June 21, 2021
In Russia, almost ten regions have introduced mandatory vaccination for certain categories of citizens who come into contact with a large number of people. Vaccinations were required for residents of Moscow, the Moscow region, Kuzbass, Tver, Tula, and Sakhalin regions. Anyone who wants to get vaccinated against coronavirus can choose from three Russian drugs: Sputnik V, EpiVacCorona or CoviVac.
“AiF-Novosibirsk” figured out how vaccines differ, what contraindications they have and their principle of action.
Why is vaccination necessary?
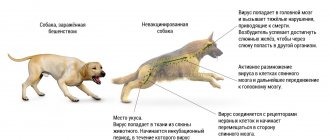
A vaccine helps a dog develop immunity to a specific infection.
It contains fragments of an infectious agent, which, when entering a living organism, causes a corresponding reaction in the form of the production of antibodies. Subsequently, if the pet encounters a similar invasion of infection, it will not get sick or the disease will be mild. Dangerous diseases of dogs for which mandatory vaccination is carried out:
- rabies;
- plague;
- enteritis (parvovirus, coronavirus);
- adenoviral infections;
- leptospirosis;
- infectious hepatitis;
- parainfluenza;
- parvovirus
There are also vaccines against lichen, trichophytosis, and microsporia.
What diseases are vaccinated against?
It is best to find out what vaccinations your dog needs and when they are recommended to be given by asking your veterinarian. The recommended list includes: rabies, distemper, enteritis, parainfluenza, leptospirosis and infectious hepatitis. The full list of required vaccinations depends on the epidemiological situation and differs by region. The listed diseases can be supplemented by lichen, adenovirus, piroplasmosis or Lyme disease.
Rabies
It doesn’t matter what vaccinations a puppy needs to have in your region - in Russia, rabies is always on the mandatory list. The virus is dangerous not only for animals, but also for humans. Unvaccinated dogs are prohibited from attending exhibitions and crossing the border. Some veterinary clinics refuse to accept unvaccinated pets due to the high risk of infection.
Plague
Canine distemper is characterized by rapid damage to the nervous system, followed by paralysis and cardiac arrest. Ask your doctor in advance when to give your puppy his first vaccination. Up to 3 months, the probability of death reaches 40-100%. Only timely adherence to the recommended schedule will help protect your beloved pet.
Enteritis
Another deadly pathology that threatens young animals and small breeds. Symptoms of enteritis include severe diarrhea and vomiting. Due to the resulting disturbances, the body rapidly becomes dehydrated and exhausted.
Parainfluenza
A viral disease that affects the upper respiratory tract. Accompanied by wheezing, whistling and pain in the sternum. It is especially dangerous for newborns, since with prolonged course it affects the intestinal system.
Leptospirosis
The disease is dangerous for humans - in dogs, cats and people it affects the kidneys, liver and gastrointestinal tract. The causative agent of the pathology is bacteria of the genus Leptospira. They are carried by wild animals and small rodents.
Infectious hepatitis
In young animals the disease occurs in an acute form, and in older animals it occurs in a chronic form. Infectious hepatitis is not dangerous for people, but is often fatal in unvaccinated pets.
Types of vaccines for dogs
Nobivak preparations for dogs help prevent the development of the most common viruses
Based on the active component, dog vaccines are divided into attenuated and inactivated. The former are pathogens capable of reproducing. However, due to their weakening, they cannot cause the disease itself, but only stimulate the production of antibodies. The inactivated version is represented by dead microbes. Such vaccinations have a slow and short-term effect, so they need to be repeated.
In addition, there are mono- and multivalent vaccines. In the first case, the composition includes antigens of only one infectious agent. Examples of such vaccines are: Biovac-D, Multikan-1, EPM, Primodog, Kanivac-SN, Rabizin. Several infections are included in the composition of polyvalent drugs. These include: Multikan-4 (6.8), Nobivak, Hexakanivac, Vanguard-7 and others. Multi-strain drugs, as a rule, are not given to puppies, as they put too much strain on the immune system.
Vaccines can be of domestic or foreign origin. Among the Russian drugs that have proven themselves well are: Hexakanivac, Multikan, Vakderm, Polivac. Among the “foreigners” the following stand out: Nobivak, Eurikan, Vanguard, Hexadog. Each drug has its own characteristics and administration regimens.
Most often, vaccines are given subcutaneously (at the withers)
Types of modern vaccines
When choosing a vaccine for puppies, take into account the place of its production and the breadth of its application. These indicators affect the final price, so it is necessary to understand their main differences.
What to choose: domestic or imported product?
Domestic products are always cheaper than foreign analogues. The main advantage of imported samples is their longer existence and a large number of positive reviews. Veterinarians recommend choosing a domestic manufacturer when vaccinating against rabies. After the use of foreign drugs, outbreaks of diseases were recorded.
Mono-vaccines
Single vaccines are aimed at preventing one disease. Their advantage lies in a more gentle effect on the body and better production of antibodies to the selected infection.
When vaccinated with mono-vaccines, it is easier to choose an individual schedule, but the pet will have to undergo many injections. If your four-legged pet experiences stress when visiting a veterinary clinic or you have too little free time, use polyvaccines.
Polyvaccines
Polyvaccines include up to 6-7 fragments of different viral codes. They are more difficult to tolerate by the body, so multicomponent formulations are indicated only for adult animals. For children, drugs containing up to 4 different viruses are used.
The disadvantage of polyvaccines is the possible suppression of some antibodies by others. The rabies virus is considered the most aggressive, so the body directs all its forces to fight this particular agent. In other cases, immunity to several diseases is achieved simultaneously with just one injection.
Effect of the vaccine on the body
When dead or weakened fragments of the viral code are introduced into the body, active production of T-lymphocytes begins - antibodies responsible for destroying the invading pathogen. These antibodies are called memory cells, so if successful, they remember the method of fighting the infection. In case of infection, they give an immediate response, preventing further spread of the virus.
This method of combating infectious diseases is used only for preventive purposes. In case of direct infection, the infected animal is injected with serum - a preparation with ready-made antibodies that forms short-term passive immunity.
Vaccination of adult dogs
Vaccination of an adult dog
Dogs over one year old are required to receive annual vaccinations: injections are given once at regular intervals. It is allowed to vaccinate four-legged friends against infectious diseases once every 2 or 3 years, but the rabies vaccination must be given strictly after 12 months.
If the dog is elderly or elderly, then the decision about whether to give injections or not is made based on its health condition. The vaccine can provoke an exacerbation of the pet’s chronic diseases and further weaken the immune system. Again, a rabies vaccination should be given in any case. According to current legislation, the owner cannot refuse it.
What to do if vaccination is missed
Violation of the recommended schedule leads to a decrease in the effectiveness of the vaccine. Actions in case of absence depend on the amount of time missed.
“
If more than 1.5 years have passed since the last vaccination, then a double injection is required, as for the first time. In other cases, the vaccine is administered as soon as possible, adjusting the original schedule.
Neglecting routine vaccinations for your puppy and adult dog puts not only other animals, but also people at risk.
Despite many controversies surrounding the advisability of vaccination, 90% of vaccinated dogs avoid cases of infection. The remaining 10% experience a mild course, but still avoid death. The article is for informational purposes only.
Contact your veterinarian! Do you like the article?
0
How to vaccinate correctly
In order for the vaccination procedure to have only a positive effect on the dog’s body and not lead to complications, you need to adhere to some rules.
- The dog must be completely healthy. Even the slightest malaise, lack of appetite, fatigue and other conditions are reasons for postponing the injection.
- Before vaccination, your pet must be dewormed. Anti-worm medication must be given 14 days before the procedure.
- It is not advisable to vaccinate dogs while they are changing their teeth. A number of drugs have the ability to change the color of tooth enamel.
- Vaccinations are not recommended for puppies under 8 weeks of age. Early administration of the vaccine will weaken the immunity acquired from breast milk. And since they don’t yet have their own, the puppies may be completely defenseless against infectious diseases.
- In addition to deworming, the dog must be treated for external insects. The treatment is carried out the same way two weeks before vaccination.
- Most vaccines have a negative effect on the development of the fetus, so if dogs are to be mated, the vaccine should not be given. At least 12 weeks must pass between vaccination and mating.
- It is best to vaccinate on an empty stomach.
- If your dog is prone to allergic reactions, you can first give it an antihistamine. Which one it is better to consult a doctor.
We should not forget that after vaccination, the pet may develop anaphylactic shock, so for the first few minutes you need to stay close to the veterinary clinic.
Where do dogs get injections for major viruses?
Vaccination depending on age
When deciding at what age a puppy should get its first vaccination, the veterinarian takes into account individual characteristics and external factors. The general condition of the four-legged patient, conditions of detention and outbreaks of epidemics in the region of residence are taken into account.
First vaccination
Most often, the first vaccination is given to a puppy at 6-7 weeks. At this age, passive immunity received from the mother gradually fades away.
An upward shift in the date is possible with a small litter and an abundant amount of milk in a nursing dog. Postponement of the procedure to an earlier date is explained by early separation from the mother, crowded housing, an imminent change of residence, or an outbreak of an epidemic. In these cases, the Puppy series puppy vaccine, developed specifically for the child’s body, is used.
Second and third vaccinations
The second vaccination is given at 7-8 weeks, the third vaccination is usually complex and includes rabies, it is given at 12 weeks. This period is explained by the low probability of infection of the baby through the main carriers of infection.
In addition to a schedule that takes into account specific diseases, it is important not to forget about revaccination (re-administration of the vaccine). It is carried out 3-4 weeks after the main one to consolidate the result and increase the volume of antibodies.
Vaccination schedule up to a year
Another danger of self-vaccination is explained by an individual approach when drawing up a schedule. Recommended regimens differ even among animals born from the same mother. In addition, the regimen may vary depending on the type of vaccine, especially if they are complex.
What vaccinations are given to puppies up to one year old, using the table as an example:
| Disease | Duration of first vaccination (month) | Revaccination period |
| Rabies | 3-4 | – |
| Plague | 2,5 | 21-28 days |
| Enteritis | 2-2,5 | 21-28 days |
| Parainfluenza | 2-2,5 | 21-28 days |
| Leptospirosis | 2-2,5 | 21-28 days |
| Infectious hepatitis | 2-2,5 | 21-28 days |
Note: the table is approximate, only the veterinarian can determine the exact dates!
Vaccination against other diseases and schedule shifts are agreed upon with the doctor. Carrying out the procedure too early will lead to a collision with passive immunity transmitted through breast milk. In this case, the body will remain vulnerable because it will not be able to create its own antibodies.
Revaccination of adults
The second revaccination occurs at 1 year of age, when the animal is recognized as an adult. It is pointless to get acquainted with what vaccinations are given to dogs by age using the table as an example. The principle of drawing up a schedule is similar, so it is better to ask your doctor all questions.
After 1 year, all further revaccinations are carried out no more than once a year. Exceptions include animals with chronic diseases and weakened immune systems. They are vaccinated every 3 years.
Veterinarians recommend observing seasonality. It is easier to cope with pathogenic infections in summer and winter, since heat and cold effectively kill bacteria and viruses.
Features of rabies vaccination
Although the overall situation with rabies in Russia is favorable, the possibility of an outbreak of this dangerous disease remains. Russian legislation obliges every owner of a four-legged friend to vaccinate him once a year. If the dog owner refuses to vaccinate his pet, he will face administrative punishment.
The law also provides for free rabies vaccination. Such vaccinations are not included in the cost of services even in private clinics. To get an injection, you can go to a state veterinary hospital. Often, primary comprehensive vaccination against infectious diseases in a state hospital is paid for, and further actions according to the scheme will be free. Moreover, if you get a rabies vaccination in such an institution, then the accompanying events will also be carried out free of charge. Among them: examination of the animal, anthelmintic therapy, registration of a dog passport, installation of a chip.
How do vaccines work?
The effect of the vaccine is reduced to the creation of an antigen-antibody complex. Simply put, it contains a weakened microorganism - this is an antigen; once it enters the body, it causes an immune response that identifies the foreign agent and produces antibodies - T-lymphocytes - to eliminate it.
T-lymphocytes (memory cells) remember the “way to fight” the virus, which will further shorten the identification of the antigen and speed up the fight against it.
When a biological product is administered, the body independently produces an immune response, thereby providing long-lasting immunity.
How much does vaccination cost?
Prices for preventive vaccinations for dogs vary depending on many factors:
- features of the vaccine (manufacturer, composition);
- vaccination location (home or clinic);
- pricing policy of the veterinary institution (budget, average, premium, luxury).
For example, giving an injection at home will cost 500 rubles more than if you bring your pet to the clinic. It will be more expensive to vaccinate a dog with an imported complex vaccine than a domestically produced one. On average, the cost of a comprehensive vaccination is about 1,500 rubles.
Don't forget to vaccinate and your dog will be healthy!
How does the procedure work?
To avoid complications, it is recommended to follow the recommendations for preparation for the procedure and mandatory quarantine after it. In this case, you don’t have to worry about the health of your four-legged pet.
Preparation at home
Preparation begins 2 weeks before the event. The owner needs:
- Make sure there are no diseases. Check your temperature and stool quality daily. If alarming signs occur, contact your veterinarian.
- Maintain your usual diet. The change is expected only on the immediate day of vaccination. If the procedure is scheduled for the morning, refuse feeding. In the case of an evening recording, reduce the usual portion by ½ with natural feeding and by ⅓ with dry feeding. The last feeding should be no later than 4 hours before vaccination.
- Treat your pet against helminths, ticks and fleas. If infected with parasites, the vaccination period is shifted, and the pet is treated again.
Before the first vaccination, walks and contact with people dressed in outerwear are excluded. An unvaccinated baby should be next to his mother, away from the corridor with street shoes. For preventative purposes, regularly carry out wet cleaning and wash your shoes after going outside.
Choosing a veterinary clinic
Choose an institution that has received a special license to carry out veterinary activities. This guarantees the safety of the services provided.
The procedure can be performed directly in the clinic or at home. The advantage of the first option is a wide selection of equipment needed for complications and the absence of the risk of damage to the drug during transportation. The second option minimizes the stress factor and eliminates the transmission of infection from other four-legged patients.
Vaccine introduction
Typically, the most painful part of the procedure is the needle piercing the skin and/or muscle. The injection itself does not cause pain, so most dogs tolerate the injection calmly.
If a puppy is being vaccinated, it is enough to hold it firmly in your arms. You can wrap a particularly active baby in a towel. But an adult dog of any breed must be muzzled. Even very calm individuals who are not receiving an injection for the first time can become nervous and bite the doctor or owner. Therefore, follow all the rules for visiting the clinic: short leash, muzzle, and sometimes you will need an assistant.
Dangerous and non-dangerous side effects
Due to the activation of protective mechanisms, a temporary decrease in immunity occurs, causing a number of side effects. Non-hazardous ones include:
- one-time vomiting or diarrhea;
- lethargy and fever (not higher than 39.5°C) during the first 3 days;
- loss of appetite (fasting is permissible for no more than a day);
- pain accompanied by barking and whining, or temporary lameness (no more than 4 days);
- the formation of a lump at the injection site, which disappears on its own within a month.
If a month has already passed and the lump has still not resolved, contact your veterinarian. This phenomenon is typical for a benign tumor. Surgery is used to remove it.
Mandatory assistance from a veterinarian must be sought in case of progressive deterioration of the condition, growth and suppuration of the lump, as well as the development of anaphylaxis (allergy).
An allergic reaction is accompanied by swelling and discoloration of the mucous membranes, profuse salivation and difficulty breathing. If these symptoms appear, give the animal an antihistamine and call a doctor immediately.
Cost of vaccine and clinic services
The final price depends on the chosen manufacturer and location of vaccination. Foreign drugs and calling a doctor to your home will cost the most. The most popular vaccines include:
- French Eurican;
- Dutch Nobivak;
- American Vanguard;
- Russian Polivac and Multikan.
The clinic’s services include not only the procedure itself and consumables, but also a preliminary conversation with a therapist. Prices vary greatly by city and region, so it is better to call the clinics yourself and compare the cost of services.
Where is the best place to vaccinate?
Many owners try to vaccinate their pet at home. On the one hand, the dog feels more confident, which has a positive effect on its health and ability to tolerate vaccination. However, there is a danger that the animal’s condition may sharply worsen, for example, due to an allergic reaction, anaphylactic shock, and then emergency veterinary care will be required.
It is best to bring your pet to the clinic, undergo a preliminary examination, get a vaccine and wait a while. You can walk around the clinic or sit in the car. After making sure that everything is in order with the body’s response, you can go home.
Any owner wants to see their pet healthy and cheerful. The key to such a dog’s condition is timely vaccination.
What is a vaccine, how does it work and why is it needed?
Often, owners vaccinate their pets without thinking about what the vaccine consists of and how it works. Although understanding the whole process is not only interesting, but also necessary for preparing your pet for vaccination and further caring for it.
A vaccine is a biological product designed to create and maintain active immunity against certain infectious diseases.
In other words, this drug contains either live, weakened pathogens or killed ones. Based on this, vaccines are divided into groups.
Live vaccines
They consist of living but weakened strains of pathogens. Such biological products are not capable of causing disease, but are capable of inducing an immune response in the body.
Advantages of live vaccines:
- creation of long-lasting and intense immunity (more than 1 year, sometimes a lifetime);
- in most cases, single administration, small dose;
- immunity is developed in a short time;
- the production technology is cheaper than that of inactivated ones.
Disadvantages of live vaccines:
- post-vaccination complications in pregnant bitches and weakened dogs;
- reversion (return of the strain to its original virulent form);
- features in transportation and storage;
- duration of receiving the attenuated (weakened) vaccine.
Inactivated vaccines
Biological products based on a completely killed strain of the virus.
Advantages of inactivated vaccine:
- does not cause complications after vaccination;
- immunity is less tense;
- ease of production and relatively low cost.
Disadvantages of inactivated vaccine:
- low immunogenicity;
- need for 3-4 times application, large volume;
- immunity, compared to a live vaccine, does not last long;
- increased likelihood of allergic reactions.
Difference in vaccines by number of strains
- Monovalent - against one strain of pathogen.
- Polyvalent - against several strains of one pathogen.
- Associated (combined) – against several pathogens.
Most often, associated live vaccines are used in practice.
When and how do Yorkies get their first vaccination?
The first 1.5-2 months after birth, puppies are protected by antibodies from the mother's milk. But when switching to artificial feeding, there is no longer any protection against infections. At this time, Yorkshire Terrier puppies receive their first vaccination . Usually the breeder takes care of this; it is advisable to buy already vaccinated dogs.
When is the best time to carry out
The breeder should know when to vaccinate their puppies. It is advisable to vaccinate Yorkies before 2 months of age, at which time they are sold to new owners. But you can’t get your first vaccination too early. If the antibodies that entered the body with mother's milk have not yet disappeared, it will be useless.
Hello! My name is Yorkin and I am the owner of Yorkin's House, woof! Thanks for reading my magazine, rrrrr woof! I highly recommend that you read another article, I wrote it with great love! woof!
The best food for a Yorkshire Terrier
Preparing your Yorkie for an injection
Before vaccinating puppies, you need to observe their condition for 3-5 days. You need to take your temperature, it should be 39˚. Babies' noses should be wet and cold and their appetite should be good. A healthy puppy is inquisitive, active, and plays. One day before the procedure, he should not be bathed.
Should I worm my Yorkie?
Before vaccination, it is necessary to drive away worms and fleas. An animal infected with parasites has a weakened immune system. It is impossible to introduce pathogens, even weakened ones, at this time; serious complications may develop or the vaccination will not work.
Yorkie deworming
Yorkshire terriers need to be dewormed 10 days before vaccination. It is imperative to weigh the puppy and check his well-being.
IMPORTANT! To properly deworm your pet, be sure to consult a veterinarian; do not give your puppy anything on your own, as this can harm your Yorkie!
What you should pay attention to
Some owners vaccinate their Yorkie puppies themselves, because special products can be purchased at a veterinary pharmacy. But if a person without special education is involved in vaccination, it can be dangerous . There are several nuances that must be taken into account so that the procedure does not harm the health of the Yorkie.
- Vaccination should be carried out 2-3 weeks before mating. A pregnant bitch cannot be vaccinated.
- The Yorkshire Terrier, which participates in breeding and exhibitions, must be vaccinated only in large clinics that will stamp the dog’s veterinary passport.
- Be sure to find out from the breeder what product was used for the first vaccination. Revaccination should be carried out with the same means.
- Vaccinations can cause an allergic reaction. If the procedure is carried out by a specialist, he will be able to respond immediately.
- If your Yorkie has already moved to a new home and the time for vaccination is approaching, you need to wait a week. The pet must adapt, and shifting the deadlines by 7 days is acceptable.
Complications after vaccinations
Over the next two days after immunization, the dog’s body develops immunity to viruses.
- At this moment, the pet may be a little depressed and refuse food. There is no need to be afraid of this, everything should go away within the next 48 to 72 hours . Otherwise, you will have to contact the clinic again.
- Allergic reactions to vaccinations are possible in theory, but in practice such cases are extremely rare. Despite this, many modern veterinary institutions value their reputation and give an injection of an antihistamine before administering antiviral serum.
If your pet begins to experience allergic reactions after the vaccine (swelling, itching, redness and discharge from the mucous membranes), you need to seek help from the doctor who administered the injection. And at the next immunization, use a different serum.
Thanks to an increase in the level of canine literacy of the population and a breakthrough in veterinary medicine. Over the past two decades, it has been possible to reduce the mortality rate of animals under 3 months of age by almost 3 times. It was possible to reduce rabies epidemics in populated areas by 5 times. This is how many lives are saved thanks to a simple injection in the withers.
3.7 / 5 ( 3 voices)
Vaccination table for puppies in their first year of life
The table below will help you figure out what vaccinations puppies receive:
| Dog age | What is the vaccine for? | Notes |
| 1 month | Vaccination series PUPPY | Do as needed |
| 8-10 weeks | From plague, enteritis, hepatitis, parainfluenza, leptospirosis | Primary vaccination |
| 11-13 weeks | From plague, parainfluenza, hepatitis, enteritis, leptospirosis | Revaccination |
| 11-13 weeks | For rabies | Primary vaccination |
| 6-7 months | From plague, parainfluenza, plague, enteritis, hepatitis, leptospirosis | Repeated vaccination |
| 6-7 months | For rabies | Repeated vaccination, then after a year |
| 1 year | From plague, parainfluenza, hepatitis, leptospirosis, enteritis | Repeated vaccination, then after a year |
Post-vaccination period
Owners also need to know about the rules of care after vaccination. If you understand how a puppy should feel, it is easy to recognize serious complications and take action in time. After the first vaccination, it is not advisable to take your Yorkie outside. Immunity is formed within 1.5-2 weeks.
How long after vaccination can you bathe your dog?
Do not wet the injection site for 3-5 days. You can bathe the puppy no earlier than a week later; it is better to wait until the mark completely disappears. If complications are observed, you need to wait for the pet to fully recover.
Veterinarians recommend waiting a two-week quarantine period, which gives the dog’s body time to adapt, then you can go for a walk. It is important to protect the puppy from drafts, dampness, and temperature changes.
Feeling normal
Yorkies often feel worse after vaccination. The following signs are considered normal:
- slight increase in temperature;
- drowsiness;
- stool liquefaction;
- refusal to eat;
- anxiety.
These symptoms should subside within a few days. If the puppy does not feel better, you need to take him to the vet.
If the puppy is lethargic after vaccination, does not play and sleeps a lot, this is normal. It is necessary to provide the pet with rest and adequate nutrition. In 1-2 days he will become cheerful and active again.
Lump formation
A lump often forms at the injection site. This is a normal post-vaccination reaction. It can last 5-7 days. It usually goes away on its own, but you can apply iodine to it twice a day. If the injection site itches, you need to make sure that the puppy does not scratch it, as it can cause an infection.
What medications are needed?
- Typically, two types of vaccines are used to vaccinate puppies:
- Monovalent. They protect the dog from only one disease, but it is very effective, since the antibodies produced are of higher quality. At the same time, they put little stress on the body. The dog will be able to recover quickly after vaccination. However, if you want to reduce the risk of other diseases, you will have to get several vaccinations. Such drugs are convenient in cases where you need to create an individual vaccination schedule.
- Polyvalent. Aimed at producing antibodies to combat several diseases at once. They are slightly weaker than monovalent ones, but they still give a positive effect. Such vaccines place a large burden on the animal’s body, so they are recommended to be administered only to adult dogs.