Is it possible to make mantu for a runny nose and cough?
Many parents do not know the answer to this question, but doctors insist that preventive vaccination is necessary.
But are they right in this case?
How will the test affect the child’s general condition? Will a runny nose and cough affect the result?
Parents should know that the mantoux reaction is not a vaccination at all, but an immunological test that is aimed at identifying tuberculosis bacteria.
In this article we will answer the question of whether it is possible to use mantu for a runny nose. You can find out the opinions of doctors and parents. It is worth noting how to correctly evaluate manta rays for diseases, and whether errors can occur.
Is Mantoux given to a child with a runny nose?
What is a runny nose?
Most often this is the result of an attack by rhinoviruses with the addition of a bacterial infection. Other respiratory viruses may be the cause. There is also exclusively bacterial rhinitis. Respiratory viruses weaken the immunity of the respiratory tract, bacteria take advantage of this and settle on the nasal mucosa and can penetrate the nasal sinuses. Children often have a fever, which, among other things, is intended to increase the “aggressiveness” of the immune system in relation to the invading microbiological threat.
Thus, when a child has a runny nose, the immune system is stressed. We remember that the administered tuberculin, if there is a reason for it, begins to interact with the immune system. Tuberculin “checks” the strength of the immune system against tuberculosis bacteria, which are not at all similar to those that cause a runny nose. However, any “disturbance” of the immune system has the potential to distort the response to the administered tuberculin.
Considering that Mantoux is a far from accurate method, the results of which are often interpreted in two ways, the emergence of additional distorting factors further confuses the already complex interpretation of the tuberculin test.
If an adult has a runny nose?
The reaction to Mantoux in an adult is more definite and less like fortune telling on coffee grounds. At the same time, the adult immune system is more advanced and predictable in its reactions.
However, a cold can distort test results in adults. It's not catastrophic. This will not make a negative result positive. But it can become doubtful. Therefore, the recommendation is the same as for children: first we treat a runny nose, then we do Mantoux.
Exceptions are chronic rhinitis and sinusitis outside the acute stage. They do not influence the interpretation of test results. In these cases, it is allowed to administer Mantu for a runny nose.
Can it be done if you have a cold?
The question “can Mantu be given to a child with a cold” worries many parents. Doctors say that it is not worth carrying out such a diagnostic test during a cold.
This is not only due to the fact that inaccurate results can be obtained. The child has an increased risk of complications due to acute respiratory disease. The body's defenses weaken and it cannot cope with viruses.
Doctors answer the question “is it possible to give Mantu to a child with snot” in the affirmative. However, it will not be of any use. Mantoux is not an accurate way to determine the presence of tuberculosis bacteria in the body. The presence of viruses in the body will complicate diagnosis. The child can have both positive and negative reactions.
Mantoux for a runny nose and cough: can it be done?
Every child who has been given the BCG vaccine for the first time is also given Mantoux as a result. However, every mother has the right to refuse manipulation, therefore, before proceeding with direct manipulation, medical workers must ask permission from the child’s legal representatives.
After subcutaneous administration of the BCG vaccine, a reaction test is carried out for several days. To carry out the test, the child is injected with tuberculin, the injection area is slightly below the level of the elbow on the outside. After several days have passed, the doctor should assess the situation. Such a diagnosis should be carried out for all children under 17 years of age. After this time, another method is used - fluorography.
But is it possible to get vaccinated for a cough and runny nose? Quite often, parents bring their baby to the hospital for a routine preventive examination, and the pediatrician gives a referral for manta. At the same time, the doctor does not pay due attention to the fact that your child has a cold. How to react correctly to the doctor’s behavior? Is it all about their negligence? You should not draw premature conclusions; first you should delve deeper into the essence of the manipulation.
Summarizing all existing ideas about vaccination, we can draw the following conclusion about why it is still needed:
- The main task of vaccination is to diagnose the course of diseases at their early stages.
- If parents are convinced that there is no need for their child to be vaccinated, then they have the right to refuse it.
- If the child’s place of stay is under quarantine (school, kindergarten) and the body has weakened due to this, it is recommended to postpone vaccination for a while.
- It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis of tuberculosis based on one mantoux test. To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out additional diagnostic methods.
- A more detailed diagnosis for tuberculosis infection can be done using a general blood test, which includes its own name, ELISA or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
- The reaction of the mantoux depends not only on the physiological characteristics of the child, but also on how she was cared for. After vaccination, the doctor will talk and give the necessary recommendations that should be carefully followed. If you miss something, you can end up with a positive result.
Note to parents
Parents must clearly understand that the responsibility for conducting tuberculin diagnostics falls only on their shoulders.
Yes, there is a possibility that vaccination will cause a deterioration in the child’s well-being. However, you need to understand that no other diagnostic methods will help identify tuberculosis in the early stages of its development. But only in the initial stages of the disease can you easily overcome it without causing serious harm to the child’s body. Of course, parents have the right to refuse the test, but is it worth it?
If the child’s legal representatives nevertheless decide to refuse to perform the Mantoux test, they still need to examine the baby every year, resorting to alternative diagnostic methods, which will require not only financial costs, but also time, and the results of the examination should be delivered to the institution that he visits.
Most often, the following are used to detect tuberculosis in children:
- X-ray examination;
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent test (ELISA).
In situations where parents agree to conduct Mantoux, they also need to know that:
- You cannot inject tuberculin during the quarantine period and over the next month;
- Tuberculin diagnostics cannot be performed during viral infections, including colds;
- the result of the Mantoux test is not the basis for making a diagnosis (it is used to determine the risk of infection of the child, and in order to make a final conclusion, you will need to undergo a comprehensive examination).
What is Mantoux grafting?
BCG is a vaccine that is administered to newborn children in order to develop lasting immunity against tuberculosis. Subsequently, vaccinated children are determined for the presence of the disease using the Mantoux reaction.
It represents a test aimed at determining the presence of a specific immune response after the introduction of tuberculin into the body. This is an extract from destroyed Koch bacilli, which cause tuberculosis. It does not contain toxins. The presence of a pronounced skin reaction indicates that the body is actively fighting the pathogen.
Diagnostic goals:
- identification of children with tuberculosis;
- detection of children infected with mycobacteria;
- selection of children for revaccination.
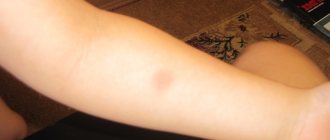
To carry out the test, an intradermal injection is made. After 3 days, the doctor measures the diameter of the resulting papule. Only the size of the lump is measured, not the redness of the skin around it. The more tuberculosis bacteria in the body, the stronger the human immune system reacts, the larger the size of the papule.
Typical Mantoux reaction
Important! The Mantoux reaction is not a vaccine. If for some reason the child is exempt from vaccination, the Mantoux test should still be done
There are cases when the test is carried out 2 times a year:
- children who have not been vaccinated against tuberculosis;
- children who are in direct contact with the patient;
- children from risk groups based on the results of tuberculin diagnosis or children suffering from certain diseases: diabetes mellitus, diseases of the blood system, HIV-infected;
- children living in unfavorable social conditions.
Such frequent diagnostics do not pose any danger to the child’s body, because an insignificant amount of tuberculin is introduced into it.
Mantoux
This test is an immunological test; it allows you to determine whether the baby’s body is infected with the tuberculosis bacillus. Tuberculin test is a diagnostic method of research, carried out by subcutaneous injection of tuberculin.
The result is assessed after three days. The appearance of the “button” determines a positive or negative reaction to tuberculosis. You need to understand that mantu is not a vaccine. Live bacteria are not introduced into the toddler’s body.
This study allows us to detect the presence of antibodies to Koch's bacillus.
Runny nose
The mucus that is produced in the nasal passages prevents the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms and drying out of the cavity. Abundant secretion of mucous substance and snot indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the nasopharynx, which is a runny nose.
It can occur independently, for example, due to hypothermia, or be the result of an allergic reaction, or it can act as a concomitant sign of a viral disease.
Do not forget that babies have not yet fully formed internal structures of their nose. Narrow nasal passages impede the intensive outflow of mucus.
Prolonged runny nose can cause complications.
It is very important that with the onset of rhinitis, parents immediately consult a doctor. Only a specialist can correctly understand the cause of this disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Important Heaviness in the chest: in the middle, difficult, difficult to breathe, what to do?
Why is it better not to do a test if you have a runny nose?
This can give a distorted result and worsen the child’s health. Obtaining an accurate test result is of great importance for the early detection of tuberculosis; it is advisable to exclude any factors that may distort it. Any symptoms of illness indicate that at the moment the immune system is aimed at fighting the disease. It is better to reschedule the test, let the baby recover and get stronger, and rescheduling the test to a later time is not at all critical.
During the test, a small, safe dose of tuberculin is injected into the patient's body. For a healthy person, according to doctors, it does not pose any danger. However, it is advisable to refuse this procedure if he is sick, since the reliability of information about the absence of undesirable consequences for well-being in a weakened state is still controversial.
Often, medical workers at school and preschool institutions vaccinate their children without notifying the father and mother. You should be aware that such actions are illegal. There is a corresponding article 7 of part 3 of the Law “On preventing the spread of tuberculosis in the Russian Federation”, which regulates this provision. It clearly states that anti-tuberculosis measures against minors are possible only with the consent or refusal of their legal representatives. The basis for refusal may be the child’s ill health and the likelihood of obtaining an unreliable false positive result.
Usually, parents trust doctors when it comes to the safety of Mantoux during colds. Some consider this event necessary. Although there are some pediatricians who are categorically against this.
Impact on study results
Mantoux with a runny nose, as noted earlier, can have the most unfavorable effect on the results of the study, the main one of which will be a distorted reaction.
The body reacts to tuberculin with the size of a papule. It must be taken into account that tuberculin itself is, to a certain extent, an allergen, and if the child is allergic, then it is possible to obtain a biased result.
Reasons that change the reliability of the test are:
- recent infections;
- baby's age;
- immunity developed to non-tuberculosis microorganisms;
- improperly performed injection.
Taking into account all these factors, no result can serve as a guarantee of infection with the tuberculosis bacillus or, conversely, its absence. For a more accurate diagnosis, fluorography, sputum culture and other studies will be required.
Often, in the presence of tuberculosis bacteria, the body does not produce any reaction. The reasons for this may be:
- the immune system does not respond to this antigen;
- infection has already occurred;
- the required age (1 year) has not been reached.
To understand whether it is possible to do a Mantoux test if a child is sick, it makes sense to remember the above information and the fact that an infectious disease, even in a mild form, changes the response algorithm of T-lymphocyte behavior, and the meaning of testing is lost. Moreover, it can have a depressing effect on the baby’s immune system and cause unwanted complications.
Is it possible to use mantu if you have a sore throat?
Is it possible to do Mantoux if you have a sore throat? This is a pressing question among parents. Mantoux is a test of the immune response to the causative agent of tuberculosis. It is carried out annually, starting from 12 months from birth. However, the test itself has a number of contraindications, risks and possible complications. Especially at a time when, due to circumstances (chronic and acute diseases, allergies, viral infections), the immune system is weakened. The opinions of specialists and parents themselves about whether Mantoux can be done for primary signs of illness or residual ones (runny nose, cough) differ.
What happens in the body when a tuberculin test is administered?
After a mantoux injection, consisting of an antigen obtained from suppressed pathogenic tuberculosis bacteria, has been administered under the skin, a small swelling forms at the injection site. This swelling is a specific type of inflammatory process that appears due to the accumulation of antibodies produced by the immune system in this area.
If a person has previously entered the body with tuberculosis bacteria, the immune system will produce a larger amount of antibodies that accumulate in the place under the skin where the mantu was placed, and the inflammation will be greater.
In fact, the body’s reaction to manta ray is allergic. The result after tuberculin administration can be affected by any factors that in one way or another affect the immune system.
In order to obtain a reliable result and not draw incorrect conclusions regarding a person’s predisposition to a disease such as tuberculosis, manta must be taken in a normal state of immunity and, accordingly, health. Factors influencing the intensity of the tuberculosis test:
- recent infectious or inflammatory diseases;
- age group (each age has its own normal indicators);
- the presence in the body of antibodies to other pathogens.
If the reaction to manta is positive, one should not make hasty conclusions about the presence of the disease. In such cases, a diagnosis of the health condition is carried out, and if there are any diseases or pathological processes, they must first be cured, and only then the mantu should be repeated.
The presence of a negative result also does not always indicate that the human body is clean from the pathogenic causative agent of tuberculosis - Koch's bacillus. A negative result often appears, despite the fact that pathogenic microflora is present in the body.
A false positive or negative result occurs when performing mantoux in children under 6 months of age, when the immune system is not yet fully developed and cannot adequately respond to the administration of tuberculin.
Other reasons - infection with tuberculosis occurred recently, up to 2.5 months, inflammatory processes are present in the body at the time of mantu, regardless of their intensity.
What is the "Mantoux test"
The Mantoux test is an intradermal diagnostic test to determine the body's specific hypersensitivity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Other tuberculin tests for children are the Koch subcutaneous test, the Pirquet skin test. Tuberculosis is a chronic infectious disease. It proceeds for a long time and in waves. The disease affects the respiratory organs, bones, joints, skin, and genitourinary organs. Tuberculosis is a contagious disease. The main source of infection is a sick person. It secretes the causative agent of tuberculosis - mycobacterium (Koch's bacillus, Koch's bacillus). Each patient with active disease infects on average 10–15 people. Cases of transmission of infection from cattle and goats have been described. A peculiarity of the course of tuberculosis in a child is the involvement of the entire lymphatic system in the pathological process, the slow development of specific changes in the intrathoracic lymph nodes. When seeking medical help, tuberculosis is detected in 40–60% of older children and adolescents, and in the vast majority of children in the first year of life. In this case, as a rule, the most common and severe forms are detected. The main measure to protect young children from tuberculosis is vaccination with BCG and BCG-M. The BCG vaccine (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin, BCG) provides some protection against tuberculosis, especially acute miliary tuberculosis and tuberculous meningitis. But it is impossible to guarantee that after a BCG vaccination a child will not get tuberculosis. Therefore, in conditions of epidemic troubles, mass diagnostics are carried out using the Mantoux reaction. Tuberculin is used for testing. Tuberculin is not capable of causing a disease or developing immunity to it (that is, the Mantoux test is not a vaccination), but it provokes a protective delayed allergic reaction. People with tuberculosis and those without tuberculosis react differently to the introduction of tuberculin into the body. The response begins to develop 6–8 hours after tuberculin administration. The peak of the reaction occurs on the second or third day. A specific response to the introduction of tuberculin occurs only if the body has already had experience of contact with the Koch bacillus and, figuratively speaking, has prepared for a new meeting with it. That is, the body can react to the Mantoux test either after vaccination with BCG, or due to infection. An organism infected with tuberculosis or vaccinated with BCG in response to the introduction of tuberculin can respond with the following reaction:
- local – skin inflammation of varying severity occurs at the site of drug administration;
- general – deterioration of health, increased body temperature, headache;
- focal - inflammatory reaction around tuberculosis foci.
Important Panavir suppositories: instructions for use
The purpose of the Mantoux test is to detect the presence of the causative agent of tuberculosis in the child’s body. Survey objectives:
- promptly identify a child with tuberculosis;
- identify those who are at risk of the disease (when the child’s reaction to tuberculin occurs at a high level) for follow-up with a doctor;
- select children for repeated BCG vaccination.
To produce a ready-to-use drug, dry purified tuberculin (Purified Protein Derivative, PPD), physiological solution (sodium chloride), stabilizer and preservative phenol are used. Tuberculin is dosed in tuberculin units (TU). 1 TU of domestic tuberculin PPD-L contains 0.00006 mg of dry preparation. To examine a child, only the Mantoux test with 2 TE is used.
For what purpose do doctors administer a tuberculin test?
Mantoux is a test that is necessary to determine the causative agent of tuberculosis. A subcutaneous injection is not considered a vaccination and is used for timely detection of Koch's bacillus.
Tuberculin contains dead bacteria that enter the child’s body. After administration of the drug, a button forms at the injection site, which enlarges in the presence of a pathogen.
The tuberculin test performs several functions:
- Mantoux vaccination serves to identify people who are carriers of Koch's bacillus. The immunological reaction appears only 24-72 hours after administration of the drug.
- Thanks to the procedure, it is possible to confirm the presence of an infection that is in the active phase.
Is it possible to do the Mantoux test for cold symptoms?
A huge number of parents are asking one question: is it possible to do Mantu for a runny nose, cough and cold? The opinions of doctors and scientists are extremely contradictory; there is no clear answer to this problem, because the pros and cons are divided equally. In any case, the choice remains with the parents, but it would not hurt to consult an experienced pediatrician or phthisiatrician. Mantu for a runny nose can only be done in the absence of diseases such as:
- acute bacterial or viral rhinitis;
- chronic catarrhal or allergic rhinitis;
- ozena.
Snot (especially green and yellow) and cough are the first signs of acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections, which cancel the test. In this case, it is necessary to postpone the procedure until the child has fully recovered. It is strictly forbidden to give Mantoux if the child is very sick and coughs. Unlike a runny nose, a cough indicates significant inflammation in the airways. If for rhinitis in some cases it is possible to do a test, then for cough it is strictly forbidden. In any case, this will distort the results and is fraught with complications, which means there will be no benefit from the diagnosis.
If you have a cold, a tuberculin test aggravates the course of the disease and has a detrimental effect on the child’s body’s defenses.
Impact on study results
When performing a test during a runny nose or cold, the Mantoux reaction is distorted: the injection site swells incorrectly and may show deviations from the norm. Residual snot is unlikely to affect the size of the papule, but an acute inflammatory process may well give a false positive result. In this regard, you will have to go through a number of specialists and examinations to prove that the child does not have tuberculosis.
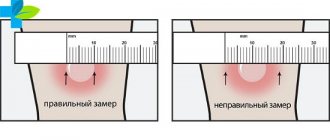
A distorted picture of the results is manifested in an increase in the border of redness of the papule and its excessive swelling. In some cases, there is a purulent injection site that resembles a burgundy sore. It is worth considering that to determine the result of the manipulation, only the size of the lump near the needle injection is assessed, and not slight redness and swelling. The accuracy of the results is influenced by various factors:
- the general condition of the child’s body, and especially his immune system;
- compliance with the rules for caring for the sample site for three days, etc.
Accordingly, we conclude that for the most reliable result of this study, the child must be completely healthy. At the time of the test, as a last resort, only residual symptoms of past diseases are acceptable.
Consequences for the child
Typically, a tuberculin test is well tolerated by the child. Even if complications occur in rare cases, they are easily corrected with medications to relieve symptoms. However, if the test is done during an acute form of a cold or immediately after it, then the risk of consequences for the child increases significantly.
After performing the Mantoux test, the child may have a fever, dizziness and nausea (we recommend reading: what to do if the temperature rises after Mantoux?)
Side effects of the Mantoux test can take a variety of forms - from disruption of the baby’s bowel movements to behavioral changes. Often this procedure causes allergic reactions. They intensify when the child is prone to allergies and the immune system is weakened by the disease. The most common complication is a runny nose, but after the test other consequences are also possible:
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness and cephalalgia;
- temperature rise up to 40 degrees;
- itching and rashes in the area of manipulation;
- runny nose and cough.
Mantoux and colds
Colds are usually caused by viruses or a mixed infection. This triggers a number of inflammatory processes in the respiratory system. Occurs:
- cough;
- runny nose;
- the temperature may rise;
- The mucous membrane will begin to swell;
- Possible intoxication of the body.
In this case, it is impossible to carry out a mantu test. The result in this condition may be false positive. Only with hyperthermia alone does the synthesis of bradykinin and histamine, characteristic of an allergic reaction, increase.
Contraindications for the test
In the following cases, you should refrain from prescribing a tuberculin test:
- acute period of acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections and bacterial infections, accompanied by a severe cough;
- relapse of chronic diseases - bronchial asthma, COPD and others;
- skin rash of unknown cause;
- increased body temperature due to various conditions;
- history of epileptic seizures;
- dyspeptic disorders - nausea and vomiting, stool disorders;
- malignant neoplasms;
- primary and secondary immunodeficiencies (AIDS, severe operations with blood loss, fasting and stress, endocrine disorders).
Immunologists and pediatricians advise not to do the test until the baby has fully recovered, and parents have reason to write a refusal of the procedure. In such a situation, a medical exemption is issued for some time.
Doctors' opinion on an exciting issue
Experts do not recommend giving Mantoux to a sick person for several reasons. First of all, this can worsen the baby’s condition, and secondly, distort the result of the reaction. It is important to know what will happen if Mantoux is given to a sick child.
Possible reactions include:
- allergy;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases, including neurological ones;
- temperature increase;
- weakness and apathy;
- cephalalgia and dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- rhinitis after the procedure;
- local skin deformations;
- false positive result;
- falsely low. There is a risk that next year a normal result will be regarded as an increasing reaction.
But, despite this, a number of pediatricians, for example, O.E. Komarovsky considers the tuberculin diagnostic procedure mandatory. As a last resort, it can be postponed for a short period, but it must be done once a year. However, only parents can decide whether to give their child a Mantoux test or not.
Is it possible to do a Mantoux test for rhinitis?
Runny nose in children varies. More often it is infectious, which is characterized by mucopurulent snot, symptoms of intoxication to varying degrees, and often fever. Allergic rhinitis, which has been diagnosed more and more often in recent years, also occurs with snot and sneezing, but with a normal temperature, without intoxication. To determine the possibility of a Mantoux test for a runny nose, you first need to diagnose the form of rhinitis.
If a child has an allergic runny nose, then there must be a record of this in the preschooler’s or schoolchild’s card. If it is episodic or seasonal, then the test can be planned for those months when the allergy should not appear, or done after the clinical picture has disappeared. If you have a runny nose all year round, then you shouldn’t wait for the end of allergic manifestations. In these cases, the Mantoux test for a runny nose can be performed, but only after a course of antihistamines.
In situations where a doctor at a child care facility diagnoses a child with a runny nose of an infectious nature, it is better to wait with a test for tuberculosis. Not at all because it supposedly can worsen the course of rhinitis or lead to complications.
Everything is not scary and much simpler: when a child has a runny nose, both humoral and cellular immunity changes, and all protective forces are directed toward fighting inflammation in the nasal cavity. Therefore, the test result may turn out to be unreliable; an increase in the diameter of the papule may occur, which will lead to an unreasonable referral of the child to a TB specialist.
Therefore, a tuberculin test must be done, but only after recovery - when there is no snot, sneezing, or elevated body temperature. You must first cure a runny nose, which will take a maximum of two weeks - these periods, if the test is repeated once a year, are not critical.
Important Fluorography during breastfeeding, can it be done on a nursing mother?
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Children have a runny nose quite often. It has a different nature: it occurs as a result of a cold or an allergen entering the body. You can understand whether Mantoux is allowed for a runny nose in a child after determining the nature of the inflammation of the nasal mucosa.
Severe cough before bedtime in a child - possible causes
Dr. Komarovsky believes that it is not worth doing Mantu while the baby has a runny nose. For rhinitis of an allergic nature, you need to schedule diagnostics for another period of the year.
Important! If a child has year-round coughing, sneezing and sniffles, but no fever, the test can be done.
If the doctor has diagnosed an infectious disease in the child, the test should be postponed for the recommended period.
Runny nose in a child
Dr. Komarovsky explains that administering tuberculin to a child with an infectious disease is not dangerous. However, it will show incorrect results. When an infectious disease occurs, the body accumulates all its strength for a complete recovery. In order not to disturb him, it makes sense to wait with the diagnosis.
Komarovsky warns that under no circumstances should this important diagnostic procedure be neglected. The unfavorable epidemic situation regarding tuberculosis remains in Russia. That is why diagnostics need to be done every year, preferably at the same time.
Opinion of E. O. Komarovsky
Evgeny Olegovich Komarovsky is a famous pediatrician, doctor of the highest category, author of the TV show “Doctor Komarovsky’s School.” In his opinion, most people are mistaken about the tuberculin test procedure, considering it a vaccination or inoculation. This manipulation is intended only to identify a predisposition to the disease and the fact of carriage of tuberculosis, and not to produce antibodies to it.
According to the pediatrician, the Mantoux test should not be neglected; it should be performed annually, at the same time. In Russia, the risk of contracting this disease is still high, so it is worth postponing the tuberculin test only due to the acute course of acute respiratory infections. Carrying out a diagnostic allergy test will certainly show whether the baby has had “experience” of interaction with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
This also means that manipulation is allowed in the presence of residual colds and somatic diseases. This informative diagnostic method cannot be neglected, but it should be carried out without fail. The pediatrician emphasizes that if you have a cough, there is no need to do the procedure, because the results will be incorrect and the disease will be more severe.
It is imperative to give a month to restore the child’s immunity, and then carry out this immunological test
He also draws attention to the erroneous behavior of health workers - suggesting that they take an antihistamine before the procedure. In this case, the meaning of the test is lost, since its purpose is an allergy test, and when taking an antihistamine, a correct result is impossible
How does the body react to the test?
Most often, the child’s body does not react in any way to this immunological text: the temperature does not rise, and no changes occur in the general state of health. Only at the puncture site does a local reaction to tuberculin appear - this is normal, this is why the test is done.
If the body is infected with tuberculosis, the reaction will be positive. If there is no infection, the reaction is negative. The result is checked by a doctor or nurse by measuring the reddened seal around the puncture (infiltrate) with a millimeter ruler. Deciphered according to the scheme:
- Negative reaction – infiltrate does not exceed 1 mm.
- Doubtful - the reddened spot measures 2-4 mm.
- Positive – with a diameter of 5 mm.
- Pronounced – 16mm or more.
In the latter case, additional examination is required in the near future. A positive reaction to the test does not mean that the body is infected.
Types of reactions to the mantoux test
To get a true assessment, you must completely exclude the main reasons that can provoke a positive test result. It may be affected by:
- Improper transportation or storage of the vaccine.
- Poor quality, unsterile instruments (syringes).
Before making a final diagnosis, a number of studies and additional procedures are performed.
Why is the test negative in an infected body?
Cases have been recorded where a child’s body is infected with tuberculosis, but the test showed a negative reaction. This result can be explained by several reasons:
- The immune system is weakened, so the body does not react to the irritant.
- The infection occurred relatively recently (no more than 2 months ago).
- The child’s age is too young (up to six months, the baby’s body reacts inadequately to the Mantoux test).
Why is the test positive in the absence of tuberculosis infection?
There are also explanations for this:
- There is still an infection in the body.
- The body is infected with other bacteria.
- Presence of an allergic reaction.
Is it possible to use Mantoux if you have a runny nose, when you don’t know if you are allergic to the medicine? It is allergies that become a frequent exacerbation after Mantoux.
Tuberculin is a solution whose composition includes inactive tuberculosis bacteria (Koch's bacillus), preservatives for their preservation and additives.
These additional components can trigger the development of an allergic reaction. If the cause of the reagent is determined, you should look for an alternative - a vaccine that does not contain it.
Reviews
On the Internet, mothers themselves are happy to share their opinions and personal experiences regarding the relationship between colds and the Mantoux test. Or they are looking for an answer to this eternal question.
- Elena: “I always trust the words of Dr. Komarovsky and have never been deceived. So, you can do Manta only two weeks after recovery. But! Is it possible to do Mantoux with a red throat with the permission of the parents and in the absence of other signs of inflammation and normal tests? Yes, you can!
- Natalya: “A week ago, my son got sick, but there was no fever, just a runny nose and redness. Two days after recovery, Mantoux was done and this is the result - 1.2 cm. As I understand it, more than normal. They didn’t strictly refer me to a TB specialist, but they recommended that I contact him.”
- Olga: “But with us it’s the other way around. Inflammation in the throat and nose occurred after the test, although it was given to a healthy son. Apparently it's an allergy. We’re only a year old, this is our first try.”
- Lyudmila: “We had Mantoux done immediately after the illness, there was still a slight redness, but the doctor allowed it. The result was an overreaction. Additional tests were prescribed and a repeat test six months later. The second result was normal. They also prescribed chemotherapy, but I refused. I had a good relationship with the TB doctor; she accepted the refusal without question (especially since I have the right by law).”
- Julia: “I am a pediatrician myself. And I can say with confidence that only a completely healthy baby can make Manta. Take your time and let him recover calmly. The sample won’t run away anywhere.”
Thus, if it is possible to avoid Mantoux at the time of illness and for two weeks to a month after it, then it is better to do so. This will minimize the risks of complications and additional visits to the doctor.
Is snot in a child a contraindication?
Like any medical procedure, Mantoux also has a number of contraindications:
- Any increase in body temperature. Most likely, there is some kind of inflammatory process, infectious or viral disease in the body, so you should wait until the condition normalizes.
- Chronic disease in the acute phase.
- Recent vaccinations. If you have recently been vaccinated (introducing live, albeit weakened, bacteria or viruses into the body), Mantoux should be postponed for some time - usually from one and a half to two months. Immediately after the test, you should also refrain from vaccinations, as they will be more difficult to tolerate. You need to wait about a month and a half.
- Any skin diseases and allergic rashes. To objectively assess the reaction to a tuberculin test, the skin must be clean, without redness or rash.
- Epilepsy.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Cough.
If there is no suspicion of tuberculosis, Mantoux is not used for coughing; wait for the complete disappearance of symptoms.
Important! If your pediatrician refers you for a test, be sure to tell him about the presence of symptoms of illness or recent illnesses. Perhaps the doctor will decide to postpone the vaccination for an indefinite period, if there are grounds for this
Perhaps the doctor will decide to postpone the vaccination for an indefinite period, if there are grounds for this.
Contraindications
Why does a child under one year old have a stomach ache with ARVI?
Contraindications for this study:
- acute, chronic infectious diseases;
- somatic diseases during exacerbation;
- acute and subacute allergic diseases;
- pneumonia;
- chicken pox;
Chicken pox in a child
- pyelonephritis;
- stomatitis;
- asthma;
- mononucleosis;
- inflammation of the conjunctiva.
Attention! For epilepsy, Mantoux is strictly contraindicated. It can provoke an epileptic seizure.
If a quarantine is declared in a preschool institution, at least two weeks must pass after its completion and before the diagnosis is carried out.
Sometimes there may be an individual intolerance to tuberculin by the body. In this case, the reaction is carried out, but a reduced amount of tuberculin units is introduced into the body. If your child has been vaccinated against tetanus, you must wait a month.
Before performing the test, it is necessary to measure your body temperature. Mantu should be postponed if the temperature is elevated and check if the baby’s throat hurts.