ADSM is a vaccination against infectious diphtheria (caused by Loeffler's bacillus) and bacterial tetanus (caused by gram-positive tetanus bacillus), and the Infanrix vaccine is an imported analogue of ADSM. There is also Priorix for intramuscular injections and Pentaxim. All of the above vaccines are intended to immunize humans against a number of infectious diseases.
After the injection, weakened toxins enter the human body, which are not able to provoke the development of the disease. The body produces antibodies that form the body's immunity to diphtheria infection and tetanus bacillus.
Composition of the vaccine against diphtheria in children
The main infectious diseases, which medicine practically cannot fight, have identical periods for the development of protective reactions. Due to the coincidence of time and the ability to combine several microorganisms in one preparation, combination vaccines were developed.
By reducing the frequency of injections, the serums reduced the amount of stress children experienced when seeing a health care professional. Now you don’t need to pierce the delicate baby skin with needles every month to administer a bunch of vaccines – one injection is enough.
Vaccination against diphtheria at 7 years of age; adults are given the following toxoids:
- one-component;
- two-component;
- multi-component
Vaccination of children and adults is often carried out with multicomponent sera to create complex protection. Single-component vaccinations are administered to patients prone to allergic reactions when the production of antibodies to only one disease is required.
Diphtheria toxoids are divided into 2 large groups:
- Products containing the preservative Thiomers. The drugs are produced in small ampoules, designed for double injection.
- No preservatives. They are produced in dosed doses in disposable syringes. They have a shorter shelf life, but cause fewer negative reactions.
There are several diphtheria toxoids officially approved on the territory of the Russian Federation:
- DPT;
- ADS;
- ADS-M;
- AD-M;
- Pentaxim;
- Infanrix;
- Infanrix Hexa.
There are other foreign-made drugs, but they are rare and expensive. Absolutely all mixtures are transported and stored at a temperature of +4-+8. It is prohibited to freeze solutions.
Violation of the temperature regime leads to deactivation of the serum components; it cannot be used. Imported vaccines may have different temperature values, which is indicated by the manufacturer with special markings.
Diphtheria toxoid is an essential component of every serum. These are non-living, killed diphtheria bacteria dissolved in a substance made from their toxin. It is the toxic components that cause negative consequences, so the production of antibodies is very important.
The body responds to the administration of anti-diphtheria attenuated serum by producing antitoxins. The body remembers the reaction and, when encountering a diphtheria bacillus, acts according to its usual pattern, provided that it is properly vaccinated.
DTP
- three-component serum, the abbreviation stands for pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus toxoid. The national calendar of preventive vaccinations determines a three-time course of serum administration with an interval of 45 days. Infants are vaccinated at 3, 4.5, 6 months. Revaccination is carried out once every 1.5 years.
ADS
– two-component serum, the abbreviation stands for diphtheria-tetanus toxoid. The concentration of the active substance is 10 units per ml of serum. Used for immunization of children under 6 years of age who have contraindications to pertussis components.
It is also used by those who have had whooping cough. The vaccine is administered 0.5 ml twice with an interval of 30-45 days. After 9-12 months, revaccination is carried out. The time is counted from the last injection.
ADS-M
– two-component serum, the abbreviation stands for diphtheria-tetanus toxoid. Used for immunization of adults and children over 6 years of age. The recommended dosage does not exceed 0.5 ml.
AD-M
- one-component serum, the abbreviation stands for diphtheria toxoid. Used for immunization of adults and children over 6 years of age. Recommended dose 0.5 ml. It is administered to patients vaccinated with tetanus and pertussis mixture. Used for vaccination of people who have contraindications to complex drugs or individual intolerance.
Pentaxim is a five-component injection that creates comprehensive protection against 5 dangerous diseases:
- whooping cough;
- diphtheria;
- tetanus;
- polio;
- hemophilus influenzae infection.
Infanrix
– three-component serum that protects against diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough. It is an imported analogue of DPT. The quality and effectiveness of the impact are almost the same.
Infanrix Hexa
– a six-component vaccine that protects the vaccinated patient from diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hemophilus influenzae, hepatitis B, and polio. The unique composition of the drug is not cheap.
Advantages and disadvantages of ADS-M
The ADSM complex vaccination includes toxoids against two diseases, which means the above vaccine is bivalent. There are also monovalent vaccinations such as AC and AD. Some people believe that monovalent drugs are better. They do not put a strain on the immune system of a healthy person and are easier to tolerate by a child. This is not true, but only unconfirmed speculation.
Bivalent vaccinations undergo higher quality purification at the production stage, which minimizes the risk of negative reactions from the body. This is one of the advantages of ADSM. If monovalent drugs are introduced into the body one by one, it will take more time to develop immunity. There should be a break between injections for rehabilitation after the introduction of pathogenic toxins.
The ADSM vaccine is well tolerated, like any imported analogue.
Repeated immunization cycles reduce to zero the risk of developing diseases caused by diphtheria bacillus and tetanus bacteria.
If the number of antibodies decreases, revaccination should be done.
The disadvantages include the following possible complications and adverse reactions from the body:
- Swelling, redness of the skin.
- Anxiety.
- Poor appetite, nausea, vomiting.
- Allergic reaction to the vaccine.
- Increase in body temperature.
- Pain syndrome in the limbs.
- Weakness, drowsiness.
- State of shock.
- Malaise.
- Runny nose and nasopharyngeal congestion.
The development of complications is detected after non-compliance with the rules of immunization, transportation and storage of vaccines.
What do you think are the most important factors when choosing a medical facility?
You should refuse the injection in case of acute infections, pregnancy, the development of various pathologies, exacerbation of chronic diseases, or a decrease in the overall immunity of the body.
Immunization is carried out in accordance with the rules:
- Before immunization, consultation with a doctor is required;
- vaccination is done in a medical facility;
- the procedure is carried out by specially trained personnel in a separate room or in a vaccination room;
- the injection is carried out with a disposable syringe using local antiseptics;
- before administration, the ampoule is inspected for defects and suitability;
- vaccination data is entered into the journal.
After vaccination, the patient is observed for another 20-30 minutes. In the absence of negative reactions and malaise, the patient leaves the clinic.
Revaccination: vaccination of a child at 7 years old
ADS-M is used for revaccination at 7 and 14 years of age. Further renewal of the body’s protective properties occurs every 4 years. Children over 6 years of age who have not previously been vaccinated with similar serums can receive an injection of this type - they do not have stable immunity against the diphtheria bacillus.
DTP, ADS, ADS-M are given to children over seven years of age. They are used for revaccination of patients who do not have antibodies capable of resisting the diphtheria bacillus. According to the national calendar, 14-year-old children are not vaccinated, only revaccination. A person exposed to proper immunization will grow up protected.
Time for vaccination
The complex ADS-M vaccine can be administered to a baby in the first three months after birth.
Diphtheria and tetanus are serious, seriously traumatic diseases, often resulting in death. The bacteria that excite them are almost impossible to destroy with modern methods, antibiotics and potent antibacterial drugs. It is a timely vaccination that will help to avoid the disease or reduce the complexity of its course and the severity of the consequences in case of infection.
If the patient did not receive vaccinations against tetanus and diphtheria in childhood, this is not a problem, because protection against dangerous diseases can be acquired as an adult. The drug has no age restrictions.
Frequency of diphtheria vaccinations
The first protective serum is administered at 3 months. Then, according to the national calendar, every month and a half - 4,5 and 6. Full immunity against an infectious disease is developed after the 3rd injection, provided the required interval is observed.
Two subsequent injections of a protective drug will help consolidate the result. Children undergo the fourth vaccination when they reach the age of one and a half years. The fifth anti-diphtheria mixture is introduced at 6-7 years of age. Patients are revaccinated at 16-17 years of age. Vaccination every decade will help maintain the body's protective properties.
Up to 3 years of age, injections are made exclusively into the anterolateral part of the thigh, then into the shoulder. For adults, anti-diphtheria serum is injected under the shoulder blade, into the thigh. Piercing the buttocks is prohibited.
A child's illness with diphtheria is considered the first vaccination. Infection after the first injection is considered the second injection. Subsequent human immunization is carried out according to the national calendar.
Diphtheria vaccination for children over 7 years of age who have not followed the vaccination schedule is given with weakened ADS-M twice. The interval between injections is 30 calendar days. Revaccination is done 9 months after the last injection. Further immunization occurs every 10 years.
Pentaxim
Pentaxim is characterized as an effective and comprehensive vaccine with a wide profile. Children's Pentaxim is used for immunization against tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough, polio and hemophilia type b. The analogue includes a complex of toxoids that promote the production of antibodies and the formation of healthy immunity.
Excipients include acetic acid, streptomycin, formaldehyde, etc. The vaccination regimen is determined by the attending physician. This analogue is contraindicated in case of allergies to the main components of the drug, various pathologies, or recurrent infections. Pentaxim is not used for immunization of children over 5 years of age.
Do children who have been ill need diphtheria vaccination?
There have been no outbreaks of widespread infectious diseases for several decades, which has led to a massive refusal to vaccinate. The trend of growing doubt will soon lead to the resumption of epidemics and increased mortality.
It is useful to know that in highly developed countries, where almost 100% of the population is vaccinated, infectious diseases occur only among unvaccinated visitors. Full protection of the country from infectious diseases can be guaranteed by vaccinating 95% of the population.
Parents who have concerns about administering diphtheria serum are advised to weigh the benefits:
- The risk of infection with diphtheria bacillus through contact with a patient is minimized.
- Vaccination almost completely eliminates side effects that can significantly worsen your health.
- Even if infection occurs, the disease will proceed easily, without complications.
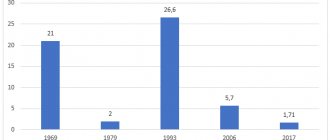
- The fatal outcome, which in the case of illness in children reached 50% before the introduction of the national vaccination calendar, was excluded.
Refusal to inject increases the risk of contracting diphtheria. Unvaccinated children experience severe disease. Almost every sick child has serious complications that leave a permanent mark on their health for the rest of their lives. Frequent deaths should alert parents writing a refusal.
Infection of vaccinated children also happens; the cause is a weakened immune system. Thanks to the antibodies produced, the disease cannot gain strength; a prepared body does not. The course of diphtheria is mild, without visible exacerbations, and death is excluded.
Doctors successfully fight bacteria that have infected the body, but they cannot remove the toxins they produce. They are the ones who cause complications. The obligatory nature of vaccination is dictated by the impossibility of combating the consequences of:
- kidney damage;
- depression of the nervous system;
- complication with the respiratory system;
- paralysis;
- heart damage.
Doctors can stabilize the temperature and eliminate inflammation in the throat, but they cannot eliminate the weakness of the neck muscles. If you lose your voice, it will also not be possible to restore it.
Newborns inherit antibodies that can protect against diphtheria bacilli, provided that the mother was vaccinated on schedule. Immunity does not last long; by the age of 3 months it subsides. It is from this age that systematic vaccination of children begins.
Reasons for decreased level of specific immunity:
- violation of the timing of administration of toxoids;
- damage to other infectious diseases;
- violation of the temperature regime during storage and transportation of the drug.