Allergic reaction to a vaccine - myth or reality?
Comments on this issue are given by allergist-immunologist, medical pediatrician Tatyana Borisovna Gubinskaya.
According to various sources, approximately 20% to 40% of people have some kind of allergy, which can be caused by aeroallergens (including pollen), food and medications. These various allergies manifest themselves in different ways: in the form of allergic bronchial asthma, contact dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, food allergy or urticaria, and in the worst case - in the form of anaphylactic shock.
On January 29, 2021, Dr. Gary J. Stadtmauer, MD, published a message regarding the risks of anaphylaxis and severe allergic reactions in patients after they have been vaccinated against Covid-19. A total of 21 cases of confirmed anaphylaxis were reported after the first 1.8 million doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine were administered (approximately 1 in 87,000 injections). Although rare, this risk is significantly higher than the risk associated with other vaccines (1.3 per million).
All reported episodes of anaphylaxis occurred within 30 minutes of vaccine administration. No deaths were recorded. Of the 21 cases identified, 5 patients had a food allergy (food allergen not specified), of which 3 also had a history of drug allergy. In total, 12 patients had previous allergies to medications or vaccines, and one patient had allergic reactions to household allergens.
Prior to this announcement, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published data on delayed reactions following Moderna vaccination in the form of isolated facial swelling in patients who had previously undergone cosmetic procedures with various types of fillers. The timing of drug administration varied from 6 months before vaccination to 2 days after vaccination.
The most likely cause of adverse allergic reactions after vaccine administration is polyethylene glycol (PEG), which is present in both the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines to stabilize the mRNA.
From the point of view of the development of undesirable consequences after vaccination, before these cases, reactions to PEG were recorded extremely rarely. Theoretically, high molecular weight PEG may be immunogenic. However, previously reactions to PEG were identified as the cause of drug allergies, local reactions to toothpaste, and contact allergic dermatitis when using cosmetic products that contain PEG.
Unfortunately, diagnostic kits that would allow a preliminary allergological examination are not available in Russia today, which makes it difficult to assess risks. Therefore, in this case, we can only talk about an empirical analysis of the allergy history, based on the data of which it will be possible to judge the likely risks.
We can only say for sure that when vaccinated with drugs that use an adenoviral vector, and not mRNA (domestic vaccines against COVID-19), anaphylaxis cannot occur with PEG. However, as with any vaccination, allergic reactions to the injected drugs are possible. In this case, the question remains open: “What is their frequency?” Clinical observations that will be carried out in the future will provide more complete characteristics of the incidence of post-vaccination complications when using vaccines against Sars-Cov-2.
In general, recommendations for vaccination against Sars-Cov-2 in sensitive patients do not differ from those for standard vaccination. If undesirable consequences develop after vaccination, repeated administration of the drug is strictly contraindicated.
American gets completely covered in rash after vaccination
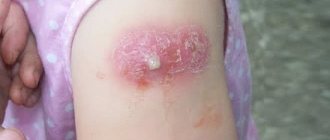
A 74-year-old Virginia resident developed a bright red rash and peeling skin after receiving one dose of the Johnson & Johnson coronavirus vaccine. This was reported by local TV channel WRIC.
Richard Terrell of Goochland developed a painful rash four days after receiving the vaccine. “I started to feel a little discomfort in my armpit and after a few days I developed an itchy rash and then after that I started to swell and my whole skin turned red. Everything happened very quickly.
Then the skin peeled off. It was stinging, burning and itchy. Every time I bent my arms or legs, for example the inside of my knee, it was very painful,” the man noted in an interview with WRIC.
Concerned about what was happening, the American turned to a dermatologist for help - he was eventually hospitalized. Doctors concluded that the vaccination caused a sharp immune response in him
After five days in the hospital, the American recovered and was able to return home. At the same time, Terrell emphasized that he does not regret his vaccination and encourages everyone to get vaccinated against coronavirus.
Terrell's reaction to the shot is similar to a side effect previously called "Covid arms," a rash seen in some recipients of the Moderna vaccine. However, it mostly disappears within a week, the Daily Mail clarifies.
“We ruled out all viral infections, we ruled out COVID-19 itself, we made sure his kidneys and liver were fine, and we finally concluded that the vaccine he received was the cause. The skin is the largest organ, and when it becomes inflamed like his, you can lose a lot of fluid and electrolytes,” explained Dr. Fnu Nutan, who treated Terrell.
Doctors suspect that Turrell may have had some rare genetic characteristics that could have caused an uncontrollable and painful reaction when interacting with the vaccine ingredients.
Terrell's case is similar to a delayed allergy, which may represent a reaction to a drug, that is, a hypersensitive type IV immune reaction, says allergist Viktor Nikinshin.
“The clinical picture indicates exactly this - the allergy could be caused either by a component of the vaccine or by a combination of these components.
Such cases have happened before, for example, with the introduction of vaccinations against tetanus, chickenpox and the MMR vaccine - this is a complex drug against measles, mumps and rubella,” noted the interlocutor of Gazeta.Ru.
However, it is impossible to reliably determine the possible cause of a skin reaction based on clinical manifestations alone. That is, the vaccine could provoke several types of rashes, and additional use of other medications could aggravate the symptoms and cause a hyperreaction, adds immunologist Veronica Kharnidze.
“An elderly person, it is logical that he takes some kind of pills, even if not constantly. This situation could lead to the most common manifestations of a surge in immunity: rash, urticaria, angioedema or Lyell's syndrome.
The latter causes a rash, and after a few hours, large flat blisters with serous or serous-hemorrhagic contents appear at the site of the rash, which lead to wounds. The skin comes off in pieces,” the doctor explained.
Experts emphasize that skin reactions are the most common manifestations of drug hypersensitivity. In addition, changes in the blood and liver are possible. In the most severe cases of a drug reaction, a rise in body temperature, pain in muscles and joints is recorded. Kharnidze added that the category of people most vulnerable to such side effects are allergy sufferers and people suffering from autoimmune diseases.
“That is why before vaccination it is necessary to visit an allergist or immunologist. In some centers they do allergy tests for drugs, and also study the entire medical history. Naturally, the most susceptible category: allergy sufferers. However, even if a person has never suffered from allergies, the reaction to new drugs can be unpredictable, and such side effects can occur in anyone,” Nikinshin concluded.
What do we know today about allergies to COVID-19 vaccines?
The joint development of American and German scientists is the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine (mRNA): 4.7 cases of anaphylaxis per 1 million doses administered. It is also known that 80% of people who develop anaphylaxis to this vaccine have previously experienced allergies to other substances. The drug contains the stabilizer polyethylene glycol (PEG, PEG 2000). If a person already suspects (or is sure) that he is allergic to PEG, then before vaccination he should consult with an allergist.
American Moderna vaccine (mRNA): 2.5 cases of anaphylaxis per 1 million doses administered. 86% of vaccine recipients who developed anaphylaxis already had allergies to other compounds. This vaccine also contains PEG with all the ensuing conclusions.
British Oxford/AstraZeneca vaccine (mRNA): about 10 cases of anaphylaxis per 1 million doses administered. Contains another stabilizer - polysorbate 80. This substance can also cause allergies, although extremely rarely, in 0.5-1.47% of cases. But doctors talk about cross-reactivity between polysorbate-80 and PEG. That is, in the case of this British vaccine, if you are allergic to PEG, it is better to consult a specialist about vaccination.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) makes the following recommendations regarding vaccination for people susceptible to allergic reactions:
- If a person is allergic to any of the components of an mRNA vaccine, regardless of the severity of the reaction, they should not receive this type of vaccine at this time. For example, if you are allergic to PEG and polysorbate, you cannot be vaccinated with mRNA vaccines containing these components.
- If a person has an allergic reaction to the first dose of a vaccine, they should not receive a second dose of the same type of vaccine.
- In any case, allergies to components or to the administration of the vaccine, as well as allergies to any other vaccines and medications, the issue of vaccination against coronavirus should only be discussed with a doctor.
- People with allergies not related to vaccines or medications, such as allergies to pets, food, or a family history of allergies, can and should get vaccinated against COVID-19, regardless of the severity of the allergic reaction.
Regarding the Chinese vaccines from Sinovac (inactivated), CanSino Biologics (vector adenoviral), Sinopharm (inactivated): there is no data yet on cases of anaphylaxis.
Regarding the Russian vaccine Sputnik V (vector adenoviral), there is currently no information on registered cases of anaphylaxis. However, the drug contains polysorbate 80, and the instructions contain a warning about possible allergic reactions. So we can assume that the recommendations voiced by CDC specialists for mRNA vaccines are applicable.
Head of the Center named after. Gamaleya A.Gintsburg recommended that allergy sufferers, before vaccination with Sputnik V, be tested for C-reactive protein and IgE immunoglobulins, which show the risk of developing allergic complications at the moment. If both of these indicators are normal, you can safely get vaccinated even if you have a history of allergies.
Russian vaccine EpiVacCorona (peptide): no cases of anaphylaxis reported. It contains aluminum hydroxide, so this drug is contraindicated in people with hypersensitivity to this substance, as well as people with severe allergies.
Russian vaccine CoviVac (inactivated): no cases of anaphylaxis reported. However, the list of contraindications includes severe allergic reactions in the form of anaphylaxis, Quincke's edema and eczema. For common allergies, the drug can be administered.
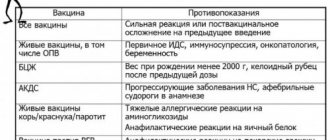
How does an allergy to a vaccine manifest itself?
An allergy to vaccines can manifest itself as:
- Urticaria is a rash accompanied by itchy skin. Occurs a few minutes or hours after vaccination.
- Quincke's edema (angioedema) is an allergic swelling of the face, throat, nose, and larynx. Occurs a few minutes or hours after vaccination.
- Lyell's syndrome is a toxic-allergic reaction that manifests itself in the spread of rashes and blisters throughout the skin, accompanied by severe itching. It may develop in the first three days after vaccination.
- Serum sickness is an inflammatory lesion of blood vessels in response to the administration of a drug to which the child was allergic. Develops 7-14 days after vaccination. Manifested by fever, urticaria, Quincke's edema, enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, joint pain. Sometimes the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and nervous system are affected.
- Anaphylactic shock is the most dangerous allergic condition that develops immediately or within 3 hours after the vaccine is administered. At the same time, blood pressure sharply decreases, a feeling of heat, weakness, redness of the skin or rash, severe itching appears, swelling of the skin and throat, choking, vomiting, and diarrhea may begin.
Although the timing of allergic reactions varies, most occur within a few minutes to an hour after receiving the vaccine. In this regard, the child is monitored for 20-30 minutes after vaccination, which allows for quick and qualified assistance in case of severe allergic reactions. All children with allergies should be vaccinated only in specially equipped treatment rooms containing an anti-shock first aid kit.