How does stimulation work before IVF: how many days does it last, what consequences can there be?
How long stimulation lasts for IVF depends on what drug is used and what protocol is implemented. Prevention of premature ovulation is important. This is achieved by suppressing the secretion of the preovulatory peak of luteinizing hormone. To block this process, drugs from 2 main groups can be used - gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists or agonists. The type of drug and the duration of its use determines how IVF stimulation occurs.
- Protocol for the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone ANTAGONISTS. This group of drugs allows you to immediately stop the spontaneous synthesis of luteinizing hormone. It is prescribed approximately on the 6-8th day from the start of taking gonadotropins, which stimulate the growth and maturation of several follicles at once.
- Protocols for the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone AGONISTS. There can be 3 types depending on the duration./li>
In the case of a “long” protocol, taking hormonal medications begins 1 week before the expected menstruation. This introduces the woman’s body into a state of short-term menopause and makes it possible to ensure that in the next menstrual cycle all follicles will be the same size (this process is called “synchronization of folliculogenesis”). After a menstrual-like reaction, the administration of gonadotropins begins, which stimulate the growth of follicles. Their puncture is carried out approximately after 3-4 weeks.
The “ultra-long” protocol does not differ in technology from the “long” one, except that the administration of agonists begins at least 2-3 months before the intended artificial insemination. This stimulation scheme is recommended for severe forms of endometriosis, when it is necessary to normalize existing disorders in advance.
All events develop in the same menstrual cycle, during which both gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and gonadotropins are administered. It takes about 2 weeks until the follicles are received.
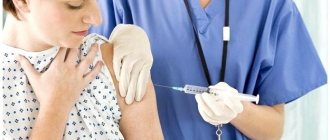
How to properly inject an injection into the buttock
The rules are almost the same. There is only one exception: if an oil injection is prescribed, then the ampoule should be preheated (rubbed with your palms, kept in a warm place). Progesterone should not be heated in boiling water. For the procedure, it is best to use a 5 ml syringe.
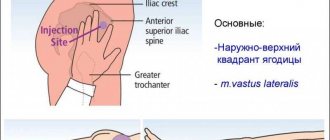
You should prepare everything for the procedure and stop being nervous. Stand in front of the mirror and make room for the injection. The buttock is mentally divided into 4 parts. The prick should be in the upper outer area. The syringe must be inserted sharply at an angle of 90 degrees, sticking the needle almost to the very end. Then slowly introduce the drug, which will be difficult to infuse because it is oily. Don't panic. Then clamp it with an alcohol cotton swab and remove the syringe. Wipe the injection site. Dispose of consumables.
Methodology
First, an ultrasound is performed to assess the condition of the follicular apparatus. When using a long regimen, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists are started in advance. In all other cases, from about the 2-3rd day, gonadotropins are introduced, which promote the growth of several follicles at once. At the same time, GnRH agonists or antagonists are used to block premature ovulation. When the follicles are 18-20 mm in size, an ovulation trigger is introduced. They contribute to the separation of the egg-bearing tubercle, containing the female reproductive cell, from the wall of the follicle.
Approximately 34-36 hours later, an ovarian puncture is performed to obtain follicles. In laboratory conditions, eggs are aspirated from the follicle and fertilized with sperm, the embryo is incubated and then implanted into the uterine cavity. After the puncture, the woman begins taking progesterone medications.
Ovarian stimulation drugs
At different stages of the procedure, different groups of drugs are used. Drugs similar to gonadotropins (recombinant or menopausal hormone) promote the simultaneous growth and maturation of several follicles. At this stage, reproductive specialists may encounter an unpleasant situation when the follicles begin to grow, but may “burst” ahead of time, i.e. premature ovulation occurs. To avoid this, the peak of luteinizing hormone is blocked. It is its rise in the blood that initiates the ovulation process. For the purpose of blocking, both agonists and antagonists of gonadotropin-releasing hormone can be used.
Against the background of hormonal therapy, the follicle continues to grow. When its size reaches 18-20 mm, ovulation inducers are introduced. They will help to finally prepare him for artificial insemination. Human chorionic gonadotropin most often acts as an inducer. After ovarian stimulation has passed, gynecologists prescribe progesterone preparations to successfully achieve and maintain pregnancy. They prepare the endometrium for embryo transfer. This stage is extremely important, because The resulting corpus luteum often turns out to be defective in stimulated cycles.
Possible complications
In most cases, ovulation induction occurs without any complications. However, in 5-10% of cases a mild form of hyperstimulation syndrome may develop. The early form appears a few days (usually 48 hours) after the induction of ovulation, and the late form appears 10 days or more later. For early diagnosis, it is important for a woman to evaluate her sensations during stimulation. The first signs are:
- nausea;
- abdominal pain, especially in the groin areas (projection area of the ovaries);
- slight increase in abdominal circumference.
These symptoms develop due to an increase in vascular permeability and the release of plasma into the extravascular bed under the influence of hormonal therapy. If the condition is not noticed in time, then the fluid begins to leak into the pleural cavity - shortness of breath appears. A decrease in the volume of circulating plasma leads to a decrease in filtration in the kidneys, therefore the amount of urine excreted decreases. These are alarming symptoms that may indicate severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. This condition increases the risk of thromboembolic complications. Therefore, if you notice any discomfort during stimulation, you should immediately contact your doctor. Timely initiation of therapy makes the use of assisted reproduction methods safe and effective.
Preparation
Before you give yourself a subcutaneous injection, you need to carefully prepare. First of all, you need to remember that the procedure should always be performed within a certain period of time. If you started injecting in the morning before work, then the entire treatment cycle should continue that way.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Details about embryo hatching
Subcutaneous injections are designed to be injected into the layer of fat under the skin.
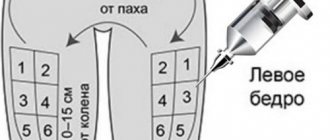
General list of permitted injection sites:
- the fatty part of the triceps on the side and in the back of the arm between the elbow and shoulder (into the arm);
- in the front surface of the thigh, closer to the outer part (in the leg);
- the thick part of the frontal abdomen below the ribs, above the hips, and not directly next to the umbilical cord (in the abdomen).
It is important to constantly change injection sites in the desired area, as repeated injections in the same area can cause scarring and hardening of the fatty tissue, which makes future manipulation difficult and prevents the absorption of the medicine.
Does it hurt to get an injection? No, if you do all the steps correctly and don’t get nervous.
Why can your head, chest, or ovaries hurt when stimulated?
Taking hormonal drugs affects the synthesis of vasoactive substances. They dilate blood vessels, increasing the distance between cells. As a result, fluid flows more easily into the extravascular space. This leads to changes in the general condition against the background of stimulation performed within the framework of IVF protocols.
Dilation of blood vessels in the brain causes headaches. The release of fluid into the intercellular space in the mammary glands leads to compression of the nerve endings and the appearance of chest pain. The ovaries may hurt slightly even normally, that is, when there is no hyperstimulation syndrome. This is due to a hormone-mediated increase in blood flow in these organs. They increase in volume and compress the nerve endings. Such symptoms usually do not cause significant discomfort to the woman, so they do not require pharmacological correction.
Treatment in Reproductive
Reproductologists approach each case individually. To select the most suitable stimulation scheme, at the first stage a detailed examination of the woman is carried out. First of all, the ovarian reserve is assessed and a forecast of the ovarian response to stimulation is made. Depending on this, a specific protocol, drug and its starting dose are selected. At the same time, possible complications are prevented. In order to create the best conditions for the development of pregnancy, the optimal number of embryos is implanted. If a couple has genetic diseases, preimplantation diagnostics is performed. All this allows us to provide treatment as effectively and safely as possible.
The most advanced achievements in the field of reproductive medicine have been introduced and successfully applied at SM-Clinic. Take care of your future and the future of your children now - sign up for a consultation with experienced reproductive specialists!
Endometrial support in the IVF program
We will definitely tell you everything you need to know about supporting the endometrium during the IVF protocol during treatment, and will also give you a special leaflet for patients to read. This same article provides more detailed information for “excellent students” or simply “advanced users” of IVF. This article is dedicated to the latest scientific achievements in the field of medicine and their implementation in IVF practice at the Nuriev Clinic.
Question 1. What drugs should be used to support the IVF program?
A woman's corpus luteum produces two hormones: estradiol and progesterone. In fact, there are more such hormones, but for simplicity we will only look at these two.
The main hormone is progesterone.
Historically, progesterone was used by injection, and was injected intramuscularly into the “soft spot” 3 to 6 times a day. Anyone who has had experience with “oil injections” has a good idea of what happens to the “fifth point” after a couple of weeks of treatment! Therefore, when the French company Besins Healthcare offered progesterone in the form of suppositories for the vagina, there was a real breakthrough in improving the quality of life of a woman, no less than the invention of pads or a washing machine. Women, however, did not immediately appreciate it, and doctors had to be convinced that the vaginal form is no less effective than the injection form. But the fact remains: 600 mg of micronized progesterone (Utrozhestan) is equivalent to 6 injections of an oil solution per day.
Somewhat later, Krinon was introduced to the market - a gel in suppositories for vaginal use. One Crinona suppository is equivalent to 800 mg of Utrozhestan. Then the synthetic drug Duphaston appeared, which is offered both in suppositories and in tablets. All three drugs are used at the Nureyev Clinic.
The second necessary hormone is estradiol.
It exists in two forms: tablets (Proginova, Estrofem) and gel for cutaneous use (Divigel, Estrogel).
Estradiol, when introduced into a woman’s body in a sufficient dose (2-3 tablets per day), in combination with progesterone, can keep the endometrium in a stable state for quite a long time. This leads to the false perception that large doses of two drugs - estrogen and progesterone - can prevent miscarriage or improve IVF outcomes. Unfortunately, no high doses of drugs can turn a bad embryo into a good one (on the contrary, they can!). Therefore, there are standard doses of standard hormones for women of the species homo sapiens. These doses are: progesterone 600 mg per day, estradiol 2 mg (tablet) twice a day. Everything else is redundant.
"How so?" – every second patient asks me. “Can I increase the dose, this is important for me, let my chances of getting pregnant be higher! You can’t spoil porridge with oil!” You'll ruin it. Excessive doses of hormones (both) in animal experiments showed a teratogenic effect on the fetus. No such trials have been carried out on women.
Progesterone support drugs over time lead to reproductive disorders in children, as well as the appearance of hypospadias, which is characterized by an abnormal location of the opening of the urethra. The severe form of hypospadias is an extremely unpleasant disease that requires surgical intervention.
The safety of estradiol for the health of an unborn child is unclear. Synthetic estrogens (the well-known DES, diethylstilbestrol) showed a teratogenic effect on a female child and were prohibited for use during pregnancy. Modern estradiol preparations, in principle, differ in structure from DES, and “should not have” a teratogenic effect. Should not. Should not. Shouldn't or don't have? This has not been proven exactly by anyone. Therefore, it is better not to use estradiol preparations after embryo transfer unless necessary or prescribed by a doctor.
Therefore, any deviations from the standard are not welcome. Overdose, as well as underdose, are undesirable, since they deviate us from the optimum, from the dose recommended for our species. So we tend to prescribe standard doses in standard situations, that is, we act according to a template. So standard that instructions on the use of drugs in this group are the responsibility of the nurse, not the doctor. The doctor has a place to use his creative abilities. Anywhere, but not in routine work to support the endometrium.
Question 2. When to start and when to end support?
When to start. Science says that we get maximum results if we start endometrial support on the day of follicle puncture, or the next day, or every other day, or on the third day. If earlier or later, the results will be worse. The sooner or later, the worse.
When to finish? This is a more difficult question. When I came to IVF, the typical support time was up to 12 weeks of pregnancy. Then the bar was lowered to seven weeks. Then up to 6 weeks.
Today it is believed that stopping all support medications on the day when hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, the pregnancy hormone) is positive does not lead to termination of pregnancy. That is, there is either a pregnancy or there is not. And if hCG is positive (more than 100 IU/l), then the drugs can be safely discontinued.
Attention! All of the above applies only to the standard IVF protocol. Cryoprotocols, protocols with a donor egg or with a surrogate mother have special features - support continues until at least seven weeks of pregnancy. If you are unsure, be sure to confirm appointments/cancellations with your ART nurse or doctor.
So, we start support on the third day after the puncture and end on the day of the hCG test. Deviations from these rules are not welcome, since the frequency of progressive pregnancies does not increase from this. But the price of the protocol and the side effects of the drugs increase. What are the effects?
Obvious effects are: bloating, constipation, puffiness of tissues due to fluid retention, drowsiness and inhibition of reactions.
And unobvious effects: the doomed pregnancy will still be terminated, but at a later date, causing significant damage to the woman’s health. Over 80% of terminated pregnancies had gross violations of the chromosome set of the embryo. That is, it was impossible to save them.
Therefore, support can be canceled earlier than intended. Moreover, support MUST be canceled as soon as possible.
Question 3. What to do if bloody spotting begins?
Nothing. Most often, bleeding begins approximately 4 days before the hCG test. This happens because its native corpus luteum has exhausted its resource and began to produce less progesterone and estradiol. If the embryo is implanted and begins to produce hCG, then it stimulates the corpus luteum and does not allow it to relax
Bloody discharge before the hCG test is the first sign of lack of implantation, and therefore pregnancy.
If the discharge is scanty, you should not stop taking the medications. There is a chance to save the pregnancy, since only the lower layers of the endometrium, closer to the cervix, are exfoliated (the embryo is transferred closer to the fundus of the uterus). If full menstruation has arrived, there is no chance - you need to cancel support without specifying the hCG.
Of course, it is psychologically very difficult to come to terms with the fact that the IVF protocol ended in failure. Too much effort was put into it. Of course, intervention with large doses of drugs (estrogens, for example) can stop the bleeding that has begun. But don't save the pregnancy! Because a non-viable embryo causes bleeding, and not vice versa.
Should I call the doctor if I start bleeding? Certainly. It is both possible and necessary. In this case, as a rule, the doctor gives his mobile number at the beginning of treatment. However, we are faced with a problem: the doctor receives over 100 (!) incoming calls to his mobile phone per day. Most of them occur during the hours of seeing other patients or during operating hours. Add to this the doctor's dream and a little personal life - it can be difficult to get through. As a compromise, we introduced an emergency telephone, issued during procedures in the Clean Zone, which is always staffed by a nurse. She will either connect you with a doctor, or replace the “native” doctor with a “foreign” one, but still competent, if her own doctor suddenly cannot answer the call. Although we try not to abandon “our own” people in trouble. Especially after IVF. Especially when bleeding.
Question 4. What hormones need to be monitored?
None. Because there are no norms. No hormone levels are a reason to change current doses. Why?
Because progesterone preparations introduced vaginally create high concentrations in the uterus and endometrium. And there the level of hormones is difficult to measure.
If the concentration of progesterone in the uterus is significantly higher than in the peripheral blood, then why measure progesterone in the blood specifically? Studying the level of progesterone in the blood is a useless transfer of money, since based on the level of progesterone in the blood, no conclusions can be drawn, no predictions can be made, and even more so, prescriptions cannot be adjusted.
That's it for progesterone.
Estradiol. This hormone, even in small doses, can retain the endometrium. The sensitivity of women's tissues to this hormone varies. Therefore, the estradiol level is very vague and variable. As with progesterone, laboratory-determined estradiol levels do not justify dose adjustment.
So why is estradiol measured before and after embryo transfer? This is done to determine the risk of developing ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. But that's a completely different story. And a topic for another article.
Question 5: What else improves outcomes? “Aspirin”, “Clexane”, “Fraxiparin”, vitamin E, leeches? Anything else?
Nothing. None of the drugs registered in the world have shown any significant effect in increasing the pregnancy rate. Fairy tales about “thick blood” were invented by pharmaceutical companies that produce “drugs against thick blood.” These misconceptions, as well as stories about the miraculous salvation of IVF pregnancy, are artificially supported, because “if the stars light up, it means someone needs it.”
I would like to note on my own that a fertility doctor feels slightly offended when he hears that any woman who self-medicated herself with strong medications during an IVF protocol and got pregnant glorifies this drug, the neighbor who recommended it, and Providence. A slight insult, because a woman becomes pregnant because and only because embryos were transferred to her and a huge amount of preparatory work was done before that.
Question 6. Sexual life, bed rest, hospital, diet.
Sexual activity does not increase or decrease the effectiveness of IVF. Live healthy! In this case, we must remember the following.
• Condoms are very toxic because they contain spermicides - substances that kill all living things. Do not use them during an IVF program.
• ovarian cysts formed during stimulation/puncture can be mechanically injured, causing at least pain and even bleeding. Be careful! If, of course, you can.
Bed rest does not improve outcomes. Be active. Just avoid sports activities. IVF for step aerobics or judo is not the best time (remember about ovarian cysts).
Inpatient treatment, contrary to popular belief, does not improve, but rather worsens, outcomes. This has been statistically proven in a large sample, but no one can explain exactly why this is so. I, too, will be careful not to express my versions. But I really don’t like hospitalizing women to continue pregnancy in the early stages, because I lose control over the appointments. However, whether or not to go to the hospital is your choice.
Diet. Kebabs, dumplings, fried mushrooms and other tasty but unhealthy foods may be poorly received by the intestines, which already “tolerate” an excess of steroid hormones. So it's better not to experiment. In addition, weight is gained much faster due to hormones. I note that the increase occurs not only due to hormones, but also due to excess food and a simultaneous decrease in physical activity after embryo transfer. But there are no prohibitions!
Question 7 (which I never get asked). Are all medications prescribed as support safe for me and my baby?
In the first trimester, it is better to do without medications at all. Based on many years of practice, I can say that any drug can have a toxic effect during this period. It is difficult to predict exactly what will lead to a negative outcome, since controlled clinical studies on pregnant women are impossible and prohibited for ethical reasons.
No one will give a woman medicine to check whether there is a risk for the child or not. We have no controlled studies, only reports of possible side effects. Reports are not precise because side effects may be infrequent and delayed. The drug may affect the child's health, but you will find out about this after 18 years if he donates sperm for analysis, or after 30 years when he is faced with infertility.
The only way out of this situation is to take only those medications prescribed by your doctor. And no amateur performances! At the Nureyev Clinic we treat women with such care that we suspect any extra medication. What kind of drugs are these?
Folic acid.
A drug that is associated with successful pregnancy, if taken in overdose, carries significant risks for the child. Taking folic acid in a common dosage of 5 milligrams per day or higher can lead to the development of autism. On the other hand, folic acid deficiency can cause a defect in the development of the neural tube in the fetus. Therefore, the World Health Organization recommends a dosage of 400 micrograms, which is equal to 0.4 milligrams. There are practically no Russian drugs in this dosage. An alternative may be drugs containing 1 milligram, but they cannot be taken at a rate of 5 tablets per day. At the Nureyev Clinic we offer dosages from 0.4 to 1 milligram. But this is only 1 tablet per day! When taking this dosage, it is important to remember that multivitamins also contain folic acid. This means that by taking them without the consent of a doctor, we again risk getting an overdose.
Aspirin and paracetamol.
These are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that increase the risk of miscarriage in the first trimester. In their regard, it is also important to remember the dosage. It’s one thing if you take 1 aspirin tablet, and a completely different matter if you take 20. Why do women often exceed the permissible dosage? Mainly because they consider these drugs harmless, and see any pain as a threat to pregnancy. For example, there is a nagging pain in the lower abdomen. This is the endometrium growing, and the uterus grows more slowly and does not keep up with the endometrium. The process is completely natural, but the woman takes aspirin, thinking that she is ensuring the safety of her pregnancy. The effect is completely opposite.
What else is unsafe, but is practiced by many women?
It is unsafe to prolong support after hCG, as pregnant women do in secret from doctors and in the hope that prolonging the use of drugs will lead to the continuation of pregnancy. It is very dangerous. Weak and sickly embryos with genetic abnormalities will not develop from this support. There will be a frozen pregnancy, which will be terminated later, causing more damage to the woman’s body. A miscarriage at 6-7 weeks is one thing, and quite another at 8-9 weeks, when it is no longer possible to do without surgical intervention.
Question 8. How does support depend on the type of IVF protocol?
It depends a lot. All of the above about estradiol and progesterone was said about the standard long protocol. The Long Protocol (historically) was the first reliable treatment protocol with good results. In the long protocol, native hormones were suppressed the most, and therefore good (great!) endometrial support was required.
Currently, the most commonly used protocol is a short protocol (we call it the “Antagonist Protocol”). For an antagonist protocol, the use of estrogen support is not mandatory. Quite the contrary: women who took and did not take estrogens had the same chances of becoming pregnant and carrying a pregnancy to term. This is one of the good reasons why the long protocol is being intensively replaced from clinical practice by the antagonist protocol.
Question 9. In what cases are hCG drugs used?
I almost forgot. Human chorionic gonadotropin ("Pregnil", "Ovitrel") stimulates the corpus luteum of the ovaries, and is therefore used to stimulate the endometrium. However, the likelihood of getting hyperstimulation syndrome with it is an order of magnitude greater, and the increase in pregnancies is insignificant. Therefore, we use these drugs if no more than five follicles have grown in the ovaries during stimulation (for both ovaries).
Question 10. What else do I need to know?
This is a very good question, ask your doctors more often! The quality of the drugs used for support is subjected to a thorough statistical analysis by the staff of the ART Department of the Nuriyev Clinic. If a series of drugs is of poor quality (unfortunately, this happens), then these drugs are withdrawn from circulation as soon as possible. Therefore, the medicine we give you almost always works without failure. Until you take him outside the clinic. If we control injectable drugs at all stages, right up to the injection, then with support drugs everything is the other way around. Most of the time it is used and controlled by you. Room temperature in summer often exceeds 25 degrees, which is critical for Crinona, Utrozhestan and Proginova. Don't forget this. Perhaps, numerous myths about weak support appeared not least due to the fact that it is hot in our country in the summer and cold in the winter?
Conclusion
Very often in medicine the approach of redundancy of prescriptions is used.
- Money? - Doesn't matter!
- Risks? - We don’t know!
- Side effects? - Let's be patient!
If it were only these issues, it would probably not be worth spending so much time on this topic. However, excessive attention to endometrial support obscures the true problem of IVF: most failures are not due to poor endometrial preparation and support, but to the quality of the embryo
Ask your doctor the following questions on the day of your embryo transfer:
– what was the proportion of good embryos I had in the current protocol?
– did my embryos develop optimally for my age group?
– could the stimulation be done better?
– what could be done to increase the number of high-quality embryos for the next protocol, if it is not possible to get pregnant in this one?
That's probably all on this topic. See you on the transfers!
Please do not try to take hormonal medications uncontrollably. This article was written not for self-medication, but for self-education.