The Mantoux test is used to measure the human body's immune response to tuberculin, a heat-treated, specially processed fragment of tuberculosis bacteria. Intradermal administration has been used for over 70 years worldwide. In adults, the test shows whether a person is infected with the tuberculosis bacillus or not. For children, the Mantoux test is used for a slightly different purpose.
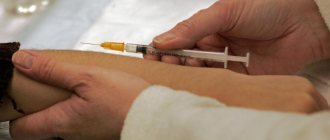
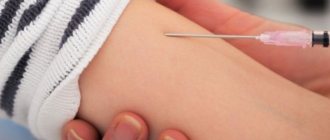
The sample is injected into the top layer of skin by lifting the skin with a needle. Intradermal administration is used mainly for the forearm, for its middle part.
What it is?
The Mantoux test or tuberculin test is a specific diagnostic method that allows you to detect the fact of infection with the bacteria that cause tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Koch bacillus).
The essence of this test is the intradermal injection of a tuberculin solution. In this case, the body, which has previously encountered tuberculosis bacteria, responds to the Mantoux test with a pronounced allergic reaction - the formation of an infiltration zone, thickening of the skin (induration).
Tuberculin itself is a combination of extracts obtained from the mycobacteria M. tuberculosis, M. bovis and M. avium. Essentially, these are antigens to which the human body's antibodies react.
Video on the topic
About the Mantoux test at Dr. Komarovsky’s School:
Thus, the Mantoux test is necessary to detect Koch bacillus in the body. It is carried out periodically for prophylaxis and each time before BCG vaccination. Proper preparation for a tuberculin test is the key to obtaining a reliable result and preventing the development of unwanted reactions. It is important to follow a number of simple rules. Children with allergies should be prepared more thoroughly for diagnosis.
Why is Mantoux test done?
The tuberculin test is used as a means of mass screening of children aged 122 months to 18 years for tuberculosis. The test is easy and cheap to perform, and the results are easy to interpret. In children, the Mantoux test may be used if symptoms suggestive of tuberculosis infection are present.
This diagnostic test only shows the presence of antibodies to mycobacteria, that is, the fact of prior contact or infection. It does not make it possible to assess the activity of the tuberculosis process in the body or the degree of protection against the disease obtained after administration of the tuberculosis vaccine (BCG).
WHY DO THEY MAKE MANTU FOR CHILDREN?
There are several purposes for testing in childhood:
- Identification of uninfected patients for subsequent vaccination. Using a test, you can find out whether there is a response to tuberculin.
- Checking the dynamics of test results over several years. Using this information, one can determine the Mantoux “turn”, the presence of tuberculosis with a high degree of probability.
- Determination of a severe reaction that requires additional research.
In adult patients, the test is a reliable, sensitive test for determining the presence of the tuberculosis pathogen in the body.
Children begin testing at age 1 and finish testing at age 15. Mantoux is administered annually.
Technique for performing the Mantoux test
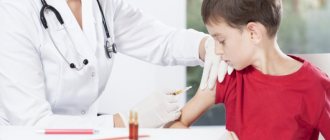
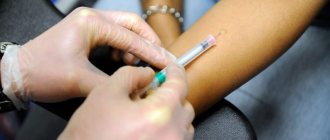
The Mantoux test is performed by injecting 2 units of tuberculin (TE) into the skin on the inner surface of the forearm. The injection is carried out with a special tuberculin syringe with the needle cut upward.
The tuberculin test is an intradermal injection. If performed correctly, it should cause the formation of a pale raised skin (blister) 6 to 10 mm in diameter immediately after the procedure.
At the same time, since tuberculin is injected directly into the skin, the Mantoux test can be exposed to contact with water - it is not able to penetrate into the skin and interact with tuberculin. A really important limitation is to minimize mechanical stress, which can affect the size of the induration area. In other words, the sample site should not be scratched or even touched again.
How they do it
The technique of performing Mantoux is regulated by the relevant documents of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. To carry it out, special (tuberculin) syringes with a volume of 1 g are used. They have a short and thin needle. Other types, including insulin syringes, are prohibited. The ampoule with tuberculin is wiped with medical alcohol and opened. 0.2 ml of tuberculin (2 doses) is drawn into the syringe and the needle with which the injection will be performed is attached. 1 portion (0.1 ml) of the solution is dispensed into a cotton swab.
The area on the hand from the inside of ½ of the forearm is wiped with alcohol. The skin is stretched with your fingers and a needle is inserted parallel to the surface under its upper layer so that its cut is directed upward. 0.1 ml (1 dose) of tuberculin is injected intradermally. If the Mantoux technique is followed precisely, then a papule with a diameter of no more than 7-9 mm is formed at the injection site, and the skin above it has the appearance of a lemon peel and turns pale.
Mantoux can be made by a nurse who has undergone special training, as prescribed by a doctor. And only they are able to correctly evaluate the result. The implementation algorithm must be strictly followed.
Which hand?
For the convenience of medical staff, it is customary to do Mantu in the right hand in even years, and in the left in odd years. But there is not much difference - the injection can be placed in any upper limb. The injection is made on the arm, where the skin on the forearm is healthy without damage. If the test is repeated several times a year, it is recommended to change the injection site to avoid an incorrect result, since immunological cellular memory exists.
The results of the injection are compared with previous ones in the child’s outpatient record. Despite the fact that the Mantoux reaction has been performed in Russia for more than 80 years and its results are often questioned, a more informative test has not yet been created.
Sample results
The Mantoux test reaction is assessed 48–72 hours after injection. The test criterion is the diameter of the skin seal that appears. In this case, erythema (the area of redness of the skin) is not taken into account. The diameter of the compacted area should be measured across the forearm, perpendicular to the axis of the arm (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Correct measurement of the reaction during the Mantoux test. Source: MedPortal
The reaction to the Mantoux test, depending on the diameter of the induration, is:
- Negative - 0-1 mm or complete absence of reaction.
- Doubtful - 2-4 mm or the presence of hyperemia of any size without induration.
- Positive - more than 5 mm.
Photo:
Positive reactions are divided into subtypes:
- weakly positive - 5-9 mm;
- medium intensity - 10-14 mm;
- pronounced - 15-16 mm;
- hyperergic (excessively expressed) - more than 17 mm in children and 21 mm in adults.
Photo: a4ashishmishra.gmail.com / Depositphotos
Also, a hyperergic reaction, regardless of the size of the skin induration, is indicated by the formation of suppuration and areas of necrosis, damage to nearby lymphatic vessels, nodes, etc.
Induration up to 5 mm may also indicate infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the following cases:
- Recent contact with a person with tuberculosis.
- Previously obtained chest x-ray results indicating previous tuberculosis.
- Underwent surgery for organ transplantation.
- HIV infection and AIDS, other immunodeficiency conditions, for example, long-term therapy with corticosteroids.
NORMAL FOR CHILDREN
After the first BCG vaccination, children retain anti-tuberculosis immunity for up to 7 years. How well it is preserved depends on the diameter of the scar after the test. It remains on the left shoulder. If there is no such round mark, this means that the BCG vaccination was not given, and the child does not have immune protection against tuberculosis.
Table 1. Preservation of anti-tuberculosis immunity after BCG vaccination depending on the diameter of the post-vaccination scar.
| Diameter post-vaccination rib, mm. | Duration of anti-tuberculosis immunity, years |
| up to 2 | until 3 |
| up to 4 | up to 4 |
| until 6 | up to 5 |
| 8 or more | up to 7 |
The age of the patient decides what the reaction to the test should be:
- 1 year. The papule is 5-10 mm in size, regardless of the size of the post-vaccination scar.
- 2-6 years. The intensity of anti-tuberculosis immunity reaches its maximum by the age of 2 years. If the scar is larger than 8 mm, the papule can reach 16 mm. After 3 years, the immune response dies down. However, at 4-5 years old, children still have a positive or questionable reaction, and the size of the papule at the age of 4-6 years is considered normal if it does not exceed 10 mm.
- 6-7 years. At this age, patients have a negative or questionable response to the test. A negative result is a signal about the need for re-vaccination. Routine revaccination is performed at 7 years of age.
7-14 years old. As after the first vaccination, the intensity of immunity remains in the first 3 years, and then begins to subside. Therefore, the response to injected tuberculin fades by the age of 10 years. By the age of 13-14, patients have a negative, questionable response to the test.
Table 2. Correlation between the normal size of the papule and the size of the post-vaccination scar in children aged 3-5 years.
| Diameter of post-vaccination scar, mm. | Papules norm, mm |
| up to 2 | no reaction |
| up to 4-6 | 5-6 |
| 6 or more | to 10 |
Disadvantages of the Mantoux test
It is believed that after receiving the BCG vaccine, the Mantoux test loses its diagnostic value, since it can indicate not only a probable infection with mycobacteria, but also sensitization from vaccination. At the same time, most children have controversial, unclear test results.
One of the most important disadvantages of the Mantoux test is the high risk of obtaining false positive and false negative results. The human factor also plays an important role when measuring the reaction to the test.
Photo:
False positive result
Some people test positive for the Mantoux test even if they are not infected with M. tuberculosis. At the same time, induration, as a rule, does not have clear boundaries, its diameter is 5-7 mm and it disappears after 1.5-2 weeks, and not 5-7 days, as expected.
Reasons for these false positive reactions may include:
- Recent introduction of BCG vaccination. To obtain true data, the test should be carried out no earlier than 12 months after vaccination.
- Infection with mycobacteria other than M. tuberculosis.
- Incorrect measurement or interpretation of response.
False negative result
There are situations when the Mantoux test shows a negative result in patients infected with M. tuberculosis. A false negative reaction can be caused by:
- Tuberculosis infection suffered during the last 8-10 weeks.
- Age less than 6 months.
- Recent vaccination against measles and smallpox.
- Incorrect measurement or interpretation of response.
Features of training children with allergies
When a child is allergic, he needs to prepare for a tuberculin test in a special way. If you do not follow a number of rules, this can lead to severe adverse reactions and a false positive test result.
Pediatricians recommend that children with allergies:
- start taking antihistamines a few days before the Mantoux test. Doctors usually prescribe Zyrtec, Claritin, Diazolin. The drug and its dosage are selected depending on the age and weight of the child;
- a week before the procedure, exclude from the diet foods that can cause an allergic reaction. These include: citruses, exotic fruits, chocolate, peaches, red berries. You should also avoid drinking store-bought juices, sweets, and sausages. These products contain dyes, flavors, flavor enhancers, preservatives and stabilizers. Allergies may occur to these substances;
- Do not introduce new foods for the child a few days before the Mantoux test:
- If the baby suffers from an allergy to pollen, then the tuberculin diagnosis may be postponed to a month before or after the flowering period.
In recent years, more and more parents have refused to perform the Mantoux test on their child. They motivate this by the fact that phenol, which is part of the preparation for performing the test, is harmful to the growing organism. Evgeniy Olegovich Komarovsky notes that the product does contain this preservative, but it is in a negligibly small dose.
In addition, phenol is produced in the human body during decay processes that occur during the normal functioning of the body. A well-known pediatrician notes that the consequences of tuberculosis if treatment is not started in a timely manner are much more serious and dangerous than the possible harm from the test.
Alternatives to the Mantoux test
If a false-positive or false-negative Mantoux test result is suspected and in some other cases, it may be necessary to use alternative methods for the early diagnosis of tuberculosis. The most common options are:
- Diaskintest. Like the Mantoux test, it is an intradermal test in which a reaction occurs exclusively to M. tuberculosis antigens. Less common pathogens of tuberculosis and opportunistic mycobacteria do not cause the formation of induration.
- T-SPOT. It is based on the detection in venous blood of specific immune cells (T-lymphocytes) synthesized in response to infection with M. tuberculosis.
- Quantiferon (QuantiFERON-TB Gold). The principle is similar to T-SPOT, but the test evaluates not the number of T-lymphocytes, but the level of interferon gamma.
When can you take a test?
The test can only be done on an absolutely healthy child - this fact is established by the doctor during a preliminary examination of the child as part of the preparatory stage. In some cases, a medical diversion from tuberculin administration may be placed:
- elevated body temperature, regardless of the presence/absence of signs of disease;
- runny nose, even in the initial stage of its development;
- cough of any type - dry, wet, infrequent, paroxysmal;
- dermatological diseases in the acute phase of their course;
- problems in the functioning of the digestive system, regardless of the nature of the origin.
These conditions are conditional contraindications; the Mantoux test is performed after the child has fully recovered. But there are also pathologies in which the administration of tuberculin for diagnostic purposes is strictly contraindicated:
- epilepsy;
- malignant neoplasms;
- bronchial asthma;
- allergy to any irritant;
- child's age up to 1 year;
- confirmed human immunodeficiency virus.
Repeated Mantoux test
Typically, repeated tuberculin administration is not associated with any health risks. For example, if a person does not return for a follow-up examination within 48 to 72 hours to evaluate the results of a tuberculin skin test, it is recommended that a second test be performed as soon as possible. There are no contraindications to repeating the Mantoux test, except in cases where the previous test was associated with a severe allergic reaction.
Photo:
Tuberculin diagnostics, as a rule, are carried out annually, and its results are compared with previous ones. Sometimes this is an infection with M. tuberculosis since the last test.
The criteria by which a child can be referred for consultation to an anti-tuberculosis dispensary after a Mantoux test includes the following:
- a newly detected positive reaction (papule 5 mm or more) to a test that is not related to previous immunization against tuberculosis;
- long-lasting (4 years) reaction with an infiltrate of 12 mm or more;
- an increase in sensitivity to tuberculin in tuberculin-positive children - an increase in infiltrate by 6 mm or more;
- an increase of less than 6 mm, but with the formation of an infiltrate measuring 12 mm or more;
- hyperreaction to tuberculin (infiltrate 17 mm or more);
- vesiculonecrotic reaction and lymphangitis.
It is also worth mentioning the “Booster effect” - a significant increase in the resulting reaction with frequent (more than once every 2 weeks) testing. It is believed that this effect is due to an increase in the sensitivity of T lymphocytes to tuberculin. At the same time, the immunity of individuals infected with M. tuberculosis for a long time stops responding to tuberculin, which may result in a false negative result.
Skin test schedule
After birth, all children, in the absence of contraindications, receive the BCG vaccine. After this, a mantu test is performed 12 months later. Subsequently, the diagnostic procedure is carried out up to 15 or 18 years inclusive, once a year.
If the child has not been vaccinated with BCG, the test is done at 2 months of the baby’s life. It is very important that the tuberculin injection is given before other routine vaccines and serums. If the latter were carried out, the Mantoux reaction is performed after a month.
As a rule, the test schedule is once a year. However, it is more often recommended to test children who are at risk of developing tuberculosis. These include:
- Previously not vaccinated for various reasons.
- Patients with diabetes.
- HIV-affected.
- Persons undergoing hormonal or anticancer therapy.
- Children after irradiation.
- Patients with severe chronic pathologies of the respiratory and digestive systems.
- Babies who have not yet had their BCG vaccine evaluated.
Such children are tested 2 times a year.
Contraindications to the Mantoux test
In some situations, the Mantoux test must be delayed or cannot be performed at all, and therefore is replaced by alternative diagnostic methods. Possible reasons for failure to perform the test include:
- Active infection in the body.
- Exacerbation of chronic pathologies.
- Presence of skin rashes or skin diseases.
- Bronchial asthma, allergic diseases.
- Quarantine in a child's educational institution.
- Receipt of vaccinations within the last month.
Contraindications Mantoux
It is important to meet all requirements and consult with your doctor before performing a skin test. Children must be examined by a pediatrician, since the reaction has some contraindications. These include:
- Dermatological diseases of various nature.
- Chronic inflammatory pathologies in the body in the acute stage.
- Infectious conditions of atomic or bacterial origin
- Epileptic seizures and other mental disorders.
- Any allergic reactions during the period of unstable remission (asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, rhinitis).
If the patient is sick, it is worth waiting for recovery and only 2 months after the clinical signs of infection have disappeared, a test is allowed.
Is it possible to refuse Mantoux?
The Mantoux test is a voluntary diagnostic procedure that can be performed on a child only with parental consent. You can also refuse it by referring to Art. 20 of the Law on the Fundamentals of Protecting Citizens' Health.
A test is often required in schools and kindergartens before children are allowed to attend classes. If, for medical reasons or the personal beliefs of the parents, the child does not undergo tuberculin diagnostics, the educational institution must be provided with a doctor’s certificate stating that the child is healthy.
This is stated in clause 5.7 of the Sanitary and Epidemiological Rules SP 3.1.2.3114-13 “Prevention of Tuberculosis”, approved. Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated October 22, 2013 No. 60.
How to check the Mantoux reaction yourself in a child
If we found out how many hours later Mantoux is checked, is it possible to carry out the inspection yourself? Of course, you can see what size the “button” has become and compare the indicators with the norm on your own, before coming to the doctor. But only a doctor will give an adequate conclusion.
How to test Manta in a child’s home yourself:
- Note the size of the redness, but do not take it into account when measuring
- Pay attention to whether there is a seal inside and its size
- If desired, use a pen to circle the papule itself without touching the redness - this will make it easier to determine the size of the “button”
- Use a clear plastic ruler to measure the size of the seal.
- Take care in advance of high-quality natural or artificial lighting - the papule is tiny, a few millimeters in size
If on the 4th day, in good light, the Mantoux reaction is almost invisible, the test is considered negative, and the child does not have tuberculosis
Mantoux reaction dimensions:
- From 0 to 1 mm – negative reaction
- 2-4 mm – the reaction is considered doubtful, the child is included in the risk group
- A papule larger than 5 mm indicates that the child is highly likely to be sick. The diagnosis is not made based on the reaction to the tuberculin test alone. Conducts additional research
- Over 17 mm – the so-called hyperergic reaction, which is a serious symptom of tuberculosis
In children who have not been vaccinated with BCG or are older than 6 years, there should be no papule, or its size should be no more than 1 mm. Then the sample is considered negative. Previous vaccinations, allergic reactions, infection with parasites, colds and infectious diseases, blood transfusions, incorrectly performed procedures, and violations of the rules for caring for the injection area can lead to unreliable results. Mantoux vaccination can only be given a month after the previous vaccination or previous illness.
The size of the papule depends on the age of the child. The doctor also examines how much the current Mantoux reaction is greater than the previous one. If this difference is 6 mm or more, there is cause for concern.
If your child experiences itching in the injection area after the injection, do not allow him or her to scratch the area. An infection may get into the wound, and the test results will be unreliable. For the first few days, you should not smear Mantu with iodine, brilliant green, antipruritics, or wet it. This can also affect the result. For several days after the tuberculin test, it is advisable not to give the child allergens - chocolate, oranges, etc.
As we said, the Mantoux reaction is checked after 3 days, but in some cases the child must be shown to the doctor before the appointed time.
The child should be seen by a doctor immediately if the following symptoms appear:
- Significant increase in body temperature
- Weakness, dizziness and general poor health
- If severe inflammation or even pus appears in the injection area
Such a reaction may indicate an allergy to tuberculin. However, these phenomena are rare.
If the test shows a positive result, the doctor prescribes a set of other diagnostic procedures. They examine sputum, do chest x-ray, and examine other family members. If necessary, anti-tuberculosis therapy is prescribed.
Sources
- Lewinsohn et al., Official American Thoracic Society/Infectious Diseases Society of America/CDC Clinical Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Adults and Childrenexternal icon, Clinical Infectious Diseases, 2021, Pages e1–e33.
- Kim Y, Dawes-Higgs E, Zagarella S. Foreign body reaction involving a Mantoux test site. Australas J Dermatol. 2005; 46:169–71
- Tuberculin diagnostics // Great Medical Encyclopedia: in 30 volumes / chapter. ed. B.V. Petrovsky. — 3rd ed. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1985. - T. 25: Tenius - Carbon dioxide. — 544 p.
- Borodulina E. A. Issues of tuberculin diagnostics in children in modern conditions // Issues of modern pediatrics. - 2010. - T. 9, No. 1 - P. 70−74.
On what days are Mantoux performed?
Most often, the Mantoux test is performed on certain days - Monday and Tuesday, which allows you to evaluate the results of tuberculin administration before the onset of the weekend (after 72 hours). The fact is that weekends carry the risk of violating the rules for caring for the “button” - a child can visit a cafe with his parents and consume a known allergen, it is possible to go to a pool or water park, or visit guests. And these situations can provoke stress, which will give unreliable results.
How else can you identify tuberculosis?
There are several methods for determining the disease. A method similar to the Mantoux reaction is called diaskintest. The difference is that the Mantoux test involves the use of Tuberculin, and the solution for Diaskintest is prepared from artificially synthesized proteins. Otherwise, both procedures are similar, but in Russia Diaskintest is not carried out in every locality.
Fluorographic examination is carried out annually in schools and in some enterprises (for adults). The disadvantage of this method is that it can only detect bacterial infiltrates in the chest organs, whereas tuberculosis affects other organ systems.
The T-spot method is based on a blood test. But a slowly reproducing bacterium becomes noticeable when a significant period of time has passed from the moment of infection. Treatment in this case will require more time. In addition, a blood test costs about 6,000 rubles and not everyone can afford it every year.
PCR, ELISA, sputum microscopy or urine and blood tests can determine the presence of Koch bacilli after the onset of the disease. When such an analysis is done, bacteria are already present in the blood and organs of a person, causing changes in them. Only Mantoux testing or Diaskintest can detect the presence of bacteria at the infection stage. They may give incorrect results, but in this case doctors conduct additional examinations.
How is the Mantoux reaction checked at 1 year of age, what does it look like?
The Mantoux reaction at 1 year of age is checked using a standard method - using a transparent ruler, the doctor immediately evaluates what the papule looks like. If it is not clearly red, loose, and there are no signs of ulceration or abscess formation, then this is considered normal.
How to measure yourself
You can measure the Mantoux papule yourself using a ruler or tape measure. It is applied perpendicular to the forearm. Things to remember:
- if there is no papule, then only the area of redness is measured;
- If there is a seal, the area around it is not taken into account when measuring.
When measuring redness without compaction and a characteristic “button”, it is worth using a ballpoint pen - it is used to outline the visually defined boundaries of the changed skin in order to obtain accurate results (when pressure is applied to the pen with a ruler, the area will automatically expand).
How long does it take to check?
The Mantoux test is checked strictly 72 hours after the intradermal administration of tuberculin; earlier measurements may give a false positive result, and later measurements may give a false negative result.
What can distort the result
A variety of factors can distort the result:
- increased sensitivity of the child's skin;
- history of allergies;
- problems with balancing the baby’s diet;
- living in regions with unfavorable environmental conditions;
- improper administration of tuberculin, violation of the rules for its storage and transportation.
Allergic rash
What to do in case of deviations
If, when measuring Mantoux, the doctor finds any deviations from the norm, then the child will be referred for additional examination to a phthisiatrician - a specialist who diagnoses and treats tuberculosis specifically. What they can do:
- prescribe other types of tests to detect tuberculosis;
- perform X-ray diagnostics of the lungs, but this method is used extremely rarely for children, as there is a restriction - it is not possible for children under 14 years of age;
- refer the small patient's immediate environment for examination.
Beforehand, parents will be interviewed about proper care of the injection site.