Tetanus vaccination for children: why vaccination is necessary
Tetanus is an acute infectious disease caused by the anaerobic bacterium Clostridium tetani, which is usually found in soil, dust, and manure.
The pathogen spores usually enter the body through a wound. Tetanus produces toxins that interfere with muscle contractions, leading to the characteristic symptoms of the disease. The main symptoms of tetanus in humans are muscle cramps. They usually start in the jaw (trismus) and then move to the rest of the body. Spasms last several minutes and can be so severe that they cause bone fractures.
Other symptoms of tetanus:
- fever;
- sweating;
- headache;
- problems with swallowing;
- high blood pressure;
- cardiopalmus.
Symptoms usually appear 3-21 days after infection. Recovery may take several months. The patient is not contagious to others. About 10% of those infected die.
Complications
Any vaccination has side effects that lead to complications. Such reactions occur rarely, but you need to be prepared for them. They are divided into local and general.
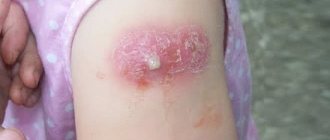
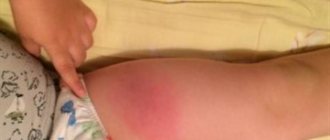
A local reaction is the appearance of a lump, lump, or redness at the injection site, the area of which increases to 8 cm in diameter.
Acute immune reactions:
- Rash, redness, and hives can appear not only at the injection site of the serum, but also in any part of the body. An allergic reaction usually occurs 30 minutes after the injection, in some cases – after 2-3. Antihistamines will help relieve discomfort.
- Rapid heartbeat or slow pulse. This reaction is temporary, but requires consultation with a doctor.
- Severe swelling that extends beyond the injection area spreads to the neck, arm and back.
Cramps and pain in joints and muscles. In some cases, inflammation of the joint capsule is observed.- Impaired consciousness and coordination of movements, darkening of the eyes, fainting, nausea, dizziness, febrile convulsions.
- Loss of appetite. This reaction lasts several days and goes away on its own; no medical attention is needed.
- Difficulty breathing, severe, cough, shortness of breath.
- Convulsive syndrome, fever up to +38 °C and above.
A rare complication is angioedema, anaphylactic shock. This is an acute reaction of the body, dangerous to human life. Occurs within the first 30 minutes after the vaccine is administered.
This is why doctors recommend staying in the hospital for half an hour after vaccination.
To avoid unwanted reactions of the body to the introduction of the vaccine, follow the general rules. The specialist warns the patient about them 1-2 days before visiting the clinic.
Vaccination rules:
- complete absence of symptoms of viral, infectious or chronic diseases;
- body temperature should be normal;
- Vaccinations are not given to persons with disorders of the central nervous system or immunodeficiency.
Patients suffering from allergies are vaccinated with a vaccine that does not contain the pertussis component.
Effect of tetanus vaccine
The only way to avoid infection is immunization with the tetanus vaccine. When and where do you get a tetanus shot? Four doses are recommended during childhood, followed by additional doses every 10 years. The tetanus vaccine for children under one year of age is given to the quadriceps muscle of the thigh, and less often to the deltoid muscle.
Vaccination is usually carried out according to the schedule:
- the first – at the age of two months;
- the second – four months;
- third – six months;
- the fourth - from fifteen to eighteen months.
Subsequent vaccinations should be carried out every ten years. For older children, adolescents and adults, the drug is injected into the deltoid muscle.
Effect of tetanus vaccine: The type of vaccination for this disease is called artificial active immunity. This type of immunity occurs when a dead or weakened pathogen in the body triggers an immune response—the production of antibodies. This means that if tetanus bacillus ever enters the body, the immune system will “recognize” it and respond quickly. After three doses of the vaccine, almost every person develops immunity.
Emergency prophylaxis of tetanus in adults is necessary when a person does not remember the date of his last immunization. In these cases, the vaccine should be given as soon as possible, preferably within 48 hours after the injury. If you stepped on a rusty nail, in the emergency room, in addition to treating the wound, they will definitely give you a tetanus injection.
Why does swelling occur at the injection site?
The human immune system is responsible for many small tasks that boil down to a single goal - protection against all diseases. In the first year of life, the child is protected by powerful antibodies received from the mother. Later, breast milk or special formulas strengthen the immune system. Their task is to form a good own immunity to most diseases. Additionally, vaccinations help them.
Any vaccination is the introduction into the child’s body of modified forms of viruses and bacteria that trigger specific processes. These reactions cause the formation of antibodies to the viruses against which the vaccine was given.
It is logical that the introduction of even weakened viruses or their specific cells will cause certain reactions. Most of them do not last long and go away within 2-3 days. These include: fever, nausea and diarrhea, a mild form of the disease, for which a vaccine was given, and some local reactions.
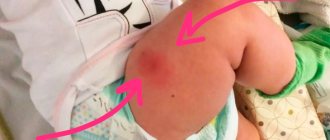
If a child's arm or leg is swollen after vaccination, then in most cases this is a normal reaction of the body. There can be no complications with a small tumor. Doctors distinguish 3 types of post-vaccination reactions: complications, moderate and mild.
The last two types are characterized by minor side effects, which are considered normal. Most often, after vaccination, the child’s injection site swells, weakness and drowsiness, and high fever appear.
The tumor is within normal limits
If after vaccination the child’s injection site is swollen, induration and redness appear, this will last on average 1-2 days. In this case, the reaction is considered normal. Statistically, lumps and redness appear in every 4 vaccinated children. Subsequent revaccination can enhance the effect, since during this period the final formation of immunity occurs.
After the DPT vaccination, the child's arm or leg in the area of the injection swells, and the lump can reach 8 cm in diameter. And all this is also considered the norm. If the lump becomes larger than 8 cm, then this indicates non-compliance with the doctor’s requirements, but usually does not pose a danger to the baby. Even a large tumor goes away on its own within a maximum of 5 days. After a BCG vaccination, a swollen lump in a child may become crusty, which is also considered normal.
The only time when a tumor is not considered normal is when additional symptoms occur:
- the appearance of suppuration;
- severe itching, irritability and crying of the child;
- rapidly developing swelling of nearby tissues;
- the appearance of a rash and other unpleasant reactions.
If the temperature rises from 38.5 degrees and persists for 2 days, you should consult a doctor. Such symptoms indicate the presence of an allergic reaction.
The injection site hurts after a tetanus shot
Side effects after tetanus vaccination:
- redness, swelling, and soreness around the injection site are observed in 25–85 percent of vaccinated people;
- fever, fatigue and muscle pain occur in less than 1% of people;
- Severe allergic reactions occur in one in 100,000 vaccinated people.
Like all medications, tetanus vaccines have side effects. The injection site hurts after a tetanus shot, there is a reaction around the injection area (redness, swelling), swelling of the entire shoulder - this means that the body “responds” to the injection of the vaccine.
More serious reactions to tetanus vaccines have been reported in Denmark: severe local edema, urticaria, arthralgia, kidney damage, anaphylactic shock. None of the cases of severe side effects resulted in death.
Patients who have had tetanus do not develop immunity to re-infection, which is usually characteristic of other infectious diseases. Therefore, everyone, without exception, should be vaccinated with tetanus toxoid.
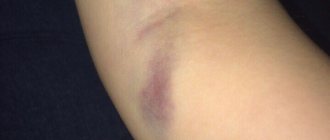
Pain and redness
After vaccination, redness appears at the injection site.
It may not be strong and goes away the next day. In people suffering from allergies, the redness can only intensify and take the form of hives.
Before vaccination, patients with allergies must notify their doctor of their diagnosis . In this case, antihistamines are prescribed before and after vaccination to reduce the allergic reaction to a minimum.
How to relieve pain
Some patients refuse to take pain medications after vaccination. You can replace medications with local anesthetics or folk remedies.
To reduce swelling, relieve redness and pain, it is recommended to apply a cabbage leaf to the injection site.
Pain relieving compress:
Crush 1 aspirin tablet, mix with 2 tbsp. l. alcohol- Lubricate the area where the vaccine is introduced with warm vegetable oil.
- Spread the mixture of aspirin and alcohol evenly over a piece of gauze folded in several layers.
- Apply the fabric to the damaged skin and secure with adhesive tape.
It is better to do the compress at night. During the day, the procedure is repeated, applying gauze soaked in the medicinal mixture for 3 hours. After 4 sessions, the pain goes away, the redness and compaction disappear.
Tetanus vaccination: pros and cons
Children under seven years of age are vaccinated with a combined vaccine against tetanus, diphtheria and whooping cough. For adults and children over seven years of age, a combined tetanus and diphtheria vaccine is usually used.
The World Health Organization certifies that maternal and/or neonatal tetanus has been eliminated. A country requires at least two years with less than one infection per 1,000 births to be certified. The scale of a possible “tetanus epidemic” can be judged by the following figures: in 1998, 3,433 cases of tetanus in newborns were reported in Uganda, of which 2,403 died. Following a massive vaccination campaign, Uganda was certified as tetanus-free in 2011. Therefore, anyone who advocates refusing vaccination should be reminded of these numbers. Read about the main contraindications to vaccination on our website Dobrobut.com.
Related services: Vaccinations Appointment with a pediatrician
Helping a child: quickly eliminating a tumor
Following the doctor's recommendations and general vaccination rules helps to avoid most complications after vaccination. So, after DPT, doctors recommend not leaving the hospital for 45 minutes. The rapid development of allergic symptoms during this period is prevented by doctors as effectively as possible.
For you: Causes of weak immunity, age-related characteristics and strengthening
There are other rules:
- You cannot actively walk outside on the day of vaccination;
- It is prohibited to consume foods that cause allergies (chocolate, nuts, citrus fruits);
- if you are prone to allergies, give Zyrtec or Fenistil to your baby a day before vaccination (after consultation with a doctor);
- After vaccination, the injection site is not wetted for 24 hours.
If you accidentally wet it, the child’s vaccination site may become swollen and red. In this situation, it is better to consult a doctor, since such a symptom when moisture gets in indicates the presence of an infection.
Doctors also recommend using simple recipes if the vaccine is swollen in a child:
- Iodine mesh. If the child has no contraindications, and the leg or arm is swollen after vaccination, apply a thin iodine mesh to the bump before going to bed.
- Fenistil or Troxevosin. The drugs relieve itching and irritation well and prevent the baby from scratching the vaccination site. Heparin ointment can be used.
- Alcohol-free compress. Use a fresh cabbage leaf as a compress. Apply it overnight and wrap it with cotton cloth.
- Rescuer or Levomikol. Suitable for eliminating itching and irritation.
Dr. Komarovsky believes that swelling and redness after vaccination are normal reactions that do not require intervention.
To prevent itching and irritation, it is recommended to wear loose, natural clothing on the baby, and at home to completely prevent the fabric from touching the affected area.
Features of edema after DTP
DTP vaccination is one of the most difficult, complex and painful vaccines. Up to 1.5 years, it is placed in the leg, since it does not contain as much fat as in the buttocks. After DTP vaccination, a child's leg swells in almost 100% of cases and pain often appears. The child tends to scratch the itchy area, but this should be avoided.
It is dangerous if the child’s DPT vaccine is swollen along with an increase in temperature to 38.5-39 degrees.
For DTP, as for other vaccinations, doctors can name a different permissible diameter of the lump - from 5 to 8 cm. However, you also need to focus on the child’s sensations. If he can’t sleep, constantly cries and complains of discomfort combined with a high temperature, you should not wait for specific complications to develop.