Please check with the clinic administrators for availability of vaccines.
Vaccination against diphtheria refers to vaccination included in the National Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations of the Russian Federation. Diphtheria is a dangerous infectious disease that affects people of any age, but in children it is severe. Before mass vaccination, every second child died from diphtheria, and even today the mortality rate for unvaccinated patients is still 5%. Diphtheria entails very serious consequences for the entire body. That is why parents should think about prevention in advance and vaccinate their children and themselves in a timely manner.
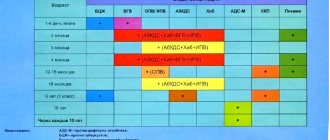
When to immunize?
Vaccination against diphtheria begins at an early age. The first diphtheria vaccination is given to children at the age of 3 months, and then at an interval of 45 days: at 4.5 and 6 months. The next important stage - revaccination - is carried out at 1.5 years, at 7 and 14 years. Further, revaccination is strongly recommended for adults every 10 years, since immunity, even after an infection, fades over time, and the risk of getting sick again increases. If for some reason a person was not vaccinated in early childhood, then he can do it at any age. This measure helps to minimize the risk of infection and prevent complications. Immunization in adulthood is especially important for employees of child care institutions, medical workers, food industry and catering workers.
The diphtheria vaccine is administered in accordance with the Preventive Vaccination Calendar or according to an individually developed plan. A pediatrician, therapist or immunologist at the Miracle Doctor clinic will help you decide on the choice of drug, taking into account previous vaccinations.
Composition of the vaccine against diphtheria in children
The main infectious diseases, which medicine practically cannot fight, have identical periods for the development of protective reactions. Due to the coincidence of time and the ability to combine several microorganisms in one preparation, combination vaccines were developed.
By reducing the frequency of injections, the serums reduced the amount of stress children experienced when seeing a health care professional. Now you don’t need to pierce the delicate baby skin with needles every month to administer a bunch of vaccines – one injection is enough.
Vaccination against diphtheria at 7 years of age; adults are given the following toxoids:
- one-component;
- two-component;
- multi-component
Vaccination of children and adults is often carried out with multicomponent sera to create complex protection. Single-component vaccinations are administered to patients prone to allergic reactions when the production of antibodies to only one disease is required.
Diphtheria toxoids are divided into 2 large groups:
- Products containing the preservative Thiomers. The drugs are produced in small ampoules, designed for double injection.
- No preservatives. They are produced in dosed doses in disposable syringes. They have a shorter shelf life, but cause fewer negative reactions.
There are several diphtheria toxoids officially approved on the territory of the Russian Federation:
- DPT;
- ADS;
- ADS-M;
- AD-M;
- Pentaxim;
- Infanrix;
- Infanrix Hexa.
There are other foreign-made drugs, but they are rare and expensive. Absolutely all mixtures are transported and stored at a temperature of +4-+8. It is prohibited to freeze solutions.
Violation of the temperature regime leads to deactivation of the serum components; it cannot be used. Imported vaccines may have different temperature values, which is indicated by the manufacturer with special markings.
Diphtheria toxoid is an essential component of every serum. These are non-living, killed diphtheria bacteria dissolved in a substance made from their toxin. It is the toxic components that cause negative consequences, so the production of antibodies is very important.
The body responds to the administration of anti-diphtheria attenuated serum by producing antitoxins. The body remembers the reaction and, when encountering a diphtheria bacillus, acts according to its usual pattern, provided that it is properly vaccinated.
DTP
- three-component serum, the abbreviation stands for pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus toxoid. The national calendar of preventive vaccinations determines a three-time course of serum administration with an interval of 45 days. Infants are vaccinated at 3, 4.5, 6 months. Revaccination is carried out once every 1.5 years.
ADS
– two-component serum, the abbreviation stands for diphtheria-tetanus toxoid. The concentration of the active substance is 10 units per ml of serum. Used for immunization of children under 6 years of age who have contraindications to pertussis components.
It is also used by those who have had whooping cough. The vaccine is administered 0.5 ml twice with an interval of 30-45 days. After 9-12 months, revaccination is carried out. The time is counted from the last injection.
ADS-M
– two-component serum, the abbreviation stands for diphtheria-tetanus toxoid. Used for immunization of adults and children over 6 years of age. The recommended dosage does not exceed 0.5 ml.
AD-M
- one-component serum, the abbreviation stands for diphtheria toxoid. Used for immunization of adults and children over 6 years of age. Recommended dose 0.5 ml. It is administered to patients vaccinated with tetanus and pertussis mixture. Used for vaccination of people who have contraindications to complex drugs or individual intolerance.
Pentaxim is a five-component injection that creates comprehensive protection against 5 dangerous diseases:
- whooping cough;
- diphtheria;
- tetanus;
- polio;
- hemophilus influenzae infection.
Infanrix
– three-component serum that protects against diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough. It is an imported analogue of DPT. The quality and effectiveness of the impact are almost the same.
Infanrix Hexa
– a six-component vaccine that protects the vaccinated patient from diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hemophilus influenzae, hepatitis B, and polio. The unique composition of the drug is not cheap.
Vaccines
Vaccines against diphtheria contain the main component that forms the body's immune response, but does not cause disease - diphtheria toxoid. Today, combination vaccines are effective. They contribute to the development of stable immunity to several infectious diseases at once. The combination of diphtheria toxoid and other components in such vaccines is immunologically substantiated and favorable. Thanks to this, the number of injections is reduced, and the effectiveness of immunization becomes higher.
- DTP (vaccine against whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus). It is a standard vaccine that is administered to children from infancy. It contains inactivated cells of the causative agent of whooping cough, diphtheria bacillus and tetanus toxoids.
- DDT (diphtheria and tetanus vaccine). The drug is classified as bivalent, as it successfully copes with immunization against two infections and is used for revaccination. This immunobiological drug is used for children who have already had whooping cough or who are contraindicated for the DTP vaccine for one reason or another.
- ADS-M (vaccine against diphtheria and tetanus). Children over 6 years of age and adults need a smaller dose of toxoids to produce the same lasting immunity, and this makes the vaccine more tolerable.
The emergence of imported polyvalent (multicomponent) vaccines makes it possible to effectively and safely vaccinate children against dangerous infections, including diphtheria. Diphtheria toxoid is included in the vaccines Pentaxim, Infanrix, Infanrix Hexa, Adasel.
At your appointment, a pediatrician, therapist or immunologist can explain in detail the differences and benefits of different combination vaccines and create an immunization schedule for diphtheria and other infectious diseases.
Advantages of the ADS vaccine:
- vaccination with the ADS vaccine guarantees a high degree of protection against two dangerous infections simultaneously
- The administration of the ADS vaccine causes the formation of a persistent immune memory in the body. During revaccination, antitoxins are rapidly formed in high concentrations.
- administration of the ADS vaccine causes fewer allergic reactions compared to the DTP vaccine.
- it is possible to use the ADS vaccine for emergency vaccination within 20 days in case of injury and contact with the ground, in contact with patients, in epidemic foci
- the ADS vaccine can be administered simultaneously (on the same day) with any inactivated vaccines and live chickenpox vaccine, provided that the injections are carried out in different parts of the body
Preparation
All types of vaccines, both domestic and imported, containing diphtheria toxoid, are administered intramuscularly. Before vaccination, it is not recommended to introduce new complementary foods into the diet, or visit crowded places.
The doctor will tell you about all the features and limitations of the post-vaccination period at your appointment. The Miracle Doctor clinic provides immunization against diphtheria with a preliminary examination by a specialist using vaccines from leading foreign manufacturers.
Sign up for a consultation by phone or on the clinic’s website.
Vaccination against whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus
A pound of prevention is worth a pound of treatment N.I. Pirogov
It’s hard to believe, but just 200 years ago, surgical instruments were washed after surgery, not before, and doctors who worked in the anatomical theater with corpses, hastily wiping their hands with a handkerchief, went to deliver babies.
The concept of preventive medicine did not exist.
Now it is difficult to imagine that such truisms as hand disinfection were not only not obvious, but seemed absurd. Thus, the founder of asepsis, the scientist Semmelweis, having made a unique discovery that the cause of childbed fever is insufficient hand cleaning, throughout his life he was never able to prove to the world that they need to be washed, especially before manipulation. The unfortunate Semmelweis died in a madhouse as a distributor of false teachings.
Meanwhile, the statistics were terrifying; the mortality rate of women from childbed fever, or, in modern terms, blood poisoning, was extremely high. 18 years after the death of Semmelweis, another scientist Lister proved that wound infection, leading to enormous postoperative mortality, is caused by a living infectious principle. Lister's discovery finally revolutionized public consciousness and formed the basis for the teaching of infectious diseases and methods of combating them.
Now modern doctors around the world agree that the disease is easier to prevent than to treat.
Vaccine prevention is a progressive method of reducing the incidence of infectious pathologies. Unfortunately, the anti-vaccination campaigns that pollute our brains strive to send us back to the times of Semmelweis, when it was believed that men attract thunder, and women vice versa.
Vaccination has saved more than one thousand lives of both children and adults. And sometimes we cannot even fully realize how much the modern world has changed for the better after the widespread introduction of vaccine prevention. In our opinion, in order to minimize possible adverse reactions, and these primarily include allergic manifestations, one should competently approach the issue of vaccination in each specific case.
This requires preliminary work. Namely, the pediatrician draws up an individual calendar of preventive vaccinations, taking into account the characteristics of the child’s health; it is important to use a high-quality vaccine that has been properly stored at the appropriate temperature; the medical office must be equipped with all necessary auxiliary drugs.
On the day of vaccination, the pediatrician conducts a thorough examination of the child, measures the temperature, and gets acquainted with the documentation (test results, if necessary, opinions of related specialists). If there are no contraindications, and written consent for vaccination is obtained, the doctor shows the parents the vaccine preparation, its name, expiration date, integrity of the individual packaging, and answers possible questions. After vaccination, detailed recommendations are given on caring for the child in the post-vaccination period, a note is made in a special certificate, and all necessary certificates about the vaccination are issued.
Currently, tactics for the prevention of infectious diseases such as whooping cough, diphtheria, and tetanus are recommended from the age of three months.
The primary course of vaccination includes three vaccinations with an interval of 1.5 months, i.e. at 3 months, then at 4.5 and 6 months.
At the age of 18 months, i.e. one year after the last administration, revaccination is carried out.
Then, at the age of 6-7 years, a second revaccination against diphtheria and tetanus is carried out (ADS-M vaccine).
Vaccinate against whooping cough up to 4 years of age. To vaccinate children from 4 to 6 years old, the ADS vaccine (adsorbed diphtheria-tetanus vaccine) is used, i.e. without pertussis component. Children over 6 years of age are immunized with a vaccine with a reduced content of antigens - ADS-M.
The Russian vaccine drug is called DTP - Adsorbed pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus vaccine. This vaccine contains diphtheria-tetanus toxoids, i.e. neutralized toxins of diphtheria and tetanus pathogens, as well as fragments of pertussis bacteria.
Foreign vaccines are now available for use (France, Belgium).
These vaccines are Pentaxim, Tetraxim, Infanrix and Infanrix hexa. These vaccines are complex, i.e. contain components that form the child’s immune defense to several infections at once.
Complex vaccine preparations have significant advantages.
By vaccinating a child against a number of infections at once, the number of necessary injections is reduced, and this minimizes pain in the baby, reduces the number of visits to the doctor, and the overall volume of ballast substances administered is reduced.
Parents are often concerned about whether complex vaccines will place an excessive burden on the child’s immune system. Studies have shown that within one day a child repeatedly encounters thousands of potentially dangerous microbes and viruses, and the simultaneous introduction of 5-6 purified components (antigens) does not have a negative effect on the development of the immune system of a growing person.
These vaccines are acellular, in other words, cell-free.
That is, unlike the domestic vaccine, which contains fragments of the cell wall of the pertussis bacterium, these preparations contain highly purified pertussis antigens.
Behind all these sophisticated arguments is a property that is particularly significant in practice - acellular vaccines are much less likely to cause side effects (including fever, etc.), and they are much more easily tolerated by children.
Vaccines based on the acellular pertussis component were developed in 1981 in Japan and have been used successfully since then.
Unlike the domestic DTP, complex acellular vaccines do not contain the mercury compound merthiolate as a preservative.
However, there are a number of studies that show that in the negligibly small amount contained in the DTP vaccine, merthiolate is not capable of causing harm to health.
And at the same time, taking into account all the above features, cell-free inactivated complex vaccines have become widespread in developed countries and deserved recognition from doctors around the world
Vaccine preparations are packaged in sterile, disposable syringe doses, which already contain the required amount of the drug, which eliminates the possibility of administering an inappropriate dosage.
All vaccines are interchangeable, i.e. if necessary, you can begin and complete a course of vaccine prophylaxis with drugs from different manufacturers (both domestic and foreign).
To summarize the above, it is worth noting that vaccine prevention is a huge area of knowledge, and in the modern world there is a wide choice of methods for preventing infectious diseases.
Therefore, I would like to urge parents, when deciding on the method of vaccinating their child, to consult a doctor whom you trust.