A complex drug based on calcium salt helps restore metabolism and prevent the development of many pathologies. Affordable and effective, it restores the normal level of one of the main macroelements in the body, relieving a variety of painful symptoms.
Composition and dosage form
Calcium chloride (CaCl2) is formed during the production of baking soda. The substance is used not only in medicine, but also in cooking, cosmetology, and the chemical industry. Without it, it is impossible to produce healthy calcined cottage cheese and hard cheeses.
The pharmaceutical form of calcium chloride is a water-based injection solution. Available in transparent glass ampoules of 5 or 10 ml. The cardboard packaging of the drug contains 10 such ampoules. The concentration of the medicinal compound in 1 ml of solution is 100 mg.
Cross-drug interactions
You cannot simultaneously use preparations containing lead salts and monovalent mercury, as this can lead to the formation of insoluble compounds.
Use with drugs from the tetracycline group is not allowed.
During the use of calcium channel blockers, a decrease in their therapeutic effectiveness is observed.
Taking Quinidine may cause deterioration of intraventricular conduction, which significantly increases the risk of toxic effects of quinidine.
Parenteral administration of drugs is not recommended, since there is a high probability of increased cardiotoxic effects with the simultaneous use of cardiac glycosides.
How does calcium chloride work?
The product exhibits anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, detoxifying properties, stabilizes the blood formula, helps strengthen vascular walls, and reduces their permeability. Calcium in the drug ensures normal functioning of the muscles and heart, regulates the conduction of nerve impulses, bone tissue synthesis, increases resistance to infections, participates in the absorption of vitamins and minerals, and maintains the necessary balance of electrolytes. Calcium chloride also normalizes the condition of the kidneys, somewhat increases diuresis, relieves and prevents swelling, helps restore the functioning of the adrenal glands, and promotes the release of adrenaline.
After use, about half the dose of the drug binds to blood proteins. Part of it is absorbed by the body. The transformation of calcium chloride occurs in the liver, the excess is excreted in the intestinal contents and urine. The intensity of excretion and absorption of the drug depends on age-related changes, dietary habits, the presence of calcium-containing foods in the diet, and hormonal status.
Contraindications for use
Contraindications to the use of hot injections include chronic renal failure. Intravenous administration of calcium chloride is not recommended if the patient has signs of atherosclerosis. This drug is capable of dilating blood vessels, which can lead to the detachment of formed plaques and the formation of blood clots.
Such injections should not be performed if the patient has elevated calcium levels. Contraindications to the use of such injections include chronic pathologies of the cardiovascular system. The combination of hot injections with cardiac glycosides is especially dangerous.
The administration of calcium supplements to patients suffering from cancer is not recommended. Such injections should be used with caution if the patient has genetic pathologies.
Indications for use
It is recommended to use a 10% solution of the drug:
- with calcium deficiency caused by malnutrition, systemic diseases, endocrine disorders, intestinal disorders;
- when there is a need for increased doses of calcium: age-related changes, periods of active growth, postpartum complications, general physical exhaustion;
- for bleeding of various origins;
- with nutritional edema;
- for hepatitis;
- with rickets, osteomalacia;
- for tuberculosis;
- for kidney inflammation;
- for allergic reactions;
- in case of intoxication with fluorine, magnesium, oxalic acid preparations.
During childbirth, calcium chloride is necessary to prevent eclampsia and to stimulate contractile activity of the uterus.
"Calcium gluconate"
Injections of “Calcium Gluconate” are given for allergies, diseases of the skin, blood vessels, calcium deficiency, and conditions accompanied by inflammation. The drug is an antidote for magnesium salts, oxalic acid, and fluoric acid, therefore its use in case of poisoning with these substances is justified. Other indications:
- dysfunction of the nervous system caused by poor signal conduction;
- various bleedings;
- allergies, including those that occur with the development of bronchitis and asthma attacks;
- severe liver condition;
- disorders of vitamin D metabolism, incl. with rickets;
- chronic diarrhea;
- long-term use of antiepileptic drugs, corticosteroids, diuretics;
- pathologies accompanied by increased permeability of cell membranes;
- sharp changes in calcium levels downwards, if the process is caused by metabolic disorders and rapid excretion of the macroelement.
Calcium gluconate is injected exclusively intravenously. The injection must be given slowly; if the injection is administered too quickly, the heart may stop. The medicine is also administered by drip and intracardiac injection. Intramuscular injections are excluded; this is fraught with necrosis.
You cannot inject Calcium Gluconate into small veins, otherwise swelling of the mucous membranes and inflammation of the vessel walls may develop. Contraindications are: hypercalcemia, drug intolerance, high probability of thrombosis, severe forms of hypercalciuria, renal failure.
Calcium gluconate should be prescribed by a doctor, and a specialist should supervise the injection. When using the product, monitoring the processes of phosphorus-calcium metabolism is important. It would be rational to keep the amount of calcium in the patient’s urine under control if hypercalciuria and nephrourolithiasis are detected. To prevent stones from appearing in the urinary tract and kidneys, you need to drink more water.
When is calcium chloride contraindicated?
The injection drug should not be used in cases of increased blood clotting, thrombosis, vascular atherosclerosis, or in conditions of hypercalcemia. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are also contraindications. An exception may be an individual indication when the benefit to the mother outweighs the risks to the child.
It is necessary to refuse therapy if you have an allergic reaction. Its possible signs: increased swelling, severe skin itching following administration, bronchospasm, suffocation.
pros
Calcium chloride or hot injection has a wide range of medicinal properties, so it is often included in the therapeutic regimen for many diseases.
Allergy.
The human body needs calcium not only for strong bones and teeth (about foods that strengthen teeth - here). Another important function is to maintain the level of permeability of cell membranes. During an allergic reaction, permeability increases, leading to swelling and itching. The drug helps control the symptoms. Read about how to prevent childhood allergies here.
Acne.
Hot injections are indicated for the treatment of acne and promise quick results. During the procedure, specialists administer calcium chloride or calcium gluconate intravenously. Active substances reduce the inflammatory process and restore tissue metabolism. (Interesting facts about skin that you didn't know are here).
Bleeding
. Calcium is used to improve blood clotting - the medicine has a hemostatic effect. Calcium chloride is used as an adjuvant in the treatment of various types of bleeding, for example, uterine or nasal bleeding. 10 facts about blood that you didn’t know are here.
Insect bites.
Hot injections are good for relieving irritation and swelling caused by insect saliva. Calcium chloride instantly improves the well-being of the victim.
Side effects
When an injection is administered, the following body reactions are likely:
- burning pain along the veins;
- redness of the skin of the face, a feeling of heat in the mouth, face, neck and throughout the body;
- decreased heart rate, arrhythmia;
- pain in the stomach, abdominal cavity;
- nausea, vomiting.
Within 20–30 minutes after the medicine enters the bloodstream, the discomfort weakens and passes. If the injection is administered too quickly, cardiac problems may occur.
The purpose of the injection against alcoholism
The main purpose of using the method of chemical protection with an injection against alcoholism is to enable a person with alcohol addiction to temporarily free himself from the addiction and adapt to life without alcohol. After the end of the chemical protection period, the effect goes away.
In some cases, the patient's intolerance to ethyl alcohol may not be sufficient. The dosage can be adjusted by a narcologist and increased if the patient does not have a pronounced aversion to alcohol.
The key point in the method of chemical protection using an anti-alcohol injection is the conscious and voluntary desire of the patient himself to give up alcohol and interrupt his addiction.
How to use calcium chloride according to instructions
In most cases, calcium chloride injections are prescribed by infusion: through droppers, at a rate of no more than 6 drops per minute. This way the drug causes fewer painful side effects. Jet injection is practiced less frequently. Intravenous injections are given slowly: administering the dose over 3–5 minutes. Subcutaneous and intramuscular injections of the drug are prohibited. The product does not dissolve in soft tissues, forming compactions and foci of necrosis.
The daily dose depends on the age and physical condition of the patients:
- For adults, the drug is administered in a volume of 5–10 ml per day;
- Children are dosed from 0.5 to 4–5 ml.
It is allowed to divide the daily dose into several parts and administer them at equal time intervals. In emergency cases, it is allowed to take calcium solution orally: consume the contents of the ampoules orally:
- for children and adolescents, the maximum dose is about 5 ml of the drug at a concentration of 10%;
- Adults can drink about 10–15 ml of the product per day.
The exact scheme, as well as the duration of the course of therapy, is determined individually.
Calcium chloride in cosmetics
The drug solution is popular as part of masks for deep cleansing of facial skin. You can use them at home:
- Apply the contents of the ampoule with a cotton swab to clean skin, repeat the procedure several times after each layer has dried;
- wash your hands with solid, fragrance-free toilet soap and apply foam to your face;
- rub the soap over the skin until characteristic pellets appear under the palms;
- Continue massaging until the entire mass is peeled off the skin.
This “rolling” removes dead particles of the epidermis, dissolves remaining sebum, softens and eliminates various imperfections, and narrows pores. Regular use normalizes sebum secretion and eliminates inflammatory processes. The mask is especially useful for dull, oily and problematic skin.
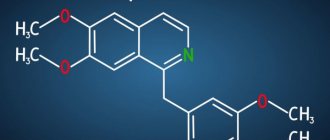
“Hot injection” for alcoholism: features of the procedure, duration of effect
Injection of a disulfiram-containing drug can be performed both at home and in a hospital setting. The manipulation itself takes a few minutes, but before that the doctor explains to the patient in detail how the medicine “works” and lists possible complications due to violating the strict ban on drinking. After this, the doctor asks you to sign a written consent for the injection.
Disulfiram is included in various medications:
- Esperal;
- Aquilong;
- Algominal;
- SIT et al.
The duration of the coding depends on the dose administered and can be up to 3 years. Alcoclinic additionally offers a double or triple block service, when several injections are made in different areas of the body.
Important!
Soon after the medical procedure, the person can return to their normal lifestyle, including driving.
Provocation
A few days later, a provocation is possible, in which the patient is given a cotton swab soaked in ethanol to sniff. The sensations that arise after this clearly demonstrate the encoding effect. Due to the high likelihood of an acute reaction to alcohol after a “hot shot” for alcoholism, this procedure is performed on an outpatient basis in the clinic (by appointment at a time convenient for the client).