The Mantoux test is one of the most frequently performed medical procedures for children. However, its implementation raises a lot of questions and concerns among parents. Many categorically refuse to do it, ignoring the importance of this manipulation and its role in the future fate of the child.
Most of the fears of young parents are based on the possible development of complications, the absence of which no one can guarantee, as well as ignorance of what symptoms should be considered normal.
Most often, questions arise about how long a Mantoux mark should last on a child’s skin and what it should look like during this period. Let's try to find out.
Mantoux in a child: on what day is the reaction checked, its result, how long does the trace last?
Usually, parents whose children have had a Mantoux test have questions about how long the Mantoux mark lasts, how to care for the injection site, and which of the symptoms that appear are considered normal. In order to understand this, you need to know the mechanism of action of the tuberculin test.
The Mantoux reaction is a kind of test of the immunological reaction of the human body, not the subcutaneous injection of an extract from Koch’s bacillus. Leukocytes that have ever been “familiar” with tuberculosis are attracted to the place where the injection was given, which is why the papule begins to redden and swell.
The baby is tested for the first time at 12 months and is subsequently repeated annually. The results obtained after testing are carefully recorded in the child’s medical record and are important for monitoring his health. The doctor pays special attention to the size of the papule and the length of time during which the brown spot persists after Mantoux.
After the child is given the test, it is necessary to carefully monitor its condition and changes:
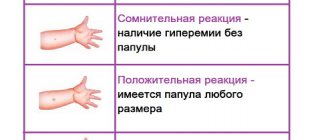
- Papule growth of up to 0.2 cm is the absolute norm and should not cause concern.
- The diameter of the injection mark from 2 to 4 mm is also considered a normal reaction of the body, but requires consultation with a phthisiatrician.
- Button sizes from 5 to 16 millimeters are a positive reaction. In this case, the child is sent to a TB specialist for a more thorough examination.
- The size of an injection mark of more than 17 millimeters in the vast majority of cases indicates the presence of a significant number of Koch bacilli in the body and possible infection.
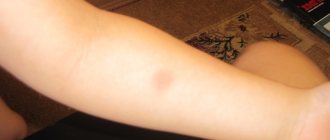
How many days does it take for the Mantoux spot to go away? This question worries many parents. The button appears most actively on the third day after the injection, which is why the test result is read at this time. After this, the trace of the sample begins to gradually disappear. Normally, a Mantoux stain does not go away for a week, and then gradually fades and not a trace remains of it.
It should be remembered that when answering the question: “When will the trace of Mantoux disappear?”, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of each organism. In some children, the spot from the test may disappear after 2-3 days. For other guys, redness or a brown mark may remain for as long as a week or even more and only go away completely after a month. If the child feels well and the injection spot continues to gradually heal, then there is no need to worry and there is no point in seeing a doctor.
The duration of how long the mark from the tuberculin test will last is also influenced by the recently administered BCG vaccination, which is given in order to create immunity in a person to the tuberculosis bacillus. If the Mantoux test is performed soon after BCG, the papule will be enlarged and red in color. In this case, the child does not pass the Mantoux point for a very long time.
In the vast majority of children, the papule reaches a size of 0.4 centimeters on the third day after the injection and disappears completely over time. If there is a stain left after Mantoux, then you should know that, due to physiological characteristics, in some people it may remain for the rest of their lives.
If a baby has this type of reaction, it can be triggered by various factors:
- heredity;
- excessive saturation of the body with protein enzymes.
Nevertheless, children whose stain from the tuberculin test does not disappear for too long are registered with a TB doctor, since the risk of developing the disease is quite high among them. Their health status must be constantly monitored.
Another reason why the “button” cannot heal may be an allergic reaction to the components of the injected drug. In this case, you need to have one of the histamine medications on hand that can suppress allergy symptoms. In the future, it is recommended to consult an allergist. Sometimes in the photo you can see that an allergy to a drug gives a pronounced false-positive result.
If, five days after the injection was given, the child’s spot from it does not disappear or, moreover, the papule has greatly enlarged, turned red and began to fester, this may indicate the following:
- The presence of Koch bacilli in the body in active form.
- Individual intolerance to the administered drug.
- Violation of injection rules and development of sepsis.
In addition, the papule may not go away for a long time if the rules for handling the injection site were violated or if the injection was given without taking into account existing contraindications.
What should be the trace of Mantoux?
After performing the Mantoux test, both parents and the doctor must monitor the trace from it - its characteristics allow one to assess the likelihood of the child becoming infected with tuberculosis pathogens. There is a gradation of papule sizes:
- the size of the “button” within 0.2 cm is the absolute norm;
- a Mantoux mark of up to 0.4 cm is also considered normal, but requires additional consultation with a TB doctor;
- an increase in the “button” to a size of 5-16 mm is considered a positive reaction, the child requires a full examination by a phthisiatrician;
- a papule size of 17 mm or more indicates the presence of tuberculosis pathogens in the patient’s body and a high probability of infection.
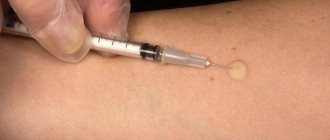
An example of how to correctly measure the Mantoux mark
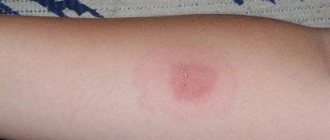
The Mantoux mark appears almost immediately after the administration of tuberculin, but its true dimensions can only be measured on the third day after the manipulation - the data will be as reliable and informative as possible.
How long does it take?
The Mantoux papule disappears within 2-3 days after measurement (5-6 days after the test), but in some children the redness and brownish spot may remain for several weeks, up to a month. If the patient feels great, his behavior has not changed, and the tuberculin injection site is gradually healing, and there are no symptoms of inflammation or purulent process, then there is no need to worry about the long-term preservation of the mark.
Rules for handling papule after Mantoux test
After the injection is given, an adult in the family should be sure to ensure that the child follows rules that will help avoid getting an incorrect medical test result.
Requirements for handling the sample site:
- Contact of the injection site with any liquids, including water, is not allowed. On the first day, water getting on the papule can lead to leaching of the drug components from the subcutaneous layer. This may result in obtaining an unreliable, false negative result. Also, bacteria contained in running water can enter the injection site and cause irritation, swelling and redness of the “button”.
- Do not cover the injection site with an adhesive bandage, as the hand may become sweaty and red under it.
- Do not scratch or irritate the skin around the injection site. The drug administered subcutaneously may cause discomfort. The child will try to scratch the papule, which is why the skin begins to turn purple and peel.
- Doctors recommend not eating sweets, carbonated drinks and other foods that can cause an allergic reaction for three days after the injection.
- It is forbidden to treat the papule with iodine, brilliant green, hydrogen peroxide and other drugs.
- Do not squeeze liquid out of the papule.
If, when examining a papule, the doctor has doubts about the reliability of the result, it is necessary to say that the rules for handling the injection site were violated.
If the child does get his hand wet, then there is no need to panic. You need to blot the wet area with a clean, dry towel and prevent it from getting wet again. It is possible that a reaction from contact of the injection site with water will not occur.
Side effects that may appear after Mantoux
An adverse reaction to the Mantoux test occurs rarely, but the possibility of its occurrence should not be ruled out.
The main side effects that sometimes appear after the injection are:
- The increase in body temperature is usually slight. This usually happens on the first or second evening after the injection.
- Pronounced drowsiness and lethargy. The younger the child, the more pronounced this is. A one-year-old baby may sleep a couple of hours longer than usual in the first days after the injection.
- The loss of appetite is temporary and goes away in two to three days.
- An allergic reaction can manifest itself in the form of skin itching, urticaria, swelling of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx and face.
Allergy is one of the most common side effects of the drug. Children may experience itching in different parts of the body.
If the Mantoux test was performed on an adult, he may also experience side effects, which, as a rule, are not as pronounced as in children.
In order to prevent the occurrence of adverse reactions in their child to the Mantoux test, parents should remember some recommendations.
You should not do a tuberculin test during an exacerbation of any disease. Sore throat, flu, ARVI are contraindications to giving an injection.
After the test, it is recommended to change the child’s diet. The table should have healthy foods rich in vitamins and microelements. This will ensure the normal functioning of the immune system. It is better to avoid heavy foods. The body will spend a lot of energy digesting it, which can lead to a weakening of its defense mechanisms. Nutritionists do not advise giving babies tangerines, fatty meats, eggs, chocolate and strawberries.
If you follow these rules, then the risk of developing adverse reactions to the test is minimal.
Why do they make Mantoux?
Despite the fact that modern medicine has a high level, the risk of developing tuberculosis remains high even in developed countries. That is why the Mantoux test is performed everywhere on children, starting from an early age. It allows you to identify the presence of the causative agent of the disease and begin treatment on time.
In order for the test result to be reliable, you need to remember the following:
- The test cannot be performed if there are contraindications (allergy to the components of the drug, recent illness - bronchial asthma, skin diseases, etc.).
- Failure to follow the rules for caring for a papule may result in a distorted result.
- After the injection, you need to ensure a varied diet, eating foods rich in vitamins.
Parents who are afraid to give Manta to their child are putting the life and health of the baby at risk. The likelihood of adverse reactions to the test is low, and timely detection of the presence of tuberculosis is much more important.
The Mantoux test has been used for seventy years and has proven itself well. The third generation of the planet's population has undergone injections. This helped save thousands of lives and protect humanity from the tuberculosis epidemic.
After how many days is the Mantoux reaction checked?
The test is quite safe and does not require special preparation. It rarely causes allergies, so a child’s severe allergic status does not become a contraindication to it.
Tuberculin should not be administered to a child who exhibits:
- acute disease - infectious or skin;
- exacerbation of a chronic disease;
- allergy with severe symptoms.
Quarantine for childhood infections is another contraindication to the test. It can be carried out immediately after quarantine is lifted and the child has fully recovered. After ARVI, influenza and other viral diseases, at least four weeks must pass, as after any previous vaccination.
You should not rush to perform Mantoux and turn a blind eye to a runny nose or poor health of the child, as this affects the diagnostic result. A viral disease can provoke a “false-positive” reaction to Mantoux.
Despite the fact that the test is usually well tolerated, sometimes after it the body temperature may rise. The child may experience weakness and headache. This is a natural response to the introduction of tuberculin. Normally, these reactions are short-term and should go away within one to two days. If the child has a high temperature or the general condition has deteriorated significantly, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor. Such a response from the body may indicate infection with the tuberculosis bacillus.
pixabay.com/
The result of the injection is assessed after 72 hours. Immediately after administration of the drug, a “button” forms under the skin, which quickly resolves. Then the injection site turns red, and an infiltrate may form - a compaction.
“You can wet the injection site,” says the pediatrician. “But in order not to provoke a false positive reaction, you should not scratch or rub this area for three days. You can’t wash it with soap or shower gel.”