The incidence of coronavirus infection continues to remain at a high level. The only way to protect yourself and your loved ones from a disease that can take life or worsen your health for a long time is vaccination. In Moscow, hundreds of thousands of people have already received vaccinations against coronavirus, but to stop the epidemic it is necessary that the number of vaccinated citizens reach 80% of the total population.
Need more detailed information? Our specialist will tell you in detail about vaccination against COVID-19 and answer all your questions.
Call us at: +7 (495) 775-73-60
In this article, general practitioner Olga Igorevna Berezhko will tell you how vaccination against coronavirus is carried out in Moscow and how it is done in our clinic, and will also answer the questions that patients most often ask.
General information about the vaccine
JSC Medicine uses the Russian-made drug Gam-COVID-Vac, better known under the commercial name Sputnik V. The vaccine was developed and produced by the National Center of Epidemiology. N. Gamaleya. This is a two-component vector-type drug, the production technology of which is well known and has been tested many times over the past decade. The basis is two types of harmless human adenovirus, the shells of which are supplemented with protein particles of the S-protein of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. When the drug enters the human body, it causes an immune response, which consists of producing a sufficient amount of specific antibodies and forming stable immunity to COVID-19 infection.
How vaccines work
What are vaccines?
These are immunobiological preparations, the main active principle of which is a modified pathogen (weakened, killed, represented by fragments or toxoids).
What are vaccines supposed to protect against?
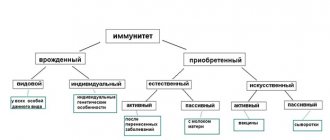
From an infectious disease. What is its reason? Is it only in the entry of the corresponding pathogen into the body? Of course not. Otherwise, everyone infected would get sick. But this never happened even during terrible epidemics of plague, cholera, not to mention smallpox, tuberculosis, polio, diphtheria, influenza, etc. That is, in addition to the pathogen itself, no less a role in putting pressure on the “scales” of health -diseases (both in the sense of the very fact of the disease and the ability to cope with the disease) are played by internal factors, both congenital and acquired. Since the second half of the 19th century, they began to be called a very familiar term today - “immunity”.
Etymologically, this word means “liberation, getting rid of something.” Immunity (in relation to the infections we are considering) is essentially the innate or acquired ability of the body to protect itself and get rid of pathogens that have penetrated it. It is this ability that the vaccine introduced into the body is designed to create.
Now we come close to answering the third question.
What is the target of the vaccine?
That same “internal factor” is the immune system, which plays a decisive role in the development of the disease and its prognosis, and not the causative agent. The latter serves as a target for other “weapons” in the fight against infections - antibiotics or antiviral drugs. And if the pathogen is more or less universal (for a specific disease in a narrow time range), then the state of the immune system is very individual!
What does the vaccine do?
Changes the state of the immune system in order to acquire the ability to recognize and destroy a specific pathogen. The expected result is the body’s resistance/immunity to this infection (for a short or long term).
Will it be formed?
- Maybe yes.
- Perhaps, for one reason or another, the body is not able to produce it, and the introduction of the vaccine will not only not strengthen, but will worsen its condition.
- Perhaps it already exists, and there is no need for vaccination.
The actual outcome of vaccination depends not so much on the characteristics of the vaccine, but on the current state of the immune system (and other systems) of a particular person. Hence the variability in the effects of vaccination (with the same vaccines) in different people.
Differences between natural immunity and post-vaccination immunity
The differences in the formation of natural and post-vaccination immunity cannot be discounted. It’s not for nothing that the latter is often called “crutches.”
Natural immunity (with rare exceptions of infection directly through the blood) is formed in response to the penetration of the pathogen through the natural boundaries of the body with the external environment - the skin and mucous membranes. In response to an invasion, a cascade of reactions is triggered: recognition, memorization of the pathogen, development of protective measures “here and now” and for a long period of time with the gradual inclusion of cellular and humoral mechanisms of fast and slow action. As a result, we have stable, reliable, and most often lifelong protection.
Very important starting points are missing in the formation of vaccine immunity. Why? Because the vaccine most often (there are several vaccines that are administered through the mouth or nose) bypasses the “border posts”, entering directly into the blood (intramuscular administration is considered optimal by many). As a result, immunity is either defective or short-term, requiring repeated stimulation.
The result of artificial stimulation of the immune system can be its depletion, subsequently leading to the so-called. delayed post-vaccination complications: allergies, autoimmune diseases, chronic infections, cancer, etc. Or - to the development of acute or chronic forms of the disease for which they were vaccinated.
Natural infections that a child’s body becomes familiar with serve as a kind of “trainer” for his immune system. For example, there are studies that have shown that frequent contact of children with “kindergarten” respiratory infections reduces the risk of developing acute lymphoblastic leukemia by 30–40%! Other scientists have proven that people who have had measles in childhood are less susceptible to cancer and significantly less likely to die from cardiovascular diseases.
Another important point. Ideas about how natural and vaccine immunity arises are based on knowledge in this area of yesterday and today. But there is every reason to believe that this knowledge is very, very incomplete, and that the process of forming protection is much more complex and “multidimensional.”
For example.
The effectiveness of post-vaccination protection is assessed by the number of corresponding antibodies formed in response to the introduction of the vaccine (antigen). But there is evidence that a large number of antibodies does not always protect their owner from infection and the severe course of the corresponding disease. This is, firstly. And, secondly, there are children (and there are many of them) who are not capable of producing antibodies to the antigen introduced with the vaccine. For example, with respect to diphtheria toxin (one of the components of the DTP polyvaccine), the proportion of such children is 10–12 percent.
On the other hand, people who were born unable to produce antibodies (with so-called agammaglobulinemia; antibodies are immunoglobulin molecules) often remained healthy during direct contact with infections and/or were capable of forming lasting immunity in case of illness.
The answer to the question: what is better - artificial stimulation of the immune response or the natural process of its formation - can only be individual.
- For a specific child with specific characteristics of the immune system, living in specific conditions.
- Regarding a specific disease and the risks of contracting it.
- Taking into account the already known principles and stages of development of the immune system of the child’s body.
When will vaccination start?
Many people are interested in when vaccination against coronavirus will begin in Moscow. We hasten to please our patients: it already began in December 2021 and continues to this day. At the initial stage, the event was held only among certain categories of people - those who, due to the nature of their professional activities, cannot limit the number of their contacts, those who are sufficiently young and healthy, and have reached the age of majority. At the clinic of JSC "Medicine" you can get vaccinated against coronavirus in comfortable conditions. The service is available to all citizens of the Russian Federation. More details on the services page.
Vaccination against coronavirus
JSC "Medicine" (Clinic of Academician Roitberg) provides vaccination against coronavirus infection (COVID-19).
You can undergo the procedure in comfortable conditions. The service is available to all citizens of the Russian Federation. Find out more
Currently, thanks to successfully completed trials, older people and patients with chronic diseases, i.e., those categories for whom COVID-19 infection poses the greatest danger, have gained access to immunization. So, if you're still waiting to get vaccinated against coronavirus, good news for you: you can get vaccinated right now.
Who can get vaccinated?
Another popular question is who can get vaccinated against coronavirus? Currently, any resident of Moscow can get vaccinated if they do not have any contraindications to immunization, which are discussed below.
We recommend that you definitely get vaccinated against coronavirus if you are part of one of the groups most vulnerable to infection:
- belong to the age group of 60 years and older, in whom the disease, according to statistics, is most severe, and also often develops post-infectious complications;
- suffer from one or more chronic diseases;
- Due to the nature of their work, they are forced to come into daily contact with a large number of people, among whom there may be carriers of the infection;
- study at a higher or secondary specialized educational institution (after 18 years).
The procedure is absolutely voluntary, and anyone can refuse it.
Who should not be vaccinated?
Now let's talk about those who cannot be vaccinated against the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. People in this category include:
- have had coronavirus infection over the past six months;
- with severe allergic reactions;
- with hypersensitivity to the components included in the Sputnik V vaccine;
- currently suffering from influenza, ARVI, or other infectious disease;
- with any other disease in the acute phase, including chronic;
- pregnant and lactating women;
- children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
For these groups, the introduction of a coronavirus vaccine can have unpredictable consequences, so it is better for such people not to take risks and postpone the vaccination for a more favorable time.
Separately, we should talk about people who have recovered from the disease: often a mild illness does not create lasting immunity. This is easy to find out: just take a test for antibody levels after COVID-19. If the result is positive for antibodies, no vaccination is needed. If the level of immunoglobulins is questionable, it is still better to get vaccinated.
Complex vaccines
For example, MMR is a vaccine against measles, mumps and rubella; pentaxim - against diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, polio and hemophilus influenzae.
Their effectiveness and safety have been questioned by many scientists and doctors due to the following observations:
1. Under natural conditions, a person never suffers from several infections at the same time.
2. One of the components of the vaccine can provoke the formation of an incomplete immune response to its other component. For example, the rubella component of the complex MMR vaccine reduces the effectiveness of measles protection.
3. Simultaneous introduction of several live (weakened) pathogens into the body (for example, as part of the same COC) significantly increases the risk of complications (for example, inflammatory bowel disease).
Should you get vaccinated?
Many Muscovites doubt whether to get vaccinated against coronavirus, and their fears are understandable. The vaccine was registered under an accelerated procedure, but its trials have not yet been completed. In addition, there is still no exact data on how the drug will affect people who have already had latent illness or are currently ill. And the period during which immunity to coronavirus will work is still not precisely known.
At the same time, there are many compelling arguments in favor of vaccination.
- The effectiveness of the Sputnik V vaccine, according to tests, is 96%. This means that 96 out of a hundred people at the end of immunization will not get sick after contact with infected people, and if infection does occur, they will suffer a mild form of the disease.
- So far, no cases of severe, let alone lethal, consequences of the introduction of Sputnik V have been registered, while a number of foreign vaccines have many questions related to their safety.
- After receiving the coronavirus vaccine, you may be freed from some social restrictions. For example, many countries are planning to introduce or are already introducing the most favorable regime for vaccinated people. It is possible that the Russian authorities will follow their example.
- At the clinic of JSC "Medicine" a thorough check of patients is carried out before administering the drug. Such strict measures serve as an additional guarantee that there will be no unpredictable consequences.
- The drug for vaccination against coronavirus in Moscow is currently provided to residents of the capital free of charge.
I am a student
Young adults, especially those living in close quarters (dormitories or barracks), should be vaccinated according to age according to the national calendar. And also annually undergo seasonal vaccination against influenza and revaccination against tick-borne encephalitis if they live in an endemic area.
In addition to the calendar, you can vaccinate against the following list of diseases:
- whooping cough (even if you were vaccinated as a child or were ill, especially if you missed a revaccination against diphtheria and tetanus at age 14);
- HPV (if not vaccinated as a teenager);
- chicken pox and hepatitis A, if you have not been sick and are not vaccinated.
- Particular attention should be paid to meningococcal infection. Due to lifestyle changes, teenagers and young adults have an increased risk of encountering this extremely nasty bacteria. They can also become a source of it for younger siblings and older relatives who are vulnerable to it.
Where to get vaccinated?
Mass vaccination in Moscow against coronavirus is carried out in all city clinics. You can easily find the address of the nearest medical institution on the websites of the Moscow City Health Service or the Moscow City Hall.
However, many Muscovites prefer to receive medical services in private clinics, so Meditsina JSC invites everyone to sign up for a coronavirus vaccination in Moscow. All medical procedures are carried out in strict accordance with international protocols. For the high level of patient service, our clinic has repeatedly received awards and encouragements from international organizations and from our government. We do everything in our power for the convenience and safety of patients.
Preparing for vaccination
It should be stated right away: the official protocol does not require any preparatory actions from the patient. You just need to bring your Moscow registration document or work certificate with you to receive the vaccine for free.
To avoid a possible negative reaction of the vaccine components to the presence of the virus, it is advisable to test for the presence of infection or antibodies in the body before administering the drug.
Smart preparation for coronavirus vaccination includes:
- examination by a general practitioner;
- PCR test or rapid test for coronavirus to detect current infection;
- a test for IgG antibodies to the coronavirus S protein to determine the level of the immune response.
These tests will determine whether there is currently an infection in your body, as well as find out the level of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 if you previously suffered from the disease in a latent form.
Features of the immune system in children
1. The immune system of a newborn child is NOT MATURE! Its maturation duration coincides with the entire period of childhood.
But this does not mean that the baby born is absolutely defenseless against external aggressors. At first, its main defense is maternal molecules (immunoglobulins), transmitted to the baby in utero and continuing to enter his body during breastfeeding. It is not without reason that the latter serves as the most effective disease prevention measure for infants.
2. The process of active development of the child’s immune system goes through several critical periods:
- the first month of life (0–29 days) - passive protection of the baby by maternal antibodies; your own defense mechanisms are still very imperfect;
- 4–6 months - the “validity period” of passive protection ends and the active formation of your own begins;
- the second year of life - a sharp increase in the variety of contacts with the outside world against the background of still insufficient internal security;
- the sixth to seventh year of life and adolescence (12–15 years) - active changes in the functioning of the immune system, temporarily increasing the body’s susceptibility to certain infections.
These periods are called “critical” because at this time the child’s immune system is most sensitive and capable of unpredictable reactions in response to a foreign agent (antigen) entering the body.
Their comparison with the vaccination calendar (easy to find freely available online) shows that many vaccines (antigens) are introduced into the child’s body precisely during periods of maximum vulnerability of its defense system. This is especially true for vaccinations in the first hours (vaccine against hepatitis B), in the first days (vaccine against tuberculosis - BCG) and in the first months (vaccine against whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus - DTP; vaccine against polio, etc.) of a baby’s life.
How is vaccination against coronavirus going in Moscow and Russia?
The procedure for administering the coronavirus vaccine is carried out in two stages with an interval of 21 days. This is necessary to cause an effect of increasing antibody production (booster effect). Most of the volunteers who participated in the drug trials developed stable immunity four weeks after the first dose.
The general procedure for vaccination against coronavirus in Moscow, as well as throughout Russia, is the same and consists of the following steps.
- When you arrive at the vaccination office, you fill out a questionnaire in which you indicate general information about yourself and medical data necessary to identify contraindications.
- You will be carefully examined by a therapist to make sure there are no acute illnesses. The examination includes measuring temperature and blood pressure.
- The epidemiologist gets acquainted with the documents, including test results, and makes a decision on admission to vaccination.
- A nurse injects Sputnik V into the muscle tissue of the forearm.
- For half an hour you rest in the hall under the supervision of an epidemiologist to prevent the development of adverse reactions in the body.
- You receive a certificate indicating the dates of the two stages of vaccine administration.
- The next day, the epidemiologist checks by phone to see if you are feeling well.
conclusions
The purpose of the above facts is not to belittle and denigrate the very idea of vaccinations as a way of protecting against suffering and death. Vaccinations may well act as an individual therapeutic drug (for example, anti-rabies or anti-tetanus). Or as a reasonably necessary means of prevention for healthy people going on a trip (to areas rich in infections that are unusual for us). There may be other individual arguments in favor of vaccination. Moreover, science does not stand still, and as our knowledge about the functioning of the immune system grows and the system of pre- and post-vaccination control improves, the effectiveness and safety of new vaccines will increase.
The purpose of the above facts and thoughts is to encourage people to think and pay special attention to the following points:
- mass vaccination of newborns and infants;
- vaccination of children without justified, individual need and mandatory availability of a genetic passport and immunological examination results;
- vaccinating children without prior parental consent (especially in maternity hospitals!);
- vaccination of children with live vaccines (BCG, DTP, polio, measles, rubella, mumps);
- use of vaccines containing toxic components;
- simultaneous administration of several vaccines;
- intimidation and other elements of economic and psychological pressure on people (both those being vaccinated and those vaccinating);
- the need to provide complete information about the pros and cons of vaccination, possible complications, the rights of parents to refuse vaccinations and its consequences, about alternative methods of preventing and treating diseases.
Yes or no to vaccinations? The choice is yours. The main thing is that it is yours - conscious and voluntary!
What are the dangers of vaccination against coronavirus?
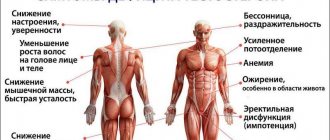
One of the most frequently asked questions by our patients is: what are the dangers of vaccination against the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus? For healthy people without contraindications, the possibility of unwanted side effects, judging by the test results, is extremely small. The likelihood of developing dangerous consequences increases for several categories of patients.
- Those who have been ill. If the body contains large quantities of IgG antibodies to the S-protein of the virus, then a person may develop a cytokine storm - a dangerous condition characterized by the rapid development of an inflammatory process, which can even lead to death. At the same time, the lack of antibodies does not create the necessary protection against re-infection. Therefore, people who have had an infection, even in a mild form, should do an IgG antibody test before vaccination.
- People with medical contraindications. In some cases, the ban on immunization is temporary. So, if you get sick with ARVI, then after recovery you need to wait two weeks, after which you can get vaccinated. If you have a severe allergy, it is impossible to predict how the immune system will react to the components of the vaccine, so you should refrain from vaccination.
- People with chronic diseases. If the disease is not currently aggravated, then the possibility of vaccination should be discussed with your doctor to avoid the risks of worsening the condition.
But even in the absence of contraindications, after the vaccine is administered, certain consequences of vaccination against coronavirus may appear. Some people experience a slight increase in temperature, chills, headache, muscle aches, and the injection site remains painful for one to two days. These unpleasant sensations usually disappear on their own. If these symptoms do not go away after three days, you should call your doctor. For temperatures above 39°C that do not go away for more than six hours, you must call an ambulance. Under the supervision of highly qualified specialists of Meditsina JSC, you do not have to worry about your health. Find out more on the services page.
Necessary conditions for vaccination
Let us repeat, a vaccine is a potent drug, the prescription of which requires strong indications and, STRICTLY, the absence of contraindications for each individual person. Especially for a child. And three times especially for a newborn. Most of those who are called “anti-vaxxers” are not against the idea of vaccines, but against their mass, thoughtless use, since numerous studies have shown that such an approach has not been justified.
Yes, some diseases are almost a thing of the past (for example, smallpox). But the winner’s laurels in these cases are ready to share with vaccines a number of other social, sanitary-epidemiological and therapeutic measures (improving the quality of food and water, the appearance of sewage systems, refrigerators and personal hygiene products; the invention of antibiotics, etc.).
Other diseases, for example, tuberculosis, on the contrary, despite mass vaccination in maternity hospitals (BCG), are confidently regaining their lost positions. So confident that currently in Russia there are tens of times more cases of tuberculosis than in countries where newborn children are not vaccinated with BCG.
Why doesn't the protection work? Perhaps because:
- 99 percent of children do not need such a vaccination at all. They are immune to tuberculosis even without it.
- In some of the remaining 1% susceptible to this disease, the vaccine may trigger the development of the so-called. “vaccine-associated” tuberculosis in severe form (it can manifest itself both immediately and years after the vaccine is administered). Children with a weakened immune system (with so-called primary and secondary immunodeficiencies) are at particular risk.
Moreover, the risk of post-vaccination complications leading to chronic illnesses, including disability and death, is present in ALL children with immunodeficiencies (as well as fermentopathy and other genetic diseases), and not only in those who are constitutionally sensitive to the causative agent of tuberculosis.
Only a preliminary special examination - genetic screening and determination of the immunological status of newborns - can identify such problems and protect children from harm. Only on the basis of its results can an individual decision be made for and against the introduction of certain vaccines. Do we conduct such an examination before the first vaccination? As a rule, no.
Genetic (neonatal) screening is carried out after the first vaccination (at least hepatitis B; often also BCG). Determining immune status is not at all included in the mandatory examinations of newborns. It turns out that the role of “screening” (“selection, sorting”) of children with a weakened immune system is played by the vaccinations themselves (which are clearly contraindicated for such children). The result is severe complications.
It is for this reason that many doctors and scientists are opposed to mass vaccination without prior examination.
How long does the vaccine last?
The developers of the Sputnik V vaccine believe that due to the booster effect provided by two-stage vaccination, effective protection will persist for at least two years after administration of the drug. However, today no one can say for sure how long the coronavirus vaccine lasts, since not a single vaccine has passed all the tests required by the international protocol. Manufacturers of Western vaccines guarantee no more than six months of immune protection for their drugs.
What vaccines do adults need?
Measles, rubella, diphtheria, chickenpox and other infectious diseases are often called “childhood diseases.”
The fact is that before the start of mass vaccination, people first encountered these diseases in childhood and either died or acquired lifelong immunity. Therefore, adults no longer suffered from them. Nowadays, adults become infected with “childhood” diseases no less often. Why?
The fact is that many vaccines do not provide lifelong protection. Yes, they can protect, but there is no guarantee. Adults need routine booster vaccinations against many diseases. And if children are given it as planned, according to a schedule, then the adult must take care of himself.