Mantoux is not done often - the standard schedule involves diagnosing tuberculosis once a year. Only clear medical indications are the reason for increasing the number of samples per year to 2-3. If BCG was not given in the maternity hospital according to the calendar, then after 2 months Mantoux is first performed and only after that, if the result is negative, can vaccination be performed.
The Mantoux schedule is observed once a year for both preschool and school-age children. For adults, the test is performed with the same frequency until the age of 16, then the manipulation can be performed once every few years and only at the request of doctors. From the age of 35, the procedure becomes impractical.
How often do preschoolers make Mantoux, how many times a year?
Mantu is given to preschool children once a year. The first vaccination against tuberculosis is given in the maternity hospital on the 3-5th day of the baby’s life (depending on the general condition of the newborn, complications during childbirth and other indicators).
The Mantoux test is performed no earlier than 12-13 months after BCG, and it is rarely perceived by doctors as informative - the antibodies produced as an immune response to the vaccine are still active in the child’s body.
Subsequent tests are carried out every year - in the 2nd, 3rd and so on.
Mantoux reaction: when is it done and how often in schoolchildren
The Mantoux test is performed with a certain frequency and for schoolchildren – once a year. They try to carry out this manipulation en masse, so it is possible to reduce the frequency of tuberculin administration, but in any case, at least 6 months must pass between procedures.
From the age of 14, the Mantoux test may not be performed at the request of the parents; diagnostics can be carried out by performing fluorography.
We recommend reading about the nuances of staging Mantoux per year. From the article you will learn about when Mantoux is prescribed per year, how it is tolerated, what complications there may be, assessing the results of the Mantoux test, and how to measure the papule yourself. And here is more information about the peculiarities of holding Mantoux at 15 years old.
How can you not give Mantoux to a child, how to write a refusal
You can avoid giving Mantoux to a child if you make a written refusal of the test:
- addressed to the head of the children's clinic, kindergarten or school director, depending on where the sample was going to be taken;
- indicate your name and child details;
- confirm refusal to carry out the procedure;
- give reasons for it, that is, refer to clause 3 of article 7 of chapter. III Federal Law “On preventing the spread of tuberculosis in the Russian Federation” No. 77-FZ of June 18, 2001, as well as Article 20 of the Federal Law “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation” No. 323-FZ of November 21, 2011;
- note that the child has no symptoms of infection and there are no people or animals with tuberculosis in his environment;
- report on the normal financial situation of the family and living conditions that meet sanitary standards;
- indicate that the parent has been warned about the consequences of refusal and takes full responsibility for them.
Such a document must be prepared each time a Mantoux test is offered. If the addressee does not accept the refusal, you should send the paper by registered mail, and keep a second copy for yourself.
How often can you make Mantoux?
You can make Mantu often - 2-3 times a year, but only if there are prerequisites for this:
- the papule at the site of tuberculin injection increases from year to year;
- the child is constantly in contact with tuberculosis patients;
- the child is likely to have HIV infection (for example, both or one of the parents are sick).
A schedule of 2 Mantoux tests per year is also established for those children who were not given BCG in the maternity hospital . It is also necessary for some other categories of small patients to monitor the baby’s health status in relation to the presence/absence of the tuberculosis pathogen:
- with diabetes mellitus;
- with frequently recurring colds and viral pathologies of the respiratory tract;
- with diagnosed blood diseases;
- with constant elevated body temperature to subfebrile levels of unknown origin;
- with diagnosed/confirmed systemic pathologies.
The decision to perform the Mantoux test more frequently is made by the pediatrician and phthisiatrician.
Watch this video about what the Mantoux test is and why it is important to carry it out among children:
Is this how Mantoux should be given to a child?
Parents decide whether Mantoux should be performed on a child; no one has the right to force him to perform the procedure. But they should keep in mind that:
- The incidence of tuberculosis in Russia is growing, and it is impossible to predict where a child might be exposed to Koch’s bacillus. It is contained in the saliva of a sick person, that is, it is transmitted to a healthy person when coughing, sneezing, or during a conversation. The infection can enter the respiratory tract in any public place, and special disinfection is not carried out either in stores, or on playgrounds, or in children's institutions. The activity of the pathogen persists for more than a month.
- You can become infected despite having a BCG vaccination. It helps cope with infection, but does not always protect against it 100%. The risk of getting sick is much higher for those who have not been vaccinated against tuberculosis.
- Without Mantoux, it is possible to suspect an infection only by external signs that appear a couple of years after infection. That is, treatment can begin when it develops, and it will be more difficult to get rid of it. There are forms of infection that are resistant to drug effects. And the test lets you know about tuberculosis at its earliest stage, when there is a 100% guarantee of recovery.
- Without Mantoux, a problem will arise when placing a child in kindergarten and school. You will need a certificate from a TB doctor stating that the baby can attend educational institutions, but the doctor has the right not to give it after a simple examination. We will have to do other studies that will confirm the absence of Koch's bacillus. For the same reason (lack of diagnosis of tuberculosis), the child may not be issued a visa to travel to another country.
- The test is not as dangerous to health as medically ignorant parents think. The solution administered to children consists of a phenol preservative and markers of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. But there is no more of the first component than in smoked meats, which are also given to children. Phenol is also produced by the human body itself. But it is impossible to become infected from the intradermal injection of an infection antigen.
Tuberculosis in Russia has long ceased to be a disease of the poor. The patients of tuberculosis dispensaries are completely socially prosperous people who eat normally and do not live in basements. Due to refusals to diagnose, some of them do not immediately find out about the infection and begin treatment as an inpatient. Unaware of their illness, they go to the same places where a child whose parents did not allow him to perform Manta might end up.
Watch this video about whether to make Mantoux or not:
How often is Mantoux given to adults, and up to what age is it done?
Mantoux is not often given to adults, but only according to indications:
- the doctor has good reason to suspect the patient has extrapulmonary tuberculosis;
- the patient has recently undergone radiotherapy, radiography or any other radiation exposure;
- a person undergoes long-term treatment with certain medications (glucocorticosteroids, immunosuppressants).
After the age of 16-18 years, the Mantoux test is done extremely rarely, unless there are clear indications for it. After reaching the age of 35, such manipulation is performed only at the request of doctors.
Most often, Mantoux is given to those adults who are at risk - they are in constant contact with patients, live in a region that is unfavorable specifically for the incidence of tuberculosis, work in correctional colonies, and so on.
Due to age-related changes in the human body, the Mantoux test is considered to be of little information; it is advisable to rely on fluorography data in diagnosis.
When can you take a test?
The test can only be done on an absolutely healthy child - this fact is established by the doctor during a preliminary examination of the child as part of the preparatory stage. In some cases, a medical diversion from tuberculin administration may be placed:
- elevated body temperature, regardless of the presence/absence of signs of disease;
- runny nose, even in the initial stage of its development;
- cough of any type - dry, wet, infrequent, paroxysmal;
- dermatological diseases in the acute phase of their course;
- problems in the functioning of the digestive system, regardless of the nature of the origin.
These conditions are conditional contraindications; the Mantoux test is performed after the child has fully recovered. But there are also pathologies in which the administration of tuberculin for diagnostic purposes is strictly contraindicated:
- epilepsy;
- malignant neoplasms;
- bronchial asthma;
- allergy to any irritant;
- child's age up to 1 year;
- confirmed human immunodeficiency virus.
Is it possible to do Mantoux and BCG at the same time according to the vaccination calendar?
The vaccination schedule does not imply the simultaneous performance of the Mantoux test and BCG. According to the regulations, if a child is not given BCG for some reason in the maternity hospital, then the procedure can only be performed after the Mantoux test has been performed.
This rule applies to cases where the BCG vaccination was not given until the child was two months old.
Vaccination after tuberculin administration should be carried out no earlier than 3 days and no later than 2 weeks. A prerequisite is that the Mantoux result must be unconditionally negative.
Mantoux and instructions for administration
According to the instructions, tuberculin for Mantoux is administered as follows:
- 0.2 ml of solution is drawn into a tuberculin syringe.
- Change the needle to an intradermal one (0.4x13 mm).
- Release an extra 0.1 ml and inject one dose into the skin, drawing the needle in parallel. surfaces.
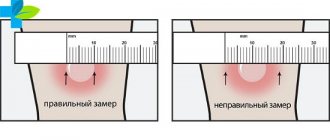
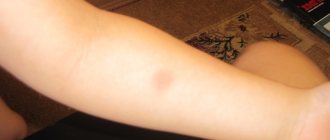
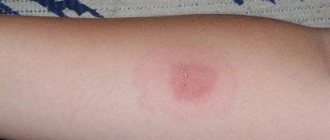
When the skin test is performed correctly, a whitish elevation is formed at the injection site - a papule that looks like a lemon peel. The test is evaluated 48-72 hours after the injection. To do this, only the diameter of the papule is measured with a transparent ruler, the redness zone is not taken into account.
The results may be:
- negative – point reaction up to 1 mm;
- doubtful – 2-4 mm or only redness of any size;
- positive – diameter from 5 mm;
- hyperergic (too strong) - from 17 mm in children and adolescents and from 21 mm in adults, blackening of the skin, blisters, hardening of the lymphatic tract, enlarged lymph nodes.
On what days are Mantoux performed?
Most often, the Mantoux test is performed on certain days - Monday and Tuesday, which allows you to evaluate the results of tuberculin administration before the onset of the weekend (after 72 hours). The fact is that weekends carry the risk of violating the rules for caring for the “button” - a child can visit a cafe with his parents and consume a known allergen, it is possible to go to a pool or water park, or visit guests. And these situations can provoke stress, which will give unreliable results.
How long does it take to check the reaction?
The reaction to the administered tuberculin is checked no earlier than 72 hours from the test. Neither sooner nor later does it make sense to take measurements of papules or redness - the data will be distorted, which will entail the need for revaccination or an extensive examination by a phthisiatrician.
We recommend reading about why Mantoux is placed before BCG. From the article you will learn how many days after BCG is given after Mantoux, when the vaccination cannot be done, and whether Mantoux can be done without BCG. And here is more information about whether it is necessary to make Mantoux.
Mantoux is given to children of preschool and school age with a certain frequency. A clear schedule minimizes the risks of obtaining distorted results and developing side effects. Typically, the test is performed once a year, but at the discretion of the doctor, the frequency can be increased.
Mantoux: composition of the drug and description of tuberculin
The drug for Mantoux is tuberculin (tuberculosis protein), which contains the protein of the tuberculosis bacillus. It has the ability to show whether the body has immune cells (T lymphocytes) that have previously encountered an infection.
It is important to consider that it is an incomplete antigen; by itself it cannot sensitize (allergize) the body. In response to its administration, new antibodies are not formed, so the effect of tuberculin is manifested only when it encounters previously formed protective proteins.
The composition of tuberculin for Mantoux is designed to detect immunity against tuberculosis, but often it does not make it possible to distinguish the reaction to the vaccine from the penetration of the tuberculosis bacillus after contact with the patient.
Therefore, when a papule (whitish elevation) with a diameter of 5 mm or more appears 48-72 hours after the injection of tuberculin into the skin, the previous results and typical symptoms are also taken into account.
In all doubtful cases, additional examination is necessary.
We recommend reading about why the child got sick after Mantoux. From the article you will find out whether a child can get sick with tuberculosis after Mantoux vaccination, what will happen if you vaccinate a sick child. And here is more information about complications in children after the Mantoux test.
Is phenol in the composition dangerous?
Phenol in the composition of tuberculin is considered the most dangerous; toxic properties for the body are mistakenly attributed to it, and because of such fears, parents write refusals to perform Mantoux. In fact:
- phenol is formed as a result of metabolism and is normally found in the body;
- the amount that is excreted in 5 ml of urine is contained in one dose of tuberculin;
- it is added as a preservative to medications used for intramuscular administration, for example, in one ampoule of a popular drug for the treatment of joints (Alflutop) there is 20 times more of it;
- For this component of tuberculin to have a toxic effect, at least one thousand injections of tuberculin are needed at a time.