Article on the topic
Prevent your child from getting sick: 5 steps to prevent asthma
Together with measles and rubella, they pose a huge danger, because we are talking not only about the health of the mother, but also about the life of the unborn baby...
“Childhood” viral diseases have a lot in common. All of them are transmitted by airborne droplets and are highly contagious. To catch any of these ailments, it is enough to inhale the tiny droplets of saliva that the patient secretes when breathing, talking, coughing and sneezing. The danger is that identifying an infected person by sight is not at all easy. It becomes contagious several days before characteristic symptoms appear. Therefore, purely theoretically, any seemingly healthy person can pose a threat to the expectant mother. Especially if it's a child. But this does not mean at all that a pregnant woman needs to panic and not go outside for the entire 9 months. It's not that scary. The main thing is to remember whether she had measles, chickenpox, mumps and rubella in childhood. If the answer is yes, the young lady can be calm: nothing threatens her and the baby. After suffering from diseases, the body has developed a strong immunity to them, so you cannot get infected again even if you want to. You only need to worry if the “childhood” sores bypassed the woman and she was not vaccinated against them.
However, even if you have been vaccinated, you should play it safe and, just in case, get tested for antibodies to pathogens. After all, 25 years after vaccination, the immunity formed to them weakens significantly, or even disappears altogether. This means that mommy has every chance of catching a dangerous infection.
Measles: strikes at a distance
Measles is one of the most contagious viral diseases. A child can catch it by being in a room where a sick person was 2 hours before. And it is enough for a pregnant woman, for example, to be in the same transport with a sick person, and they can even sit at different ends of the bus. The measles virus easily travels a distance of several tens of meters, and if it has reached a person, it will probably take over. If this trouble happens to the expectant mother, it is very important to determine the stage of pregnancy at which she fell ill. The smaller it is, the more severe the consequences. Measles infection in the first trimester in 20% of cases leads to miscarriage or various pathologies of the fetus. The baby may be born with a low level of intellectual development (oligophrenia) or serious damage to the nervous system. Moreover, these defects are the worst diagnosed at the beginning of pregnancy. Unfortunately, neither an experienced gynecologist nor a qualified ultrasound specialist will be able to say for sure whether a young lady in an interesting position will bypass trouble or whether she will fall into that ill-fated 20%. Therefore, women who have had measles in the early stages of pregnancy are often offered to artificially terminate it. But, of course, this is an extreme measure, and before deciding to take this step, a thorough examination is carried out.
The prognosis of the disease suffered after the 16th week of pregnancy is more encouraging. At this stage, measles, as a rule, proceeds more easily and does not have a negative effect on the fetus. The disease is prevented from spreading by the placenta, which by this time has finally formed and reliably protects the unborn baby from the negative effects of harmful factors. However, in the last weeks of pregnancy the danger reappears. If the mother gets sick closer to the end, then she can infect her little one when he passes through the birth canal. Back in the middle of the last century, such a “gift” could have led to the death of a child, but now that doctors have strong antibiotics and modern resuscitation methods in their arsenal, infant mortality from congenital measles infection has decreased significantly. The chance that something irreparable will happen to the baby is negligible.
Chickenpox: rare, but accurate
Doctors say that most people who think they never had chickenpox as children actually had it in such a mild form that they didn’t even notice it. Only 4% of adults are immune to this disease. Apparently, this is why it rarely occurs in pregnant women. According to statistics, out of 2,000 expectant mothers, only one catches the chickenpox virus. If a woman falls ill before 20 weeks, miscarriage and intrauterine fetal death are possible. If the pregnancy continues, the danger still remains. The baby may develop the so-called congenital chickenpox syndrome. The defects it causes include scars on the skin, underdevelopment of muscles and bones of the extremities, cataracts, various neurological disorders (atrophy of the cerebral cortex, mental retardation, urinary and fecal incontinence, etc.). Fortunately, this syndrome is no more common than the disease itself. The probability that it will form in a baby does not exceed 2%. But it’s still better to play it safe and undergo an unscheduled ultrasound, which will determine whether the chickenpox virus has reached the fetus, and if so, what is the extent of its damage.
No less dangerous is a disease contracted in late pregnancy, especially 4-5 days before birth. When a baby is born, it can become infected from its mother. The tragedy is that chickenpox in infants is very difficult and is often accompanied by complications: bronchopneumonia and damage to internal organs. Unfortunately, not all kids cope with this test. A third of them die. Therefore, if the expectant mother gets chickenpox a few days before the expected delivery, doctors often try to artificially delay it. And if this is not possible, then immediately after birth the baby is given immunoglobulin and antiviral treatment is carried out. Such measures do not protect the newborn from infection, but can significantly reduce the risk of death.
Chicken pox during pregnancy
Chickenpox is an infectious disease of a viral nature (the causative agent of the disease is a virus of the herpes virus group). It is also highly contagious and transmitted through airborne droplets.
The disease manifests itself up to 21 days after contact with a patient with chickenpox. Chickenpox in pregnant women begins with the appearance of a rash, which at the beginning is one or two reddish spots, similar to a mosquito bite; most often, the first elements of the rash appear on the skin of the face or abdomen, spreading very quickly (new elements appear every few minutes or hours). The next day, the reddish spots take on the appearance of bubbles filled with transparent contents, the patient is bothered by severe itching, by the end of the first day of the disease, general health worsens, a headache appears, and the body temperature rises (it can reach 40ºC). Symptoms persist while new rashes appear. The severity of a pregnant woman's condition depends on the number of rashes. After a day or two, the blisters open to form ulcers, which then become crusty. A pregnant woman has an increased risk of developing pneumonia.
The diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of a characteristic rash on the patient’s skin.
Rarely, if infected in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus may develop congenital chickenpox syndrome: underdevelopment of the musculoskeletal system, damage to the central nervous system, eye damage, sometimes infection after 20 weeks of pregnancy leads to the development of severe intrauterine infection of the fetus. In cases of chickenpox, a pregnant woman is strictly monitored, therapeutic and diagnostic measures are carried out, and if developmental defects are detected in the fetus (using ultrasound), the issue of terminating the pregnancy is decided.
Pig: scary only at first
Mumps, or mumps as doctors call it, is less contagious than chickenpox or measles. Even close contact with a carrier does not always lead to the development of the disease. Nevertheless, this disease is common among expectant mothers. Mumps is most dangerous in the first trimester, when the virus can easily reach the embryo. In this case, the pregnancy often stalls or spontaneous abortion occurs. As a rule, this happens 2 weeks after the woman falls ill. There is also an assumption that the mumps virus affects the ovaries and it is for this reason that a miscarriage occurs. If the pregnancy continues and the unborn baby continues to develop, then there is no reason to worry. The expectant mother can safely drive away thoughts about possible anomalies. Mumps does not cause developmental defects, so the baby will be born healthy.
If a pregnant woman catches an infection shortly before giving birth, she can infect her child, as is the case with chickenpox and measles, when he is born. Or a little later, putting the baby to the breast, since the mumps virus is easily transmitted through mother's milk. But even in this case, the prognosis is favorable. Typically, mumps, even in young children, is relatively mild and does not cause complications.
How does the disease manifest?
As a rule, the first symptoms of coronavirus develop 5-7 days after infection. There are three clinical forms of the disease:
- Easy. Accompanied only by symptoms of ARVI.
- Average. In this case, the patient develops pneumonia, but it is easily treatable and does not threaten human life.
- Heavy. Accompanied by pneumonia and acute respiratory failure
In addition, in some patients, coronavirus infection may be asymptomatic.
The most common signs of infection include:
- high body temperature, fever;
- dry debilitating cough;
- a sore throat;
- feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath;
- general weakness, exercise intolerance.
Other signs may occur less frequently: symptoms of body intoxication (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting), headaches, hemoptysis, heart rhythm disturbances, confusion, nasal congestion, muscle pain. In some cases, there is a loss of smell, the appearance of a rash on the body, and a change in the color of the skin on the arms and legs.
Signs of respiratory failure
Respiratory failure leads to oxygen starvation of the body, which affects the functioning of the brain and heart. Main signs of respiratory failure:
- Rapid breathing. Shortness of breath is a harbinger of respiratory failure. The lower the level of oxygen in the blood, the faster the body tries to eliminate its shortage.
- Cardiopalmus. The faster the heart beats, the faster the blood is saturated with oxygen.
- Loss of consciousness. This condition occurs when the brain begins to experience oxygen starvation.
- Low blood pressure. The drop in pressure is caused by blood retention in the vessels of the lungs due to passive gas exchange.
- Asymmetrical respiratory movements of the chest. For example, one lung may work less than the other. Also, the respiratory function can be carried out by only one lung.
Rubella: danger code – red!
Rubella is the most dangerous “childhood” infection for pregnant women, because the disease in the early stages always (!) leads to the loss of the child. If the infection occurs in the first trimester, the infection will certainly reach the fetus. As a result, a miscarriage may occur. In the case when pregnancy continues after an illness, irreversible changes occur in the development of the child. Most likely, the baby will be born with congenital rubella syndrome, the so-called pathological triad: cataracts, heart disease and deafness. In addition to this, microcephaly (reduction in the size of the brain), microphthalmia (reduction in the size of the eyeballs), enlarged fontanelles, inflammatory diseases of the brain, damage to the vestibular apparatus, and malformations of the skeleton and genitourinary organs may be added. And this is not a complete list of the “dowry” of a baby who was infected in utero. That is why pregnant women who have had the disease in the first trimester are recommended to have an abortion for medical reasons. Otherwise, the baby will be born defective.
If infection with the rubella virus occurs after 16 weeks, then the risk of giving birth to a toddler with developmental defects remains, but becomes minimal. It is believed that in the 4th month of pregnancy the risk of infection of the fetus is 5-6%, in the 5th and later – about 1-1.7%. Therefore, there is no need to terminate the pregnancy. But you should prepare for the fact that the baby may be born with short stature and low body weight. In the future, such children lag behind their peers in physical development. If the mother becomes infected on the eve of childbirth, the baby will develop typical skin rashes, which will soon go away. And the baby himself will remain contagious for several months after birth.
Covid threatens pregnant women and babies. The doctor gave clear recommendations
Women are hearing the diagnosis of “intrauterine pneumonia” more and more often. Premature birth, the baby is born and cannot take its first breath. Next comes resuscitation and the doctors’ struggle for life. Coronavirus contracted in the first and second trimesters can lead to such dire consequences. How to plan a pregnancy in this situation? Presenter Maria Ivatkina talked about this in the First Russian studio with a doctor of the highest category, obstetrician-gynecologist Alla Pashkova.
Maria Ivatkina: Have you encountered cases of coronavirus in pregnant women in your medical practice?
Alla Pashkova: Of course, we met. Although I do not work in a maternity hospital, which is focused on delivering births to women in labor with coronavirus, nevertheless, among my pregnant women there were patients with coronavirus infection.
– How does this complicate pregnancy? How does this affect the health of the woman and the unborn child?
– Mostly in pregnant women the disease is quite mild. Most often, this is either asymptomatic, mild, or moderate course of the disease, which does not affect the health of children. Women carry their pregnancies to term and give birth to healthy children. The risk of preterm birth, if we talk about healthy women, is about 6-7%.
Thrombosis, premature birth - what is the danger of Covid for pregnant women?
But among pregnant women with coronavirus infection, one in five may have either late miscarriages or premature births with the risk of having low birth weight babies with breathing problems, because most of them have respiratory distress syndrome. Well, and, accordingly, then, in the future, there are risks of damage to the organs of vision, hearing, cerebral palsy, and so on.
For a mother, Covid in case of a severe course of the disease is dangerous due to bleeding and thrombosis due to the fact that against the background of coronavirus infection, hypercoagulation is often observed, that is, an increase in blood clotting.
And if a pregnant woman has obesity, cardiovascular disease or thrombophilia, then, accordingly, the risk of thrombosis is even higher. In addition, there is a threat of antenatal fetal death or premature abruption of a normally located placenta.
Therefore, such pregnant women are at risk both for thrombosis in themselves and for thrombosis in the vessels of the placental bed. That is, this is both antenatal fetal death and premature abruption of a normally located placenta.
– What preventive measures can be taken in this case?
– It all depends on the course of the disease – mild, moderate or severe. In moderate and severe cases, the woman will be hospitalized and specialists will take care of her.
If the disease is mild or even asymptomatic, then it is better to stay at home. If the temperature rises above 38–38.5, then antipyretic drugs, plenty of fluids and, naturally, vitamins, possibly D3, are prescribed. Good nutrition and adherence to the regime are necessary.
In general, you need to follow the usual preventive measures: avoid close quarters, contact with large numbers of people, wash your hands more often, treat them with sanitizers, wear a mask, changing it every three hours.
– Do I understand correctly that the treatment of pregnant women for coronavirus is somewhat different?
– There are no serious differences; in general, the treatment follows the same scenario. Of course, it all depends on the form in which the disease occurs. In severe cases, if mechanical ventilation is required, the question of emergency delivery may arise, because pregnancy itself is a big burden on the body. And it turns out that in a stressful situation, when the body’s forces are aimed at survival, pregnancy is a kind of aggravating moment.
– Which takes away strength from the body.
- Yes. This includes an additional intake of nutrients, and the need to ensure placental blood flow, and to grow a new organism inside oneself.
Plus, this is a special “agreement” of the immune system. Because a fetus is, one might say, a genetically alien organism. And here an adequate immune response is needed so that it is not rejected, so that it lives and develops. And when a coronavirus infection interferes with this process, everything in the body is disrupted.
How is Covid treated during pregnancy?
– It turns out that pregnant women are a “risk group” for coronavirus?
- Undoubtedly. And studies that have been conducted have shown that the likelihood of infection in pregnant women is quite high. However, their severe form occurs in no more than 5% of cases, that is, infrequently.
– I didn’t just ask the question about treating Covid during pregnancy. Many women during this period are often afraid to take any medications. And here the question arises: what is worse, an infection that develops inside the body and can harm the unborn child, or medications that, hypothetically, can also harm both mother and child.
– This is a completely wrong approach. Unfortunately, for some reason in our post-Soviet space there is an opinion that if you are pregnant, if it is a newborn child, then the medicine should absolutely not be taken. That it is harmful, that you need to be treated with plantain, and so on.
But evidence-based medicine is evidence-based because it is based on protocols for the management of certain diseases, and they do not arise out of the blue, but as a result of serious independent studies in different countries with control groups.
For example, in the USA there is a gradation of medications. For example, group A medications are absolutely safe during pregnancy. Group B drugs must be taken with caution, and so on.
Although we encountered coronavirus not so long ago, some experience in treating the disease during pregnancy has already been accumulated, and the necessary drugs to reduce the risk of complications have been approved.
Mom is sick, how will this affect the child?
– And if a woman suffers a coronavirus infection easily and, perhaps, even asymptomatically, does this subsequently affect the health of the child? Is it possible for him to develop intrauterine pneumonia?
– According to current studies, the total passage of the virus from mother to fetus through the placental barrier is excluded. However, cases where premature babies were born with intrauterine pneumonia with confirmation of the diagnosis of coronavirus infection have already been described in the specialized literature. But these are isolated cases when children were born from somatically burdened mothers - with obesity, diabetes, arterial hypertension, and so on.
So, for the most part, coronavirus is not transmitted to the child during pregnancy. It’s another matter if the infection occurred after childbirth, as a result of close contact.
You shouldn’t assume that if a mother gets sick with Covid, then the child will definitely have intrauterine pneumonia. Of course not. This happens in isolated cases. As for intrauterine pneumonia itself, we are faced with it even without an epidemic of coronavirus infection - it can be caused not only by viruses, but also by bacteria.
– Tell me, does the form of the disease depend solely on some other diseases that the woman has? Or could it be a perfectly healthy young pregnant woman who fell ill with coronavirus, and, unfortunately, her case turned out to be fatal?
– One of the latest American studies showed that the probability of death in pregnant women infected with coronavirus is about 1 in 709 cases. Moreover, the probability of death in a healthy pregnant woman is 1 in 20 thousand. That is, the difference is obvious.
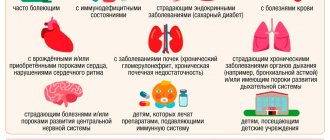
As for the risk group, as I have already said, it includes pregnant women with obesity, arterial hypertension, diseases of the cardiovascular system, severe liver and kidney diseases, as well as previous cancer.
Unfortunately, we have a large number of women with lipid metabolism disorders during pregnancy, with gestational diabetes mellitus. And all because we lack a nutritional culture and there is no proper management of such pregnant women. Often no one pays attention to properly conducting screening of the first trimester with an assessment of the risk of preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction syndrome.
– We learned about the first case of Covid in a pregnant woman in March 2021, that is, almost a year and a half has passed. What conclusions have we drawn during this time, what mistakes have we corrected and what have we learned to do?
– At present, a scheme has already been clearly worked out on how to correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment if a pregnant woman becomes infected with a coronavirus infection. Everywhere in our country there are hospitals that are focused on providing assistance to pregnant women with coronavirus infection. Naturally, experience has been accumulated in terms of treatment regimens and approaches to treating such patients.
When should pregnant women get vaccinated?
– Many people are interested in the issue of vaccination of pregnant women.
– As a doctor, I have a positive attitude towards vaccination. And think for yourself. The vaccines currently in use, including those against coronavirus, are non-living. It has long been known that only live vaccines are dangerous for pregnant women. Well, for example, the vaccine against chickenpox, measles, rubella, and the human papillomavirus is recombinant.
A dead vaccine is an inactivated virus. This is just Sputnik-V. This vaccine is an inactivated adenovirus into which only a small piece of coronavirus DNA is embedded, which is also inactivated and non-living.
When such a vaccine is administered, antibodies are produced against the adenovirus, which is the conductor and, accordingly, the DNA of the coronavirus. That is, when the body encounters a live coronavirus, its cells are not able to cling to human cells and destroy them.
Now I’ll touch on the myths associated with the vaccine. The first is that the vaccine will lead to infertility. Let's think logically. What causes infertility? Or the eggs age, the follicles are destroyed. This happens if the ovaries have been operated on multiple times.
Another reason is age-related aging. The supply of eggs at 45 years old is different from the supply at 20 years old. But not a single virus is capable of infecting follicles and destroying eggs. Only hyperthermia is dangerous for the destruction of eggs, as well as for sperm.
If a person has a high temperature for a long time, then cell denaturation may occur, that is, they will be destroyed.
– Another important question. If a woman is planning a pregnancy, how long before should she get vaccinated?
– The English Society for Reproductive Medicine has issued a mandatory recommendation for couples planning a pregnancy to be vaccinated. Considering that, according to statistics, pregnancy occurs in 90% of couples in the 8–9th month of planning, we do not know what will happen during this period. Obviously, the recommendation of British experts is quite correct.
As for the vaccine itself, it is, as I already said, inactivated. It is not passed into breast milk and does not penetrate the placental barrier.
If you listen to myths that something bad can happen in five to seven years, then let’s first turn on logic. The components of the vaccine remain in our body for no more than three weeks. During this time, either antibodies will be developed or not. After three weeks, the body will no longer remember this component of the vaccine. Therefore, questions about revaccination constantly arise.
– What week is it better for a pregnant woman to get vaccinated?
– According to the recommendations of the Ministry of Health, pregnant women at risk can be vaccinated with Sputnik-V at 22 weeks. Earlier than this period is not recommended, because the evidence base has not yet been collected.
But the same Pfizer abroad is allowed to be vaccinated in the early stages; it is also allowed for nursing mothers.
Expert opinion
Anna Mtskhvetaridze, obstetrician-gynecologist at the American Medical Center:
– Several years ago in Russia, most people suffered from “childhood” infections at an early age, so these diseases in pregnant women were not such a pressing problem. Currently, many children do not go to kindergartens, as a result of which their risk of disease increases in the future. If you did not have rubella, measles, chickenpox and mumps when you were a child, be sure to get vaccinated several months before conception. During pregnancy, immunization cannot be carried out, since the live virus on the basis of which vaccines are created can adversely affect the fetus. If pregnancy has already occurred, and tests show that you do not have immunity to pathogens of “childhood” diseases, treat your health with the utmost care and try to avoid contact with children.
Recognize the enemy by sight
Measles – fever and cough . The first symptoms of measles can easily be confused with a common cold. You feel lethargic and weak, your temperature rises, your eyes are watery, your throat hurts, you have a runny nose and a dry “barking” cough. After 2-3 days, small whitish spots, similar to semolina, appear on the inside of the cheeks. And after a few days, the ears, face, body and limbs become covered with small red spots, which gradually darken and merge into large figures, between which healthy skin is visible.
Chickenpox - blisters on the lips. Chickenpox also begins with a high fever and general malaise. After a few days, a blistering rash appears on the lips and scalp, which gradually spreads to the torso. These are raised, fluid-filled pustules that later dry out and turn into crusts. Do not scratch the blisters under any circumstances, otherwise scars may remain on the skin.
Mumps - pain behind the ears . The first sign of mumps is an enlarged salivary gland. Usually they become inflamed on both the left and right, but only one of them can be affected. If you press your finger behind your ear, you will feel severe pain. It becomes difficult for you to talk, chew and swallow food. The temperature may remain normal.
Rubella is blotchy skin . With rubella, the lymph nodes in the back of the head become very swollen. Then a rash appears behind the ears and on the face, which quickly spreads throughout the body. The lesions are small, do not connect with each other and disappear within 2-3 days.
Measles during pregnancy
Measles is an acute infectious disease of a viral nature, the distinctive feature of which is the very high susceptibility of humans.
If a pregnant woman has not had measles and has not been vaccinated against this infection, then after contact with a sick person, infection occurs in almost 100% of cases.
The measles virus is very highly volatile and is transmitted from a sick person by airborne droplets. The duration of the incubation period is 9-11 days.
The initial manifestations of the disease include an increase in body temperature to 39ºC, cough, runny nose, redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes, and severe loss of appetite. On the 4th day from the onset of the disease, a characteristic sign of the disease appears - small whitish spots on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, soft and hard palate, similar to semolina or bran, a characteristic rash appears on the face and head (especially behind the ears), which spreads throughout body. The rash consists of small red spots of various sizes, with a tendency to merge, leaving behind dark spots that last for several days, disappearing in the same sequence in which the rash appeared. The diagnosis is confirmed based on the characteristic signs of the disease and the detection of specific antibodies in the blood.
There is no specific therapy for childhood infections, so individual symptoms are treated.
When a pregnant woman is infected with the measles virus, the risk of spontaneous miscarriage and premature birth increases.
Despite the fact that the measles virus penetrates the placenta, to date there is no clear evidence of an increased risk of congenital malformations of the fetus when a pregnant woman is infected in the first and second trimester. If a pregnant woman contracts measles before giving birth, the child may be born with a characteristic rash on the oral mucosa and skin. In this case, it is recommended that mother and child stay together in the ward of the observation department and breastfeed the newborn. If a fetus is born without signs of infection, the child is isolated from the mother for the entire period of her illness.
All pregnant women who are in contact with patients with measles and who have not had this infection are prescribed prophylactic administration of anti-measles immunoglobulin intramuscularly at a dose of 0.25 ml/kg of the patient’s body weight during the first 72 hours from the moment of contact.
Women planning a pregnancy who have not previously had measles are immunized with the measles vaccine at least 3 months before the planned pregnancy. Vaccination of pregnant women with measles vaccine is prohibited.
Advertising