One of the most popular methods of treating infertility is ovulation stimulation. It is used for women with problems with the maturation of the egg and the absence of its release from the ovary. To stimulate ovulation, hormonal drugs are used, thanks to the action of which one or more eggs capable of fertilization are formed in the female body.
Methods to restore ovulation are selected taking into account the reason for its absence. Achieving a positive effect from the use of ovulation stimulation is possible only if the cause that disrupts the ovulatory process is established.
Reasons for the development of anovulation
The reasons that provoke the development of anovulation can be physiological and pathological (chronic). Physiological anovulation is considered normal, does not require seeking medical help and can occur during the following periods in a woman’s life:
• puberty: in teenage girls, ovulation may not occur for the first two years after menarche; • period of pregnancy and breastfeeding; • menopause; • “rest” period: 1-2 menstrual cycles per year; women of reproductive age may not ovulate.
Pathological anovulation can be caused by a violation of the structure of organs or diseases of the endocrine system. Most often, the presence of this particular condition is the cause of infertility.
Pathological reasons for the lack of ovulation may be the presence of the following conditions:
• dysfunction of the hypothalamus; • oncological diseases of the pituitary gland; • circulatory disorders in the brain; • hyperprolactinemia; • hyperandrogenism; • frequent stress; • injuries of the reproductive system; • inflammatory diseases of the appendages; • obesity; • anorexia; • premature menopause; • gynecological diseases (polycystic ovary syndrome, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, etc.); • diseases of the thyroid gland and liver; • when taking hormonal contraceptives.
What are the dangers of poor ovarian response?
The ultimate goal of each IVF cycle is to stimulate the production of a large number of follicles with mature eggs so that at least one of them can produce a viable embryo. It is for this reason that a poor ovarian response negatively affects the results of IVF - an insufficient number of oocytes capable of fertilization reduces the chances of a successful pregnancy and increases the likelihood of embryo transfer cancellation. A poor response often results in eggs obtained that are of poor quality, jeopardizing the viability of embryos in the laboratory and increasing complications for women.
Fortunately, patients with a poor response have several options to solve their problem.
Stages of ovulation stimulation
Stimulation using clostilbelite begins on the fifth day of the menstrual cycle, with gonadotropins - on the second. The timing of the start and duration of taking the drugs is determined by the attending physician in accordance with the condition of the woman’s uterus and ovaries.
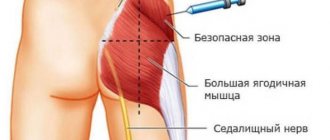
The first ultrasound examination is carried out a few days after the start of the ovulation stimulation procedure. Then ultrasound is repeated every 2-3 days until the follicles reach a size of at least 20 mm. After this, the woman is given an injection of hCG (in a dosage of 5,000 to 10,000 units), which starts the ovulation process and prevents regression of the follicles and the risk of follicular cyst formation.
An hCG injection is an injection of a hormonal drug with the main active substance - human chorionic gonadotropin: pregnyl, prophasia, choragon, humegon, menogon, choriogonin, etc. With the help of these drugs, the ovulation process is restored, as well as an increase in the level of hCG in the blood, due to which yellow body and its activity increases.
The doctor selects the dosage of the hCG drug in each individual case in accordance with hormone levels, the size of the follicles and a number of other equally important factors. Excessive amounts of human chorionic gonadotropin can trigger the development of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
An injection of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) triggers the onset of ovulation, which usually begins 24-36 hours after the injection. The release of the egg is recorded using ultrasound, after which the woman is prescribed additional support for the ovaries (corpus luteum) in the form of injections of utrogestan or progesterone.
The timing and frequency of sexual intercourse or artificial insemination when stimulating ovulation is prescribed by the doctor individually, depending on the results of the man’s spermogram. If the quality and quantity of sperm are good, it is recommended to have sexual intercourse every day or every other day, starting from the moment the woman received the hCG injection until the corpus luteum is formed.
Medical examination before ovarian stimulation with Clostilbegit and Proginova
- Checking the patency of the tubes using laparoscopy. This is necessary to exclude ectopic pregnancy. It is pointless to undergo a course of treatment if, after stimulating ovulation and fertilization, the egg cannot enter the uterine cavity and remains in the tube.
- Determination of hormonal levels. Necessary for choosing the correct dose of the drug. To do this, on the third day of the cycle, FSH, LH, prolactin, estradiol and testosterone are given.
- Carrying out an ultrasound. This study allows you to evaluate the condition of the ovaries and the presence of follicles on his body.
- Evaluation of partner's spermogram and compatibility test. It is necessary to clarify exactly how fertilization of the released egg will occur: naturally or using the method of intrauterine insemination.
What is an HCG injection?
The main factor influencing a woman’s ability to become a mother is the presence of ovulation - the process of release of mature eggs from the follicles and subsequent movement through the fallopian tubes, which determines readiness for fertilization. Sometimes, for one reason or another, a malfunction occurs in the body, as a result of which the membrane (follicle) does not rupture.
The success of conception largely depends on the level of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin in a woman’s blood, the effect of which on the corpus luteum continues until the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. In some cases, there is a need for artificial administration of human gonadotropin (hCG injection).
What is artificial insemination?
Artificial insemination is one of the easiest to perform and long-used methods of artificial insemination, which consists in introducing sperm into the woman’s reproductive tract. The procedure involves the introduction of processed sperm from a man directly into the genital (reproductive) tract of a woman. This can be the introduction of sperm into the vagina (intravaginal insemination), or directly into the abdominal cavity (intraperitoneal insemination); These days, intrauterine insemination is the most common method. The first two methods are of only historical interest and, for a number of reasons, are rarely used. The effectiveness (percentage of positive results) is 20-25%, but it is still a popular and frequently used method of treating infertility.
In what cases is an HCG injection indicated?
An hCG injection can be prescribed to women in the following cases:
• in the absence of ovulation: an injection of hCG stimulates the release of the egg and prevents the reverse development of follicles (atresia). Unruptured follicles may regress, decreasing in size and forming follicular cysts; • to preserve the vital activity of the corpus luteum: an injection of hCG helps maintain the state of the corpus luteum until these responsibilities are “transferred” to the placenta; • for the normal formation of the placenta and maintenance of its functions: when the development of the placenta is inhibited; • if the female body is unable to maintain pregnancy and has a history of miscarriages; • if there is a risk of miscarriage; • when planning in vitro fertilization.
Treatment in Reproductive
Reproductologists approach each case individually. To select the most suitable stimulation scheme, at the first stage a detailed examination of the woman is carried out. First of all, the ovarian reserve is assessed and a forecast of the ovarian response to stimulation is made. Depending on this, a specific protocol, drug and its starting dose are selected. At the same time, possible complications are prevented. In order to create the best conditions for the development of pregnancy, the optimal number of embryos is implanted. If a couple has genetic diseases, preimplantation diagnostics is performed. All this allows us to provide treatment as effectively and safely as possible.
The most advanced achievements in the field of reproductive medicine have been introduced and successfully applied at SM-Clinic. Take care of your future and the future of your children now - sign up for a consultation with experienced reproductive specialists!
Pregnancy after hCG injection
An hCG injection can cause a false positive result if a pregnancy test is performed earlier than 14 days after ovulation. This is explained by the fact that these tests are based on determining the level of hCG, which is an indicator of the onset of conception, and the artificial introduction of this hormone increases its amount in the blood for a while. A more reliable method is dynamic monitoring of hCG, the level of which in pregnant women is constantly increasing until the end of the first semester. At the beginning of the second semester, it gradually decreases to a certain level, which remains unchanged until the end of pregnancy.
HCG analysis - rules for delivery
The concentration of hormones in the body of the expectant mother is determined by collecting venous blood. Reproductologists recommend taking tests in the morning on an empty stomach - at least 8-9 hours should pass between the last meal and blood donation. If a woman is taking over-the-counter medications, she should tell her doctor a few days before the tests.
Enzyme immunoassay must be performed not only to determine gestation. The hCG test should also be taken in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy in order to identify defects in the development of the child. Correction of maintenance therapy can prevent up to 25% of congenital pathologies and anomalies.
How to Prepare for Unstimulated IVF
In order to prepare for unstimulated IVF and significantly increase the chances of success during the procedure, it is worth following a number of simple recommendations:
- Quitting smoking, and this rule should apply to both women and men. This will increase the chances of successful embryo implantation;
- Proper nutrition. A woman who cares about her health and the health of her unborn child should receive a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals, enriching her diet with vegetables and fruits, and, if possible, giving up fast food and other junk food;
- Sport. A woman's life should include moderate physical activity such as swimming, walking and dancing. This will enrich the blood with oxygen and increase overall vitality;
- Proper rest and sleep patterns.
Naturally, each couple is considered by specialists individually, and therefore it is necessary to follow all the instructions given by the doctors.
When is there no point in injecting?
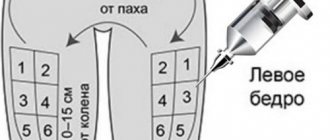
The injection must be given under specific conditions. It must be placed on a certain day of the cycle when the follicle is fully mature. If you administer the medicine earlier, ovulation will occur, but you will receive an underdeveloped egg that cannot lead to pregnancy.
Therefore, the substance is administered only with constant folliculometry using ultrasound. If you were not given drugs to stimulate the growth of the dominant follicle, then the injection is also useless, because there will be nothing to rupture due to the absence of the “main” follicle.
Recommendations after follicle puncture
Follicle puncture is performed under general anesthesia and takes no more than 20 minutes. After egg retrieval, the woman remains under observation in the ward for 2 hours, then is discharged home with doctor’s recommendations.
Driving after the procedure is prohibited.
On this day, luteal phase support and preparation for embryo transfer are prescribed.
For this purpose, progesterone preparations are prescribed (progesterone, utrozhestan, kraynon, iprozhin), duphaston, in some cases estrogens (divigel, proginova, estogel), and hCG preparations.
On the first day after ovarian puncture during IVF, a woman may experience moderate pain in the lower abdomen. This is normal, since during puncture the ovarian tissue is injured by the needle, which can cause pain in the future. But if pain occurs, you should not take painkillers, since their therapeutic effect can smooth out the picture of a possible complication, and help may be provided with a delay. If you experience intense abdominal pain, as well as weakness, dizziness, or bleeding, you should contact your doctor.
After ovarian puncture, sexual rest is required for two weeks. At this time, you should also not take a hot bath, visit the sauna, solarium, swimming pool, or gym.
The next day after the puncture, until the moment the blood is tested for hCG, it is recommended to drink a large amount of still water or fruit drink without sugar (up to 3 liters). Food should contain a lot of protein and a minimum of coarse fiber (raw vegetables, fruits, legumes, brown bread excluded). It is also necessary to limit coffee, strong tea, cola, and alcoholic beverages are not allowed.
After puncture of a large number of follicles, sometimes from 2-3 days, complaints characteristic of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome may appear: a feeling of fullness and bloating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat (tachycardia), dry cough. If such signs appear, you should immediately consult your doctor.
Chorionic gonadotropin - instructions for use
This hormonal drug is obtained from the urine of pregnant women. The main pharmacological effect of recombinant human chorionic gonadotropin is stimulation of the production of sex hormones in the tissues and ovaries, ovulation, spermatogenesis, development of secondary sexual characteristics and genital organs.
In what cases is human chorionic gonadotropin prescribed? The instructions say that the drug is effective for:
- ovarian dysfunction;
- dysmenorrhea;
- anovulatory infertility;
- corpus luteum deficiency;
- threat of miscarriage;
- habitual miscarriage.
Good results are observed in cases where human chorionic gonadotropin is used in assisted reproductive techniques - there are reviews about this.
Men are also prescribed human chorionic gonadotropin for:
- hypogenitalism;
- tissue hypoplasia;
- eunuchoidism;
- cryptorchidism (undescended testicle into the scrotum);
- sexual infantilism;
- pituitary dwarfism;
- adiposogenital syndrome;
- azoospermia;
- oligoasthenospermia;
- as well as for genetic disorders.
Human chorionic gonadotropin is produced in the form of a solution (or lyophilisate for its preparation) for injection.
Accumulation and vitrification of oocytes
To maximize the number of eggs retrieved and therefore increase the chances of obtaining a viable embryo, your doctor may suggest performing several cycles of stimulation. Oocytes recovered in each cycle are frozen at ultra-low temperatures until the required amount of biological material is collected. The eggs are then thawed and fertilized either in vitro or using ICSI.