Why is the Prevenar vaccine included in the vaccination schedule?
Prevenar is a vaccine designed to prevent pneumococcal infections.
Pneumococcus is “responsible” for 30% of all pneumonia, and such pneumonia is severe and with complications (such as pleurisy, lung abscess, pericarditis, arthritis, sepsis).
Children under 5 years of age are at risk for pneumococcal pneumonia. Pneumococcus causes from 30% to 60% (according to various sources) of childhood otitis media.
Pneumococcal infection is a common cause of meningitis and sepsis in children and adolescents.
Are there any analogues to the Prevenar vaccine?
Prevenar is not the only vaccine that prevents pneumococcal infection. Among the most famous and effective analogues of the drug are:
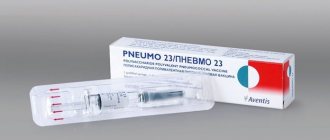
- French vaccine "Pneumo 23", containing polysaccharides from 23 serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae;
- “Pneumovax 23” is an analogue of the previous suspension;
- vaccine "Prevenar 13" - a drug based on conjugates of Streptococcus pneumoniae (13 serotypes), used for children from 2 months and adults;
- Belgian vaccine "Synflorix", which protects against 10 serotypes of the pathogen and Haemophilus influenzae.
Only the doctor should make a decision on the advisability of administering a particular vaccine solution, based on the history and examination of the child, as well as taking into account the individual characteristics of his body. Before the procedure, the pediatrician must assess the likelihood of negative consequences of vaccination. And only after making sure of the safety of preventive measures in a specific clinical case, give permission to carry out the manipulation.
Is anti-pneumococcal immunization of the population necessary? Pediatricians hear this question every day. If you believe official statistics, then recently a huge number of microorganisms have acquired relative resistance to existing antibacterial drugs. Therefore, the only way to prevent infection and avoid pathology is to use vaccine fluid to develop an active immune response against the pathogen.
Prevenar: vaccination scheme
- Children aged 2 to 6 months: three vaccinations at least a month apart (usually at 2, 3, 4 or 2, 4, 6 months), then revaccination at 12-15 months.
If vaccination was not started in the first half of life, the scheme is as follows:
- Children aged 7 to 11 months: two vaccinations at least a month apart, then revaccination in the second year of life.
- Children aged 12 to 23 months: two vaccinations at least two months apart.
- Children aged 2 to 5 years: only one vaccination.
Contraindications
The Prevenar vaccine is given only as prescribed by a doctor. Strict contraindications to the administration of an immune drug are:
- bacterial and viral diseases in the acute period of their development;
- chronic processes in the acute phase;
- past illness;
- increased body temperature;
- individual intolerance by the child’s body to individual components of the vaccine preparation;
- the child is up to two months old.
In addition, it is better to refuse the vaccine if the child has received a blood transfusion. In such circumstances, vaccination should be delayed for 3-4 months after the transfusion procedure.
Possible post-vaccination reactions
- Soreness at the injection site (36.5% of children), fever (usually up to 38 degrees, in 1% of cases - higher), vomiting and diarrhea (less than 10% of children)
- In children over two years of age, local reactions are observed more often, but they are short-lived
- Seizures and severe allergic reactions after administration of Prevenar are observed less than in 1 case in 10,000
In cases of respiratory immaturity (premature infants under 28 weeks), the child should be monitored for 72 hours after initial vaccinations, as the risk of apnea is slightly increased. It is not recommended to postpone Prevenar vaccination, because this group of children especially needs it.
special instructions
Given the rare incidence of anaphylactic reactions with any vaccine, the vaccinated patient should be under medical supervision for at least 30 minutes after immunization. Immunization sites must be provided with anti-shock therapy.
The Prevenar® 13 vaccine cannot provide prevention of diseases caused by pneumococci of other serotypes, the antigens of which are not included in this vaccine.
High-risk children under 2 years of age should receive an age-appropriate primary vaccination with Prevenar® 13. In patients with impaired immunoreactivity, vaccination may be accompanied by a reduced level of antibody formation.
The drug should be transported at a temperature of 2–25 °C. Do not freeze.
Transportation at temperatures above 2–8 °C is allowed for no more than 5 days.
Synflorix, Prevenar, Prevenar-13, Pneumo-23 - what's the difference?
- Synflorix and Prevenar 13 are close analogues of the Prevenar vaccine. The Prevenar vaccine has been used longer, it includes the 7 most common serotypes of streptococcus, Synflorix - 10, Prevenar-13 - respectively, 13.
- Synflorix and Prevenar-13 are produced in Russia under an agreement with the Pfizer concern and are included in the national vaccination calendar.
- The Prevenar vaccine is produced in the USA.
- All three vaccines can be used to vaccinate children under 2 years of age.
As for Pneumo-23, this vaccine is intended for vaccination of children from 2 years of age and protects against the 23 most common serotypes of streptococcus. This vaccine is produced in France.
Features of preparing a child for vaccination and actions of parents after it
To ensure that immunization with the Prevenar vaccine is not accompanied by side effects, the child’s parents must take care to follow simple rules to minimize the risk of negative reactions. Among these mandatory activities, the following should be highlighted:
- before vaccination, it is necessary to show the child to a doctor for an examination and to determine possible contraindications to the drug;
- after administering the suspension, it is strictly forbidden to wet the injection site, as well as bathe the child for 24 hours;
- for several days after vaccination, it is not recommended to visit crowded places with the little patient, but spend more time in the fresh air;
- It is not allowed to introduce new dishes into the child’s diet or feed him foods with increased allergenic properties;
- mothers of infants who are breastfed are prohibited from eating unhealthy foods, semi-finished products, etc.;
- if the temperature increases, the child should be given an antipyretic medicine according to the recommendations.
Vaccination does not require preliminary preparation of the baby. Despite this, some pediatricians insist on the need for a blood test before immunization, to ensure that the child does not have hidden inflammatory processes. After administration of the solution, allergy sufferers are advised to take antihistamines to prevent the development of an allergic reaction to the components of the vaccine.
Prevenar - vaccination... who did it???
Here I finally decided to ask if anyone in Russia has been vaccinated with Prevnar , a pediatric vaccine for the prevention of pneumococcal infections in children aged 2 months to 5 years, a child??
We did it, and started asking friends who have children, but no one had ever heard of this...
Prevnar is a pediatric vaccine for the prevention of pneumococcal infections in children aged 2 months to 5 years. The seven-valent conjugate vaccine Prevnar (or Prevenar) is intended to protect against seven strains of pneumococci. It is developed by Wyatt and licensed in the United States and more than 70 other countries. However, this vaccine does not include two serotypes (types 1 and 5) that cause a significant proportion of pneumococcal infections in developing countries. (Conjugate vaccines, which have been proven to be highly effective, are produced by binding purified polysaccharides—complex sugars—from the outer layer of the causative bacterium to a “carrier” protein.) The use of this vaccine in the United States has led to a significant reduction in the incidence of pneumococcal disease not only among immunized children, but also among unimmunized populations due to reduced transmission. Wyatt also completed trials of a nine-valent conjugate vaccine involving serotypes 1 and 5. A phase 3 trial involving 40,000 subjects was completed in South Africa in 2002, and a phase 3 trial involving 17,437 subjects was completed in The Gambia in 2004. During trials in South Africa, the vaccine reduced the incidence of invasive infections caused by relevant serotypes by 83% among children who did not have HIV and by 65% among children with HIV. Trials in The Gambia demonstrated that the vaccine was 77% effective in protecting against infections caused by the relevant serotypes; that it resulted in a 37% reduction in the incidence of pneumonia (as confirmed by chest X-ray) compared with the control group; and that among recipients, overall mortality decreased by 16%. Source: WHO Instructions for use of the vaccine Prevenar (Prevnar®) The pneumococcal polysaccharide conjugate adsorbed vaccine includes seven active substances, which are pneumococcal polysaccharides obtained from gram-positive bacteria Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F and 23F, individually conjugated to the diphtheria carrier protein CRM197, and adsorbed on aluminum phosphate. PHARMACOLOGICAL GROUP Vaccine for the prevention of pneumococcal infections IMMUNOLOGICAL PROPERTIES Mechanism of action Vaccine administration Prevenar causes the production of antibodies to capsular polysaccharides of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, 23F, providing specific protection of the body from the infections they cause. Immunological effectiveness In children of the first year of life, starting from 2 months of age, using various vaccination regimens, the formation of a protective immune response was demonstrated after a series of primary vaccination and a secondary immune response to the last dose, i.e. during revaccination. Prevenar induces the formation of functional antibodies to all vaccine serotypes. In children aged 2 to 5 years, a pronounced formation of antibodies to all vaccine serotypes is observed after a single administration of Prevenar, while the immune response is almost identical to that in children of the first two years of life after a series of primary immunizations. PURPOSE Prevention of diseases caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F and 23F (including sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia, bacteremia and acute otitis media) in children aged 2 months to 5 years. CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity following previous administration of Prevenar, hypersensitivity to excipients and/or diphtheria toxoid; acute infectious and non-infectious diseases, exacerbation of chronic diseases (in these cases, vaccination is carried out after recovery or in remission). METHOD OF APPLICATION AND DOSES The vaccine is administered only intramuscularly into the anterolateral surface of the thigh (children under 2 years old) or into the deltoid muscle of the shoulder (children over 2 years old). Vaccination schedule for children Age Dose Number of doses Scheme From 2 to 6 months. 0.5 ml. 3+1 revaccination 3 doses with an interval of at least 1 month, 1 dose is usually administered at the age of 2 months. The 4th dose (booster) is recommended to be administered at the 2nd year of life, optimally at 12-15 months. From 7 to 11 months 0.5 ml. 2+1 revaccination 2 doses with an interval of at least 1 month, the 3rd dose is recommended to be administered at the 2nd year of life From 12 to 23 months. 0.5 ml. 2 2 doses with intervals between administrations of at least 2 months. From 2 to 5 years. 0.5 1 1 dose once SIDE EFFECTS The safety of Prevenar has been studied in healthy children aged 6 weeks to 18 months. In all cases, Prevenar was administered concomitantly with other recommended childhood vaccines. The most common adverse reactions were pain at the injection site and fever (increased temperature). During revaccination, the most common cases observed were cases of quickly passing pain at the injection site (36.5%), as well as cases of short-term limitation of the range of motion of the limb due to pain at the injection site (18.5%). In older children who received a single dose of the vaccine, a higher incidence of local reactions was observed than in children under 1.5 years of age, but these reactions were short-lived. OVERDOSE Several cases of overdose of Prevenar, as well as the administration of the subsequent dose earlier than prescribed, have been described. The adverse reactions observed during overdose corresponded to those observed when using the recommended single doses of Prevenar. INTERACTIONS WITH OTHER MEDICINES AND OTHER TYPES OF INTERACTIONS Prevenar can be administered to children simultaneously (on the same day) with other vaccines included in the National Immunization Schedule (with the exception of BCG), as well as with the vaccine against Hemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) and the hexavalent vaccine Infanrix, according to the prescribed immunization schedule. Vaccines must always be administered to different parts of the body. RELEASE FORM: 0.5 ml of the drug in disposable syringes made of transparent, colorless borosilicate glass.
TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE CONDITIONS At temperatures from 2 to 8 0C. SHELF LIFE: 3 years