Why is streptococcal infection more common during pregnancy?
Due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, the bacterial flora of the vagina changes first of all. For this reason, streptococcal infection can enter the body much faster and begin to spread there. In this regard, it is especially important for a pregnant woman to monitor personal hygiene and avoid using aggressive detergents not intended for intimate hygiene, which can worsen the acidic vaginal environment.
A separate group of infectious diseases provoked by different types of streptococcus. Most often the skin, neck, arms, face and respiratory organs are affected.
How dangerous is streptococcal infection?
Any child can become infected with streptococcus, but the disease is localized in the most compromised place in the child’s body. A healthy carrier state is also possible, that is, streptococcus is present in the child’s body, but with a decrease in immunity it can provoke the development of the disease.
The most common and most dangerous diseases for children caused by streptococcus:
- streptococcal tonsillitis. They are characterized by the presence of a white, yellow, cheesy coating on the tonsils. However, not every throat disease accompanied by plaque is caused by streptococcus;
- Scarlet fever is an infectious disease caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus;
- skin diseases - erysipelas, streptoderma.
Streptococcal infection is dangerous for children due to its complications. If treatment is not started on time, children with weak immunity may develop complications such as rheumatism, arthritis (joint damage), heart disease, glomerulonephritis (severe kidney damage leading to disability).
Causes of streptococcal infection
The causative agent of the disease is gram-positive facultative anaerobic bacteria from the family Streptococcaceae; there are about 15 subtypes of streptococcus. Some of the subtypes of streptococci are part of the normal microflora of the respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract. The subtype of beta streptococci is dangerous to humans. Streptococcal infection can be transmitted by airborne droplets when coughing, talking, sneezing; through contact and household contact with a sick person or bacteria carrier, when using common household items. Sexual transmission is also possible.
Symptoms of streptococcal infection
Symptoms of streptococcal infection may vary depending on the specific disease. The main symptomatic manifestations in case of damage to the respiratory system: plaque on the tonsils, increased body temperature, general weakness, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes. When a streptococcal infection affects the skin, redness, itching occurs in the affected areas, rashes appear in the form of blisters and plaques on the skin, chills and weakness appear. When the organs of the genitourinary system are affected, patients experience discomfort when urinating, discharge from the genital tract, itching and pain.
What are streptococci
The genus Streptococcus comprises a variety of gram-positive microorganisms that can reproduce under anaerobic conditions. The bacteria are spherical in shape, their shells are extremely resistant to environmental aggression. In dried samples of biological materials, streptococci remain viable for more than a year. They die when boiled; chemical disinfectants kill them within 20 minutes. For this reason, superficial antiseptic treatment is often not enough.
The source of spread of streptococci is carriers: infected or sick people. The infection is found in high concentrations on the surface of the mucous membranes, in liquid secretions: pus, exudate, saliva. Germs are transmitted from person to person through airborne droplets from sneezing or coughing. Unlike viruses, streptococci spread over a relatively short distance from the source: within a radius of no more than three meters. The high resistance of bacteria in the external environment also determines the nutritional route of infection: through dirty hands, food. Streptococci persist for a long time in milk, meat and seafood, which are a breeding ground for this group of infections.
When multiplying in the human body, streptococci provoke intense inflammatory reactions:
- Group A microbes more often affect the mucous membranes of the nose, oral cavity, larynx, bronchi and lungs, hearing aid, skin, and become causative agents of sinusitis, tonsillitis, caries, sore throat, pneumonia, dermatitis, erysipelas, scarlet fever, complications of wounds and burns;
- Group B streptococci usually provoke inflammation of the tissues of the urinary system, joint structures, connective tissue, cause cystitis, adrexitis, infectious nephritis, rheumatic processes, postpartum complications in women; these microbes can be transmitted through sexual contact.
The development of streptococcal infections is facilitated by various systemic pathologies and tissue damage. Including: diabetes mellitus, malignant tumors, immunodeficiency, postoperative conditions, hypovitaminosis, open wounds.
Streptococcal infection in newborns
Streptococcal infection in newborns causes high mortality. Many babies show symptoms of infection within the first hours of birth. They are pale and breathe unevenly. This is often accompanied by inflammation of the lungs or meninges, which can cause neurological problems. These symptoms may appear up to 6 weeks after birth. Infants develop fever, vomiting, and excessive sleepiness. Note! Despite the low risk of infecting the baby, a woman should be checked for streptococcal infection shortly before giving birth.
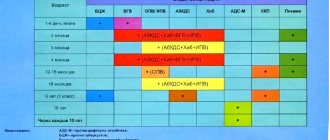
What is the name of the streptococcal vaccine?
There is currently no vaccine against group A hemolytic streptococcus, which is the causative agent of tonsillitis, purulent tonsillitis, glomerulonephritis, erysipelas or scarlet fever.
Vaccine Prevenar
But today it is possible to get vaccinated against pneumococcal infection, which is a type of streptococcus. There are several WHO-approved vaccines against pneumococcal disease in the world, which are reliable and effective.
Domestic immunologists recognized vaccine suspensions Prevenar and Pneumo-23 as the safest and most recommended drugs. These immune solutions are distinguished by their reliability, minimal number of contraindications and effectiveness.
Group B Streptococcal Infection: Treatment and Prevention
Unfortunately, there is no reliable prevention of streptococcal infection. However, you can strengthen your immune system with proper nutrition and adequate rest so that it can fight off bacteria. If you are concerned about a streptococcal infection, your doctor should prescribe a course of antibiotics. But this will not guarantee that streptococci will not settle in the body again.
If you are at risk and have had a urinary tract infection due to streptococcal infection or have already given birth to a child infected with streptococcal infection, you should be tested for streptococcal infection between the 35th and 37th weeks of pregnancy. A positive result will be recorded on your exchange card. To be on the safe side, doctors will give you antibiotics during labor and monitor your newborn closely to avoid infection.
Treatment of streptococcal infection
Etiotropic therapy consists of the use of penicillin-type antibacterial agents and macrolides (erythromycin, azithromycin, tsifran, tsiprolet). Symptomatic treatment is also used. Possible complications include: rheumatism, nephritis, erysipelas, sepsis.
Diagnosis and treatment of streptococcal infections
Specific diagnosis of pathogens requires bacteriological analysis of scrapings of mucous membranes, samples of saliva, urine, sputum, purulent discharge and other biomaterials. In addition, blood testing for antibodies to streptococci is often necessary. Laboratory tests determine the type of pathogen within 20–30 minutes.
In addition to etiological tests for various pathologies, diagnosis of the general condition of organ damage is required: examination by an otolaryngologist, ultrasound, fluorography and some others.
Treatment tactics are selected taking into account the identified disorders and resistance of microbes to medications. Therapy is carried out by doctors of various profiles: gynecologists, therapists, pulmonologists, dermatologists. To suppress the activity of infectious microflora, patients are prescribed a course of antibiotics. Azithromycin, Erythromycin, and fluoroquinolone drugs are effective against streptococci: Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin. It is important to purchase and use medications as prescribed by a doctor. Self-indulgence in this matter leads to the development of superinfections. Therapy is also supplemented with immunomodulatory agents.
Sanitary measures, hardening, and the use of antiseptics help prevent the development of streptococcal diseases.
Clinical picture of scarlet fever
The incubation period for scarlet fever usually lasts 2-3 days, with a maximum of 7 days.
At the beginning of the disease, symptoms of intoxication appear, redness of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and tonsils, a pinpoint small rash (enanthema) on the soft palate, and tonsillitis gradually develops.
This is followed by a period of rashes: a pinpoint bright pink rash appears on the skin of the torso, the flexor surface of the arms, and the inner surface of the legs. The rash thickens in the natural folds of the skin and is located against a background of redness. The rash associated with scarlet fever is characterized by the absence of a “spilling” effect. The skin rash can be hemorrhagic (pinpoint hemorrhages) or small papular (small tubercles). The rash is absent in the area of the nasolabial triangle - this is one of the diagnostic signs of scarlet fever (Filatov syndrome). Another characteristic symptom is the bright crimson color of the tongue.
By the 4th day of illness, the rash fades and becomes pale pink. From the second week of the disease, a period of recovery (convalescence) begins, during which lamellar peeling appears on the palms and soles.
Complications of scarlet fever - otitis media, sinusitis, myocarditis, nephritis.
To laboratory confirm the diagnosis of scarlet fever, serological methods are used - identifying specific antibodies Ig M, Ig G in the blood and increasing the level of antibodies to streptolysin O.
- Anti-streptolysin O.
The causative agent of scarlet fever can be identified by the cultural method - when sowing on artificial nutrient media.
- Microbiological (culture) test for beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A (Streptococcus group A, S.pyogenes).
- Microbiological (culture) test for beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A (Streptococcus group A, S.pyogenes) with determination of sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs.
Mumps is an acute infectious disease. Mumps is manifested by fever, symptoms of intoxication, inflammation of the salivary glands, damage to other glandular organs and the nervous system.
Mumps is transmitted by airborne droplets and household contact. The source of infection is a sick person.
The causative agent of mumps is the Mumps rubulavirus virus, which contains RNA and belongs to the paramyxovirus family.
The incubation period lasts from 11 to 21 days, usually 15 days. The onset of the disease is acute, with an increase in temperature, symptoms of intoxication, swelling and pain in the parotid gland appear. It is customary to distinguish between intoxication syndrome and glandular organ damage syndrome.
Intoxication syndrome - headache, loss of appetite, weakness, fever up to 38-40°C.
Glandular organ damage syndrome. The parotid salivary glands increase in size, pain appears, and swelling of the surrounding subcutaneous fat is possible. The face becomes round, the neck appears thicker. The popular name for mumps, mumps, was given to the disease for the characteristic appearance of the patient. The atypical form of mumps can occur without damage to the salivary glands.
Over the course of several days, other salivary glands – sublingual, submandibular – may also become involved in the pathological process.
Damage to the pancreas - occurs in 20-40% of cases, manifested by symptoms of pancreatitis - abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation. Damage to the gonads in boys (orchitis) develops acutely, on the 6-7th day of illness, as a rule, the process is one-sided. Characterized by a rise in temperature, pain in the testicle, which can spread to the groin area, to the inner surface of the thigh. The testicle increases in size and becomes dense in consistency. Symptoms last 3-5 days and disappear completely within 7-10 days.
Damage to the female reproductive glands (oophoritis) in girls is quite rare and can occur during puberty.
Syndrome of damage to the central and peripheral nervous system is also a rare phenomenon, most often occurring in children aged 3-9 years. Manifested by severe weakness, drowsiness, meningeal symptoms, convulsions, impaired consciousness.
Complications of mumps include arthritis, nephritis, inflammation of the cranial nerves (myelitis), meningoencephalitis, and encephalitis. When diagnosing mumps, special attention is paid to the clinical picture: swelling of the parotid glands, pain when chewing, fever, intoxication. Diagnostically significant are Murson's symptom (redness and inflammatory reaction of the mucous membrane around the duct of the inflamed parotid gland); Filatov's symptom (pain when pressing behind the earlobe). Laboratory diagnostics.
To detect pathogen RNA, a molecular biological method is used - polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A serological method is also used - determination of specific antibodies Ig M, Ig G in blood serum:
- Mumps virus (Mumps), qualitative determination of IgG antibodies.
- Mumps virus (Mumps), qualitative determination of IgM class antibodies.
With pancreatitis, a biochemical blood test reveals an increase in the amylase enzyme.