Distrust of official sources
The debate about the safety and effectiveness of vaccines in the world dates back to the 19th century. But even in the modern world, due to the growing distrust of society in government institutions and the information they provide, historical distrust in the state healthcare system, which was brought up over many generations (and not only in the USSR and Russia, but also in the USA and Western Europe), people increasingly question official medical advice and avoid interacting with the public health care system.
Fake information about vaccinations
People who refuse vaccinations or do not vaccinate their children most often base their decision on information obtained online. However, in fact, the Internet is most often the source of medical misinformation or unreliable (fake) information.
The growing wave of popular mistrust of vaccinations is based primarily on the infamous article on the dangers of childhood vaccinations published in 1998 by British scientist Andrew Wakefield. This publication, which spawned a wave of vaccine refusals around the world, provided evidence that there was an alleged link between the use of the childhood MMR influenza vaccine and autism. The study's author subsequently retracted his paper, and the British Medical Journal reported that the study was fraudulent. Dr. Wakefield was paid by a law firm that was preparing a lawsuit against vaccine companies in order for him to publish his research. In total, the researcher received the equivalent of more than half a million dollars from the company. After the fraud was discovered, Dr. Wakerfield had his medical license revoked. But due to the fake publication, vaccination rates began to decline around the world. The discredited Wakefield study thoroughly tarnished the image of childhood vaccination in the eyes of parents who were unaware that they were simply being deliberately misled for selfish purposes. Such publications are often used today in the system of “social engineering” - the deliberate distortion of reality to create certain moods and movements in society that are beneficial to certain groups or organizations. Research has shown that media reports that present a false balance between pro- and anti-vaccination camps, regardless of the compelling evidence base in support of vaccination, can strongly influence readers' intention to vaccinate themselves or their children. This confusion may potentially be exacerbated by anti-vaccination rhetoric found online, on social media, or in advertisements from naturopaths and other alternative medicine practitioners.
Conflicting scientific evidence on vaccination
Another problem with vaccine bias is the truly inconvenient fact that new published scientific data often conflicts with previous publications. And nothing can be done about it - searching is the nature of science. But the public can be confused by such conflicting information, which is often used by medical journalists to create sensationalism.
For example, in 2012, information was published that this year a paradoxical situation was observed: people who were regularly vaccinated against the flu were less protected from infection than those who were not vaccinated at all. This served as another serious argument for opponents of vaccinations.
Myth one: vaccination reduces immunity
Immunity cannot decrease after vaccination; on the contrary, after the vaccine is administered, a persistent response of the immune system to a specific pathogen is formed over a certain period. If the vaccination is done correctly and on time, immunity to the disease will form within 2-3 weeks and will begin to weaken no earlier than six months later. The main mistake is to get vaccinated if you have a cold or are starting to get sick, in this case the viruses that have entered the body, even if inactivated, can really become that additional factor that knocks you off your feet. For the same reason, if in your immediate circle there is already a sick person with a confirmed diagnosis of ARVI or influenza, vaccination should be postponed.
Tatiana Alikhashkina
doctor of the highest category, deputy head of clinic No. 1 of the Pirogov National Medical Clinical Center
People in whose immediate circle someone has already become ill should take emergency preventive measures: rinse the nose with saline solutions or seawater-based sprays, use protective ointments that are applied to the nasal mucosa and prevent viruses and bacteria from entering the body, take antiviral drugs.
Common myths about flu vaccination
The vaccine causes the flu. This myth is a good example of a cognitive bias, where people analyze incoming information and draw incorrect conclusions. People can indeed get the flu after vaccination, but this is not due to the effect of the vaccine, but to the two-week “window” while antibodies are produced that provide protection against the flu. Also, the viral composition of vaccines may not correspond to the actual circulating virus, which can lead to the development of the disease even during immunization.
Children do not get sick even without vaccinations. The myth originates from the phenomenon of herd or herd immunity, which can actually protect unvaccinated people, including infants and the elderly. Herd immunity occurs when a significant portion of a population is immune to a contagious disease because they have been vaccinated against it. When this happens, infants and people whose immune systems are compromised have a much lower risk of exposure to the infection because the circulation of the pathogen is significantly limited due to vaccinations. But this does not mean that unvaccinated people will be protected from the flu if they are exposed to the virus.
Vaccinations do not affect the incidence of influenza. This opinion stems from the fact that, due to problems in predicting the types of influenza strains for the current season, the effectiveness of newly created influenza vaccines varies significantly from year to year: from 10% to 60%.
This means that even if a person is vaccinated, he can still get the flu. However, you should know that vaccination, even if it does not prevent the disease, can significantly reduce the severity of the disease, prevent potentially fatal complications, shorten the duration of the flu, reduce the number of hospitalizations and stays in intensive care or intensive care units.
Benefits of the flu vaccine
The threat of influenza: how to resist a viral infection
Influenza, as an insidious and rather dangerous disease, threatens the planet's population with the emergence of mass epidemics every year. The calendar date for the beginning of the morbidity period is usually considered to be the last ten days of October with a transition to the first ten days of November. Every adult who pays maximum attention to their health at the end of autumn is faced with a choice - whether a flu shot will help avoid infection, and most importantly, serious complications after the disease. Moreover, vaccination and its methods raise many questions and conflicting opinions.
Important information about influenza vaccination
The main task of anti-influenza preventive measures is to form the basis of specific immunity to a certain type of influenza pathogen, which helps prevent infection. With the vaccine substance, a special set of antigenic material enters the body, including fragments of the pathogen, traces of its vital activity, as well as microorganisms killed or inactivated.
The effectiveness of the vaccine, which is valid for only a year, is assessed by the following factors:
- degree of immunity to a formidable infection;
- severity of characteristic symptoms of the disease;
- duration of development of the pathology;
- the number of complications that arose after the acute stage of the disease.
Advice: it should be taken into account that due to the constant mutation of the microorganism, new strains of influenza viruses appear every few months, so immunization involves vaccination only with vaccines that are relevant for the current year, and not with drugs from previous years.
What you should know about the influenza vaccination process
- Persistent immunity after vaccination does not appear immediately; 10-14 days must pass after it. Therefore, the vaccine is administered on the eve of an epidemic, and not during it; a solution of the antigenic complex introduced at the height of an epidemic can provoke the disease itself.
- It is known that modern epidemics develop in waves; in order to prevent diseases during the entire period of the epidemic, the flu vaccine contains a set of three pathogens.
- In order for the immune system to gain sufficient strength after vaccination, it is necessary to consider:
- quality of the drug - its purity, viability, dosage;
- the condition of the vaccinated person - his age, genetic predisposition, assess the level of the immune response;
- external factors related to nutrition, human living and working conditions, and climate.
- Strict adherence to the rules and conditions of the process will ensure that immunization will give the expected positive result - up to 90% protection.
- Due to the annual mutations of the influenza virus before the next epidemic, according to the WHO forecast on the typical properties of viruses, vaccine manufacturers promptly change the composition that will be used for vaccination.
Important: vaccination against influenza helps to reduce the threshold of morbidity, reduces the severity of the disease, becomes a reliable barrier against complications due to infection, and minimizes the number of deaths. You should not refuse the injection, especially for people at risk.
Anti-influenza serum is indicated for the following persons:
- · people who are often and long-term ill, especially those suffering from chronic respiratory diseases;
- · people with diseases of the cardiovascular, nervous and endocrine systems;
- · persons suffering from chronic kidney diseases;
- · workers of large teams;
- · for blood diseases and immunodeficiency states;
- · children attending child care institutions, as well as receiving immunomodulators.
Advice: the effectiveness and benefit of immunization for pregnant women is due to the fact that vaccination against influenza of this category is recommended during the period of pregnancy planning. If the condition is not met, then after the first trimester of pregnancy, so as not to harm the fetus. The decision on expediency is made by the doctor.
What flu vaccines are currently used:
| Name of the vaccinating drug | Country releasing the vaccine | Important information |
| Live influenza vaccine LAIV | Russia | Intranasal, persistent immunity is formed due to infection and the course of the disease in a mild form. Has many contraindications and causes side effects |
| Grippovac | Russia | The inactivated liquid centrifuge vaccine is produced in doses for intranasal administration and in the form of a suspension for subcutaneous administration to children over 7 years of age and adults. |
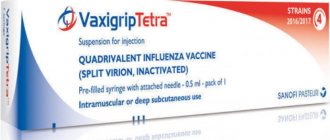
| Vaxigrip | France | The most effective vaccine among domestic and foreign drugs, a minimum of complications against the background of the formation of full immunity, administered subcutaneously and intramuscularly |
| Begrivak | Germany | The inactivated drug contains a minimum dose of virus strains relevant in the coming epidemic season |
| Fluarix | England | The split vaccine is administered to children over one year of age and adults burdened with serious chronic diseases. |
| Influvac | Netherlands | Highly purified drug with a low percentage of side effects, contains parts of antigens of viruses of groups A and B |
| Agrippal S1 | Italy | Purified subunit vaccine, designed for people (children and adults) with chronic diseases of particular severity |
| Grippol and Grippol plus | Russia | The inactivated drug and its improved analogue do not contain live viruses. Vaccinate children from three years of age, adolescents and adults |
| Inflexal | Switzerland | Virosomal vaccine made using new technologies. It is intended for children older than six months and adults for whom other vaccines are contraindicated. |
Important: according to the standard, influenza vaccination is carried out annually in October-November, so that in the remaining time before the start of the epidemic period, immune protection against infection has time to form. It is not advisable to carry out the procedure at an earlier date, because By the end of the epidemic, the number of antibodies will decrease, which is fraught with a high risk of infection.
Will the flu shot be a lifesaver?
The disease is caused by pathogens of three varieties - A, B, C; people of all ages are quite susceptible to them, at any time of the year, although the incidence threshold is exceeded in winter. During this period, due to a lack of vitamins and fresh air, as well as hypothermia, people become most defenseless against infection.
Taking into account these factors, as well as an individual approach, vaccination should become a reliable barrier against an infectious disease that threatens dangerous complications. The influenza virus, reducing resistance to other infectious diseases, causes bacterial infections, exacerbation of chronic ailments, and can cause pneumonia and otitis media, which threatens the development of meningitis.
Important: if the effectiveness of the vaccine is high, there will be fewer sick people, which will reduce the scale of the epidemic, preventing it from developing into a pandemic, when large populations of not only the population of countries, but also continents are involved in the infection process.
Not everyone and not always are allowed to get a flu shot; there are some restrictions on the seasonal injection:
- colds with fever;
- allergic reaction to chicken protein contained in the drug;
- the presence of certain chronic diseases of the heart, kidneys, nervous and endocrine systems, and respiratory tract during the period of their decompensation
Important: children under six months of age are not given an anti-influenza injection, because they are protected by maternal immunity. It is also not recommended to vaccinate children under three years of age due to a wide range of complications and contraindications to the procedure.
Once in the human body, the protein structures of the anti-influenza drug are able to recognize and destroy the virus, preventing its reproduction. The effect of the body’s immune reaction lasts from six months to a year, becoming the key to a person’s high resistance to the virus during the seasonal epidemic, even a certain protection against acute respiratory infections.
How and how to prevent seasonal disease
Currently, vaccination of society is considered the main means of mass preventive measures against the unfolding of large-scale epidemics. The effectiveness of the protection process depends on the correct choice of the type of vaccine, which contains live (weakened) or killed viruses or their fragments. Once in the human body, they force it to fight infection, thereby forming a specific response to infection (immunity).
The goal and purpose of vaccination is to help the human body produce protective antibodies in response to specific antigens received with the drug, which increases the body’s resistance to infection. Immunization is usually carried out in community clinics and specialized vaccination centers, as well as in private clinics (licensed), which can give injections at home as a paid service.
Advice: it should be remembered that in order to ensure high effectiveness, the influenza vaccine is given annually at least two weeks before the official start of the epidemic, since it will take 14 days for immunity to form. The vaccine is valid throughout the epidemic season, and 80% coverage of the population contributes to herd immunity.
The immunization procedure is performed with the following types of drugs:
- Live vaccines capable of causing mild influenza. Vaccination provides fairly stable immunity of good strength.
- Inactivated vaccines, which can be:
- whole-virion, they are characterized by stable resistance to the disease, but the percentage of side effects is high;
- split, capable of providing maximum immunity without toxic effects;
- subunit, their effectiveness is inferior to split split vaccines;
- virosomal complexes, which enhance the immune response to vaccination, are well tolerated.
What flu vaccines are provided during immunization?
| Type | Information about the drug | How to administer |
| Live vaccine (attenuated) | The drug contains weakened strains of the virus, cultivated on chicken embryos, which can cause influenza. The vaccine is prohibited for use during an epidemic and is contraindicated for people with chronic diseases, children and pregnant women | To stimulate a local response, it is administered intranasally, once for adults, twice for children. |
| Whole virion vaccine | Inactivated purified, contains a concentration of viruses killed by special treatment. The vaccine is not recommended for pregnant women due to the high rate of complications | Intramuscular and subcutaneous route of administration from 16 years of age, from 7 years of age - intranasally |
| Split-split vaccines | They contain destroyed components of the virus, but are capable of forming an immune response. Contain a combination of external and internal virus envelope antigens, which provides protection against new and old modifications of the virus | Intramuscular single injection method (shoulder muscle) from 6 months of age |
| Subunit vaccines | The composition of the drug is enriched with fragments of surface antigens of the virus envelope, which somewhat reduces the effect of vaccination. The product may contain an additional enhancing substance (polyoxidonium) and can be produced in an individual syringe dose | Intramuscular and subcutaneous route of administration, a special category of people should be administered twice |
| Virosomal vaccine | Developed using new technologies, inactivated, with the virosomal complex of surface antigens of the virus. A distinctive feature is that it is well tolerated, free of preservatives, provides lasting immunity. | Intramuscular and subcutaneous administration method, for underweight children the vaccine is placed in the thigh |
Advice: it should be noted that anti-influenza serum only protects against influenza, and not against other colds, although after vaccination their course is weakened. In addition, the injection does not reduce immunity, and the person vaccinated does not become a source of infection for others.
What complications can arise from influenza?
Doctors believe that the disease itself is not as dangerous as its many severe complications, which the vaccine is designed to stop. It is true that the flu vaccination itself can cause some adverse reactions to the administration of influenza serum. Reactions, as a rule, are local in nature and usually pass quickly, appearing one day after the injection, and disappear without a trace after a maximum of three days.
Adverse reactions to the vaccine include the appearance of redness, mild swelling and heaviness in the injection area. Sometimes appetite decreases, the temperature may rise, accompanied by mild malaise. These symptoms indicate that the vaccine has begun to take effect.
Advice: if the temperature has exceeded the 38-degree barrier against the background of general weakness and a broken state, and the injection site has become very swollen with signs of suppuration, such signs are considered a deviation from the norm. It is necessary to immediately notify the doctor.
Fear of side effects from administering influenza serum should not be a reason to refuse vaccination, since complications from influenza affect a number of important life support systems of the human body.
As a disease, influenza is unpredictable, and complications after it are divided into the following groups:
- Complications after the disease associated with its immediate course cause the development of:
- hemorrhagic pulmonary edema;
- meningitis, as well as serous meningoencephalitis;
- infectious-toxic shock.
- Complications after the flu, caused by the addition of bacterial infections (secondary), cause the disease:
- pneumonia;
- otitis and sinusitis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- purulent meningoencephalitis.
Advice: it is for the prevention and prevention of deadly complications that vaccination against influenza is so important, especially since severe side effects after it are quite rare.
In addition to vaccinations before the outbreak of an epidemic, as preventive measures, doctors advise supporting the body with vitamins and herbal preparations, and hardening. Emergency prevention and treatment of rapidly spreading influenza is recommended to be carried out using passive prevention methods, using drugs from a number of immunoglobulins strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
What are the actual benefits of the flu vaccine?
- Flu prevention. Vaccination is the most effective existing way to prevent disease in children.
- Reducing the severity of the disease. Vaccinated children will be better able to cope with the flu, even if they get sick.
- Reduced risk of hospitalization or complications. Influenza vaccination reduces the risk of influenza-related complications or hospitalizations in older adults, children and infants, pregnant women, and those with diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- Protection within the community. Vaccination creates herd immunity, which prevents the spread of infection among unvaccinated people, including infants under 6 months of age and those children for whom immunization is contraindicated.
Myth five: if you have chronic diseases, it is better to refuse vaccination.
In fact, the influenza vaccine has few contraindications and limitations, including an allergy to the chicken egg protein on which it is made, severe allergic reactions to a previous vaccination, an acute infectious disease or exacerbation of a chronic disease, inflammation or a cold on the eve of vaccination, malignant neoplasms and other serious diseases. As for most chronic diseases outside the acute stage, the opposite is true: a flu shot is necessary for chronically ill people. First of all, those suffering from diseases of the bronchopulmonary and cardiovascular systems, diabetes mellitus; people who often suffer from ARVI: complications of influenza are especially frequent and most dangerous for them.