The question is ambiguous. Old-school pediatricians and young specialists, reinsuring themselves, are more likely to prohibit vaccination for a certain period. The arguments will be very different. These are weak immunity during and after illness, the risk of complications, a hidden picture of newly appeared symptoms (i.e., that they were caused by vaccination or new manifestations of pathology).
Modern pediatricians, focusing on European and world medicine, believe that banal rhinitis or “snotty childhood” is not a reason to slow down the vaccination schedule. They explain that vaccines contain weakened viruses or bacteria, and such injections cannot cause serious reactions. Complications occur only in exceptional cases, and their occurrence is in no way related to a runny nose in a child.
The question of whether it is possible to get vaccinated or not for snot is difficult for ordinary parents who do not have a medical education to understand.
It happens that the baby begins to runny nose in the fall, and the breaks without a runny nose are a maximum of 10 days.
And how to get vaccinated then? After all, diseases such as whooping cough, measles and other dangerous infections, especially in the first two years of a baby’s life, are very dangerous to health.
First of all, you need to find a competent and competent doctor. The pediatrician collects a primary medical history, examines the baby and draws conclusions about admission to vaccination, not to mention whether there is snot or not.
There are various reasons that are much more dangerous than a runny nose, and first of all the doctor should pay attention to them.
Admission to vaccinations in state children's clinics
Many pediatricians say they have to follow protocols.
If the doctor at the appointment notes that the baby has running snot, a red throat and other signs of a viral infection, vaccination is cancelled.
If the body temperature is normal and there are no other pathologies, the pediatrician makes a decision independently.
In 90% of cases in public clinics with a runny nose, pediatricians refuse to vaccinate. Moreover, doctors recommend getting vaccinated no earlier than 10–14 days after recovery.
Experts name contraindications for coronavirus vaccination
Infectious disease specialist and chief medical officer Evgeny Timakov told the publication that during vaccination a person should not show signs of ARVI (malaise, fever, cough, runny nose). In addition, during the month before vaccination, “there should be no exacerbations of chronic diseases.” The infectious disease specialist also advised not to abuse alcohol, fast food and heavy foods three days before and three days after vaccination. Timakov recommended that people suffering from allergic reactions take antihistamines the day before and the day after the vaccination. In addition, contacts should be limited several weeks before vaccination to avoid infection with coronavirus while immunity is developing. Equally important, according to the doctor, is psychological readiness for the vaccine, since strong anxiety can lead to increased blood pressure.
Director of the Helix laboratory service Dmitry Denisov, answering a question from RBC, noted that before vaccination you should take a PCR test for coronavirus to make sure there is no disease that occurs in an asymptomatic form. In addition, Denisov recommends taking an antibody test before and after vaccination to monitor the formation of immunity to the virus.
In October, the press service of Rospotrebnadzor said that contraindications for the use of Epivaccorona are hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, severe forms of allergic diseases, complications or adverse reactions to a previous vaccine administration, acute infectious and non-infectious diseases, chronic diseases in the acute stage, primary immunodeficiency , malignant blood diseases and neoplasms, pregnancy and breastfeeding. For mild ARVI and acute infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, vaccination is carried out after the temperature has normalized. As for the Sputnik V vaccine, Rospotrebnadzor does not recommend vaccination in case of the presence of class G immunoglobulins, acute respiratory viral infections, acute infectious and non-infectious diseases, exacerbation of chronic diseases, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as at high temperature.
On December 2, Russian President Vladimir Putin set the task of organizing vaccination against coronavirus throughout the country. Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin added that vaccination should be “completely voluntary and free.” First of all, teachers, doctors and social workers should receive the vaccine. At the same time, regions can expand this list.
At a meeting of the Presidium of the Coordination Council on December 15, Mishustin noted that vaccination against coronavirus had begun throughout Russia. To carry it out effectively, a schedule for supplying the drug to the regions has been developed. In addition, logistics passports of readiness for vaccination of all constituent entities of the Russian Federation have been submitted to the government.
Which vaccine is better to choose?
Today there are many problems with the issue of vaccination.
Parents are trying to vaccinate their children with drugs from Belgium and France, which children's clinics do not always receive in sufficient quantities.
Russian vaccines are time-tested, but pediatricians claim that children tolerate them less well. Indian vaccines do not have a very good reputation, but there are no problems with their supply. This turns out to be another task that, in addition to snot, parents face - choosing a drug for vaccination.
By communicating with each other, mothers share their experiences. The doctor advised one to only use the French vaccine, the pediatrician told another woman that many people are vaccinated with Indian drugs, there is no need to invent anything, calmly go for the injection.
- The child has snot, can he be vaccinated?
- Temperature after Mantoux is quite common;
- - white transparent snot.
Flu and vaccination against it
Today, quite a lot of influenza viruses have emerged. There were so many of them that they began to assign different letters and names to them. Life does not stand still, and the virus does not sleep either. It begins to adapt to our environment and produce more and more new bacteria. Therefore, the medications that everyone is used to using when they are sick are no longer effective. Flu shots. Doctors encourage us to get vaccinated against the flu, so that there are no complications after a possible illness. Thus, people think that vaccination is necessary only in the autumn, before viral infections arise. But that's not true! You can get vaccinated even at the height of the disease. There are practically no special contraindications, so every person should think about this injection. If the vaccination was done last year, it does not count. It is no longer a valid vaccination. Doctors do not give a one hundred percent guarantee, even for a new vaccination, since it is not foreseen what kind of influenza virus will come to us this year. Mostly group vaccines (A and B) are made. Symptoms of the disease The first sign is an increase in body temperature, accompanied by chills, aches, pain, both in the throat and throughout the body, including headaches. Symptoms can appear very quickly and unexpectedly. It can easily be confused with the disease ARVI. But with the flu, the cough becomes painful and hurts in the chest. Increased fatigue, profuse runny nose, and insomnia. Experts say that the flu has no specific symptoms. And there is a similarity with the symptoms of ARVI. This disease can be diagnosed by a doctor. You can also test for influenza; it is usually carried out if a person is in a hospital. The test itself is, in fact, not difficult to use, but it still requires caution. Doctors say not to self-medicate, but to contact competent professionals. Adults often decide to endure the disease “on their feet” and are treated with what they prescribed for themselves. In this case, it is worth noting that there is a high probability of complications, including pneumonia or worse. The best thing you can do during the cold season is to prevent colds. Take vitamins, do not overcool, get enough rest, no matter what puts a big strain on your immune system. At the moment, there is a multiple choice of drugs to stimulate and improve the health of the body.
Contraindications to vaccination in children (stop factors)
Exemption from vaccinations is conventionally divided into permanent and temporary.
Permanent restrictions
This group of contraindications includes:
- primary hypogammaglobulinemia;
- pronounced allergic reactions to the composition of vaccines;
- complications after previous vaccinations that caused serious side effects from various organs and systems;
- anaphylactic shock;
- malignant neoplasms;
- post-vaccination toxic erythema;
- immunodeficiencies.
Temporary restrictions
Vaccination should be postponed in the following cases:
- the patient is in the stage of acute illness or exacerbation of chronic pathology;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- increased body temperature;
- carrying out radiation or chemotherapy;
- hormonal treatment in large doses;
- the child's body weight is less than 2 kg 500 g;
- pregnancy.
After the end of the acute phase of the disease, with the permission of the doctor, the necessary vaccination is carried out. After immunosuppressive therapy (cytostatics, corticosteroids, radiation therapy), vaccination is allowed only after 30 days.
If during a previous vaccination there was a reaction to a live vaccine, for example, against polio, you can replace the drug with an inactivated IPV vaccine.
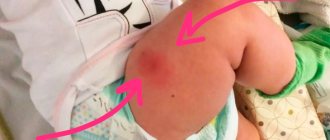
Now pediatricians are trying to use inactivated vaccines to protect children as much as possible from severe allergic reactions. For example, there are many cases when a child tolerates DTP vaccination with symptoms such as fever, convulsions, neurological symptoms (long crying, screaming, drowsiness). Of course, this is very scary for parents.
On this occasion, Dr. Komarovsky said in one of his programs that encountering a disease is much worse than having a reaction to a vaccine. While working in intensive care, he had to see the suffering of children suffering from various dangerous infections. Evgeniy Komarovsky’s opinion is clear – vaccination is necessary.
When a child with a runny nose is vaccinated with DPT and measles
The time for vaccination is limited by age; if you miss the vaccination period, the entire schedule of vaccinations will be disrupted. On the other hand, prolonged rhinitis reduces the protective functions of the body's immune system.
Important!
Whether it is possible to vaccinate a child with a runny nose is decided by the pediatrician, assessing the patient’s condition. If necessary, a consultation with an otolaryngologist is included.
DTP is a combined vaccine that has the ability to protect the body from the appearance of white films on the walls of the larynx and increase the protection of children's immunity against diseases of bacterial and infectious etiology.
The administration of DTP and measles vaccines leads to the production of antibodies that form immune memory cells. Vaccination causes these diseases at an insignificant stage. This manifests itself in a slight weakening of the body, due to which the child develops rhinitis.
Also read: How to treat wet cough in children
If a child has a common runny nose, DTP vaccination is possible. Even if nasal discharge increases after it, parents don’t have to worry. Vaccination is carried out with Russian-made vaccines - Infanrix, Bubo-cok or foreign-made drugs - Pentaxim, Tetracok, Tritanrix-HB.
All of these drugs contain a minimum content of preservatives and additional components, which reduces to almost zero the likelihood of side effects occurring after vaccination. Based on the assessment of the child's condition, the pediatrician may recommend that parents purchase another vaccine.
The famous Ukrainian pediatrician E. Komarovsky claims that it is possible to vaccinate a child with an uncomplicated runny nose. Here we should take into account the importance of vaccination, which protects children from dangerous diseases.
The response to the vaccine depends on the child’s general well-being. If parents are afraid to vaccinate their baby, they must constantly:
- monitor your lifestyle;
- support natural feeding;
- harden the child;
- eliminate sources of possible allergies.
Vaccinations must be carried out strictly according to age; the accuracy of adherence to the vaccination schedule significantly increases its preventive effectiveness.
Vaccine classification
There are several types of vaccines:
- Live (whole virion). The name of the vaccine is due to its composition, which contains undestructed virus virions.
- Subunit. Consists of two surface viral proteins that have a major effect.
- Inactivated (split vaccine). This vaccine is also called a split vaccine. Consists of destroyed virions, does not contain chicken protein and viral lipids, due to high purification during manufacturing. Inactivated vaccines are reactogenic, that is, they are not prone to causing allergic reactions.
When choosing a vaccine, you should pay attention to its composition, since some compounds (for example, chicken protein) can provoke unwanted reactions. This is especially important for children, the elderly and patients with reduced protective qualities of the body. Otherwise, snot may appear after a flu shot, as well as other more serious symptoms.