When should I get tested for children before IgE vaccination (ImmunoCAP)?
– a study on the eve of vaccination in children with a predisposition to allergies; – adverse events after vaccination that occurred within a period of no more than a month before the study.
If more time has passed since vaccination, the result may be negative. A more sensitive method for determining an allergic reaction associated with vaccination, in this case, is skin allergy testing. The Gemotest laboratory does not perform allergy tests; to conduct this study, you must consult an allergist.
When should you take a clinical blood test?
The term general blood test, as a rule, is mistakenly understood as a clinical blood test, since since ancient times in medical practice it has developed that if a doctor prescribed a general blood test, this meant that the analysis would only determine leukocytes, red blood cells and hemoglobin levels, in while a clinical blood test is a much more complex modern analysis of the composition of human peripheral blood, which can be used to diagnose many acute and even chronic diseases. And although a general (clinical) blood test refers to screening methods of examination, that is, accessible, fairly quick, but “not very informative” studies, nevertheless, modern laboratory diagnostics makes it possible to determine dozens of different peripheral blood parameters in a patient, which in the hands of an experienced A therapist or pediatrician allows for very accurate and, most importantly, timely diagnosis of various pathological conditions.
Detailed description of the study
Allergies occur when the immune system reacts abnormally to proteins entering the body. Immune cells perceive them as foreign antigens and cause a special inflammatory reaction, accompanied by vasodilation and tissue swelling under the influence of the chemically active substance histamine.
Proteins to which such a reaction occurs are called allergens. Specific immunoglobulins are formed for them - IgE, which form a compound with these proteins and promote their removal from the body. This is similar to how the immune system fights infectious agents.
The first encounter with an allergen is often asymptomatic, but leads to the formation of IgE aimed at combining with the protein, and repeated contact with it leads to the development of an allergic reaction. The following symptoms often develop:
- nasal congestion; – runny nose with clear discharge; – lacrimation; – burning in the eyes; – sneezing; – dry cough; - urticaria-type rashes.
Allergies to a particular protein most often occur in childhood, and in some cases disappear with adulthood. A predisposition to allergic reactions can be inherited, but is sometimes detected in people whose family has never suffered from such diseases.
Given the existence of many allergens, it is important to promptly identify the cause of the allergy. The ImmunoCAP method allows you to determine the presence of antibodies to allergen proteins with high accuracy even in a small volume of blood serum. The test results are not affected by drug therapy, which is extremely important for people who cannot stop taking it.
Sometimes the development of an allergic reaction is observed after vaccination. In most cases, this problem is caused by components of the vaccine and not by the immunizing agent itself.
Substances in vaccines that can cause allergic reactions include gelatin or egg whites, baker's yeast, formaldehyde and thimerosal, and latex contained in vial stoppers or syringe plungers. Administration of the first of a series of necessary vaccines to children can lead to sensitization of the body to these substances, which subsequently causes the development of an allergic reaction.
Diagnosis of allergy or sensitization to vaccine components is aimed at preparing for vaccination of children who suffer from allergies. For this purpose, the ImmunoCAP method is used, which serves as a reliable way to determine the cause of allergic reactions. The information obtained allows you to predict the risk of complications after vaccine administration and draw up an individual vaccination plan.
When should you take a clinical blood test?
Since childhood, we have all become accustomed to undergoing a medical examination at least once a year, and we know that during this procedure we need to undergo a general (clinical) blood test and a general urine test. Thus, if over the past year there has been some kind of disorder in our body, then by taking a clinical blood test and a general urine test once a year, we can, with the help of our attending physician, timely identify certain disorders in the body and eliminate them as soon as possible. early stage, with little bloodshed, so to speak. In general, clinical examination is carried out precisely in order to identify not a disease, but a functional disorder in the organs and tissues of the body, which, if preventive measures are taken in a timely manner, should not turn into a chronic disease. This is the first one.
Secondly, if you are already sick, then you have two options: the first is to treat yourself with folk remedies, the second is to consult a doctor. The doctor also has two options: the first is to treat you “as is”, having first carried out only a physical, that is, a general examination (palpation, percussion, auscultation), on the basis of which he will establish a preliminary diagnosis and can already prescribe treatment. And the doctor’s second option is to still send the patient to at least the first, screening stage of laboratory tests, which primarily means a clinical blood test and a general urine test. This is what a competent doctor should do so that by the time you come for a follow-up examination, he would already have the results of the primary laboratory diagnosis, and with them, an understanding of how far your illness has progressed. And the tactics of your further treatment will depend on this.
What research should I do?
Some contraindications are obvious: under 18 years of age, breastfeeding, pregnancy after a certain period.
Analysis for β-hCG levels
However, in the early stages of pregnancy, its symptoms do not always appear, so to be completely sure, it is better to use a test or get tested for β-hCG levels.
A blood test with a leukocyte formula and erythrocyte sedimentation rate is one of the basic studies that can provide a lot of useful information.
This method will allow you to learn about the qualitative and quantitative composition of the blood - the leukocyte formula will indicate the presence of an infection in the body, determine the nature of its causative agent and identify an allergic reaction.
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate can tell not only about inflammatory processes, but also chronic autoimmune diseases.
Analysis for creatinine levels
A creatinine level test will help check the filtration function of the kidneys. If the value is elevated, then there may be problems with it - the doctor conducting the examination before vaccination should know about this.
ALT and AST tests
Tests for alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) will indicate damage to liver or muscle cells - in such cases, the level of these enzymes in the blood increases.
Immunoglobulin E test
The immunoglobulin E test detects allergic reactions that do not show external symptoms such as itching, redness or rash.
Antibodies of IgM and IgG classes
It is recommended to check the level of IgM and IgG antibodies to coronavirus. These immune proteins appear in the blood within one to two weeks after infection.
They circulate in the bloodstream for a relatively short time and quickly disappear - usually one to two months after complete recovery.
IgG antibodies appear in the blood later than IgM, but in the case of the new coronavirus, they can appear in the blood almost simultaneously. Typically, IgG remains in the blood of people who have had an infection longer, but disappears over time.
It is important to note that those who have recovered from COVID-19 within the last six months are not eligible for vaccination.
Medical examination of infants at different periods
Let's consider the list of diagnostic measures that are indicated for children under the age of one year.
Neonatal screening
In the maternity hospital, each child undergoes neonatal screening to exclude severe hereditary pathologies. These include:
- phenylketonuria - a disorder of amino acid metabolism;
- cystic fibrosis - cystic fibrosis, which is characterized by damage to the exocrine glands and dysfunction of the respiratory system;
- galactosemia - a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism: galactose metabolism;
- hypothyroidism - insufficient production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland;
- adrenogenital syndrome is a complex of disorders in the production of corticosteroids.
If neonatal screening was not carried out immediately after birth, it can be done before the age of 1 month.
Also in the maternity hospital, audiological screening is carried out, with the help of which specialists can diagnose even the most minimal hearing impairment in an infant. If this test was not performed after birth, it should be performed before 3 months of age.
Vaccinations
If the child is healthy and you consent to his vaccination, then immunization is carried out against:
- Viral hepatitis B is an infectious disease that damages liver cells. Severe consequences of infection - cirrhosis, oncology;
- Tuberculosis is an infection that affects the lungs and other internal organs. Immunization is carried out using the BCG vaccine.
First month of life
The day after the newborn is discharged from the maternity hospital, a local pediatrician will come to your home. Visiting the clinic with the child begins later: when the baby is 1 month old. The pediatrician will listen to the baby with a phonendoscope, examine the throat, nose, and genitals, and give useful recommendations for caring for the baby.
At the age of 1 month, the baby undergoes its first comprehensive examination :
- Ultrasound of the brain . The study is carried out through the fontanelles. During an ultrasound, the doctor receives a two-dimensional image of the structure of the brain, information about the state of brain tissue and the circulatory system.
- Ultrasound of the heart. The study can detect myocardial pathologies, fluid inside the heart sac, abnormal shape of the chambers, coronary heart disease and many other disorders.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity . During diagnosis, the condition of the stomach, pancreas, intestines, liver, urinary and reproductive organs is assessed.
- Ultrasound of the hip joints . A newborn's bones are soft. This is necessary for its successful passage through the birth canal. In the first months of life, bone tissue begins to strengthen, so at this time it is necessary to monitor possible pathologies. For example, ultrasound can exclude or confirm the presence of hip dysplasia.
- Examination by a neurologist. The specialist evaluates the condition of the fontanelles, muscle tone, intracranial pressure, symmetry and proportions of the body, head position and circumference.
- Examination by a pediatric surgeon. The doctor conducts a visual examination of the baby. The examination allows you to identify or exclude the presence of inguinal, umbilical hernia, phimosis, torticollis and other pathologies.
- Examination by an ophthalmologist. Consists of a visual assessment of the tear ducts, examination of the fundus to exclude increased intraocular pressure and inflammatory processes.
- Examination by an otolaryngologist. The purpose of the examination is to conduct audiological screening.
- Examination by a pediatrician. During the consultation, the child’s weight and height, basic reflexes, and muscle tone are monitored.
Vaccinations
Based on research by specialists, the pediatrician makes a conclusion whether the child has any contraindications for vaccinations. If they are not detected, then a second vaccination against viral hepatitis B is carried out.
Age 2-5 months
During this period, preventive examination of the baby consists of a monthly visit to the pediatrician. In addition, at 2 months, clinical blood and urine tests are taken, and at 3 months of age, the child is examined by a traumatologist-orthopedist.
Vaccinations
Age 2-3 months:
- revaccination against viral hepatitis B. It is carried out for children included in the risk group: living in unfavorable social conditions, with reduced immunity, autoimmune pathologies;
- first anti-pneumococcal vaccination . Pneumococcal infection can cause pneumonia, acute otitis, inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, pleural layers, joints;
- administration of DTP - adsorbed pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus vaccine. Whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus are acute infectious diseases that can lead to serious disruption of the functioning of internal organs, as well as death;
- the first vaccination against polio - spinal paralysis;
- vaccination against hemophilus influenzae . Recommended for babies included in the risk group: with an immunodeficiency state, on artificial feeding, born from mothers with HIV infection.
At the age of 4.5 months, revaccination is carried out against:
- pneumococcal infection;
- polio;
- whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus;
- hemophilus influenzae infection (risk group).
Age 6 months
At six months the child undergoes a second comprehensive examination. The baby should be examined by an orthopedist. By 6 months of age, many babies begin to crawl and sit up. Using these skills, the specialist will assess the condition of the child’s muscles.
In addition, consultations with a neurologist, ophthalmologist, and pediatrician are indicated every six months.
Vaccinations
Revaccination is carried out against:
- diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus;
- viral hepatitis B;
- polio;
- hemophilus influenzae infection (risk group).
Age 7-11 months
This period is relatively calm. Preventive examination consists of a monthly visit to the pediatrician. Vaccination is not performed.
Age 12 months
At one year old, babies begin to pronounce their first words and are able to express their emotions using gestures. The child’s communication skills are assessed by a neurologist during a consultation.
It is important to show the baby to an orthopedist. At the age of one, many children begin to walk, so the load on the feet and bones of the lower extremities increases. A visit to an orthopedist will allow you to exclude or notice in time the development of longitudinal and transverse flat feet, deformation of the knee and hip joints.
Also recommended per year:
- consultations with an ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, dentist, pediatric surgeon, orthopedic traumatologist, pediatrician;
- conducting an electrocardiogram;
- taking clinical blood and urine tests.
Vaccinations
- Vaccination against measles, rubella, mumps.
- Revaccination against viral hepatitis B (risk groups).
Leila Askerova, consultant physician, Independent Laboratory INVITRO Young children often get sick, but they can’t always tell what exactly hurts them. Children's tests will help you start treatment correctly. In addition, many studies are carried out before scheduled vaccinations to make sure that the baby is healthy. What tests should a child take and when?
For the prevention of all childhood diseases
The main tests for a child of preschool and school age are a clinical blood test and a general urine test .
They are usually given out:
- At the first symptoms of disease (this applies to any organs and systems of the body)
- Infants - before each vaccination
- Children over one year of age - every year, as well as before vaccinations
Are you afraid of exposing your child to an unpleasant procedure once again? But in vain! Many modern medical offices are equipped with equipment that allows you to easily take blood even from an infant. In addition, timely test results will allow you to make a correct diagnosis and start treatment on time. Let's take a closer look at these basic studies.
A general clinical blood test is the most common test and is used as one of the most important examination methods for most diseases.
How to submit. In children, blood can be taken either from a vein or from a finger. It is important that the test is taken on an empty stomach. This means that the child cannot eat or drink anything before going to the laboratory; milk (even breast milk - 2-3 hours before the test) and juices are also excluded.
General urine analysis . The main indications are routine examinations, assessment of the course of the disease, monitoring the development of complications and the effectiveness of therapy, differential diagnosis of kidney and urinary tract diseases.
How to submit. The day before, it is not recommended to eat vegetables and fruits that can change the color of urine (beets, carrots), as well as diuretics. The container for analysis must be clean and dry (a sterile container is better, it is usually included in the price of the analysis). First of all, it is necessary to thoroughly wash the child’s genitourinary organs. When urinating for the first time in the morning, you should try to release a small amount of urine into a pot or toilet, and then place a container in which to collect about 100-150 ml of urine. For infants, a special urinal bag is usually used, which is tightly glued to the body.
For gastrointestinal disorders
Quite often, in the first year of life, a baby may experience various ailments, for example, indigestion, constipation, and bloating. There is no need to “sound the alarm” right away, but you need to pay attention to these symptoms, especially if they recur. To exclude any diseases in this area, you can take a biochemical blood test to measure the functioning of the liver, pancreas and gall bladder. Usually it is enough to explore exactly the direction that worries you.
Does your baby have frequent intestinal upsets? It may be advisable to take a stool test for dysbiosis, which will help identify an imbalance of normal and pathogenic flora. Does your child have increased gas production, bloating, or does he spit up frequently? Get your child's stool tested for carbohydrate content - this is necessary to rule out lactose intolerance (a condition in which the body is unable to break down milk sugar - lactose). In this case, the child is transferred to dairy-free formula.
How to submit . The container for analysis must be clean and dry (a special container is best). If the material for analysis was collected the day before, do not forget to put the container in the refrigerator.
For viruses and infections
Children are especially susceptible to infectious diseases, colds and ARVI. Sometimes diseases occur in a similar way: the child has a sore throat, he coughs, the temperature rises to 37-38 C. However, the causative agents of the disease are different, which means they need to be treated differently. And, what is especially important, tests should be taken when the first symptoms appear, before starting treatment. Many bacteria are sensitive to therapy, so a “late” analysis will be uninformative.
At the first symptoms (runny nose, inflammation of the larynx, cough, etc.), it is recommended to conduct a venous blood test for the presence of antibodies to viruses, as well as a PCR diagnostic test (test of blood, sputum or urine).
To prevent diseases of the ear, throat and nose (otitis, pharyngitis, etc.), which may be caused by Staphylococcus aureus, it is also recommended to conduct microbiological studies of swabs from the throat and nose . This test must be taken at the first symptoms of the disease (without starting treatment), as well as for preventive purposes if someone in the family is already sick.
In addition, preventive testing for infections from the herpesvirus family is relevant - Epstein-Barr and cytomegalovirus. They can be transmitted both by airborne droplets and in utero - from the expectant mother to the fetus. The danger is that these viruses can be present in the baby’s body asymptomatically, but become more active during any infection, reducing immunity and prolonging the course of the disease. Sometimes viruses manifest themselves in the form of “chronic fatigue” syndrome and increased temperature (37-38 C). To eliminate the risk of the presence of the virus, it is necessary to examine venous blood for the presence of specific antibodies in order to identify the acute period of development of the virus - conduct a study using PCR diagnostics (biomaterial - blood, urine, saliva, oropharyngeal swab).
If a child has recently suffered a streptococcal infection (tonsillitis, scarlet fever), it is recommended to take a urine test 1-2 weeks after recovery.
How to submit. Blood and urine tests - see General clinical blood test and General urine test. Before taking smears, you should not brush your teeth or drink water (for a throat smear), you should not treat your nose with solutions or use drops, at least for 24 hours.
For allergic symptoms
If your baby occasionally develops a rash, redness on the skin, runny nose, watery eyes... This means we are dealing with an allergy. How often do these symptoms appear? Seasonal or periodic? Did a product, substance or animal cause this reaction in the body? A study of venous blood for specific antibodies of allergic reactions will help answer all these questions. This is how you can determine which allergen is the cause of the child’s illness. For example, in spring and summer, hay fever is most common - the body’s reaction to plant pollen.
How to submit. See General clinical blood test.
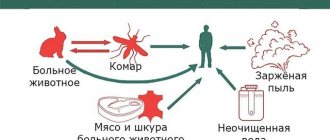
For the prevention of parasitic infestations
In the summer, the baby played to his heart's content in the sandbox, pulled a fallen toy into his mouth, ate something with unwashed hands... and here we are, a phenomenon called helminthiasis. Children can become infected both at home and while walking, visiting or in kindergarten. According to statistics, 8 out of 10 children are infected with parasites, and only one out of three sick children exhibit obvious symptoms of the disease. This means that you need to be tested for helminths regularly. You should be especially alert to such signs as: restless sleep of the child, loss of appetite, lack of weight gain, allergic manifestations in the form of a rash on the face and body, abnormal bowel movements, itching in the anus, cough. An equally dangerous disease is giardiasis.
Tests are taken:
- If any of the following symptoms appear
- For preventive purposes - every year, upon admission to kindergarten, for schoolchildren - at the beginning of each school year
How to submit. For greater reliability, it is advisable to test stool for worm eggs for at least 3 days in a row (helminths go through different stages of development in the body). If there is reason for concern, it is advisable to undergo an in-depth examination, including special blood tests that detect antibodies to helminths. This is a blood test for IgG antibodies to the main parasitic infections: Toxocara, Echinococcus, Opisthorchia, Trichinella, Giardia and Ascaris.
Examination and interview with a therapist
Dmitry Zelenukha, deputy chief physician of the clinic for general medical practice at the Scandinavia clinic , said that there is a special “questionnaire” and regulations for examining a patient who wants to be vaccinated.
“A standard therapeutic examination is expected. The survey is aimed at collecting complaints, life history, and finding out whether the patient has chronic diseases. Attention is also paid to the presence of previous COVID-19 disease, pregnancy, breastfeeding, medications taken, immunosuppressive and antitumor drugs. During the conversation, additional questions may arise to decide on admission to vaccination,” he explained.
Despite the absence of patient complaints, the therapist must examine the oral cavity, assess the condition of the throat, listen to the rhythm of the heart and lungs, measure blood pressure and oxygen saturation.
If the patient has accumulated complaints or concomitant diseases, the doctor’s examination will be more detailed. If something in the patient’s health status is alarming, the doctor should refer him for further examination and only based on its results make a decision on admission to vaccination.
Why do babies need frequent screenings?
Despite the fact that modern medicine has a high level of development, doctors continue to face untimely detection of pathologies in children in the first year of life.
Many of these disorders could be prevented with regular medical examination. From the moment of birth, the baby needs constant medical monitoring, medical supervision, and thorough diagnostics. According to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, medical examination of children in the first year of life implies regular preventive examinations at established age periods.
The purpose of a comprehensive medical examination of infants is the early detection of pathological processes, diseases and factors of their development. In addition to examination by specialists, preventive measures include instrumental and laboratory research methods.
Antibody test before vaccination
Another contraindication for vaccination is the presence of IgG antibodies in the blood. Antibodies of this class indicate an acute stage of coronavirus; vaccination cannot be vaccinated during this period. The introduction of an additional dose of even an inactive virus is a blow to reduced immunity.
antibodies are detected in the blood after testing for the presence of the pathogen SARS-CoV-2 , this confirms the fact that stable immunity to coronavirus has been formed. A person with such a set of antibodies does not need to be vaccinated at the time of the test.
Having coronavirus disease does not provide lifelong immunity. Over time, the antibody titer decreases, and when the virus enters the body, it will be able to multiply and attack healthy cells. When conducting an examination before vaccination for coronavirus, the number of antibodies is detected. When their number decreases to an acceptable minimum, it makes sense for a person to undergo the procedure:
- less than 50 AU/ml – the critical amount of IgG antibodies at which vaccination is recommended;
- more than 50 AU/ml – the immune response to infection is strong, no need to be vaccinated.
If the test for IgG antibodies is positive, vaccination is possible no earlier than six months after the test results are obtained.
A comprehensive examination before vaccination for Covid at the private clinic “Harmony” includes a laboratory test for the presence of antibodies and a PCR test. The result is delivered in hand, or, if desired, by email to the patient. You can sign up for tests at any time.
Do I need to take a clinical blood test and a general urine test before vaccinations?
In addition to medical examination and acute illness, the third reason for taking a clinical blood test and a general urine test is the upcoming vaccination. If you or your child last had blood and urine tests a year ago and everything was fine, this is not a reason to refuse them.
Vaccination is a rather serious intervention in the body, requiring 100% confidence that the patient is healthy. This is why I always recommend that my patients preparing for vaccinations take a clinical blood test and a general urine test at least 30 days before vaccination, but the closer, of course, the better.
Contraindications to vaccination
There are several contraindications to vaccination with Sputnik V. These include, for example, hypersensitivity to individual components of the drug and a history of severe allergic reactions.
In addition, the contraindications included acute chronic or infectious diseases, pregnancy, breastfeeding and age under 18 years.
However, the presence or exacerbation of chronic infectious diseases will not completely prohibit the patient from vaccination against coronavirus. According to official guidelines, it is carried out two to four weeks after recovery or remission.
Also, for mild ARVI and acute infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, vaccination is carried out after the temperature has normalized.
What tests should be taken before vaccination?
According to the current medical standard, the examination begins with a general blood test. It shows the presence of a latent inflammatory process or anemia, in which vaccination is contraindicated.
Analysis for beta-hCG levels
Recommended for women of fertile age to confirm or refute the fact of early pregnancy. In men, hormone measurements indicate the presence/absence of testicular cancer.
ALT and AST activity
Before vaccination, a biochemical blood test is performed to show liver function indicators. If endogenous enzymes are produced in large quantities, this may indicate cytolytic syndrome - damage and destruction of liver cells.
Creatinine test
A blood test for the content of the final link of protein breakdown shows the ability of the kidneys to cleanse the blood. If the indicator increases above the reference value, acute renal failure may be detected. If creatinine numbers are below normal, the patient may have anemia.
Blood test for immunoglobulins E
The analysis helps to identify allergies even if a person has never complained of symptoms in the form of rash, itching or redness. Determining the level of immunoglobulin E in blood serum helps to diagnose allergies, atopic reactions, and bronchial asthma.
Antibodies IgM, IgG
Mandatory blood test for antibodies to Covid. The results indicate that the person is in the active stage of coronavirus or has already suffered a new viral infection and has strong immunity.
PCR test
A swab from the nose and throat shows the presence of viral RNA in the human body at a stage when there are no clinical manifestations of the disease.
In order for the results of laboratory tests to be as reliable as possible, it is necessary to follow the preparation rules. When making an appointment for tests, our manager will warn the patient about all prohibitions before the examination.