Carrying out the Mantoux test in all preschool and school institutions serves to detect tuberculosis in the early stages, when the disease has not yet manifested itself. Tuberculin, a substance containing weakened and killed mycobacterium tuberculosis, is injected subcutaneously on the right or left forearm, then wait 72 hours and evaluate the results. The fact that Mantoux itches after the injection is most often a completely normal, natural reaction of the body to the test, along with redness and slight swelling. But itching can also be a sign of latent tuberculosis. Therefore, it is worth clarifying a few points for your peace of mind and safety.
Causes of itching and redness
Doctors always explain to parents what kind of reaction may occur after they do the test. Itching at the site of tuberculin injection is a natural response of the body to two irritating factors:
- puncture of the skin at the injection site;
- entry of a foreign substance intradermally.
This is why Mantoux itches in most cases. If Mantoux begins to itch on the 2-3rd day after the procedure, then the matter may be due to non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations:
- the parents covered the wound with a plaster;
- went to the pool after the test;
- lubricate the papule with various cosmetics or alcohol-containing solutions.
Important! In any case, doctors will evaluate not so much the itching as the degree of redness and the size of the button.
Causes of the rash
There are several reasons for the appearance of a rash on the body after Mantoux vaccination. Regardless of whether it is a child or an adult, allergies appear in the same cases. This:
- Intolerance to many medications. The immune system of such a patient is hostile to any chemical invasion, including the contents of the vaccine.
- Individual intolerance to tuberculin. With such a pathology, the Mantoux test should be abandoned forever, replacing it with another.
- Allergy to phenol. This is a substance that is part of tuberculin.
- Weakened immunity. In this case, even someone who has never experienced anything like this before can develop an allergy.
- The test was taken during a period of exacerbation of allergies. To avoid this, the skin must be clean during the procedure.
Whatever the cause of the rash, it is necessary to find out. It is quite possible that the injection has nothing to do with it, and this is a food allergy that coincided in time. Therefore, before going to the doctor, it is better not to give the victim any medications, so as not to blur the clinical picture. In severe cases, you need to call an ambulance.
Positive Mantoux reaction options
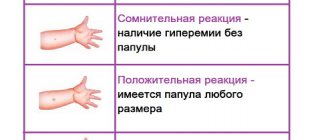
A positive Mantoux reaction is considered to be a papule whose size exceeds 5 mm. But even here there are some peculiarities and nuances that must be taken into account before making a final diagnosis.
Expressed reaction
The size of the papules exceeds 15 mm, the redness and swelling are very strong, and blisters and ulcers may also be observed. As a rule, local skin reactions are accompanied by general symptoms of severe intoxication - increased body temperature, weakness, headaches and muscle pain. Most likely, the person has tuberculosis, but it could also be an allergy to tuberculin or a reaction after an infectious disease.
Positive reaction
With a moderate positive reaction, the size of the papule varies from 10 to 15 mm, the compaction may be insignificant, ulcers and blisters, as well as other symptoms of intoxication, are often absent. A positive Mantoux reaction is not a reason to panic. But this is a good reason to immediately undergo additional examination, which the TB doctor will recommend.
Questionable reaction
If the diameter of the papule is less than 10 mm, but more than 5 mm, there is no redness or it is insignificant, we are talking about a questionable or false-positive reaction. This phenomenon is observed if BCG vaccination has recently been carried out, the child has suffered an infectious disease, or the drug was administered incorrectly. With such a reaction, a tuberculin test is done again a month later, or Diaskintest is performed. To exclude or confirm tuberculosis in this case, additional thorough examination is required.
Results and types of reactions in children and adults
The injection analysis is carried out using the same parameters in adult and minor patients, the reaction is considered:
Negative
If the spot does not bleed and there is no open ulcer or large swelling. The spot itself is close to flat and stands out from the healthy epidermis with slight redness, has a round shape and no more than 4 millimeters in diameter. If one of the parameters does not match, the analysis is considered doubtful and a survey is conducted to determine the need for further diagnosis.
Doubtful
A small but obvious swelling and a visible correlation with healthy skin, as well as an increase in the diameter of the spot ranging from 4 to 12 millimeters are considered questionable reactions. If the form of redness is violated, it is customary to give a second injection on the other hand and monitor the child’s behavior more carefully so that he does not wet it or scratch it. A questionable result means that the body’s reaction is not as obvious as with a positive one, but still raises concerns about tuberculosis at the obvious stage or stage of infection. A survey is conducted to find out the reasons for the distortion of the tests and, if necessary, further diagnostics are prescribed in order to make a clear diagnosis whether it is worth re-vaccinating.
Positive
Is the spot noticeably bleeding or has it developed into an open ulcer, has the swelling risen significantly above the epidermis, and is its diameter over 14 millimeters? The analysis is considered definitely positive and a full diagnosis is prescribed to determine the presence of Koch's bacillus in the body. The child undergoes a culture and a general blood test with urine. And if, as a result, doctors find nothing, Mantoux is considered a false positive.
False positive
When a positive or questionable reaction is brought to culture and collection of general tests, as a result of which the absence of the disease or symptoms not associated with it are established, a false positive reaction is determined. According to statistics, 54 percent of all positive results turn out to be false positive, so there is no need to worry if your baby’s injection area begins to itch and the swelling increases in size. Panicking parents will only make the situation worse, causing additional stress for the child and creating discomfort for themselves.
If Mantoux itches, is it tuberculosis?
Important! Even if the mark after Mantoux is very itchy, this does not mean that the person is necessarily infected or sick with tuberculosis.
It's all about the impulses that the body sends to the central nervous system in response to irritation of the epidermis. An irritant gets into the skin, the body doesn’t like it, so it pays attention to it and requires some action - for example, scratching the sore spot. But under no circumstances should the wounds be scratched - this risks secondary infection and inflammation. In addition, assessing the test results will be significantly difficult due to improper distribution of the drug under the skin, hyperemia, irritation, and possibly even bruising at the site of the injection mark.
How to help a child if Mantoux itches very much?
- put the child on clothes with long but loose sleeves;
- make sure that the room is not too hot - sweat will make the button itch even more;
- do not wet Mantu;
- distract yourself with an interesting activity or walk.
The button can be lubricated with antihistamines, disinfectants, anti-inflammatory ointments and lotions only after examination by a doctor and evaluation of the results. Then you can take systemic antiallergic drugs. Sometimes mothers and fathers themselves provoke severe itching in the baby. The more the child is told that the button should not be touched, the more they frighten him, the more attention he pays to the problem area and the more he wants to touch and scratch it. Therefore, you need to monitor your baby, but at the same time you should not remind him about the Mantoux test again.
How to prevent a child from scratching Mantu?
Parents fall into despair when the baby again and again feels for a button on the arm and begins to comb it until it bleeds. Unfortunately, nothing can be done here, since the use of alcohol and antihistamines is strictly prohibited. All parents can do is distract the child with walks and interesting games. You cannot seal the wound or smear it with anything.
What does the phthisiatrician recommend?
With Mantu combed before the doctor assessed the results, the situation is more complicated. Obviously, the injection site will be swollen and red. And, most likely, the doctor will advise you to redo the sample and undergo several additional examinations, for example, Diaskintest or PCR diagnostics. You should not refuse additional examinations - perhaps severe itching, which the child could not tolerate, is a manifestation of tuberculosis. It is better to pass all the necessary tests and make sure that everything is in order, or start treatment as early as possible.
Is it possible to scratch?
Is it possible to scratch Mantu? Regardless of the reasons for the itching and how intense it is, scratching the Mantoux area is strictly prohibited. With constant scratching, the area of redness increases, a papule does not form, and the swelling intensifies.
For example, in very young children you can observe that the hand is completely swollen. If there is no allergic reaction to tuberculin, then severe itching can be avoided by avoiding contact with water; for this reason, doctors do not recommend wetting the reaction area for three days.
What happens if you comb Manta? As mentioned above, such actions lead to an increase in the reaction zone, increased swelling and redness. This can lead to distortion of the test results, since 72 hours after the injection, the doctor uses a ruler to measure the size of the papule, and depending on this, makes a conclusion about the presence of the disease. If you scratch Mantu, the result will be distorted.
Why can't you scratch Mantu other than this? Scratching can lead to infection in the wound and the development of inflammation. Not only is this in itself, although not dangerous, not very good, it can also distort the results of the study.
What does a bruise at the Mantoux site mean?
If a bruise appears at the site of Mantoux, this most likely indicates that the procedure was performed by an inexperienced or careless healthcare worker with violations of the drug administration technique. In this case, you need to consult a doctor. If a bruise has formed at the site of the bruise, and Mantoux has also become ill, this may be a symptom of the development of complications - for example, an abscess. There is no point in self-medicating, heating, steaming, or smearing brilliant green on the mark; it is better to trust the specialists. If, after a test for tuberculosis, you begin to experience itching, swelling, and discomfort, this does not necessarily indicate a positive Mantoux reaction. Most likely, the matter is due to individual intolerance to tuberculin or non-compliance with the rules of caring for the injection site after the procedure. But scratching the injection site is strictly prohibited if the Mantoux itch is severe. It would be wisest to consult a general practitioner or phthisiatrician to find out the causes of the Mantoux allergy and determine further actions.
What is mantu
Mantoux is an injection of tuberculin under the skin. The solution contains specific proteins and other chemicals obtained from dead cells of the tuberculosis bacillus.
The injection is given in the area between the hand and elbow or in the forearm. Within 72 hours, the immune system will send antibodies to the injection site. As a result, inflammation should appear on the skin, the so-called mantoux button.
A positive reaction is considered to be the appearance of redness with a diameter of more than 6 mm. If the diameter is 2-5 mm, the mantoux result is questionable. If the diameter is 0-1 mm, then the result is negative.
We are not talking about illness even if an infectious agent is detected in the body. Scientists suggest that almost every third person on the planet today has a Koch bacillus in their body. But the immune system prevents you from getting sick. And in the case when the BCG or BCG-M vaccination was not done, mantu still needs to be done.
The introduction of specific substances, aggressive, in fact, helps stimulate the formation of a response. Mantoux vaccination is an unreliable insurance and ineffective from a scientific point of view. It has an indirect relation to immunization.