynecologist when ovulation occurs after an hCG injection. Here, a lot depends on the amount of active substance and the individual characteristics of the expectant mother’s body.
HCG injections for ovulation are made from a protein structure contained in the urine of a woman carrying a baby. The substance can activate the natural production of sex hormones. HCG for injection can have different medical names - Menogon, Novarel, etc. The doctor performs an injection with a special insulin syringe into the groin area. The main indications for such a procedure can be considered:
- Pathologies accompanied by ovarian dysfunction.
- Painful periods, clear signs of PMS.
- Infertility is associated with the lack of release of an egg or the formation of a dominant follicle.
- Suppression of the corpus luteum.
- Frequent cases of spontaneous abortion.
- Stimulation of the formation of an active egg during preparation for the IVF protocol.
How to understand that pain is associated with ovulation
It is important to understand that pain in the lower abdomen can be associated with much less pleasant reasons than ovulation.
How to understand that this is exactly “it”.
- The pain lasts 1-3 days and goes away on its own.
- The pain is repeated in several cycles.
- About 14 days after such pain, the next menstruation comes.
Pain during ovulation is moderate and does not require painkillers. Severe pain indicates a health problem. If the pain is severe on the days of expected ovulation, you should consult a gynecologist. Other alarming symptoms that accompany pain in the lower abdomen and which may indicate a problem with the uterus and appendages: increased body temperature, increased discharge (leucorrhoea) from the genital tract, change in color of leucorrhoea from transparent or white to yellow-green, bloody discharge. By the way, taking painkillers and NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) on the days of expected ovulation or shortly before ovulation can reduce the chances of conception.
Possible complications
In most cases, ovulation induction occurs without any complications. However, in 5-10% of cases a mild form of hyperstimulation syndrome may develop. The early form appears a few days (usually 48 hours) after the induction of ovulation, and the late form appears 10 days or more later. For early diagnosis, it is important for a woman to evaluate her sensations during stimulation. The first signs are:
- nausea;
- abdominal pain, especially in the groin areas (projection area of the ovaries);
- slight increase in abdominal circumference.
These symptoms develop due to an increase in vascular permeability and the release of plasma into the extravascular bed under the influence of hormonal therapy. If the condition is not noticed in time, then the fluid begins to leak into the pleural cavity - shortness of breath appears. A decrease in the volume of circulating plasma leads to a decrease in filtration in the kidneys, therefore the amount of urine excreted decreases. These are alarming symptoms that may indicate severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. This condition increases the risk of thromboembolic complications. Therefore, if you notice any discomfort during stimulation, you should immediately contact your doctor. Timely initiation of therapy makes the use of assisted reproduction methods safe and effective.
Home test
Ovulation can be determined using a home test, which is sold at the pharmacy. The principle of the study is based on determining the concentration of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the urine. LH levels in women fluctuate depending on the period of the menstrual cycle. Immediately before ovulation it reaches its maximum values. An ovulation test makes it possible to register the peak of LH release into the blood. After the maximum LH surge, ovulation occurs within the next 36 hours. Therefore, with a positive ovulation test, this and the next day are the most favorable for conception.
Folliculometry
This is a series of ultrasound examinations performed over one or more menstrual cycles. During folliculometry, the growth of follicles and changes in the endometrium are assessed according to the day of the menstrual cycle, and the fact of ovulation is also stated. The average size of the dominant follicle at which ovulation can occur is 18-25 mm. If folliculometry determines the size of the dominant follicle to be 18 mm, this and the next few days are most favorable for pregnancy. It is advisable to do the next folliculometry in 3-4 days to confirm that ovulation has occurred.