Is it possible to drink alcohol with antibiotics?
Almost all instructions for the use of antibacterial drugs contain a note regarding the prohibition of drinking alcohol during treatment. However, actual side effects are rarely reported. Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages leads to a decrease in the protective functions of the immune system. The patient's body stops fighting infections. Even “approved” antibiotics become ineffective.
Excessive alcohol consumption can also impair the absorption of antibacterial drugs taken orally. During the metabolism of ethyl alcohol, acetaldehyde is produced. The component causes nausea and headaches (popularly called a “hangover”). People who take antibiotics in tablet form also experience digestive side effects. Drinking alcohol during antibiotic therapy can lead to exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease and a general deterioration in concentration and coordination.
Consequences of taking antibiotics and alcohol at the same time
In most cases, alcohol does not affect the effectiveness of antibiotics. However, some combinations may cause unpleasant side effects. Ethyl alcohol is broken down in the liver by special enzymes. Some antibacterial drugs are metabolized by similar enzymes. The liver of people who drink alcohol too often cannot metabolize antibiotics. At best, the drug becomes ineffective, at worst, the liver cells are destroyed.
Disulfiram-like reaction is one of the most common side effects of simultaneous use of alcohol and antibiotics. The patient complains of the following complications:
- nausea and vomiting;
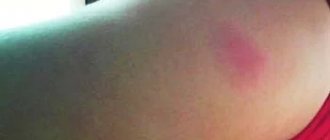
- skin redness;
- stomach cramps;
- colic;
- headache;
- cardiopalmus;
- labored breathing;
- tremor.
Symptoms of the antabuse effect (the second name of the pathology) occur within 15-30 minutes after ethanol and medications enter the body. The intensity of the pain increases over several hours and reaches its peak after 8-12 hours. The danger of a disulfiram-like reaction is that unpleasant symptoms can occur even 1.5-2 weeks after quitting alcohol. The antabuse effect can be fatal. It is extremely important to seek professional medical help when the first symptoms develop. Even weak alcohol can cause complications.
Ethanol depresses the central nervous system. Medicines containing metronidazole also impair nerve conduction. The combination of the two components leads to:
- drowsiness;
- depression and confusion;
- dizziness;
- motor retardation.
The additive effect is especially dangerous for older people, drivers, and knowledge workers.
The consequences of mixing alcohol with antibacterial drugs directly depend on individual factors. For example, women experience side effects much more often than men. Due to metabolic rate disturbances, older people do not tolerate disulfiram-like reactions well and suffer from complications longer. Patients who take antidepressants, opioid painkillers, muscle relaxants, and anticonvulsants do not tolerate the simultaneous use of antibiotics and alcoholic beverages.
What are the dangers of drinking alcohol after a binge drip?
Drinking something alcoholic right after a medicinal break from binge drinking is tantamount to provoking a second heart attack after the one you just suffered - it is obvious that this will not end in anything good.
Of course, in the case of repeated drinking of alcohol after a drip, everything is not as critical as in the example of a heart attack, but in general these situations are similar:
- the body was first subjected to the intense toxic effects of alcohol, as a result of which many of its internal functions were disrupted, including the ability to self-heal;
- then the toxins were neutralized;
- soon the patient swallows a new portion of the same poison that just nearly brought him to the grave.
In this case, due to the weakening of the body, repeated intoxication will be many times more pronounced, and the negative consequences of such poisoning will be larger and much more critical.
Usually, when drinking alcohol again immediately after a restorative drip, the same organs and systems that were affected the first time are affected. This means that if the heart suffered the most during a binge, then when drinking alcohol again, it will receive a new, but much more noticeable toxic blow. The situation is exactly the same with the liver, kidneys, stomach and all other organs that usually suffer from heavy drinking.
Another danger of drinking alcohol after emergency sobering up is the high risk of developing mental disorders. A weakened body turns out to be much more sensitive to the effects of alcohol, and therefore intoxication occurs faster, and its degree is completely disproportionate to the amount drunk. As a result of this increased susceptibility to alcohol, often from one glass of vodka full-fledged hallucinations, unmotivated aggressiveness, delusions and other mental abnormalities suddenly arise.
When can you drink alcohol after taking antibiotics?
A person who does not suffer from chronic diseases and has not undergone radiation or chemical therapy within the last year can drink a small portion of alcohol one day after completing antibiotic therapy. Patients taking metronidazole should avoid drinking alcohol for 48 hours after the last tablet or injection. After tinidazole therapy, alcohol is prohibited for 72 hours. Patients who suffer from cirrhosis and hepatitis are advised to avoid alcoholic beverages for at least two weeks.
Important! Dietary supplements, natural medicines, sprays and mouth rinses may also contain ethanol. It is worth consulting with your doctor regarding the advisability of simultaneously taking antibiotics and using ethanol-containing drugs.
Complications and consequences
If a patient ignores medical recommendations and drinks alcoholic beverages (even beer) during a course of antibiotic injections, the possibility of the following complications cannot be ruled out:
- discomfort and pain in the liver area;
- severe nausea and periodic bouts of vomiting;
- headaches turning into migraines;
- frequent dizziness, loss of coordination of movements;
- gastrointestinal disorder.
In most cases, the occurrence of such complications is due to the fact that antibiotics contain potent components that affect the human immune system and weaken it, as a result of which sensitivity to the harmful effects of alcohol increases several times.
To minimize the risk of unwanted complications, it is recommended to abstain from drinking alcohol for 10 days after the end of antibacterial therapy.
When can you take antibiotics after drinking alcohol?
Antibiotic therapy is often prescribed for exacerbation of diseases. Should I stop taking the medicine if I have alcohol in my body? The final decision is made by the doctor, based on the medical history and health status of the patient. If the benefits of antibiotic therapy outweigh the potential threats, then the first injection is given without taking into account the time that has passed since the last time you drank alcohol. If the underlying disease does not directly threaten the patient’s life, then the start of a course of antibiotic therapy is postponed until ethanol is completely removed from the body. The exact timing depends on the type and amount of alcohol consumed.
Doctors categorically do not recommend giving antibiotics to people who are acutely intoxicated. In a person who drinks large amounts of alcohol over a short period of time, liver enzymes are inhibited. This means that the medicine will not be able to be metabolized. The amount of active substance in the blood will increase. The risk of side effects will increase.
If antibiotic therapy is required for a person who has been abusing alcohol for a long period of time, a blood test will be performed first. The liver enzymes of chronic alcoholics break down medications too intensively. As a result, the concentration of active components in the blood decreases. It is necessary to review the dosage of the prescribed drug and conduct a test for resistance to antibacterial agents.
Types of injections
Medications that can quickly stop the craving for drinking alcohol can be administered in several ways. There are the following types of injections for alcohol dependence:
- intravenous
- intramuscular
- injection under the shoulder blade
- injection into the liver
The choice of method of drug administration is made taking into account the patient’s contraindications and his individual characteristics of the body. Only the doctor selects the drug that is suitable for the patient. Immediately before its administration, an alcohol-dependent person is given a hot injection, which contains vitamins and magnesium. This action is necessary to eliminate a hangover.
Injection into a vein
The most common, due to its high efficiency, injection encoding method. However, intravenous administration of drugs that relieve binge drinking has a number of contraindications. This coding method is not used if the patient’s medical history includes the following pathologies:
- Mental illness
- Disturbances in the functioning of the brain (encephalopathy, atherosclerosis, intracranial hypertension, etc.)
After administration of the medicine, the patient’s heart rate increases, a panicky fear of death appears, and a feverish state is present - the fever is replaced by chills. In some cases, confusion or hallucinations are noted. These signs will disappear on their own an hour after the injection, and the patient will have to sleep for some time.
Intramuscular coding
This coding is considered the most gentle. When performing it, drugs are used that block opioid receptors in the brain, as a result of which a person ceases to experience pleasure from alcoholic beverages, so drinking them loses its meaning. The effect of the drug develops after administration for several hours. The best results of this coding are achieved if a psychotherapy session is carried out simultaneously with the injection. The advantages of intramuscular administration of drugs that eliminate alcohol dependence are the possibility of doing it at home and the absence of adverse reactions.
Injection under the shoulder blade
The basis of this method is the introduction of a gel-like drug under the shoulder blade, directly into the subcutaneous layer. The procedure is quite painful, so it is performed under local anesthesia. The gel remains at the injection site for a long time and gradually releases its main active substance into the bloodstream, which blocks the liver’s production of enzymes that break down ethanol. If these biologically active substances are insufficient, even a small amount of alcohol can provoke the appearance of signs of a severe hangover.
Injecting medication into the liver
Coding for alcoholism with an injection into the liver belongs to the category of aversive techniques aimed at inducing disgust. This method of eliminating alcohol addiction has recently gained great popularity due to its effectiveness. However, coding by injection into the liver is rarely used in practice and with great caution, since it often provokes the development of serious complications.
What medications are strictly prohibited from taking alcohol?
There are several specific antibiotics that directly interact with ethyl alcohol. Drinking any amount of alcohol is strictly prohibited during treatment with drugs from the list.
- Metronidazole: An antimicrobial agent most often prescribed to treat dental and vaginal infections. Metronidazole is added to external products intended for cleaning trophic ulcers and treating deep bedsores.
- Tinidazole: An antibiotic designed to fight simple infections. Included in drugs aimed at combating Helicobacter pylori.
- Cycloserine: prescribed for the treatment of tuberculosis, lung infections. In combination with ethyl alcohol it causes convulsions.
- Linezolid: Used to treat skin infections and is effective against bacteria that are resistant to other types of antibiotics.
Alcohol in combination with the above drugs provokes a sharp increase in blood pressure, headaches, and drowsiness. It must be remembered that side effects occur even if the antibacterial agent is used in the format of an external cream or gel.
What antibiotics are safe to drink alcohol with?
It is better to completely abstain from drinking alcohol during illness. However, medications from the list below do not have a negative interaction with alcohol:
- amoxicillin;
- azithromycin;
- ciprofloxacin;
- cephalexin;
- clarithromycin;
- clindamycin;
- levofloxacin;
- penicillin.
Antibiotics of the tetracycline group, including Doxycycline, have little interaction with alcohol. There is no need to worry about the development of a disulfiram-like reaction. However, ethyl alcohol significantly reduces the amount of tetracyclines in the blood. You must tell your doctor about the amount of alcohol you drink. The specialist will recalculate the dosage of medications and change the duration of the course of therapy.
Even if the doctor prescribes an antibiotic compatible with alcohol, it is necessary to take the treatment process responsibly. Any infection weakens the body, and the entry of ethyl alcohol into the blood will only worsen the resistance of the immune system.
Instead of strong drinks, it is better to drink clean water, eat right and get plenty of sleep. Alcohol interferes with the body's ability to absorb vital nutrients and increases blood sugar levels. And chronic alcoholism will even provoke constant relapses of infectious diseases, the development of multiresistance, bacterial resistance to all known types of antibiotics.