Tuberculin diagnostics (Mantoux test)
Tuberculin diagnostics (Mantoux test)
The Mantoux tuberculin test, colloquially “button”, is a specific diagnostic test (not to be confused with vaccination!), used in mass screening of the population for tuberculosis.
To carry out tuberculin tests, tuberculin is used, which is a complex compound in its composition. It does not contain live or killed tuberculosis mycobacteria, but only their metabolic products, microbial cell elements and part of the medium on which tuberculosis mycobacteria grew.
To the introduction of tuberculin, an allergic response (positive tuberculin test) occurs in those vaccinated with the BCG vaccine against tuberculosis (post-vaccination allergy) and in those infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (infectious allergy). In both cases, there are tuberculosis bacilli in the body of the subject. Only in the first case they were introduced with the BCG vaccine and support immunity to tuberculosis, and in the other they entered the body from the environment and are virulent, i.e. under certain conditions can cause disease.
The Mantoux test is not a vaccination, it is a method for detecting the incidence of tuberculosis. It is carried out annually, and for some categories of children (chronic lung diseases, kidney diseases, diabetes mellitus, hormone treatment, HIV infection, etc.) 2 times a year. The Mantoux test is absolutely harmless for both healthy and sick children.
Contraindications to the Mantoux test:
- Skin, acute and chronic infectious and somatic diseases in the period of exacerbation;
- Allergic conditions, rheumatism in the active phase, bronchial asthma in the acute stage;
- In children's groups under quarantine regime;
- 1 month after vaccinations.
The Mantoux test is performed 1 month after the disappearance of clinical symptoms or immediately after quarantine is lifted.
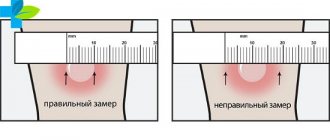
Accounting of results after 72 hours:
- negative test - with complete absence of changes on the skin, or a “prick” reaction;
- doubtful - hyperemia (spot) of any size or papule (tubercle) 2 - 4 mm;
- positive – papule (tubercle) 5 mm or more;
- hyperergic – papule 15 mm or more and/or blistering rash, inflammation of the lymph nodes for any size of papule.
Normally, within 2-4 years after BCG vaccination, the Mantoux test is positive, this is the so-called post-vaccination allergy; by the age of 4, the size of the papule decreases and becomes negative. If a child becomes infected with tuberculosis within a year, the size of the papule increases sharply and it becomes positive. Such children need urgent further examination and consultation at an anti-tuberculosis dispensary. The referral is given by a local pediatrician or a doctor at a children's institution.
Possible side effects
In most cases, after the administration of tuberculin, a person does not experience any discomfort. But sometimes this procedure can be accompanied by unpleasant symptoms: swelling after Mantoux can be accompanied by redness and itching of the skin, and pain occurs when you press on the injection site.
There may be several reasons for the development of such consequences:
- A severe allergic reaction to the drug or individual intolerance to it, possibly an increase in body temperature.
- When performing the Mantoux test, no contraindications are taken into account. Perhaps this effect occurred as a result of the presence of some kind of infection in the body, or not enough time has passed after recovery.
- The injection site was scratched, resulting in infection in the wound.
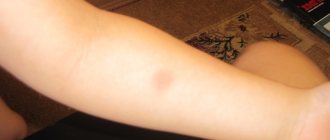
Most often, such negative symptoms appear in young children, since it is most difficult to convince them not to touch the “button” and to keep track of it. If a child’s Mantoux is very swollen, it is likely that the injection site was not sufficiently protected, and the baby, scratching the “button,” caused such a reaction.
Visually, Mantoux resembles an insect bite mark, so the child has a natural desire to touch and scratch this place. The easiest way to protect your baby from this temptation is to hide the injection site under clothing with loose long sleeves. This way the “button” will not attract the child’s attention, and at the same time it will be protected from excessive pressure and friction.
You need to remember that you should not bandage, treat with iodine or brilliant green if the Mantoux is swollen! Such manipulations will not bring relief, but they can spoil the picture of the reaction, which will complicate its further correct assessment by a TB doctor.
The mantoux may become red and very swollen due to an allergic reaction; in this case, antihistamines will help reduce itching and swelling. If a child is susceptible to allergies, it is recommended to take such medications a couple of days before Mantoux and for three days after (before evaluating the results).
If the above symptoms persist for three days (before the sample is examined by a health worker), the patient is sent for further examination to a phthisiatrician.
However, if such symptoms become pronounced, cause severe discomfort, and your hand hurts when you press Mantoux, then there is no need to self-medicate and look for answers on the Internet, trying to establish a “diagnosis from a photo”; in this case, you should consult a doctor without waiting for the date appointed to evaluate the reaction.
Test for tuberculosis
With tuberculosis, a strong reaction will certainly begin, which will manifest itself as redness at the site of drug administration, the formation of an infiltrate, and general malaise. But sometimes all these symptoms occur even if the child is completely healthy. At the same time, they can bother you either immediately after the test or on the second or third day.
Important: Before checking, the area should not be combed, heated or overcooled, or lubricated with any alcohol solutions or cosmetics. Inflammation of the wound and its infection make it difficult to evaluate the results and is the basis for a repeat test.
Why does the sample turn red?
The immune response to the tuberculin test is formed within 72 hours, so the reaction is not assessed on the first day.
Normally, in the first 24 hours there should be no manifestations at the injection site, only slight redness of the skin is allowed.
But under the influence of a number of factors, adverse reactions of the body are possible, which can cause swelling, swelling, itching, etc.
The reasons that influence the result of a tuberculin test include:
- poor quality raw materials or incompetence of medical staff (the injection was given incorrectly);
- unbalanced diet;
- individual reaction to the drug;
- increased sensitivity of the skin.
Attention! On the first day, the Mantoux reaction is uninformative, regardless of the presence or absence of visible changes in the skin. The results are assessed after three days, since during this time the situation can change dramatically in one direction or the other
Wet the injection site: what to do
Contrary to popular belief, water does not have any effect on the Mantoux reaction - this can only happen if the liquid gets directly under the skin. But experts still advise avoiding skin contact with water after the test, since water ingress can cause skin irritation and intensify the reaction. For this reason, you should postpone visiting the pool or sauna for the first three days.
Before hygiene procedures, the place where the injection was given can be covered with a scarf or towel.
It is strictly forbidden to have physical impact on the papule (rubbing or combing it), as well as to seal the injection site with a plaster or wrap it with polyethylene - this can cause changes in the reaction of the skin.
In addition, you should not heat the test site or lubricate it with iodine or other antiseptics. If your hand does get wet, you should carefully blot it, and when assessing the results, be sure to tell your doctor about it.
Reference! The myth that the injection site should not be wet dates back to the last century, when instead of subcutaneous administration of the drug, it was applied to the skin (Pirquet test)
A special substance was applied to slightly damaged skin, so those who inadvertently washed it off had to repeat the test
Reasons for rising temperature
The temperature after Mantoux can rise for many reasons, which is important to consider when assessing the results of vaccine administration
Tuberculin intolerance
If there is individual intolerance, the body will reject the vaccine, and the immune system is actively involved in this process. For this reason, the temperature may rise, papules increase to critical sizes, pus may appear, and severe pain at the injection site. Moreover, any administration of the drug causes such reactions. Children with these symptoms are not recommended to take Mantoux. Other diagnostic procedures should be used to assess the risk of developing tuberculosis.
Increased allergic readiness of the body
An allergy to a test is a response of the immune system to foreign substances introduced into the body. Therefore, it is not uncommon for the temperature to rise after Mantoux. Or a lot of rash appears on the body, the child’s Mantoux becomes very red and itchy.
Infection of the body
Any infectious disease has an incubation period, during which there are no characteristic symptoms, although the body has already been infected with pathogens. The introduction of tuberculin leads to the active proliferation of microbes. As a result, the child’s general condition worsens and the Mantoux temperature rises.
Inflammatory foci in the body
Inflammatory processes can be observed if the child is ill or has an infection, with simple cuts, or during tooth growth. If a runny nose appears after Mantoux, or the temperature rises, this may indicate that the administration of the test has become an additional burden on the weakened body. This can lead to increased pathological processes.
Inflammation at the injection site
After the Mantoux test, the temperature may rise due to an infection. This happens if a child scratches or often touches the skin with dirty hands, which leads to tissue infection.
Poor quality sample material
In rare cases, the temperature after Mantoux vaccination may rise if the child was given a poor-quality injection (if the drug was expired or stored incorrectly). In this case, in addition to fever, other symptoms may be observed: headaches, weakness, convulsions.
If a child develops a Mantoux fever or other negative reactions are observed, this should be reported to the doctor so that the information can be included in the vaccination certificate, which will help eliminate side effects in the future. If an undesirable reaction is detected in children, alternative research methods may be prescribed.
Reaction to test administration, rules, timing, contraindications
Individuals with a high degree of sensitivity to tuberculin experience fever, malaise, and headache.
You cannot do the test if you have epilepsy, the presence of infectious and skin diseases, allergic and somatic conditions.
Mantoux should also not be given to children along with other vaccinations and injections.
If before this the child managed to receive other vaccinations or was sick and took medications, then you need to wait a month and a half after a complete recovery.
Only then do Mantoux in order to get the correct diagnosis, and not a red button with a false positive reaction.
Until the age of five, children may have a positive reaction to the Mantoux vaccination with large swelling, redness, itching due to the BCG vaccination performed in the maternity hospital and immunity to Koch bacilli (by the age of seven, these symptoms disappear in children).
Leukocytes actively react to the administered medication and receive an allergic reaction with redness at the injection site.
Therefore, phthisiatricians often ask for additional tests to refute a positive Mantoux test in children.
If a positive reaction to the vaccine is detected, treatment should be started immediately.
A person can be registered in the zero group of anti-tuberculosis surveillance for tuberculosis infection if the tests are not too bad, and with critical tests they will offer medical examination in the hospital.
But most of all, parents should be wary of the moments where previous tests were doubtful, and then immediately became sharply negative.
Most likely, the patient is highly susceptible to tuberculosis, although the disease itself has not yet manifested itself.
In this case, you need to check whether the immune system is weakened. This also directly leads to redness of the papule.
Why it itches and what to do
It’s easy to explain why children scratch the injection site. When tuberculin is injected under the skin, foreign substances penetrate the body, causing the epidermis to swell. In this case, the body sends reflexes to the nervous system, which are a reaction to foreign stimuli. This leads to the fact that the injection site begins to react unpleasantly: redness, itching, and slight pain appear.
If Mantoux itches and hurts, just wait 2-4 hours - after that the discomfort will go away. But itching can persist for a longer period in the presence of allergies, increased irritability, or diseases of the nervous system.
Itching rarely indicates side effects from the administration of the drug, but parents still need to be careful and monitor the child’s condition. You should consult a doctor if Mantoux itches and the following symptoms are observed:
- the body's sensitivity to the administered drug increases;
- if, in addition to itching, the papules increase in size;
- the child had contact with a person who has tuberculosis.
What happens if you comb
If, when itching, a child tries to scratch the injection site, you need to tell him that he cannot do this. The main problem with scratching is that it can cause the papule to enlarge, which will lead to the need for additional tests. You can loosely wrap your arm in a bandage or wear a long-sleeve sweater.
It happens that it is not possible to trace. If a child has combed Mantu, nothing needs to be done: antiseptics, ointments and gels are not used - this can also negatively affect the final result. If you suspect the development of an allergic reaction, you can give a tablet of any antihistamine, but before taking it, it is advisable to consult a specialist.
However, it is better to go to the doctor if a large and red papule appears, resembling a ball. This may indicate a negative reaction from the immune system.