home
Our directions
Treatment room
Subcutaneous injections
The method of injecting medications into the fat layer under the top layer of skin is called subcutaneous injection.
Why choose us?
We will relieve pain and inflammation
Experienced staff with experience
All manipulations are absolutely safe
We give injections at home
- Prevention program as a gift
- Save on treatment up to 30%
- FAQ
Where is the subcutaneous injection given and how?
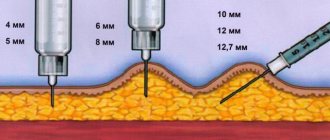
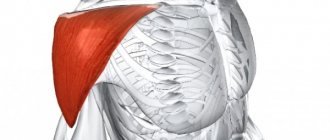
The outer surface of the shoulder, the area under the shoulder blade, the outer and front surface of the thigh, and the side of the abdomen are excellent sites for subcutaneous injection. In all these areas of the body, you can easily gather the skin into a fold and at an angle of 45 degrees and through a thin needle, smoothly inject the medication solution. Thanks to this method of drug administration, blood vessels and nerves are not injured.
Administering a subcutaneous injection requires special skill so as not to pierce the skin to the muscle or vice versa and introduce the medicine intradermally. All manipulations are carried out in compliance with the rules and requirements of sanitation, under sterile conditions.
The method of performing subcutaneous injections is quite simple, so many patients suffering from type 1 diabetes mellitus regularly self-administer insulin. The rate of absorption of the administered pancreatic hormone directly depends on the location of its entry. Therefore, subcutaneous insulin injections cannot be given as intramuscular or intradermal injections, as this can have a negative impact on the patient’s condition at any time. Patients with normal or underweight are recommended to use syringes with short needles.
Intradermal and subcutaneous injections differ in the method of execution and the depth of administration of medications. Subcutaneous injections are made to a depth of 15 mm. Allergy tests are performed using intradermal injections and the Mantoux reaction is checked.
The staff of our medical center will provide quality care at home or in the clinic’s treatment room. All our specialists have extensive experience and will perform the necessary subcutaneous injections almost painlessly. We are always ready to help you regain your health!
The cost of subcutaneous injections can be found out by calling the Healthy People clinic or looking at the website in the prices section.
Indications for injection of drugs under the skin
Most often, drugs are administered subcutaneously that do not have an irritating effect and are well absorbed into the subcutaneous layer. In special cases, the use of intravenous injections is allowed.
Also, this procedure is caused by the need to introduce an oily medicinal solution or suspension, the volume of which does not exceed 10 ml, into the muscle tissue. This is usually how anti-infective vaccinations are done.
Subcutaneous injection into the shoulder or thigh is a common way of administering medications due to:
- rapid absorption of the active substance;
- the ability to perform at home;
- no need to have a medical education.
The main thing is to have the appropriate skills and a little experience.
This method is suitable for:
- administration of insulin to patients with diabetes mellitus. For this, a syringe pen is usually used, but the technique does not change;
- treatment with growth hormones;
- introducing oil formulations and medicinal suspensions, which should not enter the circulatory system;
- administration of drugs intended for local anesthesia;
- administration of the drug when it is necessary to create a supply of the drug in the subcutaneous layer or maintain its concentration in the blood at a certain level for a long time. After all, drugs administered in this way are slowly absorbed into the tissues. As a rule, this takes at least 20-30 minutes.
Solutions of heparin and its derivatives are administered intramuscularly, because injections contribute to the formation of hematomas in the body.
When performing the procedure, you must remember: the volume of the drug administered subcutaneously should be small. Experts recommend using 5 ml at a time or not exceeding 10 ml.
Failure to comply with this condition causes excessive stretching of the tissues and the formation of an accumulation of cellular elements in them, consisting of a mixture of blood and lymph. It is better not to administer drugs that can cause necrosis or abscess at the puncture site subcutaneously.
To carry out the procedure, the following sterile equipment should be prepared:
- syringe;
- napkin;
- the drug is in a sealed state.
If the patient's condition is complex and emergency medical assistance is required, it is better not to perform the injection yourself.
Algorithm for intravenous injection
• Explain the purpose of the procedure to the patient. Clarify information about the drug, individual tolerance to the drug, and obtain his consent to the injection.
• Prepare a rubber pad and tourniquet.
Check the name of the drug, dose, release date, solution quality, color, presence of sediment.
• Wear a mask.
• Treat your hands according to the algorithm.
• Take a syringe (10-20 ml), put on a wide bore needle.
• Fill the syringe with medication. Change the needle. Release the air. Place the syringe in a sterile tray.
• Put on your glasses. Wash your hands. Wear gloves.
• Ask the patient to straighten his right (left) arm at the elbow joint. Place a rubber cushion under it.
• Place the tourniquet on the middle part of the shoulder with the loop down, first place a napkin or shirt sleeve under the tourniquet.
• Ask the patient to pump his fist and select the most filled vein.
• Treat the injection site with two balls soaked in 70° alcohol, first the large surface, then the injection site.
• Ask the patient to clench his fingers into a fist. With your left hand, pull the skin over the vein (fix it).
• Take the syringe so that the needle is facing up and pierce the skin parallel to the vein.
• Insert the needle into the vein (a “failure” is felt).
• Pull the piston towards you. If there is blood in the syringe, ask the patient to unclench his fist.
• Remove the tourniquet. Pull the plunger towards you (to check if you have popped out of the vein).
• Give the medication slowly. Monitor the patient's condition. During insertion, it is necessary that the puncture site does not swell, the tip of the needle is palpable in the vein, the patient does not feel a burning sensation at the insertion site and does not move his hand, as the needle may come out of the vein. Leave 1-2 ml in the syringe.
• Apply a cotton ball soaked in 70° alcohol. Remove the needle. Apply a pressure bandage over the ball and ask the patient to bend his arm at the elbow joint for 5-10 minutes.
• Place the syringe in the disinfectant solution. Remove gloves and wash your hands.
With the correct injection technique, complications are rare. If it is not followed, tissue necrosis, local inflammatory and general infectious processes can most often occur.
Needles and syringes should never be washed or thrown into the trash after use. They must be immersed in a disinfectant solution (0.1% Javelion, 0.5% sulfochloranthine) for 1 hour, after which they are collected in yellow bags and centrally disposed of as Class B medical waste.
How to inject yourself?
The procedure for self-administering a subcutaneous injection is as follows:
| Stage | Description |
| Removing the tip | Holding the prepared syringe by the central part, carefully remove the fixing tip. After this, you cannot put the syringe on the table and you need to make sure that the needle does not touch surrounding objects, the body or fingers. If this happens, the needle will have to be thrown away, even if you are sure that the surface was sterile. |
| Checking the syringe for air | To remove air, just lightly tap the flask with your finger and slowly move the piston so that droplets appear at the end of the needle. In some cases, the presence of a bubble is a mandatory condition and without it one cannot be sure of the effectiveness of the medicine. Then you will have to use another syringe. In most cases there should be no air inside the syringe. |
| Preparing the skin for injection | With your free hand, take an alcohol wipe and wipe the skin in the selected area. This should be done carefully, moving from the center to the edges and not missing sections. Then the skin should dry. Hold the syringe with the hand with which the injection will be given. The grip is the same as when writing with a pen or pencil. With the other hand, the skin is grabbed into a fold. |
| Inserting a needle under the skin | With a sharp, confident movement, insert the needle into the skin at a right angle. It should enter the skin completely, without placing your thumb on the plunger. After inserting the needle, the fold opens. After this, by pressing your thumb, the piston slowly moves down until it stops. All the medicine should go under the skin. |
| Removing and removing the syringe | When the syringe becomes empty, smoothly pull the needle out of the body vertically to its surface. If necessary, apply a plaster or bandage. Carefully remove the needle and, covering it with the nozzle, throw it into a waste container, just like the syringe itself. Reusing a used syringe is strictly prohibited. This is fraught with infection or other negative consequences. |
Subcutaneous injection allows you to deliver medicinal substances to the desired organs in adjusted doses. Such injections can be given in the shoulder, thigh, under the shoulder blade or peritoneum. The procedure can be done in a clinic or at home. It’s easy to learn how to administer medications yourself; the main thing is to study the theory and only then do it practically, observing all the nuances of this process.
Vaccine care rules
After the injection, a small bubble forms on the skin and turns red. This is a normal reaction of the body that does not need to be paid attention to. Redness may last from several days to a week. It is very important to closely monitor the baby during this period so that he does not scratch the injection site or break the blister. There is no need to use antiseptics, ointments, or apply a bandage. This will not affect the process of scar formation in any way, but the integrity of the wound can be compromised. Since the bacteria in the vaccine are unstable, they will not withstand contact with disinfectants. As a result, the vaccination will not have the desired effect. It is also forbidden to pick off the resulting crust - it will completely come off on its own.
Vaccination in the arm of a baby is a painless procedure: it is done with minimal damage to the skin. The size of the scar will depend not on the skills of the nurse, but on the individual characteristics of the body. Even for those babies whose injection site has healed quickly and with virtually no inflammation, a mark will remain on the skin. Don't refuse vaccination
| Author of the article: Tatyana Nikolaevna Kukushkina graduated from the Chuvash State University named after I.N. in 2004. Ulyanova with a degree in Pediatrics, after which she completed internship training. He has a certificate in the specialty "Pediatrics". Experience: 17 years of medical practice. |
What vaccinations are given in the shoulder?
Previously, babies were given two injections at once. The first is from smallpox. However, this serious disease was completely defeated, and since the late 70s, vaccination against it has ceased to be included in the list of mandatory ones.
Today, infants aged 3 to 7 days receive only the BCG vaccine in the arm. This helps protect the baby’s body from another serious disease – tuberculosis. Repeated vaccination is also done at 7 and 14 years of age. Live, but significantly weakened bacteria are injected under the skin. As a result, a natural reaction develops in the body, which is expressed in the form of an inflammatory process. A bubble appears at the injection site, which over time turns into a small scar with a diameter of no more than 5 millimeters. This is evidence that the vaccination was completed correctly and the child has developed immunity.
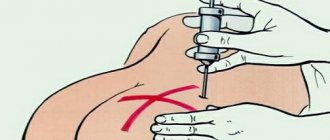
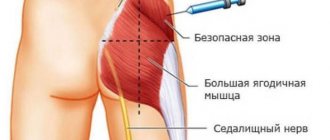
What is the difference between a subcutaneous and an intramuscular injection?
Unlike the subcutaneous injection, I give an intramuscular injection into a deeper muscle layer. As a result of such manipulations, a “pocket” is formed in which the drug is deposited.
If, with subcutaneous administration, the drug quickly enters the bloodstream and is transported along with the blood to the target organs, then in the case of intramuscular administration, the drug is “stored”, being released into the blood gradually.
Thus, a given concentration of the drug is maintained in the body for a certain time. Such injections are necessary in cases where therapy is being carried out (for example, antibiotics) and continuous exposure is required. Subcutaneous injections are not suitable in this case.
If the intramuscular injection is given subcutaneously
Administration of the drug intramuscularly when administered subcutaneously is not dangerous to the patient's health, but the expected therapeutic effect will not be obtained: instead of a prolonged action (extended over time), the effect will be rapid. Therefore, it is imperative to clarify how a particular drug is administered, and then begin treatment.