Immunization against tetanus is mandatory for everyone: children and adults. It is thanks to this vaccine that millions of people are protected from such a dangerous disease.
However, the tetanus vaccine, like any other, is not without side effects. And a lump after a tetanus shot is one such example. We will talk about this problem and its solution.
When should adults and children get vaccinated?
The reason people get tetanus is because the tetanus bacillus (or Clostridium tetani in Latin) gets into the blood.
In the process of life, the microorganism begins to release many toxins that threaten a person with breathing problems, muscle cramps and nervous system disorders. For prevention purposes, all children are given a combination vaccine containing tetanus toxoid.
Types of combination vaccines include:
- tetanus toxoid (i.e., AS);
- adsorbed pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus vaccine (abbreviated DTP);
- adsorbed diphtheria-tetanus vaccine (which means ADS);
- adsorbed diphtheria-tetanus with reduced diphtheria toxoid (abbreviation ADS-m);
- plus many other vaccines sold in pharmacies (Tetraxim, Bubo-Kok, Infanrix and so on).
There is no natural immunity to tetanus. Therefore, all children who have reached the age of three months receive their first immunization. The next two vaccinations follow with an interval of 45 days.
Revaccination takes place at 18 months of life (that is, a year after the third vaccination). The next revaccinations are given at 7 and 14 years of age. Then every decade until the end of life.
Why might a lump form under the shoulder blade/shoulder after a tetanus shot?
Each person is individual and tolerates the vaccine differently.
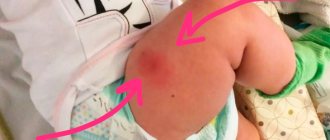
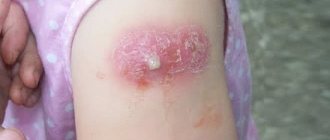
Although it is very rare for a tetanus shot to cause complications, some people may experience a lump after the shot. The swelling is formed due to the vaccine toxoid injected under the skin, which is adsorbed on aluminum hydroxide. Thanks to it, viral cells remain in the body for a long time, creating the necessary immune response.
Therefore, it is very important to inject the vaccine into the area where muscle tissue is best developed. It is in such places that the absorption of the drug components occurs most quickly. For children who have not reached the age of one and a half years, the most suitable place for injection is the thigh.
Then the vaccine is placed in the shoulder area or under the shoulder blade. The final decision on the injection site is made by the examining physician. As already mentioned, the muscle is considered the most optimal area for administering a tetanus shot.
But if the drug is not injected deeply enough, but only under the skin, it penetrates into the blood too slowly. This is the main reason for the formation of a lump at the injection site. The vaccine accumulates in the puncture area and takes longer than usual to dissolve.
The lump may be painful, but it does not pose any health hazard. You just need to wait for it to completely disappear (the process takes no more than two months).
How to relieve pain?
If the tetanus injection site is swollen and painful, it is worth taking some measures that will quickly ease the pain, relieve swelling and alleviate the general condition. Taking medications such as Ibuprofen and Acetaminophen will help reduce pain and possible fever. The medicine is taken for several days, 1-2 tablets throughout the day.
An ice compress applied to the injection site will help get rid of swelling and reduce pain. Ice helps relieve inflammation and swelling. It is recommended to do such procedures for 10-15 minutes (it is important to avoid hypothermia) several times a day for the first couple of days after vaccination.
If the pain remains 2 days after the injection, then it is better to apply dry heat. A good effect is obtained by applying a heating pad or cloth treated in warm water.
You can speed up the absorption processes of the active components of the vaccine and, therefore, improve your well-being, using ointments and gels that have absorbable, anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory properties. The product is rubbed into the swollen area of skin with light, massaging movements 2-3 times throughout the day.
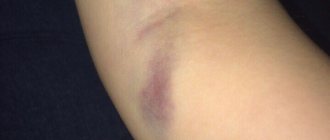
What should I do if, after a tetanus shot, the injection site hurts, is swollen and red?
The presence of unpleasant sensations after a tetanus vaccination is caused by such reasons as:
- aluminum hydroxide in the vaccine . This substance is designed to hold the toxoid at the injection site, ensuring its gradual absorption into the blood. Despite its harmlessness, aluminum hydroxide can cause unpleasant reactions at the vaccination site;
- anti-pertussis component . Included in complex tetanus vaccines. It causes adverse reactions in few cases, since it carries weakened but still living whooping cough bacteria;
- improper storage and transportation of vaccines;
- injection of the vaccine into the subcutaneous fatty tissue . If for one reason or another the injection was not given in the muscle area, then there is a high probability of compaction, redness or swelling. Fortunately, they all go away with time.
Swelling with a diameter of less than 8 centimeters is considered normal, and induration is up to 5 centimeters. Exceeding these standards is a reason to consult a doctor. In general, pain in the arm area after a tetanus vaccination is the most common reaction of the body. It is normal and should not cause any concern.
The most common question from patients suffering from pain at the vaccination site is how long can these unwanted symptoms last? If all immunization rules have been followed, the pain should go away within a couple of days after the procedure.
You can treat a bump in children with Troxevasin ointment.
But if the vaccine gets under the skin and forms a lump, then the unpleasant sensations can last for months. Compresses and non-aspirin painkillers will help here.
You can also recommend absorbable ointments for children (this could be Troxevasin or Children's Rescuer). A single dose of Nurofen will not do any harm. But only a pediatrician will be able to select the most suitable means for effective and rapid resorption of the tumor.
Adults are also recommended to use ointments. Anti-inflammatory drugs (for example, Nise or Ibuprofen) can cope with unpleasant sensations after vaccination.
There should be no reason to worry if there is pain at the injection site. All unpleasant symptoms will certainly pass after some time.
What should you do if a tumor forms on your back/arm and does not go away for several days?
Most people get a tetanus shot without serious complications. However, there may be many side effects and complications for some people.
Tetanus toxoid
As already mentioned, the appearance of a tumor at the site of vaccination is nothing more than the result of the vaccine getting under the skin. Despite the fact that the resorption process may take months, this is not a cause for concern and does not require intervention.
Only if negative symptoms last longer than expected should you consult a doctor. More attention should be paid to other human conditions that may be caused by the tetanus vaccine.
The most dangerous complications include:
- convulsions;
- severe allergic reactions;
- loss of consciousness;
- vomiting;
- asthma;
- diarrhea;
- and circulatory disorders.
The above side effects are a serious cause for concern and require prompt medical intervention. Adults generally respond better to tetanus immunization than children. Each child’s reaction is individual and if after vaccination the injection area is swollen and painful, then this is normal.
In addition, the child may experience:
- migraine;
- lack of appetite;
- tearfulness;
- headache;
- elevated temperature.
Severe symptoms that require immediate attention include:
- convulsions;
- severe runny nose;
- obvious skin reactions;
- changes in myocardial function;
- vomiting and diarrhea.
But such complications in children are quite rare. Some people worry that getting the bud wet after grafting can cause a lot of problems. In fact, the injection site is allowed to be wetted with water.
The only thing you really shouldn't do after a tetanus vaccine is:
- drink alcohol within a week after immunization;
- visit saunas or steam baths within five days after vaccination;
- rub the injection site, apply cosmetics there;
- take heavy physical activity for the above period.
If all rules and recommendations are followed, a person should not have problems or complications after vaccination.
When to see a doctor
If a child or adult experiences convulsions after vaccination, it is necessary to take him to the hospital.
Serious complications occur rarely - less than 1%. However, there is a risk, and you need to be able to recognize dangerous conditions in time:
- The reaction to the vaccine lasts more than two days.
- The pain under the shoulder blade is jerking, shooting in nature and intensifies.
- The area of redness increases.
- Vomiting more than once.
- The headache is difficult to relieve with painkillers.
- Convulsions appeared.
- Hives all over the body.
- A drop in blood pressure immediately after vaccination or on the first day.
- Difficulty breathing.
- The pain radiates to the arm or the other half of the back.
There should not be such signs even with a very severe reaction to the vaccine. If they occur, the patient should immediately consult a doctor. With timely assistance, these conditions pass without leaving serious consequences. If they were observed, in the future this will become a contraindication for repeated vaccinations with the same drug.
Video on the topic
An allergist-immunologist explains why the injection site swells and hurts after vaccination:
Tetanus vaccination is the simplest and most proven way to protect a person from this disease. Although this vaccine is not without side effects, there is always the opportunity to purchase the necessary product that can alleviate the patient’s condition after immunization.
The appearance of a lump after vaccination is a small price to pay for the risk of contracting tetanus. Especially considering that the compaction always goes away on its own.
Features of the preparatory stage
It is better to prepare for the procedure in advance. This will protect the body from unwanted manifestations and reduce the risk of severe complications. When you sign up for a tetanus vaccination, you need to follow simple recommendations regarding the preparatory period:
- before visiting the treatment room, it is better to undergo general tests that will help ensure your good health;
- Before vaccination, the shoulder blade of an adult or child should be examined by a doctor and make sure that there are no inflammatory rashes or other damage on the skin;
- Before manipulation, a mandatory measure is to measure the temperature, as well as to exclude these symptoms of intoxication, such as headaches, nausea, chills;
- on the day of vaccination, you should avoid eating heavy and “harmful” foods that can provoke a hypersensitive reaction to the presence of the vaccine in the body;
- three days before vaccination, you can start taking antihistamines in maintenance dosages against allergies;
- immediately before vaccination, the shoulder blade or other selected injection site should be treated with an antiseptic solution, which will avoid infection of the wound;
- It is better to temporarily refuse immunization for patients who feel unwell on the appointed day, have a runny nose, cough or other symptoms of a cold (in this case, it is better to do the tetanus vaccination later).
During the preparation process, close attention is paid to the child being vaccinated. It is very important to take blood and urine tests, take care of your psychological state, and follow other recommendations of the pediatrician. When vaccinating against tetanus, it is better to protect the child from contact with other potentially sick children in the clinic, and also not to stay with him for a long time in a stuffy room. Parents should remember that overheating, infections and nervous shock can cause an overreaction to the vaccine.