The concept of “vaccination” implies a medical process that is intended to immunize the body against certain groups of diseases. The basis of the grafting material is active (weakened) and inactivated (dead) infectious pathogens.
According to general concepts, all groups of the population are subject to vaccination - from infants to the elderly. There are a number of separate types of vaccinations that are included in the National Calendar and are supposed to be mandatory for all categories of persons.
Other options can be used for health reasons, for example, an anti-rabies vaccine (rabies). In her own works, Galina Petrovna Chervonskaya says unequivocally about vaccinations that such techniques should be used wisely.
Who is Galina Petrovna Chervonskaya?
Galina Chervonskaya, by her own education and area of work, is a specialist in virology. He is an active participant in the anti-vaccination movement in Russia, a member of the national committee on bioethics and the author of a large number of publications on the topic of immunization, epidemiology and virology.
Also, Galina Petrovna was involved in the development of individual legislative acts:
- Fundamentals of legislation on protecting the health of citizens - 1993;
- On immunoprophylaxis of infectious diseases - 1998;
- About medicines - 1998
These acts were adopted and are part of the current legislation. Galina Petrovna’s main activity is education on a paid basis, as well as the commercial publication of books on vaccination and virology.
The most controversial of these works is “Vaccinations: Myths and Reality.”
According to the Academy of Sciences, Chervonskaya does not have an academic degree or medical education. The only work in this direction is a candidate's dissertation, which was not approved.
Russian legislation: voluntary vaccination
In Russia there are 3 laws on the voluntary nature of vaccinations. G. Chervonskaya, who took part in their development, introduced them to the participants of the seminar - young mothers and women planning to become mothers in the coming months. In the “Fundamentals of Legislation on the Protection of Citizens’ Health” (1993), articles 30-34 in different versions speak of the voluntariness of a citizen in taking any medicine and providing him with any medical care. According to international rules, forced provision of medical care is possible only if a person is incompetent (that is, unconscious), mentally ill and currently dangerous to others, or is a carrier of an infectious disease (tuberculosis, diphtheria). But today the Russian sanitary and epidemiological service is not involved in identifying carriers.
Only in Russia were vaccines not classified as medicines, and only the Law “On Medicines” adopted in 1998 introduced them to this list. The same law stipulates the voluntary participation of citizens in the experiment. In all countries, such volunteers receive large rewards. If we talk about children, then all over the world it is carried out only in contaminated areas and only with the consent of the parents. Referring to the film “Fear Vaccine,” Chervonskaya noted that Russia is included in the category of countries where free experiments are carried out on children. With whose connivance it is still unknown, but Galina Chervonskaya warned the mothers present at the seminar that they may face a situation where a vaccine experiment will be imposed on them on their child with reference to international rules. “And you say, I’m not interested in international ones, I’m interested in my child,” she urged the mothers.
Also in 1998, the Law “On Immunoprophylaxis of Infectious Diseases” was adopted, according to which we are required to warn us in advance about post-vaccination complications. Article 5 of this Law states that a citizen has the right to refuse vaccination. The refusal is issued in writing. In general, this means that the doctor writes on the child’s medical record: the parents refuse vaccinations. But many doctors require a signature from parents. The seminar participants were promised to be given the Law “On Immunoprophylaxis” and to dictate the text of the refusal receipt at the next lesson. The presentation of this law has an unfailing effect on doctors in clinics.
Only parents can enforce laws. In the meantime, many of them, not legally armed, buy vaccination certificates. The Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision Service, which issued an order to combat diphtheria in 1993, “feat” the doctors to accept bribes. Among other things, this order also contains recommendations for economic incentives for doctors who will cover as many children as possible (not to vaccinate competently, but to cover as many as possible). You should always say “to us an order is not a decree.” Orders of the Ministry of Health must comply with the Law. And the Law gives the right to refuse.
Highlights of Galina Petrovna Chervonskaya’s book “Vaccinations: Myths and Reality”
Galina Petrovna Chervonskaya’s book raises questions about the adequate use of vaccines and the importance of educating the population in these areas. To a greater extent, the author refers to the work of a scientist (immunologist Edward Jenner), who was the first to develop such tools and introduce their use based on his own knowledge in the field of virology.
The main topics covered in the book are:
- vaccines, when administered to a child (usually an infant) with a weakened and immunocompromised state, can lead to undesirable consequences and general paralysis of the defense systems of a fragile body due to a large number of side effects;
- certain types of vaccinations contain genetically modified components that can lead to changes in the general structure of the human genome and cause a whole list of autoimmune pathologies;
- a combination of religiosity, in particular certain theses of Orthodox Christianity, and the methodology of instilled health. Basically, the contradiction between the existence of diseases and general interference in the natural process is monitored.
Also in support of her own position, Chervonskaya cites the assumption that the compositions used for children may be untested.
The use of vaccines provokes unexpected adverse reactions, both local and system-wide:
- increase in body temperature;
- rash at the injection site;
- loss of consciousness;
- gastrointestinal system disorders;
- allergies;
- headache.
A separate factor is that before vaccinations, no one checks children for the integrity of their immune system and does not draw up a genetic map. Such a technique could make it possible to reduce the number of people vaccinated with increased risks to health and life, which would accordingly influence the statistics on the development of severe side effects.
If any negative symptoms are observed after vaccination, in particular loss of consciousness or a temperature reaching 38°, you should immediately seek emergency help at the hospital.
Galina Chervonskaya - Vaccinations: myths and reality
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Galina Petrovna Chervonskaya is a virologist with many years of experience.
She began her scientific and practical activities while still a student in the laboratory of especially dangerous infections, renamed the INSTITUTE FOR POLIOMYELITIS STUDY OF THE USSR Academy of Medical Sciences, now the INSTITUTE OF POLIOMYELITIS AND VIRAL ENCEPHALITIS (IPVE) RAMS. Academician M.P. Chumakov, the founder of this institute. Here, having mastered the methods of “cultural virology,” she was directly involved in the production of the first series of the domestic version of the vaccine against polio viruses (using the primary technology of Dr. Seibin), as well as in the development and implementation in our country of a unique biological model - CELL CULTURE. Later, Galina Petrovna defended her dissertation on the problems of chronic viral infections at the INSTITUTE OF EPIDEMIOLOGY AND MICROBIOLOGY (IEM) named after. Academician N.F. Gamaleya of the USSR Academy of Medical Sciences. Then she worked for 12 years at the State Research Institute of Standardization and Control (GNIISK) of medical biological preparations named after. L.A. Tarasevich of the USSR Ministry of Health, where she did everything possible to improve hopelessly outdated methods for assessing the safety of vaccines, widely used in pediatric healthcare practice.
Galina Petrovna is the author of more than 70 scientific articles, several methodological developments approved by the USSR Ministry of Health and the Federal Center for State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance of the Russian Ministry of Health (1982,1991,1999). The methodological instructions are devoted to the use of CELL CULTURE as an alternative biological model that replaces experimental animals, helping to obtain more reliable information about the safety of drugs, including vaccines, as well as food products, cosmetics, medical products, etc.
Chervonskaya is the main executor of two inventions (1984, 1986) and co-author of three monographs:
VACCINE PREVENTION AND HUMAN RIGHTS (1994),
INTRODUCTION TO BIOETICS (1998),
BIOETICS: principles, rules, problems (1998).
Galina Petrovna took part in the development of laws on healthcare in the Russian Federation - “ Fundamentals of legislation on protecting the health of citizens ” (1993), “ On medicines ” (1998), but her main work in this area is the law “ON IMMUNOPROPHYLAXIS OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES” (1998) . In addition, the Forensic Medical Examination Committee of the Moscow Department of Health regularly invites Galina Petrovna Chervonskaya as a specialist - an expert on the problems of post-vaccination complications.
Now Galina Petrovna continues her scientific and practical work as a virologist, being at the same time a member of the Russian National Committee on Bioethics (RNBC) of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the International Society of Human Rights (ISHR). Being engaged in teaching and educational activities, she actively transfers her knowledge to young people, not only doctors and biologists, but also all those who want to receive comprehensive information on vaccinology in order to make an informed and voluntary decision on any vaccination as a preventive medical intervention in an individual and unique way. the nature of each of us. It is for this purpose that the book is written in the language of popular science literature, in order to awaken the interest of different layers of citizens of our country, who are truly concerned about preserving the health of Russian children, to this controversial problem, which is at the intersection of many disciplines and not only practical medicine.
Dedicated to my daughter E. A. Sovetova
with deep gratitude for your help,
support and great patience, as well as
in memory of her husband, professor-physiologist A. N. Sovetov.
FOREWORD BY THE AUTHOR
The purpose of this review on the basics of vaccinology is to orient the literate young reader in the “jungle” of this multifaceted medical and biological discipline. It is clear that this requires literature that is not only of special scientific content and accessible in presentation form, but also quite informative and popular.
Immunoprophylaxis - vaccinations - is considered here, firstly, as one of the sections of complex science - vaccinology, and secondly, from the standpoint of various disciplines not only medicine, which allows us to evaluate mass medical preventive intervention in human nature as serious, not only immunological, general biological, but also a social, environmental and legal problem.
We deliberately do not dwell on the importance of immunology in general and do not present its sections, using, at the same time, key provisions in the context of vaccinology, since over the past 25 years numerous monographs and textbooks by both domestic and foreign authors have been devoted to immunological issues.
Let us only recall that over the last quarter of a century immunology has become one of the most common subjects, and its principles are applied in many biomedical disciplines and in clinical research.
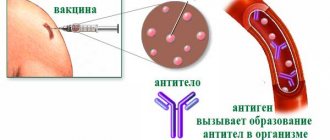
The paradox is that, while rapidly developing, new immunology (based on modern approaches), nurtured on the classic old one - “vaccination” - did not bring either theoretical or practical achievements to the immunology of infectious diseases, to the section of vaccinology. Along with this, the concept of “one’s own” and “alien”, being an integral part of successes in the recognition of “not my self” - from genetics to human ecology, from neonatology to pediatric oncology, etc., relates primarily to violent (“decreed ") the entry into the child's body of antigens ("ANTIGENS"! - against human genes) - foreign proteins - vaccines.
In order for the content of sections (lectures) to also meet the requirements of the textbook, a list of specialized reference literature has been compiled for each of them. It also includes old classical works that are directly related to vaccinology, however, undeservedly forgotten by the “new” infectious disease specialists and epidemiologists, who, meanwhile, have not done or invested anything new in the development of these disciplines. And the further time went, the more and more the truth became distorted about the purpose of vaccines and “saving humanity from infectious diseases through vaccination alone,” about the original orientation of the WHO Expanded Program on Immunization (EPI)... Along with this, as is known, “the nation does not include only human generations, but also the stones of churches, palaces and estates, old manuscripts and books... you need to hear these stones, read the decayed pages...” (N. Berdyaev, “Philosophy of Inequality”).
The monograph presents publications of the last 10–15 years, which, from our point of view, are significant for the health of modern children. Some of the modern popular scientific literature was also used, which compares favorably in terms of depth of information with domestic specialized journals on microbiology and epidemiology. This refers to such popular science publications as “Knowledge is power”, “Chemistry and Life”, “Man”, “Cosmetics and Medicine” and a number of others.
It is assumed that the presented material about medicinal preventive biological products - vaccines can benefit not only highly qualified specialists, clinicians and researchers who are faced with various immunopathological processes and cellular pathology in their work. I would like to hope that it will attract the attention of teachers of medical institutes, as well as some of the thinking youth, who, not limited by the framework of textbooks and scant information about what and how “is required by order of the Ministry of Health,” strive to master the knowledge intended in our country, as a rule , exclusively for doctors.
Non-specialists in this field who do not have specialized medical knowledge receive information exclusively about the “positive” aspects of vaccinations. At the same time, a huge amount of material has been accumulated about the negative consequences - side effects of vaccines, since any vaccine is “inevitably unsafe.”
Informed, conscious and voluntary consent to any medical intervention is the basis of existing requirements for the protection of human health and for the legal relationship between a citizen and the healthcare authorities of the Russian Federation. In particular, Russian citizens “are not forbidden to know,” and medical workers are obliged to inform not only about the benefits of vaccinations, but also about possible post-vaccination complications — “in a language understandable to citizens.” According to this principle, information should be compiled in the “insert leaflet” for any medicinal product, and therefore for vaccines: “with a brief description of the drug (part of the registration certificate), presented in a language understandable to the consumer,” domestic employees of the Ministry of Health notify us in Bulletin “Medicine for You” (No. 18, September 1996).
A virologist’s opinion on some vaccinations from the National Calendar
The national vaccination calendar is a legislative document that regulates the mandatory immunization plan for citizens. According to Chervonskaya, this method of vaccination is fundamentally incorrect, since some of its points are applied incorrectly.
Also, the population is not educated in the intricacies of vaccination:
- a person may be interested in the composition of the vaccine used;
- a medical professional is required to report contraindications and potential side effects of the vaccine;
- Every citizen has the right to refuse compulsory vaccination (for children under 15 years of age, this issue is decided by parents).
Based on the vaccination schedule, immunization of all citizens - children and adults - is carried out.
The calendar is regulated in accordance with the articles of the Federal Law adopted in 1998 (“On Immunoprophylaxis of Infectious Diseases”), which also indicates the features of the interaction of medical services with the population in these matters for the purpose of protecting health:
- methodology for considering all cases of side effects from the vaccine and the development of complications (including death) with mandatory compensation payment;
- the presence in practice of a certification document that identifies all vaccinations received by a person, indicating the specific composition (in the form of a code);
- immunoprophylaxis is a list of actions that are aimed at preventing (limiting) the spread of infectious diseases.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Galina Petrovna Chervonskaya is a virologist with many years of experience.
She began her scientific and practical activities while still a student in the laboratory of especially dangerous infections, renamed the INSTITUTE FOR POLIOMYELITIS STUDY OF THE USSR Academy of Medical Sciences, now the INSTITUTE OF POLIOMYELITIS AND VIRAL ENCEPHALITIS (IPVE) RAMS. Academician M.P. Chumakov, the founder of this institute. Here, having mastered the methods of “cultural virology,” she was directly involved in the production of the first series of the domestic version of the vaccine against polio viruses (using the primary technology of Dr. Seibin), as well as in the development and implementation in our country of a unique biological model - CELL CULTURE. Later, Galina Petrovna defended her dissertation on the problems of chronic viral infections at the INSTITUTE OF EPIDEMIOLOGY AND MICROBIOLOGY (IEM) named after. Academician N.F. Gamaleya of the USSR Academy of Medical Sciences. Then she worked for 12 years at the State Research Institute of Standardization and Control (GNIISK) of medical biological preparations named after. L.A. Tarasevich of the USSR Ministry of Health, where she did everything possible to improve hopelessly outdated methods for assessing the safety of vaccines, widely used in pediatric healthcare practice.
Galina Petrovna is the author of more than 70 scientific articles, several methodological developments approved by the USSR Ministry of Health and the Federal Center for State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance of the Russian Ministry of Health (1982,1991,1999). The methodological instructions are devoted to the use of CELL CULTURE as an alternative biological model that replaces experimental animals, helping to obtain more reliable information about the safety of drugs, including vaccines, as well as food products, cosmetics, medical products, etc.
Chervonskaya is the main executor of two inventions (1984, 1986) and co-author of three monographs:
VACCINE PREVENTION AND HUMAN RIGHTS (1994),
INTRODUCTION TO BIOETICS (1998),
BIOETICS: principles, rules, problems (1998).
Galina Petrovna took part in the development of laws on healthcare in the Russian Federation - “Fundamentals of legislation on protecting the health of citizens” (1993), “On medicines” (1998), but her main work in this area is the law “ON IMMUNOPROPHYLAXIS OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES” (1998) . In addition, the Forensic Medical Examination Committee of the Moscow Department of Health regularly invites Galina Petrovna Chervonskaya as a specialist - an expert on the problems of post-vaccination complications.
Now Galina Petrovna continues her scientific and practical work as a virologist, being at the same time a member of the Russian National Committee on Bioethics (RNBC) of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the International Society of Human Rights (ISHR). Being engaged in teaching and educational activities, she actively transfers her knowledge to young people, not only doctors and biologists, but also all those who want to receive comprehensive information on vaccinology issues in order to make an informed and voluntary decision on any vaccination as a preventive medical intervention in an individual and unique way. the nature of each of us. It is for this purpose that the book is written in the language of popular science literature, in order to awaken the interest of different layers of citizens of our country, who are truly concerned about preserving the health of Russian children, to this controversial problem, which is at the intersection of many disciplines and not only practical medicine.
Dedicated to my daughter E. A. Sovetova
with deep gratitude for your help,
support and great patience, as well as
in memory of her husband, professor-physiologist A. N. Sovetov.
FOREWORD BY THE AUTHOR
The purpose of this review on the basics of vaccinology is to orient the literate young reader in the “jungle” of this multifaceted medical and biological discipline. It is clear that this requires literature that is not only of special scientific content and accessible in presentation form, but also quite informative and popular.
Immunoprophylaxis - vaccinations - is considered here, firstly, as one of the sections of complex science - vaccinology, and secondly, from the standpoint of various disciplines not only medicine, which allows us to evaluate mass medical preventive intervention in human nature as serious, not only immunological, general biological, but also a social, environmental and legal problem.
We deliberately do not dwell on the importance of immunology in general and do not present its sections, using, at the same time, key provisions in the context of vaccinology, since over the past 25 years numerous monographs and textbooks by both domestic and foreign authors have been devoted to immunological issues.
Chervonskaya's comments regarding certain types of vaccines
The main factor that Chervonskaya wants to explain is the right of every citizen to avoid medical procedures that are dangerous to him.
BCG
This drug is administered in maternity hospitals to almost all newborns, without preliminary tests to check the immune state.
Side effects from BCG include:
- local negative reactions : cold abscess (formation of a minor abscess in the injection area), development of necrotic skin lesions, ulcer formation, appearance of keloid scars with severe itching, enlargement of regional lymph nodes with possible complications;
- disseminated BCG infection : skin tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, osteitis, keratoconjunctivitis;
- post BCG syndrome : anaphylactic shock, erythema nodosum, exanthema, etc.
Generalized BCG infection, caused by system-wide tuberculosis, is highly likely to lead to death.
Measles, rubella, mumps
The drug CPC, which is also administered in childhood to immunize the body against measles, mumps and rubella.
Side effects include:
- toxic lesions;
- increased body temperature;
- nosebleeds;
- development of abdominal syndrome.
The following types of allergic reactions often occur:
- hemorrhagic rashes with the presence of bleeding;
- asthmatic syndrome;
- Quincke's edema;
- hives and other skin rashes;
- thrombocytopenic purpura.
Neurological complications include:
- post-vaccination encephalitis;
- cerebral disorders;
- convulsive syndrome, including febrile convulsions (often with loss of consciousness).
Most complications primarily lead to disability.
Polio
When using live polio vaccines, the following side effects occur:
- dermatitis;
- hives;
- intestinal disorders;
- paralysis and paresis;
- Quincke's edema.
There is also a possibility of developing VAPP (vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis) after using the vaccine.
Criticism from immunologists and other specialists
Regarding the book, authored by Galina Petrovna Chervonskaya, many specialists in immunology and vaccinology responded negatively, since this work relates to a medical focus, and the author is not provided with such education.
In contrast to the described factors, they give the following arguments:
- side effects in humans occur only in cases of violation of the method of transportation and storage of the drug or the presence of hidden contraindications, in particular individual intolerance to the components;
- elevated temperature from vaccination is a particular variant of the norm and an indicator of activation of the immune system. This condition does not require the use of any medications or calling an ambulance (depending on the indicators);
- Local manifestations in the injection area disappear on their own with proper care. This implies the absence of irritating factors - water, sunlight, friction (on clothing or scratching);
- systemic manifestations require emergency care, which is ensured by a mandatory 30-minute stay of the vaccinated person on the territory of the medical institution - the treatment used depends on the symptoms and its origin.
There is a danger of severe complications when using vaccines for immunization. However, with modern methods of manufacturing these drugs, as well as the development of medicine, this probability is reduced to a minimum.
The preparations used for immunization contain low concentrations of the pathogen, more often dead variants, so there is no need to worry about post-vaccination damage to the body.
To vaccinate a child or not: all the pros and cons of vaccination
From a legislative point of view, the book authored by Galina Chervonskaya about vaccinations does not contradict existing norms - every person has the right to refuse medical services, including vaccination.
But, when considering in detail this method of preventing infectious pathologies, all risk factors should be assessed.
Among the positive aspects, the following are emphasized:
- the formation of protective reactions (to the causative agent of the disease), which are fixed in the body;
- stimulating the development of the immune system and increasing overall resistance to infectious disorders;
- planned monitoring of the child’s condition and timely adoption of measures in the event of the progression of severe disorders.
However, before agreeing to such a procedure, it is necessary to be attentive to the health status of both your own and the child. To do this, you should attend preventive examinations and receive timely treatment. Experts also recommend listening to your doctor and studying statistical information provided to explain the risks and dangers of the procedure.
Section I - introduction to vaccinology
I. 1. Preface to the LAW “ON IMMUNOPREVENTION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES”________________________________________________________________________________8
I. 2. ADDRESS BY SCIENTISTS TO THE PRESIDENT OF THE RF_________________________________10
LAW of the Russian Federation “ON IMMUNOPROPHYLAXIS OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES”________________________________________________________________________________13
I. 3. VACCINOLOGY - the science of medicinal preventive biological products - vaccines___________________________________________________________________________18
I. 4. PAGES OF THE HISTORY OF VACCINE PREVENTION: reality and myths________22
Tuberculosis incidence chart for children__________________________________________34
I. 5. HISTORICAL AND ANALYTICAL SUMMARY ABOUT THE PROBLEMS OF Vaccinations_________35
LITERATURE for SECTION I______________________________________________________________39
Video on the topic
Lecture by Galina Petrovna Chervonskaya “Vaccinations - myths and reality”:
The main goal of Chervonskaya’s activities and published works is to explain to the population the dangers of such an event as vaccination and to draw attention to the need to study all the intricacies of such medical procedures.
Refusal to vaccinate in the presence of contraindications or for individual reasons is an inalienable human right. Therefore, before agreeing to carry out such a manipulation, it is necessary to consider all the risks of post-vaccination reactions and the importance of the procedure itself.