Pregnancy and the period of breastfeeding are a test of strength for the female body. In order to bear a baby, the expectant mother's immunity levels decrease, so she becomes vulnerable to infections. A similar situation occurs after childbirth. Are there safe antiviral drugs that nursing mothers can take?
The importance of breastfeeding (BF)
The text of the joint WHO and UNICEF Global Strategy on Infant and Young Child Feeding states: “Breastfeeding is the best way to provide ideal nutrition for the healthy growth and development of children.” Both pediatricians and mothers themselves agree with this statement.
Breast milk has a complex chemical composition and few people do not know that its biological value for a child is superior to all other products found in nature. Human milk contains more than 30 fatty acids, 20 amino acids, about 40 different minerals, 17 vitamins, specific growth factors, dozens of enzymes, various carbohydrates, hormones, prostaglandins and a complex of factors with anti-inflammatory activity. Breastfeeding is the best thing a woman can give to her child.
Use of medications during breastfeeding
It happens that during lactation a woman gets sick. And she needs to choose medications that would help fight the disease and not harm the child. It should be borne in mind that a wide range of antiviral drugs are absolutely not suitable for treating a nursing woman.
After all, not only useful substances are transmitted with mother’s milk, but also medications that a woman takes, and as you know, not all drugs are suitable for babies. There are also medications that can reduce milk production or stop it altogether. Therefore, when prescribing drugs, the risk for the baby and the benefit for the mother are always taken into account.
The degree of adverse effect of the drug on the infant’s body is determined by the following factors:
- toxicity of the drug;
- the true amount of the drug entering the child’s body (it depends on the dose, concentration of the drug in breast milk and on the amount of milk consumed by the child);
- the peculiarity of the drug’s effect on the child’s internal organs;
- the duration of removal of the medicine from the child’s body (this depends on the maturity of the enzyme systems, the maturation of the baby’s liver and kidney function);
- duration of medication taken by a nursing mother;
- the child’s individual sensitivity to this drug;
- risk of developing allergic reactions.
Features of treatment
When feeding a child, it is extremely dangerous to self-medicate; all medicines and traditional medicine methods can only be used after consultation with a specialist. This is important to avoid complications and not harm the baby.
If the flu is severe, you should urgently call a doctor. Features if the following symptoms are present:
- High temperature up to 40 C or more.
- Severe cough, shortness of breath and pain in the chest area.
- Prolonged persistent fever.
- Fainting.
- Nausea with vomiting.
- Abnormal stool, mainly diarrhea.
- Intense headaches.
You cannot endanger your health and jeopardize the condition of your child. Since his immunity is not fully formed and there is a high probability of negative consequences.
Treatment during breastfeeding includes a whole range of measures:
- Use of drugs. The basis of treatment for a viral disease, dosage, course duration and administration are prescribed by the doctor.
- Compliance with the work and rest regime. To make it easier to bear the symptoms of pathology, it is recommended to spend more time in bed.
- Warm drinks and balanced nutrition. You should eat fortified foods at least 3 times a day and drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid.
- Using traditional medicine recipes. Since a woman is prohibited from taking most medications during lactation, folk remedies are included in the treatment complex.
What to do if a mother has a fever while breastfeeding
Experts say that most medications are not suitable for use during lactation. It must be remembered that a nursing mother can take any medications, including antipyretics, only as prescribed by a doctor. The use of antipyretic drugs is advisable only when the temperature rises above 38 0C. Lower temperatures are an adequate response of the body to the virus and do not require medical intervention.
If the temperature rises and a nursing mother needs help in the form of taking medications, it is recommended to take antipyretics, which include ibuprofen and paracetamol, during breastfeeding.
Antiviral and immunomodulators
During lactation you can use:
- Grippferon is effective for the treatment and prevention of infectious diseases. It has a convenient release form: drops, spray and ointment. The drug strengthens the immune system and relieves inflammation.
- Aflubin is a natural remedy in the form of drops and tablets. Helps reduce temperature, eliminates signs of intoxication.
- Viferon is an effective drug for flu and colds. Dispensed in the form of ointment, gel, suppository.
How to treat allergies during lactation
An allergic reaction during lactation is a fairly common occurrence. To prevent and combat allergies, a nursing woman should follow these rules:
- Ventilate your living space daily and do wet cleaning.
- Avoid eating the following foods: citrus fruits, chocolate, fish, honey, nuts, take a test to determine your tolerance to certain foods.
- Clean carpets, curtains and stuffed animals from dust and mites frequently.
- Wash bedding sets regularly, and the water temperature should be at least 60 0C
- During the warm season, do not walk in places where there are many flowering trees.
- When traveling by car, do not open the windows.
Antihistamines can only be prescribed to nursing women by a doctor, taking into account all contraindications.
What antiviral drugs can nursing mothers take for colds and coughs?
Treating cold and flu symptoms while breastfeeding
Women during lactation, in consultation with their doctor, are allowed drugs containing naphazoline nitrate, which help temporarily relieve swelling of the nasal mucosa. These drugs have a short period of action.
Sometimes drugs containing xylometazoline are recommended, which have an average duration of anti-edematous action and are also intended to relieve swelling, hyperemia of the nasal mucosa, restore patency of the nasal passages and facilitate nasal breathing.
Preparations containing oxymetazoline have the longest duration of active action - when administered intranasally, they reduce swelling of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract for 10-12 hours.
To reduce cough, expectorants are prescribed to thin the mucus, which allows you to cleanse the bronchi and restore their functions.
Herbal preparations based on:
- licorice root;
- anise;
- ivy;
- thyme;
- thyme;
- plantain and other plant components that promote the removal of mucus from the bronchi.
For a runny nose, oil drops in the nose are additionally used, which have an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect, and sprays to moisturize the nasal mucosa, which are made on the basis of sea water. These drugs thin out mucus, improving its discharge, and help normalize the functioning of the nasal mucosa.
For a sore throat, it is possible to use local antiseptic (antimicrobial) drugs, gargle solutions and lozenges. An aqueous solution of potassium iodine is used to lubricate the pharyngeal mucosa.
Contraindications
Drugs whose main active ingredient is bromhexine are contraindicated for lactating and pregnant women.
Treatment of the virus with antiviral drugs for hepatitis B
But all these drugs only temporarily relieve unpleasant symptoms. To combat various viruses, including the influenza virus, it is necessary to use antiviral drugs approved for use during lactation. One of these drugs is VIFERON. This drug is available in the form of suppositories, ointment or gel. He carefully takes care of women’s health and allows them not to interrupt the feeding of the child during the course of treatment. It is advisable to start using suppositories when the first signs of the disease appear, but at a later date their use will be justified. Lactation is also not a contraindication for the use of VIFERON Gel/Ointment; you just need to remember that they cannot be applied to the nipple area during feeding. VIFERON can also be used in combination with other medications recommended by your doctor.
Rumyantseva, md.
During lactation, a woman must ensure maximum safety for her child, who is too small to fight the flu on his own.
Until 12 months, a child is not capable of fully producing his own antibodies in the quantities necessary to protect against infections.
In the first months of life (up to 3-6 months), the child is protected by antibodies received during pregnancy from the mother. It must be taken into account that if a woman did not have the flu during pregnancy or was not vaccinated against the flu, the child may not have a sufficient amount of antibodies. Undoubtedly, the child receives maternal antibodies through breast milk, but most of them act in the intestinal lumen, and therefore the baby is protected much better from intestinal infections than from respiratory ones.
In this regard, it is necessary to know what the flu is, how to prevent it and when to seek treatment. There are signs that can presumably distinguish influenza from ARVI. Influenza is characterized by an acute onset (a full picture of the disease develops within a few hours), high body temperature, and severe intoxication. However, influenza can only be reliably diagnosed based on laboratory test results (nasopharyngeal swabs or blood are used for analysis).
Flu symptoms:
- increase in body temperature (usually sharp and significant);
- a sore throat;
- muscle pain;
- cough;
- headache;
- runny nose.
Safe flu prevention:
- wash your hands as often as possible (be sure to wash your hands after traveling on public transport, before eating, after meeting with friends/colleagues, after communicating with children, etc.);
- use hand disinfection gels if it is not possible to wash your hands;
- try not to touch your eyes, nose and mouth with unwashed hands, especially when in public places;
- do not communicate with sick people;
- Cover your coughs and sneezes with a handkerchief and ask those around you to do the same. Sick people in your environment should wear a mask;
- avoid visiting crowded places, spend more time outdoors;
- Get a flu shot. This is the only effective method of flu prevention! Flu vaccination for nursing mothers is recommended by leading health organizations: WHO, CDC (Center for Disease Control and Prevention, USA), Rospotrebnadzor.
Vaccination safety:
Vaccination during lactation is safe for mother and baby. The components of the vaccine do not lead to the formation of adequate immunity in the child, however:
- protect mother from illness,
- Antibodies produced by the mother partially penetrate into the milk and enter the baby’s body.
Vaccination must be carried out in October-November each year. Flu in infants is extremely severe, so please take care of your baby's health. All family members should also be vaccinated against influenza.
Unsafe or ineffective flu prevention:
"Immunostimulating" drugs
No “immune-stimulating” drugs have been proven to prevent or treat influenza. Their use in nursing mothers is prohibited due to the lack of clinical trials confirming the safety of the drugs for mother and child.
Examples of “immunostimulating” drugs: Amiksin, Kagocel, Cyclofern, Arbidol, Anaferon and other “ferons”. The use of homeopathic medicines (Oxolinic ointment, Oscillococcinum, Aflubin) also does not reduce the likelihood of infection.
ethnoscience
Unfortunately, eating lemons and garlic in large quantities also does not affect the likelihood of getting the flu.
Cups and mustard plasters are not a means of preventing or treating influenza.
Wearing a mask and preventing the flu
It is believed throughout the world that a mask does not protect if worn by a healthy person, but is effective if worn by a sick person. Rospotrebnadzor recommends a mask to protect a healthy person when visiting crowded places. Decide for yourself, but there is definitely no harm from it!
If you are sick:
- consult a doctor immediately;
- if the body temperature rises, it is possible to use Paracetamol (before the doctor arrives, then follow the doctor’s instructions);
- There is no need to stop breastfeeding during illness. In the acute phase of the disease, the most reasonable tactic is to pump and bottle-feed the baby to another family member. As soon as you recover, you can resume breastfeeding.
If a family member gets sick:
- move him to a separate room;
- do not use utensils that have been used by a sick person;
- wash your hands thoroughly after interacting with a sick person;
- Make sure that the sick family member wears a mask and changes it every 30 minutes;
- ventilate all rooms in the apartment.
Sources:
- Zaman K, Roy E, Arifeen SE, et al. Effectiveness of maternal influenza immunization in mothers and infants. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1555–64. (Effectiveness of a woman's flu vaccination for mother and child);
- Rasmussen SA, Jamieson DJ, Uyeki TM. Effects of influenza on pregnant women and infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;207(3 Suppl):S3–8. (The impact of influenza on pregnant women and children);
- Steinhoff MC, Omer SB. A review of fetal and infant protection associated with antenatal influenza immunization. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;207(3 Suppl):S21–7. (Review of data on the effectiveness of protecting the fetus and child from influenza when pregnant women are vaccinated);
- Esposito S, Bosis S, Morlacchi L, Baggi E, Sabatini C, Principi N. Can infants be protected by means of maternal vaccination? Clin Microbiol Infect 2012;18(Suppl 5):85–92. (Can children be protected by vaccinating their mothers?);
- Jamieson DJ, Kissin DM, Bridges CB, Rasmussen SA. Benefits of influenza vaccination during pregnancy for pregnant women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2012;207(3 Suppl):S17–20. (Benefits of Flu Vaccination for Pregnant Women);
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee opinion: influenza vaccination during pregnancy. Washington, DC: American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; 2010. (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Flu vaccination during pregnancy);
- cdc.gov
- https://www.rospotrebnadzor.ru/
- who.int
Similar
Facebook comments
Instructions for use of Viferon gel, suppositories and ointment for nursing mothers
Scheme for using the antiviral drug VIFERON Gel during breastfeeding
| Disease | Frequency/duration of use | Mode of application |
| ARVI and influenza (treatment) | 3–5 times a day / 5 days | A strip of gel no more than 0.5 cm long is applied to the previously dried surface of the nasal mucosa |
| ARVI and influenza (prevention) | 2 times a day / 2–4 weeks | |
| Herpes infection of the skin and mucous membranes | 3–5 times a day / 5–6 days | A strip of gel no more than 0.5 cm long is applied using a spatula or a cotton swab / cotton swab to a pre-dried affected surface 3-5 times a day |
Scheme for using the antiviral drug VIFERON Ointment during breastfeeding
| Disease | Frequency/duration of use | Mode of application |
| Herpes infection of the skin and mucous membranes | 3–4 times a day / 5–7 days | It is recommended to begin treatment immediately when the first signs of damage to the skin and mucous membranes appear (itching, burning, redness). |
| ARVI and influenza (treatment) | 3–4 times a day / 5 days | The ointment is applied in a thin layer to the mucous membrane of the nasal passages |
Scheme of use of the antiviral drug VIFERON Suppositories (rectal suppositories) for nursing mothers
| ARVI and influenza | 5 days VIFERON® 500,000 ME |
| Herpetic infection | 10 days VIFERON® 1000,000 ME |
| Urogenital infections, including human papillomavirus infection | 5-10 days VIFERON® 500,000 ME |
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
Reference and information material
Loading...
Take other surveys
Flu symptoms and complications
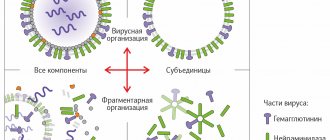
All types of influenza are divided into three categories: A, B, and C. Each category includes many varieties. According to doctors, they themselves are not sure that they know about all existing types of this disease. The disease is caused by a viral infection.
The virus has a complex structure, which makes its treatment more difficult. If you get the flu, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
The presence of this disease can be determined by a number of signs:
- general intoxication of the body;
- damage to the respiratory system.
The first sign is characterized by:
- the appearance of chills;
- increased temperature;
- the occurrence of fever;
- pain in the head and dizziness;
- sensitivity to light.
A complex of additional symptoms is also identified. A sick person feels weak, begins to sweat, suffers from pain in the back and muscles, and discomfort in the joints.
When you get the flu, the temperature rises to 39-40 degrees.
Respiratory tract damage is accompanied by:
- sore throat;
- runny nose;
- cough and difficulty breathing.
If you don't see a doctor promptly, the flu can lead to serious complications. Complications can be caused directly by the influenza virus, or by microbes.
The most dangerous complications are:
- pulmonary edema;
- swelling of the vocal cords;
- swelling or inflammation of the brain.
Less dangerous complications are expressed in the activation of chronic diseases such as radiculitis or arrhythmia.
If not treated in a timely manner, one type of flu can develop into another. In this case, a completely different treatment method will be required.