Description of the drug
Imovax Polio vaccine is an inactivated (non-live) vaccine for the prevention of polio.
Poliomyelitis is an acute infectious disease caused by RNA polioviruses (serovars I, II, III), characterized by damage to the central nervous system, lymphatic system, and gastrointestinal tract. The disease is characterized by the appearance of flaccid paralysis, mainly of the lower extremities. In the most severe cases, damage to the spinal cord leads to respiratory arrest and death. Clinically, poliomyelitis is manifested by fever, headaches and muscle pain, followed by the development of paralysis.
The primary goal of the polio vaccine is to eradicate the poliovirus.
The inactivated vaccine was developed to replace the live attenuated polio vaccine (oral polio vaccine - OPV) because OPV can cause a dangerous complication called vaccine-associated polio.
Vaccine-associated polio is a disease similar to polio, but the causative agent is not a virus, but a vaccine strain. The clinical manifestations and outcomes of the two variants of polio are similar. The introduction of at least two injections of the inactivated vaccine Imovax Polio reduces the likelihood of developing vaccine-associated polio to zero.
Possible reactions
The nature of the side effects is determined by the type of drug administered. The live vaccine has almost no manifestations. Occasionally, the temperature may rise and stools may become more frequent. The condition of the vaccinated child returns to normal within 1–2 days. The inactivated vaccine causes local swelling. There may be redness and soreness at the injection site. Body temperature rarely rises. If you want to reduce the risk to zero, children should be vaccinated against polio at the myMedicus family clinic. Here you can count on 100% safety of vaccination and high-quality information support for the patient.
Our clinic is located in Peredelkino Blizhnoe, Rasskazovka metro station. We also serve nearby areas - Peredelkino, Solntsevo, Rumyantsevo, Salaryevo, Vnukovo, Solntsevo Park, Moskovsky village. The nearest metro stations to us are Peredelkino, Borovskoye Shosse, Solntsevo, Rumyantsevo, Salaryevo.
Vaccination scheme
The course of primary vaccination with Imovax Polio consists of 3 injections with one dose of vaccine (0.5 ml) with an interval of at least 1.5 months, at the age of 3, 4.5 and 6 months, respectively.
Subsequent revaccinations are carried out with live polio vaccine within the periods specified by the National Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations of the Russian Federation: 18 months (or 1 year after the administration of the third vaccine) and 20 months (or 2 months after the first revaccination).
If there are medical contraindications to the use of a live vaccine, revaccinations can be carried out with inactivated polio vaccine according to the following scheme: the first revaccination of Imovax Polio is carried out 1 year after the third administration of the vaccine. Subsequent Imovax Polio revaccination is carried out every 5 years until the patient reaches the age of 18 years and then every 10 years.
Imovax Polio
Imovax Polio. Vaccine for the prevention of polio, inactivated. Description Imovax Polio is a clear, colorless liquid. Purpose The Imovax Polio vaccine is intended for the prevention of polio, incl. in persons for whom vaccination against polio using live attenuated polio vaccine (oral polio vaccine - OPV) is contraindicated. Contraindications Imovax Polio is not used against the background of diseases accompanied by fever, acute manifestations of an infectious disease or exacerbation of a chronic disease. In these cases, vaccination with the Imovax-Polio vaccine should be postponed until recovery. Hypersensitivity to streptomycin, neomycin and polymyxin B, as well as to the components included in the Imovax Polio vaccine. Use during pregnancy: There is insufficient data on the use of Imovax Polio during pregnancy.
The Imovax Polio vaccination during pregnancy can only be used for epidemic indications.
Directions for use and doses
The Imovax-Polio vaccine is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously in a dose of 0.5 ml. The Imovax Polio vaccination course consists of 3 injections of one dose of vaccine (0.5 ml) with an interval of at least 1 month. The first revaccination of Imovax Polio is carried out 1 year after the third administration of the vaccine. Subsequent Imovax Polio revaccination is carried out every 5 years until the patient reaches the age of 18 years and then every 10 years. In accordance with the National Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations of the Russian Federation, the polio vaccination course consists of 3 injections of the drug with an interval of 1.5 months, at the ages of 3, 4.5 and 6 months, respectively. For children whose immunization with Imovax Polio for any reason was limited to one or two vaccinations, subsequent vaccinations against polio can be carried out with a live attenuated vaccine (OPV vaccination) within the time frame determined by the National Preventive Vaccination Calendar.
Use simultaneously with other medications
Imovax Polio can be used simultaneously (on the same day) with other vaccines (with the exception of the BCG vaccine - in accordance with the National Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations of the Russian Federation), provided that they are administered to different parts of the body using different syringes.
Adverse reactions
The frequency of all adverse reactions recorded during the practical use of the Imovax Polio vaccine is very small, amounting to less than 0.01% of the total number of vaccine administrations. The most commonly observed local reactions to the Imovax Polio vaccine (swelling, soreness, redness and hardness at the injection site, these reactions can occur within 48 hours after administration and last up to 2 days) and a short-term increase in body temperature within 48 hours after administration, about 20% and 10% respectively for all reported cases of adverse reactions. After vaccination with Imovax Polio, the following common adverse reactions are observed:
- on the part of the hematopoietic organs and lymphatic system, enlargement of lymph nodes;
- on the part of the immune system, hypersensitivity reactions to vaccine components such as allergic reactions (rash, urticaria), anaphylactic reactions and anaphylactic shock;
- from the musculoskeletal system, muscle and joint soreness for several days after administration;
- from the nervous system: excitement, drowsiness, irritability; short-term convulsions, convulsions caused by increased body temperature; headache; short-term and medium-duration paresthesia (mainly limbs), within 2 weeks after administration.
Release form
The Imovax Polio vaccination is available in 1-dose syringes, 1 syringe per package; or in ampoules of 1 dose, 20 ampoules per package
Compatibility of Isovax Polio with other vaccines
Imovax Polio can be used with an interval of 1 month or simultaneously (on the same day) with other vaccines (with the exception of the BCG vaccine - in accordance with the National Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations of the Russian Federation), provided that they are administered to different parts of the body using different syringes.
The use of the Imovax polio vaccine in combination with other vaccinations does not affect their immunogenicity (ability to develop immunity). Tolerability of vaccines does not deteriorate, and the number of adverse reactions does not increase. Administering several vaccines on the same day does not place an excessive burden on the immune system. Imovax polio can be used to continue and complete a vaccination course started with other polio vaccines, both live and inactivated. All vaccines in the Russian national vaccination calendar are interchangeable.
Types of vaccines
The main goal of vaccination is to completely eradicate polio from the planet - WHO oversees a special program against polio. Russia is certified as a polio-free country, but the presence of infected people in outbreaks in other countries could cause the number of cases to rise to 200,000 per year in just 10 years.
Today, two types of polio vaccinations are used: IPV and OPV. The invention of these vaccines was one of the greatest achievements of the 20th century. Since 1988, the number of diseases has fallen by 99% due to the high effectiveness of vaccination. 95% of those vaccinated with three vaccinations developed immunity to all types of viruses after just 1 course.
Some countries have switched to OPV (oral drops) only after a significant decline in the incidence of the wild form of the virus, but some continue to use IPV due to its unique ability to generate strong local immunity in the intestines. The presence of such immunity eliminates the incidence of wild polio, which is common in the natural environment. IPV is recommended for people with immunodeficiencies (HIV) and those in whose family they live.
Vaccination against polio is included in the National Vaccination Calendar of the Russian Federation. When traveling to countries and areas where there is a threat of infection, you must also get vaccinated.
How is vaccination carried out?
Vaccination is carried out in a vaccination room, in compliance with all sanitary requirements. All drugs are certified. A certificate for the drug is provided upon request.
Without reminders, before vaccination, the medical worker must show the drug and the expiration date of the vaccine.
Only sterile and disposable instruments are used. The vaccination must be carried out using disposable medical gloves.
On the day of vaccination, the child is examined by a pediatrician and the temperature is measured. In the absence of contraindications, vaccination is carried out. Information about the vaccination performed is entered into the card, vaccination certificate, and detailed recommendations for caring for the child in the post-vaccination period are given.
Before vaccination, the doctor will answer all your questions. Be sure to bring information about previous vaccinations to your appointment!
Please note that vaccination of a child, Mantoux test, Diaskintest can only be carried out in the presence of parents or legal representatives of the child (guardians), or if the accompanying person has a NOTARIZED power of attorney to carry out the manipulation (indicating the drug planned for administration) . Otherwise, vaccination will be denied. We comply with the laws of the Russian Federation.
Only here!
Where to get vaccinated?
·In district clinics Vaccination in district clinics in accordance with the National Vaccination Calendar is carried out free of charge. Before vaccination, the child is examined by a doctor. Information about vaccinations given is entered into the child’s card, which is stored in the clinic. The disadvantages of this option include the fact that before vaccination, you and your child may have to sit in line for a long time, and that the pediatrician has too little time to properly examine your baby. In addition, local clinics often offer not the best vaccines.
·In medical centers Here you can find better modern vaccines. The cost of vaccination will consist of the cost of a doctor’s examination (200-1200 rubles) and the cost of the vaccine itself (100-2000 rubles). If you want to contact a paid center, then carefully consider its choice - it is advisable that the medical center has a good reputation and its doctors have been involved in vaccination prevention for a long time. Information about the vaccination done must be documented - for this it is advisable to have a vaccination certificate with you (a booklet in which all information about the vaccinations given is entered).
·At home Vaccinations at home can only be done by doctors who specialize in vaccine prevention. For a child, this is the most gentle option - the baby will not have additional stress in the form of a visit to the clinic. However, it must be taken into account that vaccines must be stored under strictly designated temperature conditions. And these conditions must be observed even during transportation, otherwise the vaccine may deteriorate. Therefore, vaccination at home can be carried out only if you completely trust the doctor who will do it or the medical center in which he works. Make sure that information about vaccination is included in the vaccination certificate.
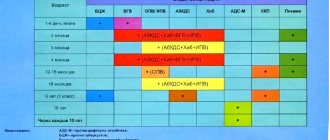
Russian national vaccination calendar
Newborns (in the first 24 hours of life) First vaccination against viral hepatitis B Newborns (3-7 days) Vaccination against tuberculosis 3 months Second vaccination against viral hepatitis B, first vaccination against whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus, polio 4.5 months Second vaccination against whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus, polio 6 months Third vaccination against whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus, polio, third vaccination against viral hepatitis B 12 months Measles, rubella, mumps 18 months First revaccination - diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, first revaccination - polio 20 months Second revaccination - polio 6 years Revaccination - measles, rubella, mumps 7 years Revaccination against tuberculosis, second revaccination - diphtheria, tetanus 13 years Viral hepatitis B (previously unvaccinated), rubella (previously unvaccinated girls or those who received only one vaccination) 14 years Third revaccination - diphtheria , tetanus; third revaccination - polio; revaccination - tuberculosis (if you were not vaccinated at 7 years old)