Tetanus is a serious disease caused by a bacterial toxin that attacks the nervous system and leads to painful muscle contractions, especially in the jaw and neck muscles. Tetanus can interfere with the ability to breathe and can be life-threatening. The main habitat of dangerous bacteria is soil, saliva and animal feces.
The daily life of children and adults is impossible without injuries that affect the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes. And if the wound is contaminated with soil elements in the absence of immunity to tetanus, this can cause an infection to develop. The tetanus vaccine is the only protection against this disease. In order for the human body to develop immunity to the disease, it is necessary to administer special vaccines containing neurotoxin and tetanus toxoid. When children receive a tetanus shot, these substances are released into the bloodstream, activating the immune system and producing protective antibodies.
Where can I get a tetanus shot? The RebenOK clinic in Moscow vaccinates the population in accordance with established standards and deadlines. You must first make an appointment with a pediatrician to rule out possible contraindications.
Why is tetanus dangerous?
Once tetanus toxin binds to nerve endings, it cannot be removed. To fully recover from a tetanus infection, new nerve endings must develop, which may take several months.
Consequences of tetanus infection:
· Fractures. The severity of muscle spasms can lead to fractures of the spine and other bones.
· Development of pulmonary embolism. A displaced clot may block the main artery of the lung or some of its branches.
· Death. Severe muscle spasms caused by tetanus can cause respiratory failure, which is the most common cause of death.
To prevent a sad outcome, it is recommended to vaccinate your child against tetanus on time.
Is it possible to get the ADSM vaccine during early pregnancy?
The regulations of the Ministry of Health state that pregnancy is a contraindication to the administration of the ADSM vaccine.
Sometimes the situation is such that the next revaccination coincides with pregnancy or breastfeeding.
In such a situation, the vaccine can only be given after childbirth, provided the woman is in good health. Sometimes women find out about their situation after vaccination has been carried out.
There is no need to terminate the pregnancy; you should notify your gynecologist about this fact and carefully monitor the intrauterine development of the fetus. There have not been any cases of negative effects on the fetus of this vaccine.
Termination of pregnancy can be discussed only if malformations of the child are identified.
In the United States today the situation is somewhat different. After 25 weeks of pregnancy, women are given the diphtheria and tetanus vaccine. The need is caused by a sharp jump in the number of people infected with the infection. A child under two months cannot be vaccinated, so epidemiologists decided to vaccinate pregnant women in order to transfer protection to newborns through the placenta.
Types of vaccines
The tetanus vaccine is an inactivated vaccine (not live) and contains a toxin produced by the bacterium but has no toxicity (toxoid). Once injected, it cannot cause disease, but retains its ability to stimulate the production of antibodies. The tetanus vaccine is always part of a combination vaccine that includes other components.
Where do you get the tetanus shot? It all depends on the drug. The vaccine is administered intramuscularly into the subscapular region, thigh or shoulder.
Types of tetanus vaccines at the RebenOK clinic:
· "Adasel". The vaccine is intended for patients 4-64 years of age. Efficacy and safety have been confirmed. Revaccination is carried out once in a dose of 0.5 ml. The vaccine is injected into the deltoid muscle of the shoulder intramuscularly.
· "ADS-M". Used for children aged 6 years and adults. Introduced every 10 years. It is prescribed mainly if other drugs need to be replaced due to complications. Forms strong immunity. Requires revaccination every 10 years. The graft is introduced under the shoulder blade or into the anterior outer part of the thigh.
· "DTP". Adsorbed drug for tetanus, diphtheria and whooping cough. It is carried out for children from 3 months of age to 4 years. Vaccination consists of three injections with an interval of 45 days, followed by revaccination one year after the third vaccination. Good protection is guaranteed if revaccination recommendations are followed.
· "Pentaxim". Vaccination against tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough, polio and infection caused by Haemophilus influenzae. Forms stable immunity throughout life. The vaccine is given to children from 3 months of age.
· "Infanrix Hexa" (Belgium). A combined drug for tetanus, hepatitis B, diphtheria, Haemophilus influenzae, whooping cough and polio.
The choice of drug remains with the doctor. The pediatrician must first study the child’s medical history and select the most appropriate vaccine, taking into account individual characteristics.
Video on the topic
Who should not be vaccinated? Answers in the video:
Adults must undergo an ADSM revaccination. Diphtheria and tetanus are dangerous diseases that can be fatal. Even today, tetanus has no cure.
The vaccine is well tolerated and provides immunity for the next 10 years. Before vaccination, 85% of people with tetanus died. A number of countries, including the United States, tried to refuse vaccination, which provoked an epidemic. Vaccination has resumed as part of the state program.
Contraindications
Tetanus vaccination for children has low reactogenicity, so there are practically no restrictions on the composition. The main contraindication is the occurrence of allergic reactions or neurological damage after the previous injection.
Temporary contraindications for tetanus vaccination:
· influenza and acute respiratory infections;
· diathesis, eczema and other skin manifestations;
allergic reactions and immunodeficiency;
· increase in body temperature.
In these cases, vaccination is carried out after complete recovery. A preliminary consultation with a pediatrician is mandatory.
Advantages and disadvantages
The clinical effectiveness of tetanus toxoid is estimated at 100%. After the initial vaccination series, all vaccinated individuals have antibody titers above the level of protection. How long does the tetanus shot last? Protective antibodies in properly vaccinated people last for more than 20 years.
The decrease in the incidence of tetanus since the introduction of systematic vaccination confirms the effectiveness in preventing this disease. Tetanus toxoid is considered a safe drug.
Alternative ways to prevent tetanus and diphtheria
In addition to vaccination, the main measures to prevent diphtheria include:
- administration of serum after contact with the patient;
- isolation of patients;
- disinfection of premises.
After contact with the patient, specific prophylaxis is carried out using a special serum. Antibacterial drugs may also be prescribed. It is necessary to inform the doctor about contact with the patient.
For prevention purposes, surface disinfection is very important. Linen and other textile products should be washed at high temperatures and using disinfectants.
The infected person's clothing should be washed separately. Carpets also need to be disinfected; to do this, they are cleaned several times with a brush and the addition of disinfectants. Preventing tetanus primarily involves avoiding injury.
In case of injury, you must go to the emergency room, where the following measures will be taken:
- treating the wound to prevent the development of infection (rinsing with hydrogen peroxide, removing non-viable tissue);
- emergency administration of toxoid (tetanus) if routine vaccination took place more than 5 years ago.
Adverse reactions
All vaccines should be considered medicine and may have side effects. In the case of the tetanus vaccine, adverse reactions are moderate.
The most commonly reported symptoms are:
· pain, redness and inflammation at the injection site;
· headache and slight fatigue;
Nausea and vomiting (especially in adolescents).
Currently, there are fewer contraindications, as purified antigens are used. If adverse reactions occur, you should consult a doctor to prescribe symptomatic therapy.
Is there a fever after vaccination?
A slight increase in temperature after vaccination should not cause alarm. This is how the child’s body can react to the injected substance. The process of processing vaccination antigens and the formation of immunity to the disease occurs. Components are released that cause an increase in temperature.
It should be remembered that any manifestations are individual in nature. Adults and children may react differently.
If the temperature does not rise above 37.5 degrees and lasts no more than 3 days, there is no need to consult a doctor. This is considered a normal reaction of the body. Fever, as a reaction to vaccination, usually appears after 5-7 hours, in some babies the next day. If the temperature lasts longer and an increase is noted, you should seek help, as there may be other causes for this symptom.
How many vaccinations are given against tetanus?
In the children's clinic, during preventive examinations, parents are informed when tetanus vaccinations are given. Full vaccination of children includes the administration of a total of 6 doses of the drug in accordance with the recommendations of the childhood vaccination schedule:
· 3 doses during the first year of life at 45-day intervals, starting at 3 months of age (3.4, 5 and 6 months), administered as a combination pentavalent or hexavalent vaccine;
· after a year, a booster (additional) dose is administered - in the form of a pentavalent combined vaccine;
· 6-7 years another dose that uses low antigen load vaccine in combination with diphtheria toxoid and low antigen load pertussis component (dpaT), standard combination (DPaT) can also be used.
· At 14 years of age, another dose is given using a low-load vaccine (diphtheria toxoid antigen plus tetanus pertussis toxoid (dpaT)).
How often do you get a tetanus shot? Revaccination is offered every 10 years to the entire population.
Why is DPT vaccination given during pregnancy?
This vaccine is given to pregnant women as it protects the baby from whooping cough immediately after birth. After vaccination, your body will have high levels of antibodies, which will be passed on to your baby, protecting him from whooping cough from birth until he can get his first vaccine. The earliest age at which a baby can be vaccinated is 2 months. More information about the infant vaccination schedule can be found in the childhood vaccination calendar.
Importance of vaccination
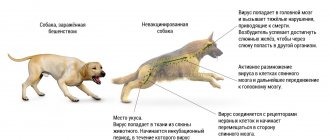
The causative agent of tetanus - clostridium (tetanus bacillus) is widespread everywhere and is resistant to environmental influences. When the rod enters a child’s body, it releases an exotoxin, which is highly damaging. The course of the disease is lightning fast and very fast. The increase in symptoms occurs instantly, and mortality rates are very high.
Treatment of tetanus is carried out inpatient conditions in intensive care wards. Muscle relaxants are prescribed to relieve seizures. Quite often, patients are transferred to artificial ventilation. The pH level of the blood is adjusted with medication, and support for the functioning of the cardiovascular, excretory and respiratory systems is also required. To prevent secondary infection, antibacterial therapy is carried out.
Parents must clearly understand that even modern medicine is not able to cope with the disease in all cases. Mortality rates remain quite high. The only correct solution is vaccination against tetanus.
ADSM vaccination: contraindications in adults and children
There are circumstances why children are not vaccinated. Among them:
- intolerance to vaccine components or hypersensitive reaction of the body;
- fever (for two weeks);
- at birth the child was underweight;
- pathologies of the respiratory system, cardiovascular, genitourinary during exacerbation;
- hemolytic disease;
- delay in fetal development;
- autoimmune diseases;
- intestinal infection, ARVI, bacterial intoxication a month before vaccination;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- preoperative condition;
Before vaccinating parents, the doctor is obliged to clarify whether the child has one of the contraindications. If there are coincidences on at least one point, children should not be vaccinated.
You should not get vaccinated without consulting a doctor, as the consequences can be unpredictable. The composition of the vaccine is quite specific, so the drug can provoke a severe allergic reaction.
Regarding adults, the list of contraindications is small, but still exists. You should refuse vaccination if:
- pregnancy;
- weakened immune system;
- allergies to medications;
- acute viral or chronic disease.
Warning for the unvaccinated
After all of the above, we can say with complete confidence that a tetanus vaccine is necessary. This is the only way to prevent the disease and all the complications it can bring.
In addition, depending on the dose, the drug will provide immunity against other diseases dangerous to children. The charts, developed by experts, are designed to cover the most prominent risks for each age group.
If in doubt, consult your general practitioner or pediatrician. Experts consider immunization for each case individually, and also warn whether there are any contraindications for delaying or not completing doses.