Flu vaccination in Moscow starts on September 1. Who should be vaccinated? What side effects might there be? Why do people who are not sick need a vaccine? The most frequently asked questions from Muscovites about vaccinations were answered by the head of the laboratory of vaccine prevention and immunotherapy of allergic diseases, the Mechnikov Research Institute of Vaccines and Serums, Mikhail Kostinov.
Photo: portal of the mayor and government of Moscow
Who needs to get a flu shot?
– In terms of importance and necessity of vaccination, pregnant women come first, then children from six months of age, people with chronic diseases, doctors and teachers (in general, everyone who works in organized teams), then everyone else, including healthy people.
Priorities are allocated according to the severity of influenza in certain groups of people. Children up to 6 months have immunity from their mother, and then they become “sterile” and need to be protected. In people with chronic diseases, any disease worsens and creates delayed complications associated with exacerbation of the underlying disease. The trigger may be the flu.
Should vaccination be postponed during long-term antibacterial treatment?
Antibiotics do not affect the production of antibodies. The mechanisms of action of pharmaceuticals and vaccines are fundamentally different; the drugs do not come into contact with each other. Therefore, there is no urgent need to cancel immunization. Delaying a flu shot can be deadly for the following categories of patients:
- with chronic pathology of the heart and respiratory organs;
- with type 1 diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent);
- with renal failure;
- with immunodeficiency conditions.
Vaccination may be postponed if the patient is on long-term drug treatment, and previous immunization with this type of vaccine caused reactogenic complications.
If the patient has been prescribed a standard course of antibiotic therapy, it is better to postpone immunization for a couple of weeks. This is not due to the interaction of antibacterial and vaccination drugs. This recommendation is explained by the stressful effect of antibiotics on the body, resulting in a decrease in immunity. It is better to give the body time to recover.
When is the best time to get vaccinated?
- The earlier the better. Especially now, when the incidence is spreading all over the world. As soon as the vaccine appears, you need to take it immediately. But in general, flu vaccination can be done year-round. It is clear that it is better on time, but if a person had an exacerbation of the disease, if he came for vaccination after the New Year, it can also be done. Flu can occur in autumn, winter, and spring. But the priority is to do it before the season.
Photo: portal of the mayor and government of Moscow
Drug-vaccine interactions
Antibiotics are synthetic agents with a specific chemical structure. Vaccines are preparations of biological origin to stimulate the development of acquired immunity to a particular type of infection. Vaccines contain a microbial agent (part of the pathogenic microflora, proteins, toxins). Antibiotics and immunization drugs do not conflict, and no chemical reactions occur between them.
Do medications affect the effectiveness of vaccinations?
Pharmacological antimicrobial agents do not affect the effectiveness of the vaccine and the formation of immunity. The vaccine contains no living microorganisms that could be affected by the antibiotic. The vaccine contains a weakened influenza virus, and antimicrobial drugs attack bacteria.
Patients who have previously received blood products - plasma, immunoglobulins - are at risk for influenza and immunization failure. After vaccination, antibodies to the virus may not form in the body. In such cases, doctors insist on medical withdrawal from vaccination for a period of 3 months.
If one family member gets sick, should everyone postpone vaccination?
- Depending on the situation. If there is an epidemic of influenza, then, of course, it is necessary to take preventive measures for all family members. If this is a favorable situation, then you can wait 3-5 days while the incubation period for this infection lasts. Once the family member has recovered, the vaccine can be given.
If a situation with the active spread of influenza is created in the city, in the house and at the entrance, this is not a contraindication for healthy people to get the flu vaccine.
What else is important to know about the CoviVac vaccine?
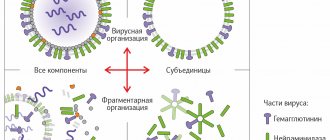
The vaccine was developed by the Chumakov Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Refers to the classic type of vaccine. Immunological efficiency - 85%. The inactivated vaccine is based on real COVID-19. Scientists in the laboratory kill the virus and “turn off” its ability to reproduce—it is no longer capable of causing harm.
But it causes an immune response: as if the person has already been ill. An adjuvant, aluminum hydroxide, is added to the “decapitated” virus. The substance collects virus particles on itself. It is in this form that the vaccine is administered to patients.
No serious side effects were identified after vaccination. In rare cases, compaction is observed at the injection site. CoviVac is recommended for patients aged 18 to 60 years. Inactivated vaccines have been produced all over the world for several decades. This is old technology: there is no doubt about its effectiveness. Influenza vaccines are created using a similar scheme.
Inactivated vaccines are not contraindicated in people who are immunosuppressed or immunocompromised. However, patients using immunosuppressive drugs may not develop a sufficient immune response. Therefore, taking such drugs is contraindicated for at least one month before and after vaccination. However, only the attending physician can adjust drug therapy.
Now more and more information has begun to come in about the so-called post-Covid syndrome. Even those who have suffered a mild form of the disease complain of disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, problems with the lungs and heart, and hair loss. Therefore, it is better not to experiment and risk your health, but to get vaccinated.
Can things get worse after vaccination?
– It can be bad for men and teenagers. They just see the injection and fall. I've been working in this field all my life and I see things like this. Once at the enterprise they were vaccinating healthy, strong men who were 35 or more years old. You vaccinate, it falls like a sack. From what? Because of fear.
Of course, a person is alive, and he must react. Only the corpse does not react. The faint of heart may experience dizziness and discomfort (those who are afraid of injections). For allergy sufferers, there may be redness and pain at the vaccination site for 2-3 days. A mild temperature (37–37.5 degrees) can last for a day and a half. These are normal reactions, but if they occur, it is better to consult a doctor. No one on the planet has ever gotten sick from the flu vaccine.
Are there any restrictions and contraindications?
Patients who develop allergies after taking antibiotics can limit their medication intake. Immunologically mediated reactions occur to metabolites (degradation products) of drugs.
Who is at risk:
- elderly people over 60 years of age;
- infants of the first year of life with a hereditary predisposition to allergies to antibiotics;
- a history of cytomegalovirus infection, mononucleosis, chronic leukemia, gout, HIV.
For atopic diseases such as bronchial asthma, food allergies, dermatitis, hay fever, there are no contraindications to prescribing antibiotics after vaccination. Limiting the use of antimicrobial therapy in these cases is unjustified. However, such patients should be under outpatient medical supervision, since anaphylactic reactions are severe in them.
If I get sick with ARVI, how long after can I get vaccinated?
– Depends on the disease. If you have a minor runny nose and cough, you can get vaccinated after 3-5 days. At temperatures of 38 and above, wait 2 weeks. For severe illnesses, when the temperature lasts 3-5 days and you are taking antibiotics, you need to wait 3-4 weeks.
Consult your doctor. Depending on the severity of the disease, he will determine who should be vaccinated in 2-3 days, who in a week, and who in a month.
Photo: portal of the mayor and government of Moscow
“SPUTNIK V”: WHO SHOULD DELAY WITH THE VACCINATION
Contraindications are:
- hypersensitivity to any component of the Sputnik V vaccine or another vaccine containing similar components (this is determined by the doctor in the vaccination room when examining and interviewing the patient before vaccination);
- history of severe allergic reactions (these include: Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock);
- acute infectious and non-infectious diseases - vaccination is carried out 2-4 weeks after recovery. For mild ARVI and acute infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, vaccination can be done after the temperature has normalized;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases - vaccination is carried out 2-4 weeks after the onset of remission;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding. Important: as the head of the Sputnik V development team, academician Alexander Gunzburg, said, in the very near future it is planned to make additions to the instructions allowing vaccination of pregnant women;
- age up to 18 years. Note: according to Moscow Deputy Mayor for Social Development Anastasia Rakova, clinical trials of Sputnik V for adolescents 12-17 years old will start in the capital from the beginning of July.
! There are also certain contraindications for administering the second component of the vaccine. The patient is given a medical exemption from the second Sputnik injection if severe post-vaccination complications occur after the first injection. These include:
- anaphylactic shock,
- severe generalized allergic reactions,
- convulsive syndrome, temperature above 40°C, etc.
If, after the first injection, antibodies have not formed, and the second component of Sputnik is contraindicated, the doctor may decide to carry out a full course of vaccination with another vaccine - EpiVacCorona or CoviVac, the deputy director for clinical and analytical work of the Central Research Institute of Epidemiology told KP Rospotrebnadzor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Natalya Pshenichnaya. “Re-vaccination with another drug is possible no earlier than 3 months after the administration of a dose of the previous vaccine to which an allergic reaction occurred,” the expert clarified.
“EPIVACCORONA”: NOT EARLIER THAN A MONTH AFTER ACHIEVEMENT OF CHRONIC DISEASES
Contraindications are:
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug (in particular, to aluminum hydroxide and others);
- severe forms of allergic diseases;
— a reaction or post-vaccination complication to a previous administration of the EpiVacCorona vaccine;
- acute infectious and non-infectious diseases, chronic diseases in the acute stage - vaccinations are carried out no earlier than a month after recovery or remission. For mild ARVI and acute infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, vaccination is carried out after the temperature has normalized;
— immunodeficiency (primary);
- malignant blood diseases and neoplasms;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- age up to 18 years.
The vaccine is used with caution (for what this means, see the explanations in Sputnik above) for the following diseases:
- chronic liver and kidney diseases,
- severe dysfunction of the endocrine system,
- severe diseases of the hematopoietic system,
- epilepsy, strokes and other diseases of the central nervous system,
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (history of myocardial infarction, myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis, coronary heart disease).
The vaccine may pose a risk and is used after a physician has assessed the risk-benefit ratio for a particular patient:
- for primary and secondary immunodeficiencies,
- for autoimmune diseases,
- in patients with allergic reactions.