Photo: simptomyinfo.ru
Victoria Mamaeva
Chief editor of Filzor. Specialist in the field of Pharmacy
Mikhail Lebedev
Leading expert of the Research Institute of Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor
Doctors say that every year on the planet the number of rabies victims among humans alone is more than 50 thousand. Almost half of the cases are children and adolescents. The disease is fatal, and the only way to escape from it is to receive an anti-rabies vaccine .
Rabies is a viral disease that affects the nervous system. Without adequate treatment, the probability of death is estimated at 100%. A person usually becomes infected through close contact with an infected animal. Immediately after the pathogen enters the body, an incubation period begins, lasting from a week to a year. Most often, the duration of the incubation stage is from a month to three, with the first signs usually visible by the eighth week of infection.
The suspected diagnosis is confirmed based on laboratory tests. True, they will find out how to vaccinate a person against rabies before the results are ready: they cannot delay.
Stereotypes say that you can become infected through contact with dogs, and sometimes cats and foxes. In fact, the list is much wider. Any mammal is a potential source of risk. The disease can be transmitted by livestock - cows, horses. Infection occurs through contact with the saliva of an infected individual. The virus is transmitted even if the incubation period is still ongoing, so rabies vaccinations after a bite are necessary even if the animal seemed completely healthy.
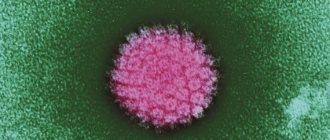
Rabies virus, rabavirus (Rabies lyssavirus). Photo: dotphoto.com
It has been established that the disease occurs in more than 160 countries. The virus exists on all continents except Antarctica. Preventive measures against it were first actively carried out in Australia and Europe, Japan and the UK. Some countries are considered particularly safe. These include Finland, Slovakia and Belgium. But cases of infection are consistently observed in our country, in Ukraine, in Belarus. The situation is considered unfavorable in both Croatia and Lithuania, where people also sometimes find themselves in quarantine after being vaccinated against rabies, if the doctor sees the need for it.
This is interesting: where are the most dangerous houses? In our country, both wild and domestic animals often suffer from rabies. In 2016 alone, more than 2,000 sick individuals were observed. The most dangerous regions were the capital and the areas around: Ivanovo, Kaluga, Smolensk, Voronezh, Belgorod. The disease is most often recorded in foxes, followed by dogs, and cats close the top three.
Prevention of rabies
To minimize risks, you need to follow simple rules of behavior. All pets must receive vaccinations, information about which is recorded in a personal card. When purchasing a new animal, you must obtain a certificate from a veterinarian. Any animal taken from the street is a potential source of danger, so it must be immediately shown to a specialist. Wild animals must be avoided both in the city and in nature. If potential contact occurs, you should immediately, without delay, consult a doctor in order to receive a course of rabies vaccinations.
Polio vaccine 10
548
Animal rabies can be atypical, violent or silent. In humans, the disease after the incubation stage manifests itself with fever. The area of damage is itchy, and the condition is generally depressed. The patient becomes fearful, finds it difficult to breathe, and develops a fear of water. Then it gradually paralyzes the muscles: first of the face, then of the arms, legs and the whole body.
The state-level health insurance program requires citizens of our country to receive a certain set of vaccinations. This complex does not provide an injection that protects against rabies, but anyone can contact doctors privately to receive the procedure. Administration of the vaccine is indicated immediately after a bite from an infected and potentially dangerous individual. This event is considered therapeutic and preventive.
The doctor referring you for the procedure will tell you which rabies vaccination is needed (usually KOKAV ). Preventive vaccination is indicated for those who could potentially come into contact with an infected individual. Knowing how long the rabies vaccination lasts is necessary, for example, for foresters and veterinarians, shelter workers and hunters. Not everyone knows whether a person is contagious after a rabies vaccination, and therefore avoids preventive injections. In fact, this is a myth: the vaccinated person is completely safe.
COCAV vaccine against rabies. Photo: simptomyinfo.ru
Rabies vaccination schedule
A therapeutic and prophylactic rabies vaccination is required for a person who has been bitten by a potentially dangerous animal. If you are injured, you should immediately go to the hospital. You should also visit a doctor if there are no injuries, but the animal’s saliva gets on the skin. The doctor will immediately direct you to the procedure for administering the first portion of the medicine. The next injection is given on the third day, then after a week and after two; a person receives another injection on the 30th day, and the last one on the 50th.
Vaccination DTP 3
518
Sometimes it is possible to keep an eye on a potentially dangerous individual. If she has no symptoms of the disease within ten days, it is enough to give three injections (in accordance with the beginning of the standard rabies vaccination regimen). If you cannot monitor the animal, you will have to go through the entire cycle.
The disease will not develop if the saliva of an infected individual comes into contact with a person’s skin, but a rabies vaccination was given after the bite (for a child or an adult, it doesn’t matter) within two weeks after that. If there has been a bite, doctors will recommend administration of a vaccine and rabies immunoglobulin. To continue the course, only a vaccine is enough. Immunoglobulin is effective if it is used in the first three days after injury. There are no contraindications for administering the drug, since such a vaccine is the only way to save a person.
When not to vaccinate
The reasons why it is necessary to get the vaccine have been sorted out, and in which case you can completely refrain from vaccination, even if there was a bite.
- You can take time with the injection if there is no full penetration of the skin (for example, the animal bit a limb through dense tissue and simply did not reach the skin);
- contact of the saliva of an infected animal with intact human skin;
- the scratch was caused by a bird (birds are not carriers of rabies);
- the bite or scratch was caused by a pet that had previously been vaccinated according to all the rules;
- after eating the meat of an infected animal (the rabies virus cannot withstand high temperatures and dies within 2 minutes when heated).
The virus in its external nature is weak and dies almost immediately, in the air or in the soil.
Necessary actions after an animal bite
There is always some time between receiving a potentially dangerous injury and seeing a doctor - at a minimum, you need to get to the hospital. There should be no doubt about how long it takes to get a rabies vaccination: you should see a doctor immediately, but if you become a victim of an animal, you must first drive it away. Whenever possible, turn to others for help.
Bites can be superficial or deep. In the first case, the wound should be washed with running water using antibacterial soap, then dried and secured with a bandage. In case of a deep bite, you first need to stop the bleeding, then call an ambulance. Already in the hospital, the doctor will explain what kind of rabies vaccination is given to a person, what scheme is used to administer it, and what restrictions are associated with it.
Symptoms and vectors of rabies. Photo: yandex.ru
Where do you get the rabies vaccination?
The rabies vaccine triggers the production of antibodies from the virus. These are produced in the human body approximately two weeks after receiving the first injection (this explains the specific schedule of rabies vaccinations). The maximum concentration is achieved after a month or a little more. The standard dosage is 1 ml of medication per procedure. The drug is injected into the muscle. For patients under five years of age, it is recommended to inject the medicine into the front and side of the thigh, for older people - into the deltoid brachialis muscle. It is strictly prohibited to administer the drug into the gluteal region! It is also not worth giving injections yourself. The workers in the treatment room know best how rabies vaccinations are done - they should be trusted with this.
Tetanus shot 9
1.8K
This is interesting: an alternative insertion technique! At the discretion of the doctor, half the dose of the rabies vaccine is administered to the person around the injury area, irrigating it, and the other half - into the thigh muscles. Rabies immunoglobulin can be injected into the gluteal area.
Vaccines used
There are several types of rabies vaccines, both domestic and imported. The imported version will be more expensive than the domestic one.
The vaccine contains an inactive rabies virus (it is not live), which is not dangerous to humans, but it helps the patient's body produce its own antibodies. Thus, the virus is not killed by the vaccine itself, but directly by the antibodies produced by the body.
In addition to the inactive virus, there is also a so-called rabies vaccine, which, as a rule, is injected directly into the bite site (a distinction is made between a vaccine created on the basis of human and horse immunoglobulin; in the first case, its dosage will be less).
The most common vaccines:
- Nobivak.
- Rabies.
- Rabikan.
- Rabik.
- KOKAV.
- Rabipur.
The doctor will recommend which vaccine to inject based on the availability of a particular drug in the medical institution. You cannot administer the injection yourself, since only the doctor selects the dosage based on several parameters.
Prevention by vaccination
As a preventive measure, the rabies vaccine is given in three doses: when visiting the clinic, on the third day and on the 30th day. If it is necessary to prolong immune protection, first the vaccination is repeated after a year, then the procedure is done every three years. This is how long the drug works. At each revaccination, the doctor will remind you how many rabies vaccinations are given for prevention, and indicate the exact days on which you will need to come for a repeat appointment.
When should you not be vaccinated against rabies for preventive purposes?
If the vaccine is prescribed as a therapeutic and preventive measure, there can be no exceptions. There is no doubt whether pregnant women are vaccinated against rabies: since there is no alternative, in case of suspected infection, vaccination is mandatory. But for preventive use there are certain restrictions. The drug should not be administered:
- pregnant women;
- those who have previously had a systemic allergy to rabies vaccine;
- It is forbidden to give injections if there is an acute illness or an aggravated chronic one. In this case, wait a month or more, after which injections are prescribed.
How to avoid the negative consequences of vaccination?
To prevent rabies vaccination from causing harm to the body, doctors recommend adhering to a number of rules:
- It is strictly prohibited to consume any alcohol-containing drinks. Alcohol puts a strain on the liver and the body as a whole, which makes it impossible to form an adequate immune response. The ban should last at least two months, or better yet, up to six months;
- During the immunization period and for several days after it, it is better to refrain from visiting crowded places where it is easy to catch any infection. This is especially true in the autumn-winter period;
- It is better to refrain from swimming in open water and public places (sauna, swimming pool, etc.). It is not prohibited to wet the graft at home, in your own bath or shower;
- overheating or hypothermia of the body after administration of the vaccine should be excluded, therefore it is not recommended to walk for a long time under the scorching sun or in severe frost;
- It is worth limiting heavy physical overload, including sports;
- It is important to combat stress, which also seriously weakens the body.
You can avoid being vaccinated against rabies only in the only case - when the bite or injury is caused by a domestic animal that is vaccinated and undergoes annual revaccination.
Expert opinion on the need for rabies vaccination
Answered by Mikhail Yuryevich Lebedev, leading expert of the Center for Molecular Diagnostics CMD of the Central Research Institute of Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor.
One of the most dangerous infections for humans is rabies (rabies, hydrophobia). This acute infectious disease affects not only humans, but all warm-blooded animals. The causative agent of the disease is the rabies virus . The virus affects the central nervous system, resulting in irreversible pathological changes in the nerve cells of the cortex and other parts of the brain (polyencephalitis). If an infected person develops clinical manifestations of damage to the central nervous system, then death is inevitable. To date, no specific treatment for rabies has been developed, and symptomatic and pathogenetic treatment is ineffective.
Around the world, 30-70 thousand people die from rabies every year, which is approximately 150 deaths per day! These are the data of the World Health Organization (WHO).
Rabies is recorded in more than 150 countries around the world and on all continents (with the exception of Antarctica). The vast majority of cases of the disease occur in developing countries.
Flu shot 2
265
Rospotrebnadzor data: in 2021, 2 cases of human rabies were recorded in our country, in January - July 2021 - 1 case. WHO classifies Russia as a country with a medium risk of human rabies infection.
All mammals can carry the rabies virus. But most often these are foxes, dogs, wolves, raccoons, cats, rats, mice, hedgehogs. Farm animals - cows, horses, goats, etc. - are less often infected.
Important! In 2021, Rosselkhoznadzor identified 2,273 outbreaks of rabies in our country, 2,566 animals fell ill and died. In the first quarter of 2021, the largest number of disadvantaged areas (27) were registered in the Moscow region.
How do animals and humans become infected with rabies? This requires direct contact with the saliva of an infected animal (not only one that is already sick, but also one that is in the incubation period). For the virus to penetrate the body, the integrity of the skin must be broken, which most often happens with a bite. But there is a possibility of infection if saliva gets on damaged areas of the skin (abrasions, scratches, wounds, etc.). This mechanism of infection is called “salivation.”
Important! Every year in Russia, about 400,000 people visit medical institutions due to bites from wild, stray and domestic animals. In Moscow, the number of people bitten by animals in 8 months of 2021 was 17,565 people (in 2021 - 21,921), of which 43 contacts were with animals infected with rabies (in 2021 - 100).
What to do after dangerous contact? Immediately after the incident, you need to wash the wound with any antiseptic, or, in extreme cases, with soap and water, apply a bandage and urgently seek help from the nearest medical facility! There should be no delay, because we are talking about mortal danger!
Immunoprophylaxis (administration of rabies vaccine) is the only possible way to treat rabies (and, accordingly, save lives). Moreover, the vaccine must be administered during the incubation period of the disease (that is, before symptoms develop).
In Russia, the post-exposure rabies vaccination scheme looks like this: the first vaccination is on the day of treatment, then on the 3rd day, 7th day, 14th day, 30th day and 90th day.
Are there any contraindications to rabies vaccination? Is it possible to use the vaccine in pregnant and lactating women?
Everything is clear - THERE ARE NO CONTRAINDICATIONS TO POST-CONTACT VACCINATION (and cannot be), because the development of the disease means 100% death. Therefore, the vaccine is administered to absolutely everyone, including pregnant and lactating women.
Diphtheria vaccination 9
378
Of course, it is highly advisable to provide specialists with the animal itself with which there was potentially dangerous contact (or information about its vaccination against rabies). But this is only possible if the animal is domestic, “familiar.” But if the bitten animal is wild or stray, there is no such option.
To protect yourself and your family, you must follow the following rules:
- vaccinate your pets against rabies (especially those traveling out of town with you);
- purchase animals only with a veterinary passport;
- do not come into any contact with wild and stray animals (do not feed by hand, do not pet). And under no circumstances should children be allowed to do this!
But if dangerous contact does occur, seek medical help URGENTLY!
REMEMBER: EMERGENCY VACCINATION IS CRUCIAL AND CAN SAVE A LIFE!
Etiology and routes of transmission of rabies
The virus is extremely dangerous for birds and animals due to its ability to cause various pathologies in them. It exists thanks to circulation in nature, spreading with the help of living warm-blooded organisms. People most often become infected from dogs (both domestic and stray), and they from wild animals. People become infected directly from representatives of wild fauna in no more than 28% of cases. Cats become a source of infection in 10% of cases.
Infection occurs through contact with the saliva of a sick animal, most often through a bite. Injuries to the head and arms are especially dangerous in this regard. The more bites, the higher the risk of infection. The peak incidence occurs in spring and summer. Theoretically, a person is a source of danger during the development of disease symptoms, especially during the period when he ceases to control his own behavior.
Foxes, the population of which is large in the country, are considered to be the carrier of the disease. So, for every 10 square kilometers there are up to 10 individuals. In order to prevent the spread of the disease, there should be no more than one animal in the same area.
In addition, the population of wolves and raccoon dogs is growing; they spread the infection no less actively than foxes. Hedgehogs, moose, lynxes, and bears can also get sick, although this is not typical for them. Cases of attacks on people by rabid crows have also been recorded.
This is why rabies vaccination for pets is so important. There are frequent cases of unvaccinated dogs being taken out into the wild, where they attack infected hedgehogs. After some time, their behavior becomes inadequate, they go into dark places and die.
In the past, the vaccine was administered to a person only after 10 days. At this time, the animal that attacked him was observed. If it did not die during this time, then the victim was not vaccinated. However, if a person does not see a doctor within 4 days of the first symptoms appearing, the chance of survival is 50%. If a person began taking the vaccination course only on the 20th day, the probability of his death is 100%.
And if after a bite you promptly seek medical help and undergo a course of vaccination, then any consequences can be avoided in at least 96-98% of cases.
Incubation period for rabies in humans
The incubation period of this disease can be either short (9 days) or long – up to 40 days. The disease will develop faster if the virus enters the body through a bite on the face and neck. Bites on the hands are also extremely dangerous - in this case the incubation period can be reduced to 5 days. So the virus, moving along the nerve pathways, enters the spinal cord and brain, causing cell death. If infection occurs through the legs, the incubation period increases significantly. There have been cases where the virus did not manifest itself for a year or more. It is worth noting that the disease develops faster in children than in adults.
Structure of patients with clinical manifestations of rabies
Since a modern vaccine can rid a patient of the disease, patients arriving with obvious clinical signs of rabies are a very rare occurrence. The onset of the disease may be due to the following factors:
- Prolonged lack of medical care;
- Violation of the vaccination regime;
- Independent early completion of vaccination.
In most cases, the cause of the disease is people’s lack of necessary knowledge, as well as a careless attitude towards their own health. A person often does not attach due importance to the fact that he was bitten. He treats this wound as an ordinary scratch, which in fact poses a direct threat to life. While you need to seek help not only after a bite, but even after saliva gets on the skin, the integrity of which is compromised.
In the body, after infection, the following processes occur: the virus enters the spinal cord and brain, destroying its cells. The death of the nervous system causes a number of symptoms and leads to death.
Diagnosis of rabies in humans
In order to make a diagnosis, the doctor will need to find out whether an animal has bitten or gotten its saliva on a person. The clinical picture is the same for all patients. The level of lymphocytes in the blood increases, eosinophils are completely absent. A fingerprint smear taken from the surface of the cornea indicates the presence of an antigen produced in response to an infection that has entered the body.
Symptoms of rabies in humans
The virus can exist in the body asymptomatically for 30 to 90 days. Less often, the incubation period is reduced to 10 days, and even less often it increases to a year. The duration primarily depends on the location of the injury. The longer the virus has to get to the brain, the longer a person will remain outwardly healthy. In medicine, cases have been described in which the disease manifested itself even 4 years after the bite of an infected cow.
The disease goes through three stages of development, each of which manifests itself with different symptoms.
The first signs of rabies in humans
The initial stage, which lasts from 24 hours to 3 days, is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The wound is the first to worry the patient. Even if the bite has already healed by this point in time, the person begins to feel it. The damaged area hurts, the sensations are of a pulling nature, localized in the center of the injury. The skin becomes more sensitive and itchy. The scar becomes inflamed and swollen.
- Body temperature does not exceed 37.3 degrees , but does not fall below 37 (low-grade fever).
- Headaches occur and weakness appears. The patient may feel nauseous and vomit.
- When a bite was applied to the face, a person often develops hallucinations : olfactory and visual. The victim begins to be haunted by odors that are actually absent, and non-existent images appear.
- Mental abnormalities appear: the patient becomes depressed and is haunted by causeless fear. Sometimes increased anxiety is replaced by excessive irritability. A person experiences apathy towards everything and becomes withdrawn.
- Appetite disappears. Night rest is disrupted, normal dreams are replaced by nightmares.
Symptoms of the second stage of rabies in humans
The next stage lasts from 2 to 3 days, it is called the arousal stage. It is characterized by:
- Due to damage to the nervous system, there is an increase in the excitability of the neuro-reflex system. The tone of the autonomic nervous system predominates.
- A clear symptom of disease progression is the development of hydrophobia. When an infected person tries to take a sip of liquid, a spasm occurs. The respiratory and swallowing muscles are affected, until vomiting occurs. As the disease progresses, a similar spasm will occur in response to the sound of flowing water and even the sight of it.
- The patient's breathing becomes rare and convulsive.
- Facial spasms appear. Any external irritants cause an acute reaction of the nervous system.
- Convulsions become a response even to stimuli that are insignificant for a healthy person: bright light, wind or draft, sharp sound. This causes fear in the patient.
- The pupils dilate, the eyeballs protrude (exophthalmos), and the gaze is fixed at one point. The pulse quickens, profuse sweat appears, saliva flows continuously, its volume increases significantly.
- Mental disorders progress, the patient is overly excited and becomes violent. He poses a threat to himself and others, behaves aggressively and even violently. Infected people rush at others, fight and bite, tear things and hair, and hit walls. In fact, during such an attack, a person suffers terribly from haunting eerie images and sounds. During the peak of the attack, a person may stop breathing and also stop beating.
- When the attack passes, people behave adequately, non-aggressively, their speech is logical and correct.
Symptoms of the third stage
The final phase of the disease is the stage of paralysis. It lasts no more than a day and is characterized by loss of motor function. The patient's sensitivity is impaired, convulsions and hallucinations no longer haunt him. Various muscle groups and organs are paralyzed. Outwardly, the person appears calm. In this case, a significant temperature jump occurs. It rises to 42 degrees, the heartbeat increases, and blood pressure drops. A person dies due to paralysis of the heart muscle or respiratory center.
From the onset of symptoms of the disease until the patient dies, it takes from 3 days to a week. Sometimes rabies is characterized by rapid progression and an erased clinical picture. In this case, the victim may die during the first day, after the first meager symptoms appear.
Treatment of rabies in humans
Once symptoms first appear, the disease becomes incurable. All actions of doctors will be reduced only to making a person feel better. They try to isolate him from external stimuli, administer opioid analgesics, and perform maintenance therapy. Artificial ventilation helps prolong life, however, death is inevitable.
Post-exposure vaccine
Providing first aid to the victim is the responsibility of the surgeon working in the anti-rabies care center. The patient receives an injection on the same day he seeks help.
If previously up to 30 vaccinations were administered in the abdominal area, under the skin, then since 1993, such a scheme for preventing the disease was abandoned. A modern vaccine (COCAV) is currently in use. It is purified and makes it possible to significantly shorten the treatment course, as well as reduce the dosage administered once.
It is important to know: the vaccine is not injected into the buttock! For children it is placed in the thigh (outer surface), and for adults and adolescents in the deltoid muscle. Standard dosage is 1 ml. The effect of the administered vaccine reaches 98%, however, it is important to give the first injection no later than two weeks after receiving an injury or bite.
When a patient first contacts him, even months after dangerous contact, he will be prescribed a course of treatment.
After the vaccination has been done, the first antibodies to the virus will appear after 14 days, their maximum concentration will occur in a month. When there is a risk of shortening the incubation period, the patient is administered rabies immunoglobulin.
When the course is completed, the person will develop immunity, which will begin to work 14 days after the last injection.
The formed protection will operate throughout the year.
Despite existing vaccines and immune globulin, people continue to die from the virus. This occurs as a result of their low awareness of the dangers of the disease and due to their failure to consult a doctor. Some victims refuse medical care and in 75% of cases die due to infection. Sometimes the blame for the death of such patients lies with doctors who incorrectly assessed the degree of threat to human health (up to 12.5%). Some patients (up to 12.5%) die due to interruption of the course or violation of the vaccination regimen.
It is strictly prohibited for patients undergoing treatment, as well as 6 months after its completion: to consume any alcoholic beverages, excessive physical fatigue, being in a bathhouse or sauna, or hypothermia. This is due to a decrease in antibody production and deterioration of immunity. If the patient receives concurrent treatment with immunosuppressants or corticosteroids, monitoring of antibodies to the virus is necessary. If they are produced in insufficient quantities, then additional therapy is necessary.
Typically, most people do not experience any side effects after receiving the vaccine. It is most often well tolerated. Minor allergic manifestations are observed in no more than 0.03% of cases.
There are no contraindications for administering the rabies vaccine, due to the mortal threat of the sick person.
Injections are administered to women carrying a child and to patients with acute pathologies.
In what cases is it not necessary to get vaccinated?
- If an animal gets in contact with saliva or touches the intact skin;
- If an animal bites a person through thick fabric and it is not damaged;
- When an injury occurred from the beak or claw of a bird;
- When bitten by animals living at home, if they have been vaccinated against the virus and have not shown signs of illness for a year.
The injured animal must be monitored; if it shows signs of illness, vaccination should begin immediately.
If infection is likely to occur. The vaccine must be given if you have received an injury (bite, scratch, saliva on damaged skin) from a wild animal.
Anti-rabies immunoglobulin
Therapy using immunoglobulin is necessary for implementation within 24 hours after injury. This period should not exceed 3 days after possible infection and before the 3rd vaccine was administered. The dose is 20 IU/kg immunoglobulin.
One half of the calculated dose is injected around the damaged tissue (the wound can be irrigated). The rest is injected into the muscle (into the thigh - into its upper third or into the buttock). The vaccine and immunoglobulin are not administered with the same syringe!
They can be combined if there are the following indications:
- The bite is deep, bleeding is observed;
- There are multiple bites;
- Injuries occurred in hazardous areas.
You should remember the deadly danger of the virus. It is necessary to consult a doctor immediately after an injury or after situations involving a risk of infection arise.
Prevention of rabies
It is important to know that even with a minor bite, a person needs to seek medical help. The further course of therapy will be determined by the doctor. It provides emergency treatment by administering either an active or passive rabies immunoglobulin vaccine.
Immediately after a bite, it is important to wash the injured area with running water. In addition, the preventive vaccine can be administered to persons with occupational risks, for example, trainers, hunters, and veterinarians.
The vaccine is administered immediately after the affected person goes to the hospital. It is performed on the first day, then on days 3 and 7, then on days 14 and 28. The World Health Organization recommends vaccination also 3 months after the last injection was administered, it is injected into the muscle. This is a sufficient scheme to generate an immune response.
The vaccine is administered if:
- There was a bite by wild rodents;
- Saliva has come into contact with the skin, or there has been a bite or scratch from an animal that definitely carries the virus or even suspects its presence;
- A bite occurs through a thin layer of tissue, after injury by any object contaminated with the saliva of an infected animal.
The vaccine is not administered if:
- Injury by a bird (not a predator);
- A bite occurred without damaging the skin (through dense tissue);
- When ingesting milk or meat of an infected animal that has undergone heat treatment;
- There was a bite from a domestic rodent;
- A rodent bite occurred in an area where the disease had not been recorded for 2 years;
- There was contact with an infected person without damaging the skin or getting his saliva on the mucous membranes;
- Contact occurred, but the animal did not die 10 days after contact (the measure is not relevant).
The vaccine has minor side effects compared to the possible illness. In some cases, allergic reactions occur; the injection site may become swollen, hard, or painful. Sometimes there is an increase in body temperature (no more than 38 degrees), chills and headaches appear. Lymph nodes may become enlarged.
Which doctor should I contact?
Primary anti-rabies care is provided by a surgeon (traumatologist) and an anti-rabies care center.
The rabies vaccine is administered on the first day of treatment at the emergency room. When preparing the material, information from the site https://www.ayzdorov.ru/lechenie_beshenstvo_chto.php was used
Side effects of vaccination
The introduction of a vaccine may cause complications. The most common reactions to rabies vaccination are local side effects:
- itching;
- tissue swelling at the injection site;
- enlarged lymph nodes near the injection site.
Also, vaccination can lead to fever and general weakness. Moderate pain and fever after rabies vaccination are considered a normal reaction. Others have headaches. A general state of malaise is possible. There is a risk of neurological symptoms and serum sickness. There are known cases of anaphylactic shock. Such complications after vaccination against rabies in humans require urgent assistance. In general, the incidence of side effects is estimated at 0.02-0.03%, mainly mild skin reactions and bumps after rabies vaccination.
Side effects
As a result of using the Kokav vaccine, the following may develop:
- Local reactions - itching, hyperemia, pain at the injection site, slight swelling, enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- General reactions - weakness, headache, fever, malaise, systemic allergic reactions (Quincke's edema, generalized rash).
For such side effects, hyposensitizing drugs and symptomatic therapy are prescribed. If neurological symptoms appear, urgent hospitalization of the patient is required.
The following complications may occur after using AIH from horse blood serum:
- Local allergic reaction, manifested 1-2 days after injection;
- Serum sickness, which develops most often on days 6-8;
- Anaphylactic shock.
If anaphylactic reactions occur, emergency medical care and further observation in a specialized institution are necessary.
In case of an anaphylactoid reaction, administration of a solution of epinephrine, ephedrine, and norepinephrine is required. The method of administration, frequency and dose of prescribed drugs depend on blood pressure and the severity of shock.
When signs of serum sickness are observed, injections of antihistamines (H1 histamine receptor blockers), calcium supplements, and glucocorticosteroids are prescribed.
What to do if the vaccination schedule is broken
A variety of reasons can provoke a violation of the drug administration schedule. Sometimes the time intervals are confused or medications are administered in the wrong sequence. Other specific points are also possible. In any such situation, the doctor’s task is to assess the immune status in order to develop a continuation of the course individually, taking into account the time frame for the rabies vaccination should have been received.
Chickenpox vaccination 1
54
If the next portion of the medicine was not administered or it was administered at the wrong time, this may cause the ineffectiveness of the course as a whole. The tests carried out have proven the effectiveness of the vaccine only if the deadlines are strictly followed. If temporary pauses are not observed, correction of the subsequent program is based on the specifics of the case.
Sometimes the situation develops in such a way that a person is obliged to leave. It is not advisable to receive vaccines in different cities, as this carries an increased risk of delays. The effectiveness of activities in general is reduced. Unable to cancel the trip, they visit the doctor to plan the further course, find out in advance where to get a rabies vaccination for a person in a new place. If possible, contact a highly qualified specialist - a radiobiologist .
This is interesting: I want some air! There is an opinion that you should not go for a walk after receiving a rabies vaccination. This is wrong. Usually the vaccinated person continues to lead a normal life.
Rabies vaccination and alcohol
It is believed that during vaccination and for at least the next six months, it is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol, as this will lead to a loss of the effectiveness of the drug. The instructions for the medicine actually mention a ban as a restriction after a person is vaccinated against rabies, but this is not associated with the loss of effectiveness of the medicine under the influence of alcohol: such a statement has no scientific basis.
Doctors say that after rabies vaccinations you should not drink for about six months, since alcohol negatively affects human health, weakening it in general. For the same reason, during treatment and for another six months after the cycle of injections, you should not overwork, hypothermia or overheating. You should avoid visiting the sauna or bathhouse.
Hepatitis vaccination 0
128
This is interesting: how did this happen? The explanation for where the myth about the interaction of the rabies vaccine and alcohol, about the drug’s loss of effectiveness, came from is quite simple. Previously, the only way to save yourself from rabies was medication administered in 30-40 portions. Every day a person received an injection in the stomach, this lasted at least a month. By missing at least one procedure, the patient risked not getting any effect from the course. Statistics show that most often patients miss doctor's appointments due to intoxication. These two factors have led to the stereotype that alcohol blocks reactions in the body.
Contraindications
Naturally, like any vaccine, it has contraindications, which are justified only in the case of preventive vaccination. Thus, administration of the medication is not recommended in the following cases:
- pregnancy (the baby may die in the womb due to exposure to the vaccine);
- acute period of any illness (before receiving the vaccine, a person must not only recover, but at least a month must pass from the moment of recovery);
- allergic reactions (as a rule, the presence of an allergy to the components of the vaccine becomes known after its first use).
These restrictions do not apply when it comes to forced vaccination to save a person’s life.
So, during pregnancy, if you do not get vaccinated, the mother will inevitably die, and, accordingly, the child. Well, in such a situation, when they choose between the lives of a mother and a child, the mother is always saved.
The same situation applies to other contraindications. In case of a bite, the doctor does not pay attention to them. Why? To save the patient's life.
As for drinking alcohol during vaccination, not everything is so simple. According to the recommendations of Russian doctors, there is a restriction on the intake of alcoholic beverages for the entire vaccination period. But the World Health Organization (WHO) documentation does not say anything about whether you can drink alcohol?
A drinking person will immediately seize on this loophole, and will be absolutely wrong. Any drink that contains any amount of alcohol is harmful and even dangerous during the period of the vaccine, and drinking, even beer, during a preventive vaccination, and even more so during the period of treatment after a bite, is stupid (it’s up to you to drink the last time or be patient).
Alcoholism, just like a single dose of alcohol, can provoke a decrease in the effectiveness of the vaccine, as a result of which it will not fully perform its functions, which will lead to death. The effect of the vaccine may even increase, but this does not mean that rabies will be cured several times faster, no, the patient will only experience increased side effects, which we will talk about later.
If you really can’t stand it, you can choose an alternative and try a non-alcoholic drink.
An illustrative case that occurred in the Siberian region of the Russian Federation can be cited as an example. One girl did not heed the recommendations and drank alcohol during vaccination, and as a result, her condition worsened. It was only thanks to the actions of the doctors that the patient was saved.
Do I need to get a rabies vaccination?
Some ordinary people doubt the need for a vaccine. There should not be even the slightest doubt about whether to get a rabies vaccine. For example, there is a stereotype that a minor injury is completely safe if the area is disinfected. Doctors note: a vaccine is the only way to survive if a disease pathogen has entered the body. Even if it penetrates through a tiny scratch, a slight abrasion of the skin, it ends up inside, where it gradually affects the nervous system and brain, guaranteed to be fatal. The consequences will be much more severe than any reaction to the rabies vaccine.
There is a myth that the disease was cured. In fact, the story is somewhat distorted. Not a single officially documented case of cure has been established. If infection occurs, only a course of therapeutic and prophylactic vaccination against rabies helps save a person. This is the only reasonable and completely justified measure that has no alternative.
Important! Since 2007, World Rabies Day has been celebrated (September 28 every year). It was established at the initiative of the Global Alliance to Control Rabies with the aim of attracting the attention of people around the world to this problem and making them aware of the prevention of the disease.