Home » Articles » Swollen hand after IV drip: what to do and should you call a doctor?
Prescribing a drip for alcohol intoxication is quite common, since drip injections act much faster than drugs given through injections or tablets. This method allows you to introduce a large amount of liquid into the body over a long period of time, as well as regulate the speed of its supply.
With the help of droppers, toxins are removed from the blood and the water-salt balance is replenished. A fairly harmless procedure sometimes has unpleasant consequences in the form of swelling of the arm, the mere sight of which can frighten the patient.
Causes of swelling
The body’s unpleasant reaction to a drip has several causes, depending both on the professionalism of the health workers and on the physiological characteristics of the patient. Even by the speed of development of edema at the site of needle insertion, an experienced doctor can quickly determine the causes of its occurrence and immediately provide assistance.
Hitting the vein
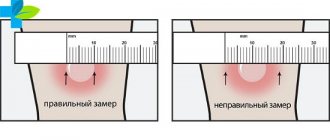
Most often, swelling is caused by the injected drug getting into soft tissue. It happens that the needle passes right through the vein or does not enter it at all, then instead of blood, the medicine penetrates into the peripheral tissues, causing instant swelling. The hand swells literally before our eyes, increasing in size two to three times, pain, burning sensations, and numbness of the limb occur.
On the one hand, the inexperience of the health worker may be to blame: in order to find a vein and accurately hit it, certain skills are required. However, it happens that, by nature or from constant injections, the patient’s veins are difficult to palpate, then the introduction of an IV becomes a real test for all participants in the procedure. Swelling if the medicine gets under the skin is eliminated quickly enough and does not pose a serious threat.
Abscess
The situation is much worse with abscesses that arise as a result of violation of the basic rules of asepsis. Any little thing can cause the formation of a purulent cavity under the skin: poor treatment of the skin at the site of needle insertion, insufficient sterility of consumables, non-compliance with the sanitary and anti-epidemiological regime in the treatment room.
Subcutaneous inflammation does not occur as rapidly as edema, so it will not be detected earlier than a few hours after the intravenous injection. Symptoms of an abscess include redness and swelling of the arm in the area of the injection, accompanied by pain, as well as an increase in body temperature. The inflammatory process threatens serious complications, so at the first signs it is necessary to urgently consult a surgeon.
Allergy
When using a dropper, swelling of the arm can also be caused by an allergy to the drugs used for injection. Externally, an allergic reaction manifests itself in the form of pinpoint redness like “urticaria” or tension and itching of tissues, as with Quincke’s edema. The first symptoms appear within half an hour and intensify progressively, which in itself is an alarming “bell”.
Most often, allergies are observed with the administration of certain types of antibiotics, analgesics, and sulfonamide drugs. Typically, patients warn doctors about contraindications for medications known to them, but there are situations when the patient is not aware of individual intolerance to a particular drug.
What to do if your hand is swollen after an IV drip
There are diseases for which conventional injections may not be effective. In these cases, an IV is placed. The advantage of drip infusion is that the medicine enters the bloodstream over a long period of time.
Another positive point is that the drug administered by drop method begins to act faster, which can be very important when providing emergency care. However, there are also unpleasant consequences of drip infusion.
In this article we will consider the question: if your hand is swollen after an IV, what to do and how to relieve the swelling.
Swelling when the medicine gets into soft tissues
One of the most common causes of swelling is that the drug gets into the soft tissue of the arm rather than into a vein.
This can happen if the needle moves during the process, or if the nurse initially placed the IV incorrectly. In this case, swelling appears instantly, the arm swells from the elbow itself.
In this case, the limb can increase in size by 2-3 times. Subsequently, pain and stiffness of movement appear.
Post-injection infiltrate
Another complication after an injection may be a post-injection infiltrate (bump). A subcutaneous lump appears at the injection site, which subsequently resolves on its own. However, if the lump is large, you should still take some measures to relieve the swelling.
Abscess
Sometimes, if the rules of asepsis are not followed, an abscess may develop. If, after an intravenous injection, your arm becomes swollen and red, your temperature rises, and the site of the swelling causes pain, a purulent cavity (abscess) may have formed under the skin. In this case, it is necessary to urgently contact a surgeon, because this type of swelling does not resolve on its own.
Allergy
An allergic reaction may occur when using certain medications. It usually occurs in the form of urticaria or Quincke's edema. Most often, an allergic reaction becomes noticeable 20 to 30 minutes after the injection. Allergies often occur to analgesics, antibiotics (penicillin group), and sulfa drugs.
Is swelling of the hand after an IV dangerous?
If the swelling of the hands after an IV drip appears as a result of the medicine getting into the soft tissues or a lump has simply formed, then they themselves are not dangerous, but they do bring some discomfort. If you take certain measures, they will resolve within 3-5 days.
The most dangerous complication after an injection is an abscess. If not treated promptly, it can cause serious complications.
Causes
Most often, a vein hurts after an injection in cases where the antiseptic technique or procedure was violated during the administration of the drug.
If the injection site turns red and begins to swell, the problem may lie in insufficient treatment of the injection site with alcohol. In this case, there is a high risk of infection.
If your arm hurts and is swollen, after the injection the problem may lie in the following violations of the procedure:
- incorrect choice of needle length and diameter;
- too large a volume of the drug;
- high speed of solution introduction;
- vein injury.
In addition, the formation of a hematoma, and sometimes an abscess, can be caused by piercing through or not bringing the needle to the vessel, which is why the drug is injected not into a vein, but into fatty tissue or under the skin. Rapid administration of certain solutions can provoke inflammation and spasm of the walls of blood vessels, as well as narrowing of their lumen. These include:
- Doxycycline hydrochloride.
- Potassium chloride.
- Calcium chloride.
- Glucose solution 40%.
In addition, when administering solutions of drugs such as Diclofenac, Ketorol and Analgin, aseptic inflammation of the vein may develop. In this case, the vein becomes inflated, which leads to pain. The arm may begin to hurt after an intravenous injection if the person did not hold the cotton wool at the injection site for the prescribed amount of time.
In this case, there is a high risk of discomfort and hematoma.
If the patient was given a drip through an intravenous catheter, which was not removed for a long time, after its elimination, undesirable reactions may appear. If the vein is swollen and painful after removing the catheter, this indicates damage and inflammatory damage to the vessel wall.
What to do
If the area swells or swells slightly after the injection, or if small bruises occur, no treatment is required. Such defects disappear in 1-3 days. To speed up the process, you can apply cold compresses to the injection site.
Large hematomas can become infected, which can cause the formation of cellulitis or an abscess. Thus, if such a defect occurs, it is necessary to consult a doctor to prescribe treatment.
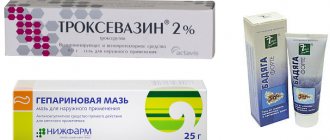
To speed up the resorption of the hematoma, it is recommended to use drugs containing blood thinning components. Gels and ointments are often prescribed, including substances such as heparin, diclofenac, troxerutin, etc.
These active components are contained in large doses in such preparations as:
What do you think are the most important factors when choosing a medical facility?
- Trust in the doctor 72%, 368 368 - 72% of all
- Modern equipment 15%, 75 75 — 15% of all
- Advice from friends 5%, 25 25 - 5% of all
- Cost of services 4%, 20 20 - 4% of all
- Close location to home 4%, 19 19 - 4% of all
- 7 - 1% of all
- Lyoton.
- Indovazin.
- Troxevasin.
- Heparin ointment.
When an abscess forms, the application of Vishnevsky ointment may be recommended. Such compresses will speed up the opening of the abscess. If there is severe local swelling, it is advisable to apply gauze soaked in a 50% aqueous solution of Dimexide to the affected area.
Polyethylene is applied over the compress to prevent the fabric from drying out quickly.
In addition, phlegmon and abscesses that form after an injection may require a course of antibiotic therapy. This is especially important if after the injection there are signs of general intoxication, incl. weakness, fever, chills, etc.
If calcium chloride was accidentally injected under the skin, the doctor should inject the area of swelling and redness with Novocaine solution. This will suppress the toxic effect of the drug on soft tissues and reduce the risk of necrosis.
When identifying signs of phlebitis, i.e. severe inflammation of the vein wall, the patient should undergo treatment in a hospital to reduce the risk of complications, incl. phlegmon and thromboembolism.
For large abscesses and cellulitis, which are associated with a high risk of sepsis, surgical treatment may be required. In this case, the defect cavity is first opened with a scalpel, the pus is removed and treated with an antiseptic. After this, a sterile bandage is applied.
How to avoid pain
To reduce the risk of adverse reactions, it is important to follow the rules for intravenous injections. It is important to carry out antiseptic treatment correctly, select the volume and diameter of the needle, control the speed of solution administration, etc.
To avoid unpleasant sensations, immediately after injections you should leave the cotton wool pressed to the injection site and bend your arm at the elbow. You need to hold your hand in this position for 15 minutes. This will reduce the risk of hematoma formation. If you have a tendency to bruise after injections, you need to apply iodine wall to the skin.
In some cases, in order to avoid the occurrence of large hematomas and other complications, it is recommended to apply cold compresses. For preventive purposes, ointments containing blood thinning substances can be used.
Source: https://Ukol.expert/posledstviya/posle-ukola-v-venu-bolit-ruka-chto-delat
Other causes of lumps, hematomas and lumps
We have already figured out that everything is quite simple: inserting a needle into a vein is itself an injury. This injury may be accompanied by others:
- When a blood vessel is damaged by a needle, blood enters the intercellular space. There it thickens and changes color, forming hematomas, which usually resolve on their own.
- When a drip is placed, for example, for alcohol, quite often the tissue around the vein is injured. This causes scars to form, allowing blood to leak into the tissue. In this case, bumps form.
- Rupture of the tissue around the vein leads to penetration of the medicine under the skin, causing seals to form.
- Poor blood clotting causes serious hemorrhages.
- If the needle is too long, it may puncture all the way through the vein. This also leads to the appearance of hematomas and compactions.
- If the needle is placed carelessly or incorrectly, the vein wall may be damaged.
If pain or swelling occurs during IV placement, you should contact your nurse immediately. There were cases when patients simply endured pain, which ended very badly.
Departure is paid separately - from 550 rubles
Request a call
Call:
+7 (499) 455-08-05
Possible complications
If you do not give importance to the swelling of the hand after an IV and do not report the painful sensations to the doctor, a harmless hematoma can develop into a serious pathology.
- Phlebitis occurs when the wall of a vessel becomes inflamed due to injury from a needle or medication. Phlebitis can be caused by an allergic reaction to the drug. Symptoms of the pathology: the skin turns red and the temperature in the damaged area rises; Red stripes appear along the line of the vein, the arm is very sore and swollen. The disease is treated on an outpatient basis.
- Thrombophlebitis is the blockage of a blood vessel by a blood clot. The cause of the pathology is also damage or infection in the vein. The hand swells, the needle insertion site hardens, the skin turns red and the temperature rises. Blood clot rupture is especially dangerous, so it is important to immediately consult a doctor at the first symptoms.
- Thromboembolism is a blockage of a vein by a blood clot that interferes with blood flow. The symptoms are as follows: the formation of a purulent lump, severe swelling of the arm, throbbing pain, fever. The disease is treated with ointments and antibiotics, which provoke the opening of the cone.
- Cellulitis is a purulent inflammation that appears as a result of improper insertion of a needle into a vein, as a result of which the medicine enters the fatty layer. The source of the disease is not limited, it spreads throughout the tissues. Symptoms: intoxication, severe pain and swelling, severe fever. At first the infiltrate is hard to the touch, but gradually softens. This disease requires emergency surgery and antibiotics.
If symptoms such as fever, sharp throbbing pain and purulent formations appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-medication may lead to the development of one of the described pathologies.
We missed a vein and the arm became swollen - HelpDiseases
Intravenous injections often result in various complications. These include nerve damage, bruising, and allergies. You can often find a lump on your arm after an injection into a vein. Sometimes it does not pose a health hazard, but sometimes it is a sign of dangerous consequences.
Lump after injection into a vein photo
If a lump appears in the vein at the injection site, it is recommended to seek medical help in any case.
If this is not possible, there are no signs of inflammation (fever, severe swelling), and the pain is practically not felt, you can try to get rid of the lump yourself.
But it is important to remember that if the infiltration does not disappear within 2-3 days, or the condition worsens, a visit to the doctor is required.
Minor swelling can be easily treated with iodine mesh. An alcohol compress also helps. It is important to apply it to skin covered with oily cream to avoid burns. The most common treatment for post-injection infiltration is heparin ointment. Preparations based on dimexide and troxerutin cope well with seals.
We must not forget that even a seemingly harmless lump on a vein after an injection can turn out to be incredibly dangerous to life and health.
Source: https://spravkabolezn.ru/ne-popali-v-venu-i-ruka-opuhla.html
How to treat
Before treatment, you need to make sure that the lump or lump after the IV does not show signs of purulent infection. Remember, if you have a fever, severe swelling and throbbing pain, you should never self-medicate! You must immediately call a doctor, otherwise the consequences will be very sad.
If we are definitely not dealing with an abscess, then we can cope with the swelling on our own. Firstly, if the swelling appears due to improper placement of the needle and the medication getting into the soft tissue, you need to call a nurse. She will reposition the needle and give some recommendations to combat swelling. Both medications and folk remedies can help.
Drug treatment
For therapy, ointments that contain heparin and/or troxerutin are usually used: Vishnevsky ointment, Ketanov, Methirulacil, Heparin ointment, Dimexide. Apply ointments every hour.
These drugs have contraindications:
- ulcerative-necrotic skin processes;
- increased vascular permeability;
- People with reduced blood clotting should use ointments with caution.
Dimexide is used for compress. To do this, mix the drug with vodka 1:1, and then dilute the mixture with distilled water 1:4. The lump needs to be lubricated with a rich cream (you can use baby cream) to avoid burns. Soak cotton wool or gauze in the solution, apply to the swollen area and cover with film. Leave the bandage on for 7-8 hours.
Among the medications used to combat swelling, Detralex and Magnesia for compress are also used. Never neglect the iodine network - although it is simple, it is a proven and effective remedy. An iodine mesh should be applied to the damaged area of skin 1-2 times a day, at approximately equal time intervals. Be sure to make sure you are not allergic to iodine.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is rich in ways to combat swelling after a drip from binge drinking in Moscow. They mainly use compresses, the most popular of which we will now look at:
- Alcoholic. The compress is prepared from water and alcohol, which are mixed in equal proportions. To prevent skin burns, it should be lubricated with a rich cream and only then apply a bandage. We soak a piece of cotton wool, cloth or a cotton pad in the solution and apply it to the seal. Cover the top with film or a plastic bag, add another layer of cotton wool and bandage it. Do not remove the bandage for 5-6 hours.
- Compress made from burdock or cabbage leaves. Take a cabbage or burdock leaf and crush it in your hands until it becomes moist. Then we apply it to the swelling and bandage it. Leaves need to be changed as they dry out.
- From aloe. Aloe is a plant known for its anti-inflammatory effect, so a compress from it will help quickly relieve swelling. The plant leaf must be washed, cut lengthwise into two parts, and the pulp crushed. Apply the resulting paste to the affected area of skin and secure with a bandage. The bandage can be left on overnight.
- Vegetable compresses. Take a potato, cucumber or carrot and grate them. Wrap the paste in gauze and keep it on the inflamed area until the compress dries.
- Honey cakes. Honey helps the seal after the drip to quickly dissolve. To prepare the flatbread, take 1 tablespoon of honey and mix it with a little flour. You can also apply the cake at night.
If hand swelling is accompanied by an abscess, consult a doctor immediately. Self-treatment can lead to even greater problems. The doctor will prescribe a course of therapy or open the “bump” to clean out the pus from it.
After an injection into a vein, the arm hurts, what to do: intravenous, swollen and swollen
Intravenous injections often result in various complications. These include nerve damage, bruising, and allergies. You can often find a lump on your arm after an injection into a vein. Sometimes it does not pose a health hazard, but sometimes it is a sign of dangerous consequences.
Causes of the phenomenon
Such a defect is called post-injection infiltration. It is a subcutaneous seal at the injection site. Usually, bumps appear when sanitary standards are not observed during the injection.
Another cause is an incorrectly selected needle. Thus, a tool longer or shorter than necessary may pierce the vein or not reach it. Then the medicine gets under the skin and forms inflammation in the fat layer or muscle. A needle that is too thick or blunt can also damage the vessel.
Some solutions require rapid or, conversely, slow administration. If this rule is not followed, complications are possible. Patients who regularly receive catheters suffer from lumps at injection sites. Sometimes the reason lies in the poor quality of materials.
httpv://www..com/watch?v=embed/rNI89SbjqB0
Most often, this problem is caused by oil-based drugs, as they are less absorbable. Carrying out injections on your own increases the risk of infiltrate formation. Thus, diabetics and drug addicts are at risk. People with weakened immune systems also go there.
What is the danger?
If a vein swells and hardens after an injection, it may simply be a hematoma that will quickly resolve on its own. But you shouldn't hope for it. You should definitely consult a doctor, because such a tumor can be fatal:
- Phlebitis. Inflammation of the vessel wall due to damage by the needle or irritation by the components of the drug. Sometimes it occurs due to an allergy to the drug. With phlebitis, the skin at the site of injection of the solution turns red and becomes hot. Red stripes appear along the inflamed vessel. I feel pain in my hand. This disease requires outpatient treatment, including conservative and physical therapy.
- Thrombophlebitis. Blockage of a vessel by a thrombus. Occurs against the background of inflammation of the vein due to its damage or infection. It is characterized by swelling of the limb and the appearance of a painful lump. The skin over the affected vessel turns red. The temperature rises. The situation is dangerous if a blood clot breaks off and enters the pulmonary artery. For treatment, tablets, ointments and compresses are used. In severe cases, surgery is indicated.
- Thromboembolism. A more dense blockage of the vein, which interferes with blood flow. At the same time, the pulse disappears, the skin of the hand becomes cold and loses sensitivity. The limb swells, loses mobility, and there is a risk of developing gangrene. Patients with such symptoms require immediate hospitalization. Patients are given heparin intravenously and given symptomatic treatment.
- Abscess. Tissue death occurs when pathogenic bacteria enter the bloodstream with a needle. If a lump swells after an injection into a vein and it is soft when pressed, it means that pus has accumulated in it. In this case, severe swelling, throbbing pain, and increased temperature occur. For an abscess, antibiotics and ointments are prescribed to provoke the opening of the infiltrate. In extreme cases, an incision is made into the affected area and drainage of pus and necrotic tissue.
- Phlegmon. It develops when the drug is administered not into a vein, but into the fatty layer. It is a purulent or putrefactive inflammation. In this case, the lesion is not limited, but spreads throughout the tissues. Patients suffer from signs of intoxication, a significant increase in temperature, and sharp pain when moving the hand or pressing on the seal. The cone is initially hard to the touch, but gradually softens, and liquid contents are felt in it. With such a pathology, surgical intervention and the use of antibacterial drugs are mandatory.
Any of the listed pathologies can be harmful to health and pose a danger to life.
Surgical intervention
Whether surgical intervention is necessary to eliminate varicose veins is decided by a phlebologist after a thorough examination and the necessary diagnostics.
For varicose veins of the first stage and the initial second stage, vein treatment with injections is used. More advanced stages of the disease may require surgical treatment of varicose veins.
When treating varicose veins surgically, the following principles are distinguished:
- Elimination of pathology caused by the discharge of blood into the superficial veins from the deep ones;
- Elimination of superficial vessels that have been dilated by varicose veins;
- Carrying out operations using the traditional method.
Any type of operation has one goal: removal of the affected areas of the superficial veins in which congestion is observed.
It is advisable to treat varicose veins with injections in the initial stages of the disease, if surgical intervention is not possible or if the venous mesh covers too large an area of the skin surface.
Types of injections
1. Systemic injection
This is the injection of the drug into the outer upper quarter of the buttock. These are the types of injections that are worth doing, as they are as safe as possible and very effective.
2. Local injection
Often, athletes want to inject an anabolic steroid into a muscle that has been trained or will still be trained. Such injections can be made with a two-cc syringe or an insulin syringe. This is basically how Winstrol, testosterone suspension or propionate is administered.
In principle, you can use local injections when administering long esters of the male hormone or nandrolone. But it is not advisable to do this with other drugs. Depending on your experience with injectable medications, they can be injected into almost any muscle.
However, beginners should limit themselves to deltoids or quadriceps.
3. Subcutaneous injection
This is how peptides and somatotropin are most often administered. To do this, you need to take your fingers into the fat fold on the abdomen, below the navel. In this case, the needle should be inserted at an angle of 45 degrees.
If drugs are administered incorrectly, various complications can occur. The most harmless among them is compaction (infiltration). This is a hard lump that appears at the injection site.
The seal dissolves quite quickly on its own. The worst case scenario is an abscess, which is a purulent inflammation of tissue.
Most often, an abscess occurs due to non-compliance with safety rules regarding sterility.
Ways to eliminate swelling
If immediately after an injection into a vein your arm swells and the drug begins to enter the tissue instead of the vein, you need to call a nurse. She will adjust the needle and give the necessary recommendations for relieving swelling. This can be either medication or traditional recipes. When a compaction (bump) forms, the same means can be used.
The medications usually prescribed are:
- Troxivazin;
- Liaton;
- Heparin ointment;
- Magnesia in ampoules for compress;
- Dexamethosone;
- Detralex;
- Dimexide.
Ointments are applied every 60 minutes. The compress with magnesium is changed as it dries. An iodine grid is also drawn at the site of swelling.
You can use the following folk remedies yourself:
- alcohol compress - mix alcohol and water in equal proportions, you can also use vodka. Moisten a piece of cotton wool or gauze with the solution, place it on the swelling, put a plastic bag on top and again a layer of cotton wool. Wrap with a bandage and leave for 5-6 hours;
- compress of cabbage leaves - mash the leaf so that it begins to ooze a little. Apply to the swelling and wrap with a bandage. Change when dry;
- aloe compress – cut the leaf into two parts, apply to the place of swelling;
- compresses made from carrots, potatoes and cucumbers. Grate the selected vegetable and wrap it in one layer of gauze. When dry, change;
- compress with Vishnevsky ointment - apply the ointment to several layers of gauze, cover with polyethylene on top and secure with a bandage. Keep for about 6 hours;
- honey cakes – 1 tbsp. Melt honey in a water bath. Mix with flour or rye bread. Apply to the area of swelling overnight. If your hands are slightly swollen after a drip, you can simply spread honey on them.
If an allergic reaction to the administered drug develops, it is necessary to take an antihistamine (Suprastin, Diazolin, Loratadine). A cold compress can be applied to the swollen area.
If an abscess occurs, it is better not to self-medicate. The doctor will prescribe the necessary course of therapy, and in some particularly advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Light swelling of the arm after an IV is not dangerous. They can go away on their own or with the help of some folk remedies. However, if the swelling does not resolve over a long period of time and is accompanied by pain and fever, then you should consult a doctor. Some serious complications can be very dangerous and therefore require timely treatment.
A bruise after an injection into a vein can have a different shade in each case: purple or dark purple. When it is absorbed, the color changes to green or yellow. As a rule, such a complication after an injection disappears on its own after one or several weeks. To speed up the resorption process, it is necessary to use special ointments and folk remedies.
For example, you can trust a trusted nurse in this matter. Most people, before visiting a specialist, get reviews from their acquaintances, friends or relatives
It is the “light hand” of the nurse that indicates her professionalism, and this is important: pain does not occur after the procedure, as well as visible marks on the skin
In any case, it is necessary to control the injection process and monitor your feelings. If there is pain, you should tell the nurse who gives the injection. In this case, we can indirectly assume that the posterior venous wall was injured by the needle.
Another method of preventing such complications is the correct application of cotton wool to the injection site and the correct position of the hand.
So, the cotton wool should firmly press the place where the injection was performed, and the arm should be bent at the elbow joint. It is recommended to hold this position for 5-10 minutes to prevent a hematoma from forming.
If the injection is given to a child who, due to his immobility, will not be able to hold his hand in this position, he will be given a tight bandage.
Source: https://MedLazaret.ru/kardio/lopayutsya-veny-pri-kapelnice.html
How to prevent swelling
Of course, preventing swelling is much better than dealing with it later. Here are some recommendations for preventing hand swelling after an IV:
- When installing an IV, you need to relax as much as possible, because tense muscles are easier to damage.
- To prevent the drug from getting into the soft tissues, the medicine must be administered slowly and smoothly.
- To quickly stop bleeding, keep the cotton swab with alcohol in place for at least 10 minutes after the procedure.
- Make sure the needle and skin are sterile, especially for at-home IV drips.
- There are doctors with a “light hand”; it is advisable to go to them for the procedure. Such a doctor will insert the needle correctly and almost painlessly, which will reduce the risk of swelling. You can call such a professional to your home.