When should the Pneumovax 23 vaccine not be given?
- if the test results do not comply with the standards
- at elevated temperature in a child
- in case of intolerance to the components contained in the Pneumovax 23 vaccine
- during exacerbation of chronic diseases
- in other cases mentioned by the pediatrician before vaccination
Additional Information
Is it possible to purchase Pneumovax 23 from us or where to buy Pneumovax 23 in Moscow?
Family Medical does not sell the Pneumovax 23 vaccine, we vaccinate.
Where to get vaccinated with Pneumovax 23 in Moscow?
You can get vaccinated with Pneumovax 23 at the Family Medical Center, the Pneumovax 23 vaccine is available. Vaccination requires a mandatory examination before vaccination, the vaccination itself and observation after vaccination.
Call us, we will tell you everything in more detail
PricesSpecialistsSign upContacts
| Name of service | |
| Reception | |
| Examination by a doctor before vaccination | 1600 |
| Examination by a doctor before tuberculin diagnostics | 800 |
| TUBERCULIN DIAGNOSIS | |
| Tuberculin (Mantoux test) | 1200 |
| Diaskintest (testing) | 2800 |
| PREVENTION OF HEPATITIS B | |
| Engerix B (for children) - vaccination against hepatitis B | 900 |
| Engerix B (for adults) - vaccination against hepatitis B | 1000 |
| Regevak B - vaccination against hepatitis B | 900 |
| Combiotech - vaccination against hepatitis B | 900 |
| PREVENTION OF WHOOPING COUGH, DIPTHERIA, TETANUS, POLIOMYELITIS | |
| Infanrix hexa - vaccination against polio, Hepatitis B, tetanus, whooping cough, diphtheria, Haemophilus influenzae infection | 4700 |
| Pentaxim - vaccination against polymyelitis, tetanus, whooping cough, diphtheria, hemophilus influenzae | 3000 |
| Tetraxim - vaccination against polio, tetanus, whooping cough, diphtheria | 3500 |
| Infanrix - vaccination against tetanus, whooping cough, diphtheria | 3000 |
| DTP - vaccination against tetanus, whooping cough, diphtheria | 700 |
| PREVENTION OF POLIOMYELITIS | |
| Poliorix - vaccination against polio | 1200 |
| Imovax polio - vaccination against polio | 1200 |
| BiVac - vaccination against polio | 600 |
| Polimilex - vaccination against polio | 2500 |
| PREVENTION OF DIPTHERIA, TETANUS | |
| ADS - vaccination against tetanus and diphtheria | 600 |
| ADS-M - vaccination against tetanus and diphtheria | 600 |
| PREVENTION OF MEASLES, RUBELLA AND MUMPS | |
| Priorix - vaccination against measles, rubella, mumps | 1200 |
| M-M-P II (MMR-II) - vaccination against measles, rubella, mumps | 2000 |
| ZhPKV - vaccination against measles, mumps | 800 |
| Rubella - vaccination against rubella | 600 |
| LCV - vaccination against measles | 550 |
| PREVENTION OF CHICKENPOX | |
| Varilrix - vaccination against chickenpox | 5000 |
| PREVENTION OF HEMOPHILUS INFECTION TYPE B | |
| Act-Hib - vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae type B | 1300 |
| Hiberix - vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae type B | 1200 |
| PREVENTION OF ROTAVIRUS INFECTION | |
| RotaTek - vaccination against rotavirus infection | 3900 |
| PREVENTION OF MENINGOCOCCAL INFECTION | |
| Meningo A+ C - vaccination against meningococcal infection | 2000 |
| Mencevax - vaccination against meningococcal infection | 2500 |
| Menactra - vaccination against meningococcal infection | 6000 |
| PREVENTION OF PNEUMOCOCCAL INFECTION | |
| Prevenar 13 - vaccination against pneumococcal infection | 3900 |
| Pneumo 23 - vaccination against pneumococcal infection | 4400 |
| Pneumovax 23 - vaccination against pneumococcal infection | 4400 |
| PREVENTION OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS | |
| Gardasil - vaccination against human papillomavirus | 9500 |
| Cervarix - vaccination against human papillomavirus | 7500 |
| PREVENTION OF HEPATITIS A | |
| Avaxim 80 - vaccination against hepatitis A | 2000 |
| Avaxim 160 - vaccination against hepatitis A | 2500 |
| Havrix 720 - vaccination against hepatitis A | 2000 |
| Havrix 1440 - vaccination against hepatitis A | 2700 |
| PREVENTION OF HEPATITIS TICK-BORNE ENCEPHALITIS | |
| FSME (for children) - vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis | 1600 |
| FSME (for adults) - vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis | 2000 |
| Tick-E-Vac - vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis | 1000 |
| EnceVir - vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis | 1000 |
| FLU PREVENTION | |
| Vaxigrip - flu vaccination | 700 |
| Influvac - flu vaccination | 700 |
| Ultrix - flu vaccination | 700 |
| Ultrix quadri - flu vaccination | 1200 |
Call us, we will tell you everything in more detail
Indications for vaccination
Diseases caused by pneumococcus are dangerous for people of any age. But children aged two to three years are considered a special risk group. During this period, the child no longer has maternal immunity, and the body’s own immune system is not yet fully formed. In young children, the disease can be very severe, and the best prevention is vaccination against pneumococcal infection.
Infection of a child can occur in the maternity hospital or when visiting preschool and school from other children. Also at risk for pneumococcal infection are older people with weakened immune systems.
Recently, pneumococci have become less sensitive to antibacterial drugs. Effective treatment requires an antibiotic sensitivity test, which takes several days. In this case, the infection can be rapid in nature, and the doctor may simply not have enough time for a targeted infectious disease examination. Therefore, vaccination against pneumococcus is the most optimal way to prevent severe forms of respiratory (breathing) infection in children and adults.
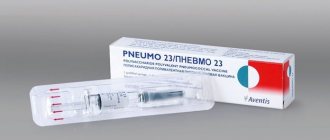
"Pneumovax 23" pneumococcal polyvalent vaccine
Characteristics of the drug The composition of the vaccine Pneumovax® 23 (vaccine for the prevention of pneumococcal infections, polyvalent) includes a mixture of highly purified capsular polysaccharides from the 23 most common and invasive serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae. The 23-valent vaccine contains approximately 90% of the serotypes that cause invasive pneumococcal infections in developed and developing countries. According to scientific publications, the most common serotypes in Russia are 3, 6B, 14, 19F and 23F. The serotypes that most often cause invasive drug-resistant pneumococcal disease are 6B, 19F, 19A, 23F.
The Pneumovax® 23 vaccine is produced using technology developed in the research laboratories of Merck Sharp and Dohm.
Immunological properties Pneumococcal infection is one of the leading causes of death worldwide and one of the leading causes of pneumonia, bacteremia, meningitis and otitis media. Drug-resistant strains of S. pneumoniae are becoming increasingly common in the United States and other regions of the world. In some regions, more than 35% of pneumococcal strains are reported to be resistant to penicillin. Many penicillin-resistant pneumococci are also resistant to other antimicrobials (eg, erythromycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and broad-spectrum cephalosporins), further emphasizing the importance of vaccine prevention of pneumococcal disease.
Immunogenicity Purified pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides have been found to induce the production of antibodies that effectively protect against pneumococcal infection. In clinical studies of the polyvalent vaccine, the immunogenicity of each of the 23 types of capsule antigens included in the vaccine was confirmed.
Protective levels of antibodies to pneumococcal type-specific capsular antigens usually appear by the third week after vaccination. Bacterial capsular polysaccharides stimulate antibody production primarily through mechanisms that are independent of T lymphocytes. As a result, in children under 2 years of age, whose immune systems are still immature, the immune response to most types of pneumococcal capsular antigens is usually weak or unstable.
Duration of Acquired Immunity Following administration of pneumococcal vaccine, serotype-specific antibody levels decline over 5 to 10 years. In some groups of people (for example, children), the decline in antibody levels may occur more quickly. Limited published data indicate that antibody levels may decline more rapidly in older adults (over 60 years of age). These results indicate that booster vaccination may be required to ensure continued protection (see INDICATIONS FOR USE, Revaccination subsection).
The CDC Pneumococcal Surveillance System seroprevalence study demonstrated a 57% protective efficacy of vaccination against invasive infections caused by vaccine serotypes in persons over 6 years of age; 65-84% effectiveness in patients of special groups (for example, people with diabetes, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, chronic pulmonary disease and anatomical asplenia); and 75% effectiveness in immunocompetent individuals over 65 years of age.
Vaccine efficacy has not been confirmed in some groups of immunocompromised patients because sufficient numbers of unvaccinated patients could not be recruited into each disease group. The study results suggest that vaccination may provide protection for at least 9 years from the first dose.
Another study demonstrated a decrease in effectiveness with increasing time after vaccination, especially in very elderly individuals (over 85 years of age).
Contraindications
Only a doctor can decide whether PNEUMOVAX 23 is suitable for vaccination
Pneumovax 23 is contraindicated if there is a history of an allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine.
Vaccination with Pneumovax 23 is contraindicated in the following cases:
- Hypersensitivity to any component of the vaccine, including neomycin; symptoms of hypersensitivity to previous vaccine administration.
- Acute infectious and non-infectious diseases, exacerbation of chronic diseases are temporary contraindications for vaccinations, except in cases where, in the opinion of a doctor, delaying vaccination entails an even greater risk.
- Vaccination during chemotherapy or radiation therapy should be avoided.
Indications for vaccination "Pneumovax 23"
- Increased risk of developing pneumococcal disease, which is one of the leading causes of death worldwide and one of the leading causes of pneumonia, bacteremia, meningitis and otitis media in children over 2 years of age and in adults over 50 years of age.
- Children over 2 years of age who have chronic cardiovascular disease (including congestive heart failure and cardiomyopathy), chronic pulmonary disease (including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and emphysema), or diabetes mellitus.
- Children over 2 years of age suffering from chronic liver disease (including cirrhosis) or leakage of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Children over 2 years of age with functional or anatomical asplenia (including sickle cell disease and splenectomy).
- Children over 2 years old living in special environmental conditions or special social conditions (including the peoples of the Far North).
- Children over 2 years of age with HIV infection, leukemia, lymphoma, Hodgkin's disease, multiple myeloma, advanced malignancy, chronic renal failure or nephrotic syndrome, persons receiving immunosuppressive chemotherapy (including corticosteroids), and recipients of bone marrow or transplantation organs.
- Routine vaccination of persons aged 50 years and older.
- People suffering from alcohol addiction.
- Persons with asymptomatic or clinically evident HIV infection should be vaccinated as soon as possible after diagnosis.
Description of the vaccine Pneumovax 23 (Pneumovax 23) and its composition
Vneumovax 23 (Pneumovax 23) is a multicomponent vaccine aimed at developing stable immunity to pneumococcal infections.
Experience of use in the world is more than 30 years.
One injection of the drug consists of:
1. Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharides, 25 mcg each:
- serotype 1;
- serotype 2;
- serotype 3;
- serotype 4;
- serotype 5;
- serotype 6B;
- serotype 7F;
- serotype 8;
- serotype 9N;
- serotype 9V;
- serotype 10A;
2.Excipients.
The vaccine is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
Country of origin: USA.
"Pneumovax 23" - vaccination against pneumococcal infection
Pneumococcal vaccine, polyvalent
Manufacturer: Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp, USA.
Protects against diseases: a vaccine to prevent 23 types of pneumococcal infections.
Try on: children aged 2 years and older and adults over 50 years old with an increased risk of contracting pneumococcal infection.
Not included in the national vaccination calendar.
IMPORTANT: vaccinations with the Pneumovax 23 vaccine are not carried out in clinics
Compatibility with other vaccines
The pneumococcal vaccine Pneumovax 23 can be given at the same time as the flu vaccine (which is given in the other arm). Such administration does not lead to an increase in the frequency of side effects or a decrease in the intensity of the immune response to the administration of each of the vaccines.
The pneumococcal vaccine can be administered simultaneously (on the same day) with other vaccines (except for vaccines to prevent tuberculosis) in different parts of the body using different syringes.
The Pneumovax 23 vaccine can be administered no earlier than 4 weeks after Zostavax vaccination.