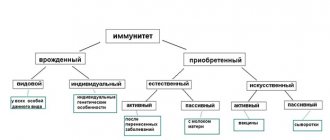
The incidence of coronavirus infection continues to remain at a high level. The only way to protect yourself and your loved ones from a disease that can take life or worsen your health for a long time is vaccination. In Moscow, hundreds of thousands of people have already received vaccinations against coronavirus, but to stop the epidemic it is necessary that the number of vaccinated citizens reach 80% of the total population.
Need more detailed information? Our specialist will tell you in detail about vaccination against COVID-19 and answer all your questions.
Call us at: +7 (495) 775-73-60
In this article, general practitioner Olga Igorevna Berezhko will tell you how vaccination against coronavirus is carried out in Moscow and how it is done in our clinic, and will also answer the questions that patients most often ask.
General information about the vaccine
JSC Medicine uses the Russian-made drug Gam-COVID-Vac, better known under the commercial name Sputnik V. The vaccine was developed and produced by the National Center of Epidemiology. N. Gamaleya. This is a two-component vector-type drug, the production technology of which is well known and has been tested many times over the past decade. The basis is two types of harmless human adenovirus, the shells of which are supplemented with protein particles of the S-protein of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. When the drug enters the human body, it causes an immune response, which consists of producing a sufficient amount of specific antibodies and forming stable immunity to COVID-19 infection.
When will vaccination start?
Many people are interested in when vaccination against coronavirus will begin in Moscow. We hasten to please our patients: it already began in December 2021 and continues to this day. At the initial stage, the event was held only among certain categories of people - those who, due to the nature of their professional activities, cannot limit the number of their contacts, those who are sufficiently young and healthy, and have reached the age of majority. At the clinic of JSC "Medicine" you can get vaccinated against coronavirus in comfortable conditions. The service is available to all citizens of the Russian Federation. More details on the services page.
Vaccination against coronavirus
JSC "Medicine" (Clinic of Academician Roitberg) provides vaccination against coronavirus infection (COVID-19).
You can undergo the procedure in comfortable conditions. The service is available to all citizens of the Russian Federation. Find out more
Currently, thanks to successfully completed trials, older people and patients with chronic diseases, i.e., those categories for whom COVID-19 infection poses the greatest danger, have gained access to immunization. So, if you're still waiting to get vaccinated against coronavirus, good news for you: you can get vaccinated right now.
General rules for vaccination
The vaccine can only be given to a completely healthy person. During the administration of the vaccine, the body is under stress, so it is important to properly prepare for the procedure.
Before vaccination, an examination by a pediatrician or therapist is required. It would be a good idea to take a general blood and urine test the day before.
You can properly prepare for vaccination and administer the vaccine in a specialized center. Each patient can count on detailed consultation, attentive attention and comfortable conditions in the vaccination room.
Who can get vaccinated?
Another popular question is who can get vaccinated against coronavirus? Currently, any resident of Moscow can get vaccinated if they do not have any contraindications to immunization, which are discussed below.
We recommend that you definitely get vaccinated against coronavirus if you are part of one of the groups most vulnerable to infection:
- belong to the age group of 60 years and older, in whom the disease, according to statistics, is most severe, and also often develops post-infectious complications;
- suffer from one or more chronic diseases;
- Due to the nature of their work, they are forced to come into daily contact with a large number of people, among whom there may be carriers of the infection;
- study at a higher or secondary specialized educational institution (after 18 years).
The procedure is absolutely voluntary, and anyone can refuse it.
Who will not be vaccinated?
The vaccine will not be given to those who have any manifestations of a cold or other infectious disease, general practitioner Nadezhda Chernyshova explained to Moscow 24.
“At the vaccination point, a person fills out a questionnaire where he answers questions about his health, vaccinations received, medications he takes, and diseases he has. Based on this questionnaire, the doctor decides whether to vaccinate today or not,” she says.
In general, experts agree that there are not many contraindications to vaccination. The procedure may be postponed to a later date in case of exacerbation of serious chronic diseases, as well as in emergency conditions.
Who should not be vaccinated?
Now let's talk about those who cannot be vaccinated against the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. People in this category include:
- have had coronavirus infection over the past six months;
- with severe allergic reactions;
- with hypersensitivity to the components included in the Sputnik V vaccine;
- currently suffering from influenza, ARVI, or other infectious disease;
- with any other disease in the acute phase, including chronic;
- pregnant and lactating women;
- children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
For these groups, the introduction of a coronavirus vaccine can have unpredictable consequences, so it is better for such people not to take risks and postpone the vaccination for a more favorable time.
Separately, we should talk about people who have recovered from the disease: often a mild illness does not create lasting immunity. This is easy to find out: just take a test for antibody levels after COVID-19. If the result is positive for antibodies, no vaccination is needed. If the level of immunoglobulins is questionable, it is still better to get vaccinated.
How long is it better to stop drinking alcohol before and after vaccination?
According to Vladimir Bolibok, before a medical procedure it is better not to drink alcohol the day before and immediately before the vaccination itself, including “for courage.” Previously, the director of the Gamaleya Research Center for Epidemiology and Microbiology, Alexander Gintsburg, also stated that it is worth giving up alcohol for three days after vaccination.
We strongly recommend abstaining from alcohol for three days after each injection. Alexander Ginzburg
Director of the Gamaleya Research Center for Epidemiology and Microbiology
“Of course, we are not talking about any complete ban on alcohol during vaccination. We are just talking about reasonable limitation of consumption until the body has formed its immune response to coronavirus infection,” Gunzburg explained.
Should you get vaccinated?
Many Muscovites doubt whether to get vaccinated against coronavirus, and their fears are understandable. The vaccine was registered under an accelerated procedure, but its trials have not yet been completed. In addition, there is still no exact data on how the drug will affect people who have already had latent illness or are currently ill. And the period during which immunity to coronavirus will work is still not precisely known.
At the same time, there are many compelling arguments in favor of vaccination.
- The effectiveness of the Sputnik V vaccine, according to tests, is 96%. This means that 96 out of a hundred people at the end of immunization will not get sick after contact with infected people, and if infection does occur, they will suffer a mild form of the disease.
- So far, no cases of severe, let alone lethal, consequences of the introduction of Sputnik V have been registered, while a number of foreign vaccines have many questions related to their safety.
- After receiving the coronavirus vaccine, you may be freed from some social restrictions. For example, many countries are planning to introduce or are already introducing the most favorable regime for vaccinated people. It is possible that the Russian authorities will follow their example.
- At the clinic of JSC "Medicine" a thorough check of patients is carried out before administering the drug. Such strict measures serve as an additional guarantee that there will be no unpredictable consequences.
- The drug for vaccination against coronavirus in Moscow is currently provided to residents of the capital free of charge.
Types of fruit tree grafting
Budding
Budding is the grafting of a dormant bud into a cut in the bark of an annual shoot. It is used for mass propagation of fruit trees and is used mainly in nurseries, where a large number of seedlings are grafted. Annual seedlings no more than 1 cm thick are budded.
The timing of budding is the period of sap flow, when the bark is separated from the wood. In central Russia this is approximately the end of April - beginning of June, depending on the conditions of a particular year.
For scions, developed buds are taken from the middle part of annual shoots. Buds for budding must be large, mature and free of mechanical damage.
Budding. Preparation of the shield, cutting and winding. The figure on the right shows the sequence of cuts to obtain a shield with a kidney.
The buds are cut out on “scutellums” - sections of wood about 3 cm long.
On the rootstock, a T-shaped incision is made in the bark in a place free from buds (opposite the bud and just above it). The edges of the incision are lifted and the shield is inserted into the incision. The place where the kidney is implanted is wrapped with a special tape. The tape is wound tightly, without folds or sagging.
In one and a half to two weeks, the established budding will become visible. The buds on them are starting to grow. If the budding does not take root, then the procedure is repeated if time permits (the bark is still peeling off).
Vaccination for bark
Grafting behind the bark is done when there is a significant difference in the thickness of the scion and rootstock. The rootstock is a skeletal branch or a central conductor, cut down so that a stump of the required length remains. On one rootstock, 2 - 5 vaccinations are made.
The optimal period for completing the work is the period of sap flow (the same as for budding), when the bark is well separated from the wood.
The bark of the rootstock is cut or attempts are made to insert cuttings without violating its integrity (the latter is better). The scion will be a cutting with three buds, taken from the middle of a one-year shoot. A vertical incision is made in the bark of the rootstock, into which a part of the cutting cut obliquely is inserted. The grafting site is coated with garden varnish or other special compound and wrapped with tape. It is important to coat the cut area - the end of the hemp.
Grafting for bark and grafting for bark with saddle.
For reliable fixation and increasing the area of contact with the rootstock, a ledge (saddle) is made on the scion. The saddle rests on the upper edge of the sawn stump. This is called "saddle bark grafting."
Grafting by copulation and copulation in the butt
Copulation is used when the thickness of the scion and rootstock is comparable. Copulation grafting is done on one-year-old seedlings and mature fruit trees.
The best results are obtained if copulation is carried out in early spring before the start of sap flow. The best time for stone fruits is the end of March - the beginning of April, and the best time for pome trees is the beginning of April - mid-June. Night temperatures should be consistently positive, with short-term frosts not affecting survival rate. The second period suitable for copulation is from the last ten days of July to mid-August.
The scion for copulation is a cutting with 3 - 4 buds, prepared in the same way as in the previous case. To improve the contact of the scion with the rootstock, an “improved” copulation (with a tongue) is made.
Copying (left) and copulating into the butt (right).
To graft by simple copulation, the scion and rootstock are cut obliquely and the sections are applied one to the other. If the rootstock is thicker than the scion, they are combined on one side. The cut length of both combined shoots is made the same.
For improved copulation, an additional cut is made on each cut, forming a tongue at the junction of the shoots. First, make an oblique cut, then retreat 1/3 from the bottom edge of the cut and make an incision along the grain of the wood another 1/3. It takes skill and training, but nothing complicated.
Copulation into the butt is done when the rootstock is so thicker than the scion that it is impossible to combine the cambial layers over a sufficient area. They do a simple copulation in the butt and a copulation with the saddle. Scion cuttings are prepared in the same way as for bark grafting. Either a regular oblique cut or an oblique cut with a saddle is made. An oblique cut is made on the rootstock so that its dimensions coincide with the dimensions of the cutting cut. The method requires practice to make good cuts on the rootstock.
Vaccinations performed using grafting pruners can also be considered a type of copulation. With this method, the scion and rootstock must be of equal diameter.
Grafting in a lateral incision
Grafting into a side cut is done on rootstocks of any thickness and allows you to achieve good fusion on apple, pear, and plum trees. According to some reports, it does not take root well on cherries.
The operation is performed throughout the entire frost-free period.
A cut 2 - 2.5 cm long is made on the rootstock with a depth of approximately 1 cm into the thickness of the wood, into which the lower end of the scion, sharpened like a wedge, is inserted. The upper bud of the scion should be directed outward, away from the trunk. 3 - 7 buds are left on the scion. A larger number of buds on a cutting accelerates its entry into fruiting.
Prepare the scion cutting by making two oblique cuts at its lower end to form a wedge equal in length to the cut on the rootstock. On the inside of the cutting, which will be adjacent to the rootstock, the cut is made slightly longer than on the outside. This will allow you to more accurately align the cambial layers of the scion and rootstock (light green stripe in the image of the cutting) at least on one side. Ideally, the cambial layers will coincide completely. The grafting site is tied with tape, trying to achieve maximum tightness.
The top of the rootstock is cut off 20 - 30 cm above the grafting site, leaving a thorn. This thorn is used to tie up a cutting that has taken root and started to grow to give it the desired position in space. After the cuttings have grown together and become lignified, the thorn is cut down into a ring.
If the work was done in the spring, the cutting will take root and begin to grow in the same summer. If in the fall - by the summer of next year.
Grafting into cleft
Cleft grafting is done to replace the entire crown of the fruit tree or some part of it. For example, to replace a broken large branch.
The operation is carried out in the spring before the buds open.
Replacing the entire crown allows you to rejuvenate the plant or save a plant damaged by frost.
To implement this method, the entire tree is cut down at the required height (usually at the height of the trunk) or a branch is cut down, leaving a stump of the required length. The tree or branch should not be old, covered with rough, cracked bark. Choose branches that are 3 to 9 years old. If the thickness of the rootstock allows, two cuttings are inserted into one split, along its edges. You can also split the stump into 4 parts and plant 4 cuttings on it. In any case, you need to imagine what to do next with the cuttings that have taken root and sprouted shoots. The grafting site is tied with tape, trying to achieve maximum tightness. The operation is carried out in the spring before the buds open. Cuttings are prepared from the middle part of well-formed growths of the previous year. The sooner you finish the job and cover the grafting site with a special compound, the better.
Proximity grafting (ablactation)
Ablation allows you to splice parts of one plant or parts of different plants without separating the scion from the plant on which it was located before grafting.
The best time for ablation is spring.
The scion can be a branch of the same tree on which the rootstock is located or a branch of a neighboring tree. Often there is simply no distinct scion and rootstock - both branches being brought together are the same. When ablacting, the branches are bent one towards the other (brought together) and tied with tape, wire, rope, even a nail or self-tapping screw, with obligatory coating. It is important that close branches cannot move relative to each other.
To align the cambial layers, cuts are made on both branches. The cuts can be simple or with tongues. The method allows you to connect branches crosswise (see figure).
Ablation is used to strengthen falling branches or trunks (for example, when a fork breaks with an acute angle), to create living architectural forms or hedges. Sometimes proximity grafting occurs spontaneously if two branches are pressed tightly against one another. This is exactly how the method was discovered by observing nature.
If ablacturing is done to fasten a branch that is breaking, it is better to cut the bridge from the same tree on which it will be grafted. Or from a tree of the same variety.
Where to get vaccinated?
Mass vaccination in Moscow against coronavirus is carried out in all city clinics. You can easily find the address of the nearest medical institution on the websites of the Moscow City Health Service or the Moscow City Hall.
However, many Muscovites prefer to receive medical services in private clinics, so Meditsina JSC invites everyone to sign up for a coronavirus vaccination in Moscow. All medical procedures are carried out in strict accordance with international protocols. For the high level of patient service, our clinic has repeatedly received awards and encouragements from international organizations and from our government. We do everything in our power for the convenience and safety of patients.
Care after vaccination
It is necessary to monitor the condition of the grafting site and care for the plant. To prevent drying, paper caps (bags) are put on the cuttings. After the buds have germinated, their upper part is cut off to provide access to light. Once the young shoots from them reach a length of 3-4 cm, protective equipment will no longer be needed.
If the grafting was carried out behind the bark or in a side cut, then after the cuttings have engrafted, the upper part of the rootstock is cut off, retreating 10-15 cm from the grafting site. The cut on the tree is coated with garden varnish. All side branches are removed from the part of the rootstock remaining above the grafting site, then a shoot grown from the grafted material is tied to it.
The grafted buds are protected from the bright sun with paper. When tying the grafting site, a strip of paper is placed under the last round of tape in the kidney area. If the grafted cuttings grow slowly or have dried out, then two shoots are left under the grafting site in order to re-graft in the future.
If the grafted material is actively growing and the shoots are long, then they are tied to support pegs to avoid breaking off. Several shoots may begin to grow at the same time at the grafting site. As soon as they reach a length of 15-20 cm, only one of them, the most developed, is left. Excess shoots are cut off with a knife or pruning shears. If 2-3 shoots turn out to be strong, then the upper one is left to grow, and the lower ones are pinched in mid-June.
During the summer, the strapping on the grafted plant is changed 2-3 times so that the growing tissues do not become overtightened. If the grafted cuttings grow well in length and thicken in diameter, then it is better not to remove the binding, but to loosen it. If you remove it in July, the growing part may break off, especially when grafted onto the bark. When the grafted shoots grow intensively and a constriction forms at the grafting site, the bark is cut longitudinally down to the wood from different sides in several places and tied again. As the cuts become overgrown with callus, the binding is loosened or replaced.
After double grafting (into the crown of the grafted plant) at the end of June or early July, the binding is removed by carefully cutting it vertically with a knife.
In summer, grafted plants are fed 1-2 times with nitrogen-containing fertilizers and watered abundantly. If necessary, spray with agents to combat diseases and pests.
Formative pruning is not carried out this year, and the shoots on the trunk are pinched. Numerous shoots usually form around the rootstock, which must be removed. The next year in the spring, the binding is removed from the grafted plants, and the thorns remaining on the rootstock are cut off at an angle of 20°. The sections are treated with garden varnish as usual, and then the treatment is repeated 1-2 times in the summer. Young shoots from the grafted material are shortened by a third to form a branch.
Preparing for vaccination
It should be stated right away: the official protocol does not require any preparatory actions from the patient. You just need to bring your Moscow registration document or work certificate with you to receive the vaccine for free.
To avoid a possible negative reaction of the vaccine components to the presence of the virus, it is advisable to test for the presence of infection or antibodies in the body before administering the drug.
Smart preparation for coronavirus vaccination includes:
- examination by a general practitioner;
- PCR test or rapid test for coronavirus to detect current infection;
- a test for IgG antibodies to the coronavirus S protein to determine the level of the immune response.
These tests will determine whether there is currently an infection in your body, as well as find out the level of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 if you previously suffered from the disease in a latent form.
How is vaccination against coronavirus going in Moscow and Russia?
The procedure for administering the coronavirus vaccine is carried out in two stages with an interval of 21 days. This is necessary to cause an effect of increasing antibody production (booster effect). Most of the volunteers who participated in the drug trials developed stable immunity four weeks after the first dose.
The general procedure for vaccination against coronavirus in Moscow, as well as throughout Russia, is the same and consists of the following steps.
- When you arrive at the vaccination office, you fill out a questionnaire in which you indicate general information about yourself and medical data necessary to identify contraindications.
- You will be carefully examined by a therapist to make sure there are no acute illnesses. The examination includes measuring temperature and blood pressure.
- The epidemiologist gets acquainted with the documents, including test results, and makes a decision on admission to vaccination.
- A nurse injects Sputnik V into the muscle tissue of the forearm.
- For half an hour you rest in the hall under the supervision of an epidemiologist to prevent the development of adverse reactions in the body.
- You receive a certificate indicating the dates of the two stages of vaccine administration.
- The next day, the epidemiologist checks by phone to see if you are feeling well.
Can pregnant women get vaccinated?
Photo: portal of the mayor and government of Moscow/Maxim Mishin
Vladimir Bolibok explained that pregnant women are now allowed to be vaccinated with Sputnik V. At the same time, the specialist classified them in the “with caution” category.
For women who are just planning a pregnancy, I recommend getting vaccinated in advance, because many people who have been ill have disturbances in the intrauterine development of the child. Vladimir Bolibok
doctor - allergist-immunologist
“COVID-19 causes microthrombosis, including in the vessels of the placenta. Blood circulation is disrupted and the child suffers. Children are often born prematurely or with signs of intrauterine infection,” he emphasized.
What are the dangers of vaccination against coronavirus?
One of the most frequently asked questions by our patients is: what are the dangers of vaccination against the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus? For healthy people without contraindications, the possibility of unwanted side effects, judging by the test results, is extremely small. The likelihood of developing dangerous consequences increases for several categories of patients.
- Those who have been ill. If the body contains large quantities of IgG antibodies to the S-protein of the virus, then a person may develop a cytokine storm - a dangerous condition characterized by the rapid development of an inflammatory process, which can even lead to death. At the same time, the lack of antibodies does not create the necessary protection against re-infection. Therefore, people who have had an infection, even in a mild form, should do an IgG antibody test before vaccination.
- People with medical contraindications. In some cases, the ban on immunization is temporary. So, if you get sick with ARVI, then after recovery you need to wait two weeks, after which you can get vaccinated. If you have a severe allergy, it is impossible to predict how the immune system will react to the components of the vaccine, so you should refrain from vaccination.
- People with chronic diseases. If the disease is not currently aggravated, then the possibility of vaccination should be discussed with your doctor to avoid the risks of worsening the condition.
But even in the absence of contraindications, after the vaccine is administered, certain consequences of vaccination against coronavirus may appear. Some people experience a slight increase in temperature, chills, headache, muscle aches, and the injection site remains painful for one to two days. These unpleasant sensations usually disappear on their own. If these symptoms do not go away after three days, you should call your doctor. For temperatures above 39°C that do not go away for more than six hours, you must call an ambulance. Under the supervision of highly qualified specialists of Meditsina JSC, you do not have to worry about your health. Find out more on the services page.
Rootstock and scion
Rootstock is the part of a tree onto which vegetative material from another tree is grafted. Usually this is a sapling or trunk, and sometimes the root collar of a tree, seedling or wild root growth that can be dug up in the forest. A scion is a part of another tree capable of engraftment and growth (cuttings and buds). As a rule, they are taken from a tree of a similar species or variety. After grafting, a plant is obtained with a crown or branch that has new properties. At the same time, its roots and trunk are well developed and adapted to growing conditions. In this way, you can get a new variety of tree in your garden or even grow two varieties of fruit on one tree. If a new variety is more demanding on soil fertility and cannot grow on your site, then by grafting vegetative material from it onto an existing fruit tree, you can get a harvest much faster. A rootstock adapted to the local soil will provide the grafted plant with all the necessary nutrients.
In order for the grafting to be successful and the new plant to grow and bear fruit, the rootstock and scion must be of high quality - young, healthy, well developed. As a rootstock, trees are usually chosen that are adapted to local climatic conditions and frosts, as well as with beneficial properties (short, dwarf, resistant to root diseases). The rootstock and scion must be compatible. Typically, plums are grafted onto plums, cherries and cherries onto cherries, apricots onto apricots and plums, apples only onto apples, and pears onto apples, pears and quinces. If a seedling or wild shoot from the forest was used for the rootstock, then after planting or transplanting to another place you need to wait 1-2 years until it takes root, and only then vaccinate. You can grow a rootstock from seeds, but this is a rather lengthy process, so existing young trees are used as a rootstock. If vegetative material is grafted onto a plant older than 10 years, it will not take root well.
For better survival, place the cuttings in a container with a small amount of water a day before grafting. In conditions of warmth and moisture, they will come to life after long-term storage in the cold and will grow faster with the rootstock after grafting. It is not recommended to immerse them in water to a significant depth to prevent the bark from getting wet.
How long does the vaccine last?
The developers of the Sputnik V vaccine believe that due to the booster effect provided by two-stage vaccination, effective protection will persist for at least two years after administration of the drug. However, today no one can say for sure how long the coronavirus vaccine lasts, since not a single vaccine has passed all the tests required by the international protocol. Manufacturers of Western vaccines guarantee no more than six months of immune protection for their drugs.
Vaccine administration intramuscularly
Perhaps this method can be called the most common and effective. It is characterized by a high rate of development of immunity due to the rapid entry of the vaccine into the body and its distribution to the desired areas.
Since the vaccine quickly spreads through the bloodstream, the risk of allergic reactions in this case is minimized.
The vaccine is given intramuscularly:
- for children under two years of age in the anterolateral surface of the thigh;
- children from two years old in the shoulder.