The number of people infected with tuberculosis has not decreased recently.
Every year the disease takes many lives. This trend causes serious concern among doctors. For these reasons, in order to control susceptibility to the disease, as well as to prevent it, during the first week, every baby born is given a BCG vaccination as a planned mandatory procedure. Next, every child under 14 years of age is given a mantoux test every year, which serves as a special test to detect tuberculosis infection in the body. If there are serious contraindications for administering the BCG vaccine or if parents refuse it, it is possible to reschedule this vaccination. The transfer period is indicated and adjusted by the doctor.
Tuberculosis test
The mantoux reaction, also called the tuberculin test, is not, in fact, a vaccination. It would be more correct to call it a preventive examination in the form of an allergic test for the presence of tuberculosis microorganisms. Carrying out such a reaction to the disease annually makes it possible to detect tuberculosis in the early stages.
Such immunological testing involves subcutaneous injection of tuberculin. This remedy is a solution of purified tuberculosis allergen. This drug was discovered in 1890 by Robert Koch, as were the bacteria that cause the disease. The latter were named after the scientist's surname - Koch's wand.
Diagnosis using intradermal injection of tuberculin was proposed in 1908 by Charles Mantoux. Since then, it has remained a generally accepted way of testing children for infection.
A tuberculin test is carried out after BCG. If the latter was not done to the child on time, the Mantoux test is given twice a year. In addition, it is important to consider that a tuberculosis test is done a month after the scheduled vaccination.
A tuberculin injection is administered under the skin of the forearm on its inner part. The effect makes itself felt on the third day - the injection site swells, and a so-called button - infiltrate - appears in the center of the hyperemic tissue. The emerging papule must be protected from scratching and moisturizing. It is forbidden to wet it until the results are analyzed by a doctor. And to avoid distortion of the reaction, it is important to remove from the diet all foods that provoke allergies. First of all, citrus fruits and sweets are excluded, as well as all foods that are red, orange and yellow.
Vaccination results
The results of the reaction are assessed 72 hours (3 days) after intradermal injection of tuberculin. First, a doctor or specially trained nurse will examine and palpate the injection site for the presence of infiltrate, and then measure its diameter with a transparent ruler perpendicular to the axis of the forearm. If there is no infiltration, the size of the redness is determined.
Depending on the body’s sensitivity to tuberculin, the Mantoux reaction can be:
- negative;
- doubtful;
- positive;
- hypergic.
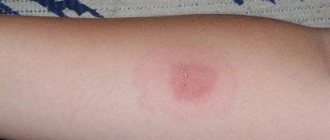
A negative reaction is characterized by a complete absence of thickening and hyperemia. You can observe a puncture mark with a diameter of up to 1 mm. This result may occur in the following cases:
- in uninfected people;
- People who have recently recovered from tuberculosis;
- In infected people with concomitant immunodeficiency disease.
If the diameter of the papule does not exceed 2-4 mm or redness of any size is observed, a questionable reaction to tuberculin is suspected. In this case, further observation of the Mantoux test continues. If the reaction does not progress, the test is repeated after 3 months. Increased sensitivity to tuberculin allows one to suspect the presence of tuberculosis and refer the patient for additional diagnostics.
A positive Mantoux test result in adults indicates infiltration of 5 mm or more. Depending on the size of the infiltrate, a positive Mantoux test is classified as:
- moderately positive - 5-9 mm;
- Average - 10-14 mm;
- expressive - 15-20 mm;
- hyperergic - more than 21 mm, presence of vesicular and necrotic changes
- degree of severity - if the size of the papule has increased by 6 mm or more compared to the previous result.
Reactions are weakly positive, moderately positive, variants of the norm are expressed. This can occur after BCG vaccination when resistance to tuberculosis develops, and in people who are infected but not sick. Such results can also be observed in patients with various forms of tuberculosis.
The magnitude of the Mantoux reaction for tuberculosis in a normal adult is shown in the photo.
A hyperglycemic reaction indicates a high risk of developing the disease, especially if the patient is in close proximity to patients with tuberculosis or lives in a region with an unfavorable epidemiological situation. This test result requires further monitoring and additional diagnostic tests.
In addition to those mentioned above, a false positive reaction is also possible. This happens when the injection site is not supported properly or if you have an allergic reaction to tuberculin and its components.
Why is the mantoux test necessary?
This reaction is carried out to:
- detect facts of primary infection or the initial stages of the disease;
- identify patients who became ill a year ago;
- diagnose infection in children under one year of age, obtain confirmation of the diagnosis;
- identify signs of latent tuberculosis.
The result, that is, the size of the papules that appear as a result of mantoux, is determined visually by the doctor. The specialist draws conclusions based on the condition of the skin at the injection site, guided by WHO requirements. A negative reaction with a button, the size of which does not exceed 1 mm, and the absence of redness around this place is accepted as the norm.
Criteria on the basis of which the assessment is made
| Range of results | Button dimensions mm | What does the injection result indicate? |
| Negative | Up to 1 | Normal, that is, the absence of tuberculosis microbacteria |
| Doubtful | Do not exceed 5 | Indicates a positive reaction, but does not convey a full picture of the presence of Koch’s bacillus |
| Positive of varying intensity | In the range from 5 to 15 | Serves as a warning about the presence of tuberculosis bacteria in the body, taking into account age and individual characteristics |
| Intensely expressed | Over 17 | Talks about the body’s predisposition to disease or the likelihood of infection |
Sample principle
The tuberculin test is performed by trained and authorized medical personnel. The Mantoux test is performed on an outpatient basis. Before the examination, the patient must be examined by a doctor. If there are contraindications, the examination is postponed until the contraindications are eliminated.
The Mantoux test is an intradermal injection of tuberculin using a special disposable syringe. The syringe is filled with 0.2 ml of the drug and 0.1 ml is poured onto a sterile cotton swab.
The inner surface of the middle third of the forearm is pre-cleaned with an antiseptic solution. The remaining amount of tuberculin is injected under the skin with a needle upward. When the procedure is carried out correctly, an infiltrate, a “lump” with a surface resembling the peel of a lemon, forms at the injection site.
Later, immune cells (macrophages and lymphocytes) from nearby blood vessels in the skin rush to the injection site. But only those who have previously been in contact with Mycobacterium tuberculosis respond to tuberculin (memory B cells and memory T cells, T helper cells). They already store information about MBT antigens and recognize them upon repeated exposure.
In addition to local reactions, general and focal reactions may rarely occur. The first of them is manifested by an increase in body temperature, pain in the joints and muscles. The second is around the lesions, depending on the location of the tuberculosis infection.
Contraindications
Performing a mantoux test on healthy people is one of the completely harmless and safe activities for both adults and children. The presence of established somatic diseases is also not a contraindication for the anti-tuberculosis procedure.
However, it is worth considering that only past infectious diseases, regular preventive vaccination, and chronic diseases can cause a distortion in the results of subcutaneous tuberculin vaccination. It is for this reason that the mantoux reaction is performed subject to final recovery and restoration of the body’s immune defense, which usually occurs a month after the disease.
In addition, as with the use of any other drugs, when using a tuberculin test, it is important to review the list of known contraindications. Such a precaution will allow you to obtain a reliable result and avoid possible complications and other negative consequences after the subcutaneous injection of a mixture of tuberculin antigens.
Contraindications to the planned performance of the mantoux test, leading to medical withdrawal:
- High body temperature is one of the important reasons for refusing vaccination until the child’s condition returns to normal. The cause of such fever is often viral and infectious pathologies. Because of them, the mantu sample is postponed for 3–4 weeks.
- Another reason to undergo a tuberculin test is if the child has a cough. This manifestation does not always indicate the presence of a cold. Symptoms are characteristic of bronchial asthma and may indicate an allergic reaction to the drug or its constituent elements. In such situations, the manta is transferred until the source of the pathology is clarified.
- In case of manifestations of a runny nose, tuberculin tests are postponed for at least a month. This applies to any cause of pathology, because a runny nose can be both cold and allergic in nature, and even be chronic.
- The acute course of a disease of any etiology, as well as aggravated forms of chronic problems, serve as a significant contraindication for anti-tuberculosis testing. In this case, diagnosis using mantoux is postponed until the child has fully recovered. Moreover, before the test, a bacteriological examination is mandatory and carried out.
- The tuberculin test should be postponed if there are symptoms of skin diseases of any etiology. The procedure is postponed until the skin is completely restored.
- There are cases when, on the eve of the planned diagnosis using Mantoux, the baby is given other vaccinations. This is a good reason to refuse anti-tuberculosis preventive testing for at least a month and a half. Such “overlays” can provoke a false reaction due to a specific immune response. And if a child has been vaccinated with drugs containing live bacteria and viruses, a waiver from the mantoux test for medical reasons is given for two months.
- In the presence of digestive disorders and other problems associated with the stomach, the tuberculin reaction is postponed until the child’s condition is brought back to normal and diarrhea and other manifestations of the disease completely cease.
- There are a number of diseases of neurological origin (including, for example, epilepsy), in the presence of which anti-tuberculosis tests are strictly prohibited. This ban lasts a lifetime.
- If your child has allergic reactions, you must notify your pediatrician. Firstly, the components of the drug, which are of chemical origin, can cause a rash or other allergic manifestations. Secondly, the reaction to tuberculin may be erroneous, for example, it may show a positive or questionable result. The test is allowed only in the absolute absence of allergic reactions after treatment with antihistamines.
What can distort the Mantoux reaction and enlarge the papule?
The Mantoux reaction will be incorrectly assessed, and the size of the papule will be larger than the true size if there is:
- previous infection in the current month;
- vaccination or administration of immunoglobulins, serums, immune stimulants;
- diseases of internal organs in the acute stage;
- worsening of allergic and skin diseases;
- mid-menstrual cycle in girls;
- helminthic infestation;
- insect bite;
- frequent contacts with tuberculosis patients;
- tuberculin diagnosis more than once a year;
- thyrotoxicosis (excess of thyroid hormones);
- scratching, lubricating or covering the papules with an adhesive plaster.
Errors in performing the Mantoux test (for example, violation of the injection technique) cannot be completely excluded. Therefore, in all cases of a reaction unusual for a child, a diagnosis is not immediately made; to confirm it, blood tests, Diaskintest, and chest x-ray are performed.
If you are aware of a tendency to allergies, the doctor recommends taking medications with an antiallergic effect (for example, Suprastin, Claritin) 3 days before and 3 days after the test.
It is also important to exclude from the diet during this period all foods that cause food allergic reactions: honey, chocolate, eggs, fish, nuts, strawberries, and reduce the amount of sweets and flour in the diet.
Complications
If the listed contraindications and a number of details associated with anti-tuberculosis testing are neglected, the following consequences may occur:
- The appearance of headaches that are accompanied by dizziness.
- Body temperature up to 40 degrees.
- The child loses his appetite, constipation, vomiting, and general weakness begin to bother him.
- Disorders of the lymphatic system occur.
- Allergic rashes appear on the skin, its sensitivity increases.
It is important to understand that anti-tuberculosis care is a voluntary activity. It is impossible to provide it against the will of a person (his official representatives). If parents have absolute confidence that the child has no contact with a person with tuberculosis, it is possible to provide in writing a refusal to undergo preventive testing of the child’s body for the presence of Koch’s bacillus. However, it is worth considering the fact that such a step may put the child at a higher risk of contracting deadly tuberculosis due to the lack of regular monitoring.