Causes of redness
The red spot after the test is not an isolated case. Currently, doctors often observe such a reaction, especially in children. This is due to the annual increase in the number of allergy sufferers .
The symptom is also one of the signs of a reaction to tuberculosis, revealing the primary stage of infection.
Allergic reactions
People suffering from allergies often experience an acute reaction to the introduction of serum. It resembles the immune response to tuberculosis infection. You should notify your doctor about this before the test.
The allergy will not disappear on its own; every year it will become more acute. For such patients, other methods of diagnosing tuberculosis are used.
Allergy sufferers are prescribed antihistamines 3 days before the test.
Skin diseases
The tuberculin test can aggravate chronic, indolent diseases. Skin reactions often occur: urticaria, rash, dermatitis.
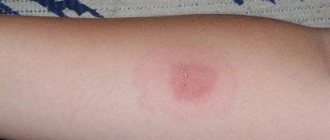
Redness of the papule can be caused by one of these diseases.
Infections
Acute viral and infectious diseases provoke a positive result after administration of the drug. The test is carried out on absolutely healthy people to get a clear result.
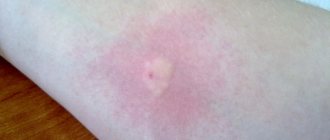
Redness on the first day
This is a reaction to damage to the skin from a syringe needle. This redness goes away on its own the next day. It is important not to treat the papule with antiseptics, not to wet it, not to scratch it.
Redness the next day
If the papule is very red, it is likely an allergic reaction to the injected drug. This immune response can develop especially acutely in a child on the second day. In this case, it is necessary to take antihistamines.
If the papule is swollen, this is a reaction to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The result will be assessed by a TB specialist 72 hours after the procedure.
Redness after a week
The injection site gradually brightens, the papule resolves, and completely disappears after 7–14 days. 72 hours after the test results are assessed by a physician, the condition of the sample does not affect the diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Expert opinion
Nikolaeva Elena Sergeevna
Practicing pediatrician.
Ask a Question
If the vaccine breaks out and turns red after a week, this means the development of a viral infection or an inflammatory process in the body. This is how the immune system reacts to the disease.
In addition to blood cells, papules contain immune cells - lymphocytes, which respond to infection. This result has no relation to the diagnosis of tuberculosis.
What is mantoux, the reasons for the unusual reaction
The Mantoux test or Pirquet test is a method widely used in the CIS for diagnosing tuberculosis infection in the body. The principle of operation is quite simple: tuberculin, an extract of tuberculosis bacteria, is injected under the skin, after which the reaction of the body’s immune system is monitored. Contrary to some rumors, this procedure is absolutely safe. However, its effectiveness is in question.
Often, an enlarged mantu in a small child causes a violent reaction from the parents. It’s not surprising, because it means that your own child is suffering from a dangerous disease!
But is this really so?
This question is quite ambiguous, because the Mantoux reaction is quite unstable and does not give an absolutely accurate result.
However, there is an official size scale:
- up to 5 millimeters. This value is considered a normal reaction to the vaccine;
- about 10 millimeters. Such an increase in induration may already indicate the presence of a disease in the body;
- more than 15 millimeters. Mantoux is increased, and significantly, which almost certainly means infection.
The problem is that if a child has an increase in mantoux, the reason is not at all that he is sick. If a child has an enlarged mantoux, then he could, for example, simply have recently had contact with a patient. But he himself, at the same time, can still be absolutely healthy. With a high probability, an increased reaction can also be observed if the child has already experienced the disease before.
It is also important to remember that the diagnosis takes into account only the size of the induration. It does not matter whether it is red or flesh-colored, whether its edges are jagged or smooth, or where it “spreads” if the reaction is unusual.
All these are unnecessary and insignificant characteristics of the sample.
In addition, such diagnostics are ineffective after BCG vaccination.
After the vaccine, the size of the mantoux will not exceed five millimeters, even if the child actually managed to become infected. So it turns out that enlarged mantoux in a child often does not have an objective reason. And this is not all possible deviations.
Should you see a doctor?
If redness is accompanied by the appearance of abscesses, fever, or painful papule, consult an infectious disease doctor.
It is important that the results are first recorded by a TB doctor. Afterwards, the attending physician first rules out the body’s reaction to tuberculosis and identifies other reasons for the growth of the papule.
Redness without papule
This is a common reaction that is considered questionable.
The appearance of redness without a papule is equated to a negative response of the body to the administration of the vaccine. This means that there was no contact with the tuberculosis bacillus, or it took place a very long time ago, and the immune system overcame the infection.
Severe redness
The Mantoux test allows you to identify the causative agent of tuberculosis in the human body. Swelling at the site of serum injection, accompanied by severe redness, is an alarming sign.
A positive reaction does not always mean that the patient is infected with pathogenic microorganisms.
Severe redness of the papule may indicate contact with an infected person.
The reaction may also be considered an allergic reaction. Every day after vaccination you should take antihistamines, which dampen this reaction of the body.
Redness without thickening
This is a negative reaction of the body to a tuberculin injection. It indicates that the body is clean and there is no infection. This immune response indicates that a repeat BCG vaccination is necessary.
Redness with swelling
The test site turns red in 90% of cases. A seal appears when the result is positive.
Phthisiatricians pay attention to the size of the papule: if it does not exceed 5–6 mm, there is no reason to worry. For prevention, additional diagnostics and treatment are prescribed.
It is important to immediately take a blood test and check your leukocyte level. If a tuberculosis bacillus is detected, then the level of leukocytes is high.
With a papule of 11 mm or more, a positive immune response is detected, which requires further research and careful diagnosis.
Swelling with abscesses, purulent discharge, pain - this is a positive reaction in 100% of cases.
The patient is prescribed fluorography and a blood test. These are additional diagnostic methods that allow you to determine at what stage the disease is.
Symptoms and telltale signs
The rash after Mantoux may look like urticaria or rubella. Only a doctor can correctly determine whether the test is related to such symptoms. But there are clear signs that it was this procedure that caused the reaction in the form of skin rashes.
They are as follows:
- The rash is localized on the limb where the injection was given. In this case, there is no doubt that the sample is to blame.
- The appearance of a rash in the most delicate places - in the folds of the skin, on the stomach and neck.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- The presence of other signs of an allergic reaction of the body in the form of fever, loss of appetite.
- If you are intolerant to tuberculin or phenol, the reaction does not occur earlier than within a day, but the symptoms can be severe.
If there is any doubt that the rash is caused by the Mantoux vaccine, doctors conduct clinical and laboratory examinations and identify the cause by exclusion.
But regardless of the cause, an allergy remains an allergy and is always accompanied by a rash. In other words, a rash is the body's first reaction to an outside invasion. And you can’t do without antihistamines.
False reaction
A false positive response of the body to the Mantoux test can occur after BCG vaccination. It is given to all children from infancy.
Weakened tuberculosis cells are injected into the body. Later, after the introduction of tuberculin, immunity gives the wrong result. At the same time, the papule turns red, swells, and breaks out.
You can determine that the test result is false by the size of the papules: up to 11 mm there is no need to worry. If the redness at the puncture site reaches 12 mm, this is a positive reaction to the causative agent of tuberculosis.
A false reaction to tuberculin occurs in people with weakened immune systems, those suffering from HIV, and in children under 6 months of age. In these cases, the tuberculin test may give a negative result even if infected.
The test should not be combined with vaccinations, especially if the vaccines use live bacteria. At least 2 weeks must pass after the medical procedure.
Otherwise, the test result will be false positive.
For allergy sufferers, during periods of exacerbation of diseases, the Mantoux test is not performed: it will be false positive. Tuberculin is not administered after any medical procedures or during epidemics.
In other cases, Mantoux gives a negative result if there is no infection or contact with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
If it doesn't last long
You should know that although the antigen reacts with human blood, it cannot by itself cause bruising. If parents have concerns about a bruise, they need to contact a pediatrician, who in turn will refer you to an appointment with a phthisiatrician. Doctors warn that there is no need to be afraid of bruising after such a test. Unlike brown pigmentation, this condition will not indicate blood poisoning.
A trip to the pediatrician is required when the baby experiences side effects after vaccination. For example, as a result of vaccination, not only does his papule turn purple, but the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is also disrupted. Sometimes a high temperature also appears. If this condition is one-time in nature, you can give the baby an antipyretic drug
This is Ibuprofen or Paracetamol. In addition, parents should pay attention to other complaints of the child (nausea and headache)
You need to know that a bruise at the site of a mantoux injection itself does not pose any danger and cannot be evidence of a positive reaction to the introduction of a tuberculin test. The occurrence of such a condition can significantly distort the measurement results. In this case, the doctor will ask you to retake the manta in 8 - 12 weeks. Urgent contact with a pediatrician is required in situations where a bruise appears at the vaccination site, turning into a purulent abscess, or the baby complains of severe itching after receiving a mantoux.
You can learn more about why a bruise appears after mantoux by watching the video below:
Redness is not due to illness
After administering tuberculin, the doctor warns that the sample should not be wetted, combed, treated with antiseptics, ointments, or bandaged..
You cannot cover the papule with an adhesive plaster: moisture accumulates under it, which, affecting the puncture, distorts the test result.
The ingress of water, microbes, or scratching of the skin in the injection area leads to redness, inflammation, and the appearance of compaction.
During the examination, you should warn the phthisiatrician that any impact has been made on the papule, otherwise the doctor will consider the test result as positive.
After the phthisiatrician evaluates the diagnostic result, the “button” is allowed to be treated with an antiseptic or anti-itching ointment.
Could there be an error in the analysis if the Mantoux is large and red
A large and red Mantoux test occurs with tuberculosis infection, but false positive results are also possible due to:
- allergies to tuberculin components;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- recent infection;
- infection with mycobacterium, but not tuberculosis;
- vaccination performed (BCG or other vaccine);
- exacerbation of chronic inflammation;
- acute stage of internal organ disease;
- helminthic infestation;
- the interval between the previous sample is less than a year.
We recommend reading about the age at which Mantu is made. From the article you will learn how often the Mantoux test is done in kindergarten and school, the test schedule, and alternative diagnostic methods in older age. And here is more information about what you can and cannot eat when performing the Mantoux test.