Tuberculosis is a difficult to treat disease transmitted by airborne droplets. Mass vaccination with Mantoux does not guarantee avoidance of the disease, but allows one to identify the body’s reaction to a tuberculin test.
Mantoux determines the level of immunity to infection with mycobacteria and the ability to produce antibodies.
Official medicine insists that the first Mantoux test was carried out at 12 months, and was repeated every year.
Parents are frightened by such a frequency of vaccinations and want to know: “up to what age is Mantoux given to children?”
Why is the Mantoux test done?
Parents are shocked not by the fact that Mantoux is administered in kindergartens and schools, but by the fact that the tuberculin test is done once a year. In their opinion, annual vaccination can cause irreparable harm to physical and psychological health.
Is it really?
Annual vaccination allows tuberculosis to be detected at an early stage; unfortunately, there are no other diagnostic methods.
For adults, fluorographic examination of the lungs and heart is used. The method is extremely harmful for children, it is rarely carried out, during the procedure it is necessary to ensure that the x-ray affects the chest, but not the heart and other organs.
The Mantoux vaccine is administered subcutaneously and consists of tuberculosis antigens called tuberculin.
The immune system, after the introduction of aggressive mycobacteria, begins to react differently: in one case a violent allergic reaction appears, in another the temperature rises, the baby feels sick.
Analyzing the body’s reaction to vaccination, a decision is made on further BCG vaccination, thanks to which it is possible to develop additional immunity to fight tuberculosis bacteria.
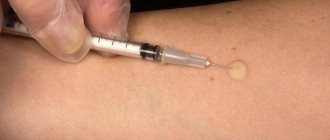
After introducing the solution into the skin, after a few hours or days a papule appears - a small bump of skin, which is used to assess the level of the child’s immune system.
Mantoux vaccination, care features
Mantoux vaccination is not an accurate diagnostic technique, as false-positive and false-negative results are often observed.
Either an additional comprehensive examination for infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis or repeated administration of a tuberculin solution is prescribed.
To eliminate all distorting factors, experts recommend following simple rules:
- exclude contact with water, which may result in infection and the development of a hyperergic reaction, characterized by an increase in the papule to a size of 17 millimeters or more in diameter;
- do not allow the injection site to be rubbed with a washcloth, towel or even clothing;
- adjust the diet: exclude foods that can provoke allergic reactions (other allergens such as plant pollen, household dust, animal hair, and chemical compounds should also be avoided);
- refrain from using bandages, bandages and adhesive plasters on the area where the solution was administered to avoid an inflammatory reaction;
- exclude visiting baths, saunas, and open reservoirs.
But there is another factor that is difficult to prevent: an allergic reaction to the tuberculin composition. Most often, distortion of results due to allergies is observed at a young age and must be taken into account when repeating the Mantoux test.
Main contraindications to the Mantoux test in adults and children False results can be obtained by ignoring existing contraindications to the administration of tuberculin solution. This is about:
- skin diseases accompanied by rashes and the appearance of ulcers on the skin;
- infectious diseases, among which acute respiratory viral infections and other pathologies involving the organs of the respiratory system in inflammatory processes are especially dangerous;
- somatic pathologies in the acute stage;
- epilepsy;
- individual intolerance to the composition used (allergic reactions to the preservative represented by phenol are most often recorded);
- bronchial asthma.
Administration of the Mantoux test is allowed only if at least a month has passed since recovery. Vaccinations can also distort the results. Experts do not recommend performing the Mantoux test on patients whose vaccination has been no more than 3-5 weeks old.
As for such a contraindication as an allergy to the tuberculin composition, the procedures should be discussed with a specialist who takes into account many factors, including the intensity of symptoms. Patients suffering from allergies are advised to take antihistamines for preventive purposes a week before the procedure. Medicines must be taken within 3 days from the date of administration of the solution. This way it is possible not only to minimize unpleasant symptoms, but also to ensure that true results are obtained.
Child's age and Mantoux
Until what age is Mantoux made?
If the child was vaccinated with BCG in the maternity hospital, then the first time is done at 12 months and continues until 15-16 years. In Russia it is done up to 17 years of age.
If the reaction to BCG was absent or normal, then Mantoux can be performed no more than 2 times a year, and then look at the results. If one of your immediate relatives has been diagnosed with tuberculosis, then you need to make mantu at least 2-3 times a year.
Possible complications in children
Understanding what size a Mantoux test should normally be allows you to figure out what the main reason for a positive test is. This can be either an allergic reaction to the introduction of tuberculin, or a signal about an infectious process in the body.
Most often, 2-3 year old children experience post-vaccination allergies. A year and a half after BCG, 60% of children have a positive tuberculin test result. This is due to the activity of children's immunity. If no papules have formed at the test site, the result is considered negative, but requires repeated BCG vaccination.
Possible complications include:
- increased body temperature;
- lethargy, apathy, lack of appetite;
- disturbances in the functioning of the stomach;
- allergies, skin rashes;
- A cough may occur 5-7 days after the injection.
Mantoux should not be combined with other vaccines. The body's reaction to mixing drugs may not be predictable.
Interpretation of results
Until what age is Mantoux performed and then the results interpreted?
The Mantoux reaction is expressed in the appearance of a papule at the injection site, which is a manifestation of an allergy to tuberculin. The appearance of a papule indicates a reaction of the immune system to antigens of tuberculin mycobacteria.
After vaccination, the nurse should take measurements of the papule a few days later, which should not exceed 12 mm. The norm varies from 4 to 12 mm. If the size of the papule is smaller or larger, then it can be argued that the child has abnormalities and possibly pathology.
A papule less than 4 mm indicates that the child is susceptible to the influence of mycobacteria, and therefore tuberculosis. The absence of a papule at all indicates that the child has developed a severe immune deficiency syndrome. If, after administering a tuberculin test, the body does not react in any way, then the child is in great danger.
At the slightest contact with a sick person or inhalation of tuberculosis pathogens, the child may become ill, because has absolutely no protective autoimmune barriers.
If the papule is more than 14 mm, this is also an alarming sign. Such a reaction indicates that the child has an increased functioning of the immune system.
This pathology can lead to a number of serious diseases, namely:
- if you do not register your child with a doctor, then at the slightest infection of the body with mycobacteria, a severe allergic reaction will occur, accompanied by Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock;
- a large papule may also indicate that tuberculosis has already appeared.
In the latter case, doctors must determine the true cause of the enlarged papule: disturbances in the functioning of the immune system or the presence of tuberculosis.
Mantoux timing for missing vaccinations
If the timing of BCG was not met, then vaccination can be done 4-6 months after birth. Before the manipulation, a Mantoux reaction is performed. The condition for further vaccination is a negative result. The result is checked after 5 days. The extended waiting period is also explained by the incomplete formation of immunity and the high risk of a false negative reaction.
If the baby has already had contact with a person infected with tuberculosis before the BCG vaccination, he is prescribed preventive treatment in a reduced dosage. The course of preventive therapy is completed by the Mantoux test. If the reaction is positive, therapy continues. If negative, BCG is performed after 7 days and isolated from the environment for 5-6 days.
Child's health status and Mantoux
Before vaccination, the child must be examined by a physician or nurse. This is done in order to avoid deviations in the result and deterioration of health.
Regardless of the age at which the test is performed, the child should not have the following signs:
- allergic reactions and skin rashes;
- fever and cough;
- weakness or dizziness;
- surgical or other interventions.
If a child exhibits at least one alarming sign, the Mantoux procedure is postponed until the baby has fully recovered. When manta is given, they never vaccinate in the same arm; they alternate each year. For example, for even years - to the left, and for odd years - to the right.
After the procedure, do not wet, scratch, pick or lubricate it with anything. All this can be done only after 1 day. After several days (4-5), signs of redness and papules at the injection site disappear.
Reasons for increasing Mantoux
Three whole days pass between the injection of tuberculin under the child’s skin and the measurement of the reaction, and during this time certain rules must be followed. Without them, an increase in Mantoux can be provoked by various external and internal factors.
- Allergy: if it is present, any contact of the child with the allergen must be excluded. If it is unknown at the time of Mantoux vaccination, parents should protect the baby during these three days from treatment with any medications, consumption of sweets and red foods, as well as from contact with animals.
- Low-quality vaccine: Mantoux is given free of charge, so low-quality tuberculin can be delivered to any medical and child care facility, which will give a positive result in any situation. The error can be identified by contacting another institution (preferably a paid one) for re-vaccination after 3 days after the Mantoux measurement, which did not satisfy the parents. This will help you draw the right conclusions and not make a mistake with the diagnosis.
- Incorrect measurement: usually the Mantoux vaccination is done by a qualified doctor, but during measurements the human factor can play a cruel joke. The specialist checking the reaction could be inexperienced, could simply not take into account some individual characteristics of a small organism, could use the wrong ruler, and could, in the end, simply make a mistake due to fatigue.
- Individual characteristics: a positive Mantoux reaction can be observed due to a hereditary factor or the abundance of large amounts of protein foods in the child’s diet. So during three test days you need to reduce your baby’s consumption of eggs, meat, and dairy products.
To reduce all these factors to a minimum, there are certain rules for caring for the injection site after Mantoux vaccination. This allows you to make measurements on the third day more accurate and trouble-free. Unfortunately, doctors do not always give such information to parents, and the latter, in turn, are of little interest in this.
Indications for the test
Mantu is made for the timely identification of a potentially dangerous and unprotected child in a group. Not protected primarily by your own immune system. Sometimes, a test is performed to confirm tuberculosis disease.
Indications for performing Mantoux will be:
- a prolonged cough accompanied by chest pain and a temperature above 38 degrees. Sometimes, such a cough lasts for years and is not treated with medication;
- diabetes mellitus of any type gradually leads to the development of immunodeficiency, which means the body’s resistance to any aggressive effects of mycobacteria decreases;
- long-term hormonal therapy for oncology or other diseases of the thyroid gland;
- children whose parents refused their BCG vaccination in the maternity hospital or subsequent periods;
- presence of relatives with tuberculosis.
Also, it is carried out for children whose reaction to Mantoux last year was pronounced, but was normal (10-12 mm). Such children are checked the next year, if the pronounced reaction has disappeared, then everything is fine, if not, they are sent for additional examination to a tuberculosis dispensary.
Diaskintest: analogue of Mantoux
Mantoux or its analog Diaskintest is given to children until what age?
Diaskintest is done over the skin, without a syringe or needle. Diaskintest is considered a more gentle procedure than the standard Mantoux vaccination, so it can be done, if necessary, several times a year and up to 18 years of age.
All schools and kindergartens are gradually switching to this procedure due to the low cost of materials, the lack of stress in children and more accurate results.
In the next 10 years, official medicine should switch to a tuberculin skin test, without measuring papules and other allergic reactions.