Today, many parents prefer imported vaccines to immunize their children, which are of higher quality and rarely cause adverse reactions. To protect against diphtheria, polio, whooping cough, hemophilic pathology, and tetanus, the French Pentaxim vaccine is used.
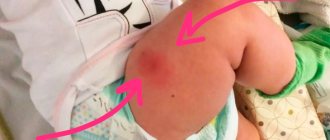
In most cases, the drug is tolerated normally. But it happens that a child develops a lump after Pentaxim in the area where the vaccine was administered. It is important to understand whether this is a normal reaction or a complication and what to do if a lump appears.
Swelling and bump on the leg after Pentaxim vaccination: normal or complication?
Over the past twenty years, abscesses and infiltrates from injections have begun to occur more and more often. This trend is explained by the altered reactivity of the body of modern people. A local reaction in the form of compaction after the vaccine is recorded in 15-25% of cases. This can be normal and a complication.
There are several reasons for the formation of infiltrate at the site of infection:
- subcutaneous tissue and muscles are compressed by the pressure of the vaccine;
- The doctors did not follow the injection technique. Pentaxim is administered only intramuscularly. If you use a syringe with a short needle, the drug may enter the subcutaneous fatty tissue. Then the absorption of the medicine will slow down significantly. This leads to the fact that the vaccine does not dissolve, but accumulates at the injection site, forming a compaction;
- the immune system sends lymphocytes to the puncture site, which respond to the penetration of foreign material into the body with an inflammatory protective reaction;
- puncture infection. This happens when doctors did not follow the rules of asepsis and antiseptics, and parents ignored the ban on swimming for the first three days. If infected, the child will experience fever, pain in the puncture area, weakness, nausea, loss of appetite, and discharge of a cloudy light liquid from the injection site. In severe cases, an abscess and blood poisoning may develop. These conditions can lead to death without timely medical care.
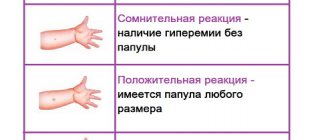
In the first two cases, the lump does not pose a danger to the baby’s health and is a natural reaction. After just a few days, the formation should resolve. If the infiltration occurs as a result of a violation of the injection technique or infection of the injection zone, then it is considered a complication and requires treatment.
Pediatrician Komarovsky notes that a post-vaccination lump measuring up to eight centimeters without pronounced redness, pain and swelling is a natural reaction of the body to immunization.
Redness and thickening after vaccination
When a child develops a lump and redness a day or two after vaccination, the mother is usually horrified!
But if she had known in advance that this was a normal reaction to the vaccine, there would have been less worry. There may be other “normal” side effects due to vaccination. There is no need to be afraid of this, doctors say. You just need to be aware of this. And “abnormal” complications are also possible, which is really scary.
But this is already off topic...
Redness and hardening after DTP vaccination
Doctors distinguish several types of post-vaccination reactions according to complexity - mild, moderate and dangerous. Mild to moderate side effects are considered normal and are quite common.
Among the general reactions, this may be an increase in body temperature, diarrhea, vomiting, weakness, dizziness and headache, deterioration of sleep and appetite, short-term loss of consciousness, prolonged incessant crying and others, that is, arising against the background of the general health of the child.
Local symptoms appear directly in the injection area: redness, swelling, swelling, induration, pain, rash.
Local reactions occur especially often after DTP, ADS, and hepatitis A and B vaccinations. These vaccines contain substances that deliberately provoke inflammatory processes in order to cause a more pronounced immune response, that is, to involve as many cells as possible in the process of developing immunity from the vaccinated disease.
Typically, such reactions occur when inactivated vaccines are administered on days 1-2 - on the leg or on the butt, depending on the site of injection of the drug.
By the way, today doctors are increasingly performing femoral injections instead of gluteal ones, because in the latter case there is a high probability of injecting the drug under the skin into adipose tissue or into the sciatic nerve, which in itself causes redness and swelling.
If the injection is given in the leg, then the medicinal substance enters directly into the muscle tissue and is quickly transported throughout the body, beginning to act actively. Therefore, getting vaccinated in the butt is not even recommended.
According to statistics, redness and thickening in the injection area occurs in every fourth vaccinated child.
And pediatricians say that with each subsequent manipulation (with revaccination), the likelihood of a recurrence of the inflammatory process only increases, and in a more pronounced manifestation.
Therefore, such a baby who reacted in a similar way to vaccination must be prepared for the procedure in advance at all subsequent times.
Judging by the reviews, hardening and redness appear most often after DTP, in particular when Pentaxim is administered (but not only, of course). At the same time, a skin rash or pain in the leg may occur, and the child may even begin to limp.
And doctors call all these reactions normal - they disappear within a few days or weeks.
Moreover, such manifestations are even considered a favorable sign, indicating that the child’s immune system has responded correctly to the entry of a foreign antigen into the body.
Redness and thickening after vaccination: Komarovsky
Pediatrician Evgeny Komarovsky also calmly reacts to such complaints from parents. Pain, swelling, redness are classic post-vaccination reactions that do not pose any danger.
Komarovsky clarifies: nothing needs to be done in this case. Just make sure that the child does not scratch the injection site and avoid any impact on it (compression and friction with clothing, mechanical damage, etc.). After a few days, the inflammation will go away. But be prepared for the fact that sometimes the process drags on for several weeks or even months.
However, if the child’s general condition is satisfactory, then there is no reason to worry. And in order not to worry without reason in the future, Komarovsky advises parents, before vaccination, to study information about the vaccine being administered: its manufacturer, technique and rules of administration, required preparation, likely consequences.
All responsibility for the child’s health lies with the parents, the pediatrician sums up.
What to do if a bump and redness appears after vaccination: treatment
Meanwhile, parents mostly disagree with this harsh stance. They believe that health workers are obliged to warn about possible post-vaccination reactions and especially about the possible complications of certain vaccinations.
However, this is quite troublesome, and in general this issue is extremely difficult - discussions for and against vaccinations for children are very tough today! And doctors prefer not to touch upon this topic again: their job is to vaccinate the child whom you voluntarily brought to the clinic. And any reaction of the child’s body can then be described as “normal.” For the most severe cases, there is another protocol explanation - the individual reaction of the body, which cannot be predicted.
In general, in order not to look for those to blame later, it is better to monitor the quality of the vaccine offered at the site in advance and buy a higher-quality analogue yourself if the need arises.
In addition, the child must be prepared for the procedure: a few days before and after vaccination, all potentially negative effects, both physiological and psycho-emotional, must be minimized. It is very undesirable for a vaccinated child to get sick, because his immune system is now weakened.
Do not forget also that there are a number of contraindications to vaccination: each time you should make sure that the child does not have any of them.
If the baby has a local or general reaction to vaccination once, then from now on 3 days before the administration of the drug and for 3 days after that it is necessary to give him an antihistamine, which is selected individually by a specialist.
This is about prevention. How to treat redness and thickening after vaccination in a child?
Ideally, contact your pediatrician. He will assess the severity of the reaction and give his recommendations. Doctors often warn mothers that nothing can be done to treat such inflammations! Iodine mesh, compresses, ointments - all this can only worsen the child’s condition.
In other cases, nurses recommend the same iodine net, compresses from cabbage leaves or vodka. By the way, about vodka: the method is quite effective, and sometimes even surgeons recommend it when mothers turn to them with similar complaints. You need to soak gauze in the drink and apply compresses to the inflamed area.
After 2-3 hours, this application is removed, and after a 2-3 hour break, it is applied again. So throughout the day.
Surgeons also prescribe treating the lump with ointments (Traumel, Troxevasin), Novocaine or Magnesia lotions, Dimexide and Chlorhexidine.
However, even without any treatment, the inflammatory process will gradually decline, pediatricians say. Normally, everything goes away in 2-3 days without any treatment, but sometimes you need to be more patient.
You should consult a doctor only if over time the lump does not decrease in size (and perhaps even increases, exceeding 6-8 cm in diameter) in size or if suppuration begins at the injection site (in this case, you need to go to the hospital immediately! ).
Especially for nashidetki.net - Larisa Nezabudkina
Source: https://nashidetki.net/zdorove-rebenka/pokrasnenie-i-uplotnenie-posle-privivki.html
What should I do if there is thickening and redness after the Pentaxim vaccination?
A lump can form after any vaccination. Pentaxim rarely gives such a local reaction. If the size of the infiltrate is within the normal range (up to 8 cm), the body temperature does not exceed 37.5 degrees, and there is no pronounced hyperthermia at the injection site, then nothing needs to be done.
It is not recommended to apply lotions to the puncture area or treat the bump with ointment or cream. If there is slight pain or the baby is capricious, then you need to distract him in every possible way and not allow him to touch the area where the vaccine was administered.
If the lump is large and red, and the child has a fever, then you should seek medical help. Trying to improve the baby’s condition on your own is not recommended. Traditional medicine methods are especially strictly prohibited.
The doctor will examine the puncture site, measure the temperature and select an effective treatment regimen. For faster resorption, the doctor may recommend treating the lump with Aescusan ointment or Troxerutin gel, which improve blood circulation. For mild inflammation, Rescuer ointment is prescribed.
The drug has a natural composition, harmless and effective. If there is severe itching, Zyrtec, Claritin, Fenistil are used. These are antihistamines that will relieve discomfort and reduce the size of the lump. If an abscess is present, surgery is performed.
How to care for the injection site on a child’s leg?
To reduce the likelihood of a lump forming after vaccination with Pentaxim to a minimum, you need to properly care for the puncture site. Doctors give all recommendations for handling the baby before or after the manipulation.
Features of caring for the injection area:
- Do not wet the puncture until the wound is completely healed. Since Pentaxim is injected into the thigh for children under two years of age, it is better not to bathe the child for several days. This time period is quite enough for the wound to heal and for infection to not penetrate into it;
- do not smear the injection area with external medications without consulting a doctor;
- dress the baby only in clothes made from natural fabric. Otherwise, an allergy may develop;
- Do not let your child rub or scratch the puncture.
How to care for the injection site?
In order for the redness to go away quickly and to avoid complications, you need to know how to care for the injection site. Doctors inform parents about all rules of behavior before or after the manipulation.
Features of caring for the vaccination area:
- Do not wet the puncture or steam it. The injection site must be kept dry until the wound is completely healed. Therefore, it is important to dress your baby according to the weather and make sure that he does not sweat;
- do not rub the puncture with a washcloth or soap it;
- do not treat with ointments, creams, disinfectants (for example, brilliant green, iodine);
- do not let your child scratch or rub the puncture;
- Dress the baby in loose clothing made from natural fabrics that are well breathable. Close contact of the injection site with synthetics can lead to the development of an allergic reaction.
When should you see a doctor?
As a rule, compaction after Pentaxim does not pose a threat and does not require treatment. But it is useful for parents to know in which cases they should consult a doctor in order to avoid negative consequences.
The following symptoms should be a cause for concern:
- severe redness;
- the lump increases in size and exceeds 8 cm;
- fever;
- the tumor hurts;
- release of liquid from the seal;
- the appearance of convulsive seizures;
- rash near the puncture site.
In such conditions, you should visit the nearest hospital or call an emergency team.
Signs of purulent tissue inflammation are:
- softening of tissue in the center of the bump;
- the center of formation is light yellow;
- the skin above the abscess is thinned;
- discharge of cloudy, light-colored liquid;
- the skin around the abscess is severely hyperemic and swollen;
- body temperature exceeds 39 degrees;
- sharp shooting pain in the area of suppuration.
It is especially important to consult a doctor promptly if an abscess develops.
Video on the topic
What kind of assistance should be provided for local and general reactions to vaccination, in which cases can parents cope on their own, and when is a doctor needed? Answers in the video:
Thus, compaction after Pentaxim occurs rarely and is usually a normal reaction to the administered drug.
If the injection technique, aseptic and antiseptic rules are violated, a lump may indicate the development of adverse reactions. In this case, the child develops a fever, the lump turns red and increases in size. If complications occur, you should seek medical help.
Redness after Pentaxim vaccination: normal reaction or complication?
After Pentaxim, sometimes redness occurs in the area where the drug was administered.
This may be normal or a complication. In addition to redness, some people experience swelling and pain at the injection site. Sometimes a lump appears. This is a common reaction to receiving a vaccine. Normally, unpleasant symptoms should go away on their own after a few days without treatment. Pediatrician Komarovsky calmly responds to parents’ complaints regarding the red spot in the injection area.
The doctor calls this symptom a classic post-vaccination reaction that does not pose any threat to health. If redness and swelling persist for more than four days, this indicates a complication .
If the injection area is hot to the touch, it means there is inflammation. This process develops when an infection enters the wound. Without treatment, the situation may worsen: severe swelling and suppuration will appear. At the same time, body temperature rises.
If yellowish or milky liquid begins to ooze from the wound, you should visit a doctor as soon as possible. Ignoring suppuration can lead to the development of an abscess and blood poisoning. Sometimes redness is caused by the appearance of a small rash. This indicates the development of an allergic reaction.
The formation of a large, dense red lump indicates a violation of the drug administration technique. This condition is considered a complication and must be treated.