Indications for Tuberculin vaccination
Tuberculin is used for tuberculin diagnostics (carrying out an intradermal Mantoux tuberculin test), which is an indicative diagnostic test for the purpose of:
- identifying the need for a patient to be vaccinated against tuberculosis with BCG
- diagnosis of tuberculosis;
- determining whether the population is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (or the state of hypersensitivity to tuberculin, if the existing post-vaccination allergy does not give grounds to talk about infection).
The active substance of the drug (allergen-tuberculoprotein) causes, when performing an intradermal tuberculin test in people infected or vaccinated with BCG/BCG-M, a specific delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction in the form of a local reaction - hyperemia (redness) and infiltrate (papule formation).
What is the Mantoux reaction
The Mantoux reaction is the main method of preventive examination of children for tuberculosis, an immunological test that shows whether there is a tuberculosis infection in the body.
The Mantoux reaction is the body’s reaction to the introduction of tuberculin. At the site of injection of the drug into the skin, specific inflammation occurs, caused by infiltration by lymphocytes - specific blood cells responsible for cellular immunity (as opposed to the antibody immune response, in which antibody proteins play the main role). Fragments of mycobacteria seem to attract lymphocytes from nearby skin blood vessels. But not all lymphocytes come into play, but only those that are already fully or partially “familiar” with Koch’s wand. If the body has already had a chance to “get acquainted” with the real Mycobacterium tuberculosis, then there will be more such lymphocytes, the inflammation will be more intense, and the reaction will be “positive” (there is an infection with Koch’s bacillus). Naturally, a positive reaction means that the inflammation exceeds that caused by the injection itself and a certain diagnostic threshold. By measuring the diameter of a papule (inflammatory “plaque” or “button”) with a ruler, you can assess the strength of immunity to the tuberculosis bacillus.
Strictly speaking, the body’s reaction to tuberculin is one of the types of allergies (for tuberculin itself is not a full-fledged antigen, but rather an allergen).
Evaluation of Mantoux test results
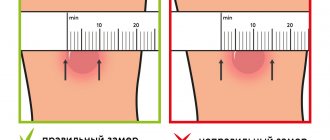
The test result is assessed by a doctor or trained nurse 72 hours after the test. A reaction to tuberculin is possible in the form of hyperemia (redness of the skin) and the formation of a papule (a dense round area rising above the skin). Assessment of the Mantoux test consists of taking into account the size of the papule and assessing the severity of hyperemia. The measurement is carried out in a direction transverse to the axis of the hand, the result is taken into account in millimeters. Only the size of the papule is measured, and not the size of the area of hyperemia (redness). The size of the redness is taken into account only when the papule has not occurred.
Reaction options for the Mantoux test:
- negative - there are no changes on the skin;
- doubtful - there is redness of any size without a papule, or a papule no more than 2-4 mm;
- positive mild - papule size 5-9 mm;
- positive of medium intensity - papule size 10-14 mm;
- positive pronounced - papule size 15-16 mm;
- excessive (hyperergic) - the size of the papule exceeds 17 mm or there are pronounced signs of inflammation (reaction of the lymph nodes, skin ulceration, etc.).
- A negative Mantoux reaction indicates that the body does not have antibodies that are “familiar” with the tuberculosis bacterium. This means that the child is not infected, or there is no immune reaction to BCG vaccination.
- A questionable sample is considered negative.
- A positive test can be either a consequence of BCG vaccination or a sign of infection.
To assess the likelihood of infection, you need to look at the turn of the tuberculin test - the transition of a negative Mantoux reaction to a positive one (not associated with previous vaccination) or an increase in the diameter of the papule compared to the result of the previous test by 6 millimeters or more.
Also signs of infection are:
- hyperergic reaction;
- persistent (more than 4 years) persistent reaction with a papule of 12 mm or more;
- gradual (over several years) increase in sensitivity to tuberculin with the formation of an infiltrate measuring 12 mm or more.
A positive Mantoux test result without taking into account other diagnostic criteria is not a basis for making a diagnosis or starting any treatment.
Only a doctor can evaluate the reaction; if necessary, the child will be referred for additional examination to a TB specialist.
What is called the turn of the tuberculin test?
Many parents, hearing the diagnosis of “tuberculosis test twist” for the first time, ask what it is. The first positive result of the test is called the turn of the tuberculin test, provided that before that the results were negative. The cause of the change may be either vaccination against tuberculosis or infection with the disease. In any case, when you hear this term, you should not panic: to finally confirm the diagnosis, the child needs to undergo several additional tests. And only after a complete examination will the doctor be able to make a final diagnosis.
Indications for the Mantoux test
The Mantoux test is performed to diagnose tuberculosis.
Children vaccinated against tuberculosis:
The Mantoux test (Intradermal allergy test with tuberculin) is performed once a year, regardless of the results of previous tests, at the age of 1 to 7 years inclusive.
For children not vaccinated against tuberculosis (children who have not been vaccinated with BCG), the Mantoux test is performed 2 times a year starting at the age of 6 months
Children not vaccinated against tuberculosis:
The Mantoux test is performed - 2 times a year, starting from the age of 6 months, the Mantoux test is performed.
If registered and prescribed preventive treatment
Children and adolescents newly diagnosed with tuberculosis have an increased risk of developing clinically significant tuberculosis - it is believed that 7-10% of such children may develop primary tuberculosis with all the inherent symptoms. Therefore, such children are subject to observation in an anti-tuberculosis dispensary for a year. Chemoprophylaxis with isoniazid is carried out for three months. At the end of this period, the child is transferred under the supervision of a local pediatrician as “infected for more than one year.”
If such a child, after a year, does not show signs of increased sensitivity to tuberculin and a hyperergic reaction, then he is observed by a pediatrician on a “general basis.” In such children, the results of the annual Mantoux test are carefully monitored. An increase in the reaction of 6 mm or more in such children indicates activation of the infection.
Those infected for more than one year with a hyperergic reaction to tuberculin and an increase in the reaction by 6 mm or more are observed in the tuberculin dispensary. Chemoprophylaxis is carried out for 3 months.
If the child’s test result is positive, but the previous test was carried out not one, but two or more years ago, the child is considered “infected with an unknown period of limitation.” It is recommended to repeat the test after 6 months. Based on the results of the second test, the issue of the need for observation in a tuberculosis clinic and chemoprophylaxis is decided.
Registration of children for dispensary registration with a phthisiatrician is determined by the provisions of the Instructions for organizing dispensary observation and registration of the contingent of anti-tuberculosis institutions (Appendix No. 7 to the Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia of March 21, 2003 N 109, part III of the Group of dispensary observation and registration of children and adolescent contingents of anti-tuberculosis institutions) .
I would especially like to note here that, according to the “Instructions for the use of tuberculin tests,” the registration of children under three years of age in group VI (in fact, by which treatment with special drugs is determined) is generally excluded! I quote: “All children (over three years old) who have had a transition from previously negative tuberculin reactions to positive ones, as well as children with increasing sensitivity to tuberculin in the presence of contact with a patient with tuberculosis, after excluding the active tuberculosis process, are registered as PTD in group VI " Over three years old! This rule is specifically stated in the Instructions, but is often violated in practice.
Let me remind you that the Mantoux test is not a 100% reliable means of diagnosing tuberculosis, and a diagnosis of tuberculosis cannot be made based on a positive reaction alone!
At your first visit to a phthisiatrician, you will be prescribed the following examinations - chest fluorography, microbiological culture of sputum, examination of family members.
If you are prescribed a preventive course of isoniazid or other drugs, then request the full range of examinations required according to the “Instructions for chemotherapy of patients with tuberculosis”: examination of sputum and other available diagnostic material for Mycobacterium tuberculosis at least three times, blood testing for antibodies to HIV, viruses hepatitis, ECG, tuberculin diagnostics (determination of the threshold of sensitivity to tuberculin, graded skin test) and a number of others.
Medicines against tubercle bacilli are very toxic, even in “prophylactic doses”, which are calculated based on the child’s weight. You yourself understand what it means to “count on weight” for a drug with a large number of side effects, children - they are not the same mechanisms, so the risk of preventive treatment for a healthy child is very high!
The chemotherapy regimen and technique are determined individually, taking into account risk factors. Demand a reliable assessment of your child's health. Check your doctor's recommendations for taking vitamins, hepatoprotectors (medicines that protect the liver) and a special diet regimen.
Contraindications
Only a doctor can decide whether the drug “Tuberculin” is suitable for testing for tuberculosis.
“Tuberculin” is contraindicated for persons with allergic and autoimmune diseases!
The use of Tuberculin is also contraindicated in the following cases:
- common skin diseases
- epilepsy
- acute, chronic infectious and somatic diseases during exacerbation; allergic conditions (rheumatism in acute and subacute phases, bronchial asthma, idiosyncrasies with pronounced skin manifestations during exacerbation).
It is not allowed to carry out the Mantoux test in those children's groups where there is a quarantine for childhood infections. The Mantoux test is performed 1 month after all clinical symptoms disappear or immediately after quarantine is lifted.
How do you feel about mandatory vaccination?
- Positively, it prevents many diseases. 60%, 2648 votes
2648 votes 60%2648 votes - 60% of all votes
- Negatively, these are all government schemes to make it easier to manage us. 26%, 1163 votes
1163 votes 26%
1163 votes - 26% of all votes
- Neutral, I don’t think it has any effect on my health. 13%, 594 votes
594 votes 13%
594 votes - 13% of all votes
Total votes: 4405
Votes: 4380
January 17, 2018
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
Possible side effects
- For most, the test process is asymptomatic.
- Headaches may rarely occur
- General weakness, sleep disturbances, and increased body temperature rarely develop.
- Individuals with altered reactivity experience allergic reactions.
- Considering the possibility of developing immediate allergic reactions (anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema, urticaria) in particularly sensitive individuals, vaccinated persons must be provided with medical supervision for 30 minutes.
Come get vaccinated at ONNI.
A full range of vaccines for children and adults, family vaccinations - at a special price! Call a doctor at home Make an appointment with a doctor or call +7 (812) 331-17-74
Causes
Koch's bacillus has a shell that is resistant to acidic environments. It is able to survive freezing, drying, exposure to alkalis, and much more. etc. Characterized by the ability to form so-called L-forms with increased adaptability. The most pathogenic microbacteria for humans are:
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis humans;
- Mycobacterium bovis.
Microbacteria enter the body through contact, air, mixed and other routes. This is how the first inflammatory focus is formed. A child can also be infected during the mother's pregnancy - through the placenta or during childbirth, if it swallows amniotic fluid. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24548085 Marais BJ Tuberculosis in children J Paediatr Child Health . 2014 Oct;50(10):759-67. doi: 10.1111/jpc.12503. Epub 2014 Feb 19
Children at risk include:
- not vaccinated with BCG;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics, hormonal or cytostatic agents;
- having HIV status;
- living in unfavorable conditions (social and/or sanitary);
- having diabetes mellitus;
- with weakened immunity;
- under 2 years of age;
- and etc.
Types and forms of pathology
According to the period of occurrence in medicine, stages are distinguished:
- infiltration;
- decay;
- contamination;
- resorption;
- seals;
- the appearance of scars;
- calcification.
| Form | Peculiarities |
| Chronic and early | It occurs against a background of body temperature up to 40℃, cough, pain in the lungs, uneven breathing, wheezing, decreased appetite, and loss of strength. |
| Respiratory damage | Includes pathologies:
|
| Other localizations | There may be lesions:
|
Treatment
Chemotherapy, antibiotics
Bactericidal and bacteriostatic drugs are used to achieve complete recovery. In this case, the correct combination of drugs is important, taking into account the resistance of some bacteria to this type of therapy. First, treatment is aimed at suppressing the growth of bacteria and eliminating their resistance to medications. Residual infection in the cells is then eliminated. Duration of therapy is 6-12 months.
Surgery
Pulmonary resection is practiced as a radical technique. The operation is performed for bronchial stenosis, fibrous-cavernous lesions, pleural empyema, abscesses in the lungs, tuberculomas prone to progression, etc. In addition, decortication is used, that is, removal of fibrous layers, and cavernotomy - cleansing of the opened cavity.
DOTS
A treatment system consisting of several levels: bacterioscopic examination, chemotherapy, anti-tuberculosis treatment.
Sources:
- N.M. Koretskaya. Tuberculosis in children and adolescents in modern conditions // Siberian Medical Review, 2010.
- A.V. Mordyk, E.A. Tsygankova, L.V. Puzyreva, A.A. Turitsa. Tuberculosis in children of the Russian Federation at the present stage // Pediatric pharmacology, 2014, v. 11, no. 3, pp. 27-30.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24548085 Marais BJ. Tuberculosis in children // J Paediatr Child Health. 2014 Oct;50(10):759-67. doi: 10.1111/jpc.12503. Epub 2014 Feb 19.
- V.N. Krivohizh. Modern methods of early detection of tuberculosis among children and adolescents // Health is the basis of human potential: problems and solutions, 2013, pp. 570-585.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.