Eczema
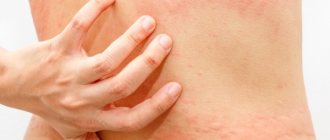
Eczema is an inflammation of the superficial layer of the skin. It can be dry or weeping, focal (limited) or diffuse (scattered).
It begins with redness, the formation of compacted elevations (papules), turning into bubbles with liquid (vesicles). The vesicular exudate then becomes purulent and bursts, infecting the surrounding surface and causing maceration.
CAUSES:
- poor skin and coat care;
- use of unsuitable cleaning products;
- ectoparasites - lice, ticks, fleas;
- mechanical impact - rubbing the skin with a collar, muzzle, harness;
- chemicals - medicines, disinfectants.
Veterinary diagnostics
A visit to the veterinary clinic is necessary if there are accompanying symptoms, a frightening appearance of the lump, or discomfort when palpating it. Before visiting the doctor, do not allow your dog to lick or scratch the affected area. This may worsen his condition.
To make a diagnosis, urine and blood tests are taken from the four-legged patient. He also undergoes X-ray, ultrasound, CT and biopsy. These studies help determine the exact size, location, depth and possible malignancy of the tumor. In the early stages, endoscopy is recommended.
Neoplasms
Tumors in dogs can be benign or malignant. It is very important to carry out correct diagnosis in a timely manner.
Benign
Benign cells retain the ability to differentiate, grow slowly, and never grow into surrounding tissues.
THE MOST COMMON BENIGN NEOPLASMS:
- Lipoma - a wen - is of soft consistency, painless, and easily movable. Develops in subcutaneous fatty tissue.
- Fibroma - can cause a feeling of fullness and aching pain. Occurs on the skin and mucous membranes.
- Adenoma is a growth of glandular epithelium. In older dogs it often appears in the perianal area. Associated with hormonal imbalance and increased androgen levels.
- Papilloma is a growth of the epidermis that occurs in aging animals. The main localization is paws, eyelids, head.
Malignant
They are formed from uncontrollably dividing cells and are characterized by a lack of cell differentiation, germination into adjacent areas, and metastasis to distant organs.
MOST COMMON:
- melanoma;
- carcinoma;
- sarcoma.
Causes of subcutaneous formations
Lumps under a dog's skin are not always associated with cancer. Most of them occur for the following reasons:
- Insect bites
. Swelling on the nose often remains after an unsuccessful encounter with bees. Their bites are always accompanied by redness and swelling.
- Mechanical injury
. After an unsuccessful jump for the ball and a not at all soft landing right into the wall, a bump may appear on the face of the unlucky pet.
- Infection
. With a weakened immune system, balls filled with pus often appear. This occurs due to infection by bacteria that cause inflammation. A virus can also cause compaction.
- Inflammation of the paraanal glands
. If a lump is found under a dog’s tail, then its appearance is affected by the inflammatory process. The affected area will be itchy and painful.
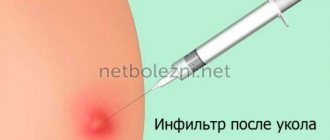
- Injection
. Swelling on the thigh or paw that occurs after vaccination is a natural reaction to the injected drug. After some time it goes away on its own.
- Tick infestation
. The attached parasite can be found on the stomach, side, chest, ear, chin and even under the eye. A mysterious growth that appeared shortly after a walk requires mandatory diagnosis. Some ticks carry deadly diseases.
Disorder of the functioning of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. When the ducts are blocked, the secreted secretion accumulates inside the gland or follicle, leading to their growth.
The prolonged presence of swelling, accompanied by its increase and the appearance of pain, requires mandatory intervention by a veterinarian. Also, other alarming symptoms that are not directly related to education may be a reason for contacting.
Hernias
Hernia is the prolapse of the omentum, uterus, or part of the intestine under the skin. When internal organs prolapse through the umbilical ring - an umbilical hernia, through the inguinal canal - an inguinal hernia. It can be congenital or acquired, infringed or not infringed.
Outwardly it looks like a protrusion in the navel or groin area. Can reach significant sizes.
Congenital umbilical lesions are common in puppies and are sometimes treated conservatively.
Infringement of the uterus or intestines by a hernial ring is fraught with peritonitis and sepsis and requires immediate surgical intervention.
It would be a mistake to believe that only malignant tumors pose a danger to the life of an animal. No less serious, for example, are abscess and phlegmon, often leading to death.
Any skin seal requires careful diagnosis and proper treatment. Only a veterinarian can diagnose the disease and determine the tactics for its management.
What symptoms may appear?
Not all balls appear under the dog's skin. Some of them are formed in soft tissues and can be diagnosed only by palpation of the affected area. Because of this, it is important to be aware of your symptoms. Alarming symptoms include:
- pain when palpating the lump;
- change in color of adjacent tissues;
- stable tumor increase;
- worsening sleep, loss of activity and appetite;
- opening of the emerging papule with subsequent release of pus or blood;
- presence of temperature.
In the absence of the listed symptoms, but the formation persists for more than 7 days, it is recommended to undergo diagnostics at a veterinary clinic. If your pet has at least one of the listed symptoms, make an appointment immediately after detecting it.
How is lymphadenitis treated?
The key to successful treatment of lymphadenitis in a dog is contacting a reliable veterinary clinic. Here they will not only quickly and accurately make a diagnosis, but also prescribe effective therapy. In the treatment of lymphadenitis, an integrated approach is important, so the veterinarian prescribes pharmacological drugs of various spectrums of action.
Firstly, the inflammatory process is suppressed. For these purposes, a course of antibiotics is prescribed, selected by the doctor taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogenic microorganisms that provoked the development of the disease in the dog.
Secondly, hepatoprotectors (drugs intended to maintain liver function) and probiotics are prescribed. They prevent the occurrence of side effects from antibiotics, since their use must be long-term and regular.
Thirdly, a vitamin-mineral complex is prescribed. Typically, special emphasis should be placed on vitamin A (retinol), vitamin B2 (riboflavin) and vitamin C (ascorbic acid). They will help the dog’s body recover much faster from illness.
In cases where inflammation of the lymph nodes is accompanied by a purulent process, surgical treatment is prescribed. It is necessary to open the inflamed area of tissue, and then install drainage (to remove exudate). Subsequently, the rehabilitation period includes regular application of anti-inflammatory ointments and the use of drugs to strengthen the animal’s immune system.
In some cases, your pet may be prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures. For example, heat treatment (ultra-high frequency therapy) helps to quickly reduce the inflammatory response. However, it is important to consider contraindications, the main of which is the detection of malignant neoplasms (oncology).
What to do if your dog has a bump
If you notice a lump or skin abnormality, start by:
- examine it and rub it with your fingers to make sure that it is really a lump and not matted fur or burrs;
- if the skin is inflamed, it can be wiped with a disinfectant (antiseptic);
- apply anti-inflammatory and wound healing cream.
Did you know? Rhodesian Ridgeback
-
fearless hunter.
Initially, these dogs were used to hunt lions. Some types of cones can be identified and helped by your pet yourself. Among these: insect bites, cuts, abscesses, hematomas, calluses and other seals.
| Cone type | How to help a dog |
| Ear hematoma | At the clinic, they will install a drainage into the hematoma and explain how to care for it at home. Before going to the doctor, you can apply an ice pack to your ear. Interestingly, in ancient times, starting from Ancient Egypt, hematomas were treated by applying leeches. If a clinic can offer this procedure, leeches are still effective and avoid the bloody mess of a drainage tube. |
| Abscess | If the abscess has opened, you need to rinse the skin with clean water. And then treat with an antiseptic and apply wound-healing ointment. For example, “Ichthyol ointment” or “Levomekol”. The procedure should be repeated 2-3 times a day for a week. But if the abscess is just developing, then you can use drugs that reduce inflammation: Simalgeks at a dosage of 2 mg/kg once a day, Carprofen 4 mg/kg once a day. If the cause of the abscess is a bacterial infection, then antibiotics will be recommended. |
| Insect bites | There is no antidote for bee stings. In most cases, its consequences go away on their own. But to relieve pain and swelling, if you are not allergic, apply an ice pack. "Hydrocortisone" ointment is applied to the bite site after cooling. If there is an allergy, then you need to give your pet an antihistamine: “Diazolin” or “Suprastin” 2 mg/kg. To relieve itching, Apoquel 0.4–0.6 mg/kg. If there is pain, use painkillers “Analgin” or “Spazgan” 1/2 tablet for a small dog or 1 tablet for a large one. |
| Pyoderma | Treated with antibiotics. The most commonly recommended are Amoxicillin, Cephalexin and Clindamycin. In severe cases - Enrofloxacin. The duration of therapy is 8–12 weeks. Topical treatments include sprays and medicated shampoos containing benzoyl peroxide, sulfur with salicylic acid, or chlorhexidine. The skin surface is treated with such preparations once a day for 3–5 weeks. |
| Inflammation of the paraanal glands | To clean the glands at home, you need to purchase petroleum jelly and medical sterile gloves. It is convenient to start treating your pet in the bathroom, since the secretion from the glands has a very unpleasant odor and can get on furniture. You need to insert your gloved index finger into the animal’s anus and feel the sides of the gland. They are shaped like balls. Using light massage movements, “pour out” the contents of these balls. After cleaning, the anal area is washed with detergent. Cleaning at home is not suitable for small dogs. Therefore, the procedure is carried out in a veterinary clinic. If the inflammatory process is not intense, then anti-inflammatory drugs are not prescribed. The pet will cope on its own. If not, then Cephalexin is prescribed for 5–15 days. Suppositories for rectal administration may also be recommended. For severe pain, anesthetics and sedatives are needed. |
General symptoms
Typically, subcutaneous bumps do not bother dogs in any way, even if they are in the active growth phase. Depending on the cause of origin, spherical seals can have different densities and diameters - from several millimeters to several centimeters. Skin irritation and itching usually occurs with insect bites. In other cases, the lump can only be detected tactilely. In short-haired breeds, “defects” are noticeable visually, but in long-haired breeds they are diagnosed only by palpation.
If the appearance of the lump is suspicious, and the ball under the skin does not resolve within 7-10 days, then the dog must be shown to a veterinarian. The following symptoms may alert the animal owner:
- The dog reacts painfully to palpation of the lump.
- The lump “grows” before our eyes, increasing in size several times in a short time.
- The subcutaneous tissue is opened, and pus or other discharge begins to ooze from the wound.
- The color of the skin around the lump changes.
- The pet becomes apathetic, eats poorly or refuses to eat at all, and sleeps anxiously.