Our expert is the director of the Research Institute of Preventive Pediatrics and Rehabilitation Treatment of the Scientific Center for Children of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Leila Namazova-Baranova.
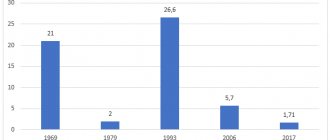
Today, parents do not know how scary it is when their baby is sick, for example, with measles - he lies with a temperature of forty and delirious. Or a severe form of whooping cough - coughing to the point of vomiting, it seems that he is about to spit out his lungs... It is only the grandparents of today's children who remember how they themselves suffered from childhood infections. Now almost all childhood infections have been defeated thanks to vaccinations. There used to be a million cases of measles a year. And now there are 27 throughout the country. Many childhood infections have been defeated, but not all. Hemophilus influenzae type b (abbreviated as Hib infection) still affects almost three million children in the world every year, causing severe purulent diseases such as meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, as well as some forms of otitis media and arthritis. And about 386 thousand of these three million cases of Hib infection, alas, end in death.
General information
Not all parents know what the abbreviation HIB stands for. This is the abbreviated name for a microorganism that can cause Haemophilus influenzae infection. Explanation of the abbreviation - hemophilus influenza type B.
This Haemophilus influenzae has a number of features that allow it to migrate from its localization site into the bloodstream, thereby spreading to the entire body. The main area of localization is the respiratory tract. Haemophilus influenzae, which has spread throughout the body, provokes purulent processes that are localized in the lungs, brain, ears and joints.
The most common pathologies that are provoked by Haemophilus influenzae include:
- purulent meningitis;
- arthritis;
- sepsis;
- pneumonia;
- epiglottitis;
- cellulite.
This infection enters the body through airborne droplets.
The drug directed against Haemophilus influenzae is represented by a lyophilisate used to prepare the vaccine. The composition also includes a capsular polysaccharide, which is a partial shell of the bacterium, which is enhanced with tetanus toxoid. The lyophilisate is a gray-white or white substance that must be dissolved before administration, after which the drug is ready for use. This vaccine is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly, depending on what type of vaccine is used.
How dangerous is hemophilus influenzae infection?
“ACT-HIB” (vaccine) is highly recommended by pediatricians for a reason, because infection in a weakened immune system can cause a number of serious complications, such as:
- meningitis - it leads to serious brain damage, the fatality rate of this disease is high compared to others, it is 15%;
- epiglottitis - the disease can lead to asphyxia, that is, suffocation;
- pneumonia - this disease caused by Haemophilus influenzae infection is characterized by a particularly severe course and a high percentage of deaths;
- sepsis - although it occurs quite rarely, it has serious consequences;
- bronchitis is not as dangerous as pneumonia, but can become chronic;
- otitis - if severe, it can lead to partial deafness.
This is not to mention the fact that Hib infection causes the development of acute respiratory infections and arthritis. The insidiousness of hemophilus influenzae infection lies in the fact that the initial symptoms in most cases do not cause concern for parents. Clinical signs, as a rule, become noticeable already when complications appear. Type b bacillus is particularly resistant to antibiotics, which is why Haemophilus influenzae (Hib) infection causes many difficulties in treatment. The vaccine does not guarantee that the child will not get sick, but it will help ease the course of the disease.
Indications for vaccination
Hib is recommended for children attending preschool.
The Hib vaccine is prescribed to all children aged three months to five years. Older children, as a rule, already have acquired immunity. Children who attend kindergarten, live in orphanages, and toddlers from large families should also be vaccinated.
There is a group of children who need to be vaccinated, regardless of their age. This includes those toddlers who, when infected with Haemophilus influenzae, develop the most severe forms of this infection: sepsis and meningitis. Thus, children with:
- oncology;
- immunodeficiency;
- developmental defects;
- HIV infection, including children born to HIV-infected parents;
- children after long-term use of immunosuppressants;
- Toddlers with asplenia.
The only way to protect
What to do? Get vaccinated. This is the only effective way to combat Haemophilus influenzae. If you take a map of the world and color in the countries where vaccination against Hib infection is included in the National Vaccination Calendar and is considered mandatory, all of North and South America, Europe, Australia, and even half of Africa will be colored. Vaccination of all children against this infection is already practiced in 133 countries around the world. But, alas, we don’t have it yet. But vaccines against this infection are registered in Russia, so parents who want to protect their child from the risk of getting very unpleasant and serious diseases can do this themselves - vaccinate their child for a fee. In a children's clinic, in a vaccination center, in a pediatric medical center.
It is clear that every mother who looks at the baby’s tiny body worries about how her baby will survive the extra injection, and so they give him so many vaccinations! In fact, the Haemophilus influenzae vaccine can be administered simultaneously with any others. And you won’t need additional injections if you use a combined vaccine against several infections at once: diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, including Hib.
Vaccination is best started at three months, the next doses should be administered at four and a half months, six months and one and a half months. But if you realize it later, it’s okay: there are vaccination schedules for children older than 6 months and older than one year.
The injection is given to infants in the thigh, and to children after two years of age - in the upper part of the shoulder. There is no need to buy the vaccine at the pharmacy; there are certain storage conditions for it that you may not know. It is better to use the vaccine from the medical institution where you will be vaccinated.
We are all very afraid of adverse reactions that can happen after any vaccination. The child seemed to be cheerful and healthy, but with our own hands we caused his temperature to rise and the injection site to become red and painful. Yes, there are no completely neutral vaccines. The introduction of any of them may cause an adverse reaction. But it normal. The child’s immunity to the infection that causes the disease will not get worse. And some experts believe that it will even become more active. It’s better to endure a rise in temperature for one day and the whims of a baby whose injection site itches than to watch your child suffer from pneumonia or meningitis. God forbid anyone to experience this. By the way, the Hib vaccine is least likely to cause any reactions.
Types of Vaccines
On the territory of the Russian Federation, you can vaccinate your child with one of three types of vaccinations against hemophilus influenzae.
- Act Hib is a drug manufactured in France, which has the longest history of use and has proven its effectiveness more than once. An important quality of this vaccine is its stimulation of the body to develop stable immunity during the most vulnerable period – up to one year of age.
- Hiberix. Produced in Belgium, it is an analogue of the previous vaccine. Not long ago it was used in Russia.
- Pentaxim is a multicomponent drug manufactured in France. Promotes body protection against hemophilus influenzae infection. Today it is often used in government and medical institutions. Since this drug also contains an element against whooping cough, Pentaxim is classified as a reactogenic vaccine.
What is the HIB component in Pentaxim?
Hib infection (Haemophilus influenzae type b) is an acute infectious disease that affects the human respiratory system. In this case, the central nervous system is often affected, and purulent foci develop in various organs of the human body. This infectious disease is considered one of the most common causes of severe illnesses in children under five years of age.
Often, Hib infection in children manifests itself in the form of the following ailments:
- purulent meningitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain. Occurs in approximately half of all cases;
- pneumonia (pneumonia) - appears in approximately fifteen percent of all cases of illness in children;
- epiglottitis is an inflammatory process occurring in the epiglottis area. Occurs in approximately seventeen percent of all cases;
- sometimes, very rarely, it manifests itself in the form of blood poisoning, inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue (cellulitis), purulent inflammation of the joints (arthritis) and the musculoskeletal system (osteomyelitis).
It should be noted that complications of meningitis are deterioration in hearing, up to its loss, and a decrease in visual function until the development of blindness. Patients may have epileptic seizures.
Neurological disorders, mainly paralysis, are common - this is possible in a third of all cases of morbidity. There may even be hydrocephalus. Complications of pneumonia include pleurisy, lung abscess, and respiratory failure.
There is only one available way to prevent the occurrence of this infection - vaccination. This is the most effective preventative method. The drug that is used to combat this infection may be part of various combination medications to prevent the disease. The number of doses of Hib vaccine that must be administered to prevent the disease in question only decreases with age. Healthy children over five years old are strictly prohibited from administering the vaccine.
It must be remembered that this infection poses the greatest danger to children whose age ranges from four months to one year. There is a risk of meningitis in children under five years of age, which is caused by Hib infection.
Haemophilus influenzae vaccine (Hib component) is a drug that is created on the basis of a defective antigen (polysaccharide of the capsule of the Haemophilus influenzae bacterium).
The antigen was combined with tetanus toxoid protein molecules. This is what allowed us to simultaneously solve several main problems:
- transformation of the antigen into a more complete one, which allows the formation of stable immunity to this pathology;
- reducing the reactogenicity of vaccines, which makes them as safe as possible for the health of children.
Among other things, you need to pay attention that the vaccine against hemophilus influenzae has a so-called booster effect: in other words, with repeated administration, the concentration of antibodies in the human body not only increases rapidly, but grows exponentially.
The manufacturer of the Pentaxim vaccine is the French corporation Sanofi Pasteur, which is located in France. This is a multicomponent drug that reliably protects the body from five dangerous infections. At the moment, this drug is used in both public and private medical institutions.
Unfortunately, due to the presence of a pertussis component, the vaccine is considered quite reactogenic. It may cause some side effects.
Vaccination schedule
The schedule is calculated taking into account the age at which the relevant vaccine was first administered.
- If the baby is three months old, then the vaccine is given together with DPT. A combination drug can be used, in particular Pentaxim. The next vaccination will be at 4.5 months and six months, revaccination at one and a half years. If the first vaccination was at four months, then the schedule may shift by a month. Three-time vaccination provides protection against Haemophilus influenzae in 95% of cases. After revaccination, this figure increases to almost 100%.
- If a child is vaccinated over six months, but who is still under one year old, then the following schedule is followed: two vaccinations, with a month interval between them. A year after the last vaccination, revaccination is done.
- If the baby is one year old and has not previously received a Hib vaccine, then a single immunization is prescribed, since it is assumed that the child may have previously had contact with Haemophilus influenzae infection. Consequently, he has already developed some antibodies to this bacterium. Vaccination allows you to develop immunity in case of secondary infection. But in this situation, the disease will develop without complications, occurring in a relatively mild form. Children are vaccinated once up to the age of five.
Act-HIB is a conjugate vaccine for the prevention of infections caused by Hemophilus influenza Type b
Sanofi Pasteur, France
Release form: 1 bottle / 1 dose + syringe with solvent.
Vaccination schedule: three times 3 months – 4.5 months – 6 months. Revaccination after 12 months.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Act-HIB is a conjugate vaccine for the prevention of infections caused by Hemophilus influenza Type b
COMPOUND
Each dose of the vaccine contains:
Lyophilisate:
| Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide conjugated to tetanus protein | 10 mcg |
| Trometamol | 0.6 mg |
| Sucrose | 42.5 mg |
Solvent:
| Sodium chloride | 2.0 mg |
| Water for injections | qs up to 0.5 ml |
RELEASE FORM
Solution for injection: A bottle containing 1 dose of the vaccine in lyophilized form + a syringe containing 0.5 ml of solvent.
HOLDER OF AUTHORIZATION TO SALE THE DRUG
Aventis Pasteur SA 2, Avenue Lons Pasteur, F -69007 LYON
INDICATIONS
Act - Hib is a VACCINE and is indicated for use in children starting from 2 months of age. The drug is intended for the prevention of meningitis, septicemia, epiglottitis and other diseases caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b. This vaccine does not induce immunity against infections caused by another pathogenic agent, as well as against meningitis of other etiologies.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
This vaccine should not be administered if:
- Hypersensitivity to any component of the vaccine, especially to tetanus toxoid.
IF IN DOUBT, CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR OR PHARMACIST.
NOTES ON USE
It is necessary to inform the doctor about the fact of pregnancy or breastfeeding.
IF IN DOUBT, CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR OR PHARMACIST.
KEEP OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN
WARNINGS
The administration of this drug (like any other vaccine) is not recommended for elevated body temperature and acute infectious diseases.
If Act-HIB vaccine is used at the same time as the measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine, both drugs must be administered at different sites.
DOSAGE AND METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION
STRICTLY FOLLOW YOUR DOCTOR'S DIRECTIONS
Dissolve the lyophilisate using a syringe with a solvent (4‰ sodium chloride solution) or a syringe containing 1 dose of the vaccine D.T. KOK (adsorbed vaccine for the prevention of diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis) or TETRACOK (adsorbed vaccine for the prevention of diphtheria, tetanus , whooping cough and polio).
Shake until the lyophilisate is completely dissolved. The resulting suspension may be cloudy and have a whitish tint.
The vaccine is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
- In children under 2 years of age, the vaccine is administered to the anterolateral region of the thigh (middle third).
- In children over 2 years of age, the vaccine is administered to the deltoid muscle area.
Before vaccinating, make sure that the needle does not penetrate a blood vessel. Do not administer intravenously.
Dosage
- For the age group up to 6 months: 3 injections with an interval of 1-2 months with the introduction of a booster dose 1 year after the 3rd injection (i.e., in accordance with the official vaccination calendar for diphtheria, tetanus and polio).
- In children aged 6 to 12 months: 2 injections 1 month apart, with a booster dose given at 18 months.
- When using the vaccine in children aged 1 to 5 years: single injection.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
AS WITH ANY ACTIVE DRUG, MODERATE AND TRANSIENT ADVERSE REACTIONS OF VARYING DEGREES POSSIBLE WHEN USING THIS VACCINE.
STORAGE
DO NOT USE AFTER THE EXPIRATION DATE STATED ON THE PACKAGING.
SPECIAL NOTES FOR STORAGE
Store at temperatures from + 2 °C to + 8 °C (in the refrigerator). Do not freeze. Rev. 06/96
← Back
Preparation
Before vaccination, do not forget to visit your pediatrician.
There are no special preparatory procedures. It is important to follow certain recommendations:
- Before vaccination, you must consult a pediatrician;
- you need to ensure that the child avoids visiting places with large crowds of people;
- Before the scheduled vaccination, it is necessary to ensure that the baby has no contact with sick people;
- it is important to adhere to the usual diet and not introduce new foods into the toddler’s diet;
- make sure that the child has a normal bowel movement process;
- a woman who is breastfeeding should monitor her diet and also not introduce any new products, because it is possible that a negative manifestation will be a response to the new product, and not to the vaccine.
Features and composition
In Russia, one of the safest and most convenient injections is the ACT-HIB vaccine. The instructions and reviews from foreign and Russian doctors claim that this drug can be mixed in one syringe with other vaccines, for example, with the DTP vaccine. The main advantages of this medicine include the following nuances:
- has virtually no side effects, which is why it is allowed for babies from birth;
- provides great assistance in producing the required amount of antibodies;
- preserves immunity for a long time;
- shows good results in the fight against type b stick.
Hemophilus inoculation is effective due to its constituent elements, which are highly active. This:
- sucrose;
- sodium chloride;
- treated water for injection;
- trometamol;
- a compound of polysaccharide and tetanus protein.
This composition allows you to maintain the immune system at the proper level even in the youngest children.
Reaction and possible side effects
Increased drowsiness is a possible reaction to the vaccine
Many parents may refuse vaccination due to concerns about possible side effects that may follow the vaccine. However, it is necessary to understand that the risk of developing serious complications is minimal, while Hib infection can cause much more harm to the body.
In 10% of cases, the following may be observed at the site of vaccination:
- compaction;
- redness;
- soreness.
Even more rarely, the following may appear:
- increased body temperature (mostly up to 38 degrees);
- tearfulness;
- irritability;
- drowsiness;
- problems with appetite;
- If an allergic reaction to the vaccine occurs, a rash may appear at the injection site.
Over the entire history of vaccine use, four cases of polyradiculoneuritis have been reported.
If a child has been administered a multicomponent drug, the following manifestations may occur:
- swelling of the lower limb;
- seizures;
- brachial nerve neuritis;
- hyperthermia;
- nausea, vomiting is possible;
- dermatitis, itching;
- cough.
If Hib was combined with the DTP drug, a more pronounced response cannot be ruled out, which will largely be a consequence of the second vaccine.
If any undesirable manifestation occurs, you must inform your doctor so that he can prescribe the appropriate treatment. As a rule, the appearance of redness or thickening goes away on its own on the second day, and the temperature returns to normal two to three days after vaccination.
- If the temperature rises significantly, antipyretic drugs can be used.
- Prolonged redness requires an anti-inflammatory agent.
- If a child exhibits allergies, antihistamines should be taken.
- If signs indicating angioedema appear, emergency help is needed.
How to minimize the development of complications
It is important to know that you can avoid the risk of negative manifestations, as well as the development of complications, by following these tips:
- it is recommended to stay near the health worker’s office for half an hour after the vaccination;
- on the day of vaccination and several days after it, you should avoid overheating and hypothermia;
- For the same period, it is not recommended to take water procedures, for example a shower;
- you should not go for long walks;
- It is unacceptable to be in places with large crowds of people.
- For several days after the vaccine is administered, it is not recommended to introduce a new product into the baby’s diet.
Vaccine
"ACT-HIB" (vaccine) was produced by the French. It was registered in Russia in 1997; until 2010, the vaccine against Hib infection was administered on a voluntary basis. Only at the end of 2010, due to the high incidence rate, it was included in the vaccination calendar legally.
ACT-HIB is a vaccine, reviews of which are very contradictory. However, it is highly recommended for parents with children under 5 years of age. This is especially true for children belonging to the following risk groups:
- premature babies;
- children who are bottle-fed;
- children with weakened immune systems who are susceptible to frequent colds;
- children with chronic diseases due to which their body cannot fight infections;
- children attending public educational institutions.
“ACT-HIB” (vaccine) is injected not only into children, but also into adults suffering from immunodeficiency.
Contraindications
You need to know that not everyone can be vaccinated with Hib. Administration of this vaccine is contraindicated:
- children with a history of allergic reactions to previous administration of CHIB and drugs containing this element;
- if there is intolerance to the components of the vaccine;
- toddlers who were allergic to tetanus toxoid, due to the fact that it is present in act-hibe in a small dosage.
Vaccination should be delayed for children who currently have a respiratory disease or manifestations of a viral infection until complete recovery.
Now you know what people are vaccinated against with the Hib vaccine. When infected with Hemophilus influenzae infection, the development of serious diseases that can lead to serious consequences is possible. Remember that your child must be vaccinated before attending kindergarten, since in a group environment the risk of infection with Haemophilus influenzae increases.
Pharmacological action Act Hib
The Hib Act is not included in the compulsory vaccination schedule, however, experts strongly recommend the introduction of this vaccine due to the high prevalence of infections with the pathogen Haemophilus influenzae type b. It refers to bacteria of the opportunistic type, which, with a weakened immune system in a child, provoke the following diseases:
- ARVI;
- Otitis;
- Meningitis;
- Bronchitis;
- Arthritis;
- Otitis;
- Sepsis;
- Pneumonia;
- Epiglottitis.
The Act Hib vaccine is intended for the prevention of purulent-septic diseases caused by the pathogen Haemophilus influenzae type b. It forms specific resistance to a given pathogen and helps stimulate the appearance of antibodies. As a result, B lymphocytes are activated by stimulated T lymphocytes through lymphokines (immune mediators). This is the reason for the immunostimulating effect of Act Hib.
It is important to note that in the case of repeated vaccinations, a pronounced booster effect is observed. It is evidence of the formation of immunological memory acquired as a result of the initial injection.