Home » Articles » How to get rid of a bruise after an injection
Intravenous or intramuscular administration of medicinal solutions is one of the most effective, safe and rational ways to deliver them to the body. Despite the fact that medicine has been actively using injections for centuries and the technique for performing them has been thoroughly developed, it is not always possible to avoid side effects during the procedure. Hematomas are one of the most common. This article will discuss the causes of bruises and ways to combat them.
Knowing how to get rid of unpleasant, painful and potentially dangerous bruises, you can avoid complications that are caused by unprofessional injections. But it is much more advisable to prevent their occurrence by entrusting the injection to qualified professionals. In this case, the likelihood of hematomas and bumps is minimized.
Nature of the phenomenon
It should be understood that any injection performed subcutaneously, intravenously or intramuscularly has a destructive effect on the skin, muscles, capillaries and other tissues of the body. But bruises, redness and bumps do not always appear after injections. Scientists explain their occurrence by the presence of the following factors (or a combination of them):
- Lack of sufficient experience from a specialist. Bruises may appear if the needle was not inserted perpendicular to the plane of the body or deeper than it should be, its diameter and size were chosen incorrectly, and the piston was pressed faster than necessary
- Specificity of the administered drug. There are medications that, when they enter the bloodstream, spasm the blood vessels at the injection site, which causes stagnation of blood flow and, as a result, the appearance of bumps and bruises
- Lack (or complete absence) of disinfection. Such an omission is unacceptable, because it can cause complications, the treatment of which will take much longer than the original disease
Adviсe
After the intramuscular injection has been performed, the patient is not recommended to sit or lie down.
It will be better if a person walks for about 10 minutes. Such actions lead to rapid distribution of the medicine, which reduces the likelihood of bruising or hematomas. However, this will not help in situations where the procedure was performed incorrectly. You can also avoid formations by performing a massage at the injection site. If a bruise does appear, then over time it will begin to slightly change its shape, as well as color. This is normal, and you should not be alarmed by the changes, which nevertheless indicate a normal healing process. You can also warm the injection site with a regular heating pad and warm water. Or a solution of Dimexide. In the second case, you need to act according to the instructions. Otherwise, there is a possibility of causing a burn to the skin, causing inflammation, or poisoning the body. Share:
Why are bruises dangerous?
Bruising that turns into bruises, accompanied by lumps, can cause complications that are not so easy to get rid of. The most common of them will be discussed in more detail below:
- Abscess. In the medical literature, this phenomenon is characterized as an abscess that forms after an injection, accompanied by severe pain of a pulsating nature in the area of the bruise. Treatment is carried out by surgery or conservatively
- Allergic reactions. Expressed in the occurrence of severe itching at the injection site, swelling, sometimes a runny nose, shortness of breath, increased tearing and sweating, hematoma.
- Blood poisoning. This is the most serious thing that can happen after the injection. In this case, hospitalization and emergency treatment in a hospital setting, possibly a blood transfusion, will be required.
Reasons for appearance
The everyday expression “bruise” includes 2 concepts:
- Bruising, when spilled blood saturates the tissue, such a bruise resolves more easily and can be treated more quickly.
- Hematoma, when blood separates tissue, forming a limited cavity. In these cases, resorption is not always successful, and intervention is often required to remove blood. Hematomas are also prone to suppuration and abscess formation.
In medical practice, bruises are caused by various injections, diagnostic tests, and vaccinations.
Injections
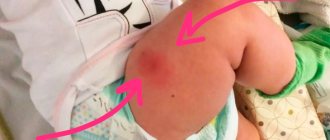
A bruise may form at the site of subcutaneous, intramuscular or intravenous administration of the drug. Subcutaneous injections are made along the outer surface of the middle and lower third of the shoulder, in the middle parts of the abdomen, intramuscular in the upper outer quadrant of the buttock, in the middle third of the thigh along the front surface.
These areas of the body are selected in places where there is no danger of damage to large vessels, but small vessels can also lead to the formation of a bruise or hematoma. Intramuscular hemorrhages are located deeper, so at first it is not a bruise that forms, but a compaction that is easy to palpate. If such a “bump” does not resolve for a long time and hurts, this indicates the formation of a hematoma and its inflammation.
Intravenous injections are performed in areas where veins are close to the skin. The cause of bleeding is the punctured vein itself: either it is pierced through, or after removal of the needle, the time of compression of the injection site is not enough for the formation of a blood clot. Hemorrhage in these cases can be quite significant.
Droppers
Bruises from IVs are common. Leaving a needle in a vein for a long time injures it, especially when the needle is poorly fixed to the skin. On the other hand, drip administration of solutions is more often carried out by seriously ill patients who already have problems with blood vessels and blood clotting. It is possible to develop a hematoma in the cubital fossa, as evidenced by swelling of the forearm.
Diaskintest and mantoux test
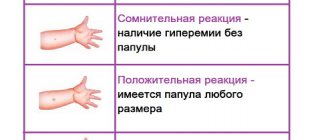
These tests are carried out to diagnose tuberculosis: with Mantoux, weakened bacilli are injected, for Diaskintest, a tuberculosis allergen is used. The technology for both tests is identical - 0.1 ml of solution is injected intradermally on the anterior surface of the forearm. An indicator of correct administration is the appearance of a “lemon peel” area.
After Diaskintest and Mantoux there should be no bruises if they are performed technically correctly. There may be slight subcutaneous hemorrhage if the solution is injected deeper into the subcutaneous tissue.
Flu shot
The flu vaccine is administered subcutaneously in the area of the outer shoulder or front of the thigh. Any noticeable hemorrhages after such injections are very rare. The introduction of needle-free injectors for flu vaccinations eliminates the problem of vascular damage and bruising.
Drug treatment
Traditional medicine has a wide range of methods and means that can help quickly get rid of bruises formed after incorrect injections. Here are the most common and effective:
- Local therapy. Involves the use of absorbable gels and creams
- The use of gels created to eliminate the consequences of varicose veins. They effectively constrict blood vessels and relieve inflammation
- Application of meshes. This is done using ordinary iodine. One of the simplest and most effective remedies that relieves swelling and removes bruises
- Lotions. To perform them, dimexide or magnesium sulfate pre-dissolved in hot water is used. A bandage or cotton wool is moistened in the solution and applied to the injection site
Treatment
A hematoma after surgery or a bruise from an injection indicates that the integrity of the blood vessels has been compromised. To speed up the healing process, doctors recommend resorting to the following remedies that are available at any pharmacy:
- Iodine network. If a bruise appears that not only spoils the appearance of the skin, but is also inflamed or painful, you can relieve the discomfort with an iodine mesh, which is applied to the affected area twice a day.
- Sodium sulfate. Treatment of hematomas is performed with a tampon soaked in the presented solution, followed by securing it to the buttock with an adhesive plaster (left overnight).
- Vishnevsky ointment. The procedure is quite simple, and involves applying a compress of the product to the area with a bruise; such manipulations also help relieve inflammation and disinfect.
There are easier ways to get rid of bruises:
Ointment bruise off
- use Bruise Off gel;
- use gel with bodyaga;
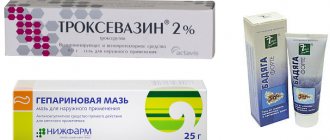
- lubricate the areas with Heparin ointment;
- resort to the help of Troxevasin;
- be treated with Traumeel.
Doctors also note that if during the injection not only a bruise appears, but also a lump, a kind of lump, then the resorption of such formations can take more than one month. Also note that you can make a mesh from iodine only if you are not allergic to the product.
Folk
Treatment of bruises and hematomas after injections can also be carried out using traditional medicine recipes. First of all, experts advise paying attention to bodyaga powder and making a medicinal ointment based on it. The product perfectly relieves swelling and inflammation, for which it is often used in cosmetology. You can also use a healing component such as a leaf of regular white cabbage. It needs to be washed, slightly warmed, and mashed with a meat hammer. Then a little smear the sheet with honey, apply it to the area where the bruise forms, cover it with polyethylene, and leave it overnight. A tandem of salt and clay helps against bruises (it’s better to take red or green). You need to mix the components in equal proportions, add a little water and make a cake, which is applied to the site of the bruise and left overnight. You can also use rye flour bread in combination with honey. As in the previous recipe. You need to mix the ingredients and make a cake out of them, and then apply it to the bruise, leaving it overnight.
Honey for bruises When wondering how to treat a bruise from an injection on the butt, you should also remember that honey, as an independent remedy, copes well with this problem. You need to warm it up a little and lubricate the buttock in the sore area, then wrap it in a warm cloth. And leave it on all night. Experienced people also advise mixing 4 parts rye flour, 2 parts honey and 1 part mustard powder and making a dough from them. And apply it to your butt twice a day.
Folk remedies
Healers, herbalists and other representatives of alternative medicine also have a lot of opportunities to influence bruises to completely eliminate them. The most effective ones will be discussed in more detail below:
- Wraps. Cabbage leaves, previously crushed and pierced in several places, are applied to the injection sites.
- Warming up. Use calcined salt or heated stones. They are applied to hematomas and held, periodically replacing with hotter ones
- Compresses. Various ingredients are used to prepare them: honey, onions, egg yolks. All this is mixed with wheat flour and applied to the bruises
- Chatterboxes. They are prepared from a solution of acetic acid mixed with raw eggs. Rub bumps and bruises with this mixture 2-3 times a day until they disappear completely.
- Apitherapy. Propolis tincture has a disinfectant and anti-inflammatory effect. Its use helps get rid of bruises, hematomas and seals
Not all doctors recognize the effectiveness of alternative medicine in getting rid of hematomas after unprofessional or unsuccessful injections, but they also fully accept their use as an aid in the process of conservative therapy.
Compresses for hematoma
If you don’t know what to do for a hematoma after an injection in the buttock, then use compresses based on a decoction of medicinal herbs or medications.
In addition, they can be made on the basis of creams intended to relieve inflammation, solutions of Dimexide and magnesium sulfate.
Apply a compress at night. To do this, cotton swabs are moistened with the medicine, placed on the lump and secured with bandages. The product penetrates into the soft tissues and promotes the resorption of the hematoma.
Preventive measures
Any qualified doctor will confirm that it is easier to prevent disease, pathology and dysfunction than to treat it. To avoid unwanted complications in the form of bruises, bruises and lumps, you must adhere to the following rules:
- It is good to disinfect injection sites
- Use only sterile syringes
- Choose the most suitable place for injections
- Use medications whose expiration date is within the acceptable range
- Inject smoothly
- Remove the needle along the same path along which it was inserted, without unnecessary movements
If you adhere to the recommendations described above, the likelihood that bruises will appear is reduced to almost zero.
Compress with Dimexide solution
The drug perfectly helps to dissolve blood clots, and also has anti-inflammatory properties and relieves irritation at the site of the hematoma.
"Dimexide" is mixed with water in a ratio of 1:10, respectively. A cloth soaked in the solution is applied to the injection site. Do not apply a compress to a hematoma.
Keep the compress for half an hour, after which it is removed and the lump is wiped with alcohol. To achieve the best result, the procedure should be performed several times every day.
Contraindications are:
- angina pectoris;
- intolerance to the components of the drug;
- childhood;
- nephropathy.
Before use, you should consult your doctor and carefully study the instructions for use.