15.10.2018
Autumn is a time when you need to take care of your health and help your body protect itself from influenza viruses.
- Influenza is an acute viral infection that affects the entire body, primarily affecting the upper respiratory tract (including the nasopharynx, as well as the bronchi; less often, the lungs are involved in the process). The main symptoms of influenza are intoxication (fever, headache, muscle and joint pain) and dry cough.
- Influenza and ARVI occupy 1st place (more than 90%) among all infectious diseases.
- Every year in the world, mainly in the winter, influenza epidemics occur, during which the infection affects more than 500 million people, of which about 30% are children.
- According to , annual seasonal influenza epidemics result in 3–5 million cases of severe illness and 250,000–500,000 deaths worldwide.
Today, the most effective way to protect against influenza and its complications is VACCINATION
.
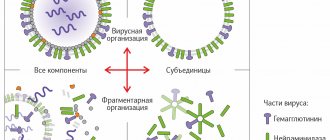
Vaccine options
The first influenza vaccines were made from killed or neutralized viruses, they are called whole virion vaccines, as well as from attenuated strains, the so-called live vaccines.
Almost all modern vaccinations for the prevention of influenza are inactivated (killed) vaccines with a replaceable strain composition. Influenza viruses for all vaccinations without exception are grown on chicken embryos, which is reflected in the list of contraindications for vaccination. Most inactivated whole-virion influenza shots consist of purified and concentrated viruses cultured in chicken embryos that have been inactivated by formaldehyde or UV irradiation. Inactivated vaccines, in turn, are divided into whole-virion vaccines, which are based on undestructed whole influenza viruses; pre-killed and purified, split, or split vaccines, which include particles of destroyed virions, that is, the full antigenic composition (external and internal proteins). Subunit influenza vaccines are also used, which consist of a mixture of two viral proteins: hemagglutinin and neuraminidase. Therefore, these vaccines have a minimal number of adverse reactions.
Virosomal vaccines are a new technology in the production of vaccination material. These vaccinations contain an inactivated virosomal complex with surface antigens of the influenza virus. Virosomes enhance the immune response to vaccination. The virosomal vaccine does not contain preservatives (thiomersal) and is well tolerated.
In Russia, the following inactivated trivalent influenza vaccinations are mainly used: “Grippovac”, “Vaxigrip”, “Begrivac”, “Agrippal S1”, “Grippol”, “Grippol plus”, “Influvac”, “Fluarix”, “Inflexal V” ( virsomal vaccine). A total of 18 vaccinations have been registered in Russia.
Classification of trivalent influenza vaccines
| Generation and type | Compound | Main characteristics | Examples |
Live vaccines | |||
| Whole virion vaccines | Live attenuated unpurified virus |
|
|
Inactivated vaccines | |||
| I – whole virion vaccines | Whole virus that has undergone inactivation and minor purification |
|
|
| II – split (split) vaccines | Particles of destroyed virus, surface and internal proteins and lipids |
|
|
| III – subunit vaccines | Highly purified influenza virus surface antigens (hemagglutinin and neuraminidase) |
|
|
| IV – subunit adjuvanted vaccines | Highly purified surface antigens of the influenza virus and an effective safe immunoadjuvant Polyoxidonium |
|
|
| Highly purified influenza virus surface antigens embedded in liposomes |
|
| |
| Highly purified surface antigens of influenza virus and adjuvant Sovidon |
|
| |
Classification of quadrivalent influenza vaccines
| Generation and type | Compound | Main characteristics | Examples |
| II – split (split) vaccines | Particles of destroyed virus, surface and internal proteins and lipids |
|
|
Reactogenicity is the ability of a vaccine to cause any side effects when introduced into the body (fever, local swelling, etc.)
What vaccines are used in Russia
Most public clinics use domestically produced vaccines Sovigripp, Grippol Plus, Ultrix, and private clinics also use the French Vaxigrip and the Dutch Influvac. A TD correspondent contacted ten Moscow medical institutions and found out that there were no new quadrivalent vaccines in either municipal or private clinics. The Medsi operator reported that the quadrivaccine was available, but had run out.
“I assume that the batch is not ready yet, but will appear soon - the vaccine season has just begun. Well, or that they didn’t release enough of it because it was the first time,” says pediatrician Sergei Butriy about the lack of a quadrivaccine. He adds that the new vaccine this season will be administered only to adults; due to bureaucratic procedures, there will be no time to obtain permission for use in children.
When calling clinics, a TD correspondent found out that the most popular vaccines this season are “Sovigripp” (in city clinics) and “Ultrix” (in paid clinics “Medsi”, “Bud Zdorov”, “Chaika” and “Alpha - Health Center” ). Both vaccines are domestically produced; foreign ones are currently unavailable. The Alpha Health Center clinic said that they were expecting the arrival of foreign drugs, but found it difficult to name the exact dates of delivery. The clinics “Mother and Child” and “Doctor Nearby” reported that they do not yet have either Russian or foreign vaccines.
Principles and purposes of vaccination
Vaccination is especially important for people at higher risk of developing serious flu complications and for people who live with or care for people at high risk. WHO recommends annual influenza vaccination for the following population groups: pregnant women at any stage of pregnancy; children from 6 months to 5 years; seniors 65 years and older; people with chronic diseases; healthcare workers.
Since 2006, influenza vaccination has been included in the National Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations of the Russian Federation. The following are subject to annual vaccination: children from 6 months of age, children attending preschool institutions, students in grades 1-11, students of higher vocational and secondary vocational educational institutions, adults working in certain professions and positions (workers of medical and educational institutions, transport, public utilities and etc.), adults over 60 years of age.
It is important to note that the composition of vaccines changes every year. This is done to provide maximum protection against the “wild” influenza virus. This process is carried out under the control of the World Health Organization. It is she who predicts the strains of the flu virus that will circulate in the expected season and sends these strains to vaccine manufacturers. In most countries, influenza vaccination is carried out annually.
Stubborn illness
Mom and daughter in the vaccination room.
Photo: Valery Titievsky / RIA Novosti The big problem is that modern medicine does not have the means to treat influenza, which means that all that remains is prevention.
Various dietary supplements and folk remedies are becoming less and less popular, since their effectiveness is also, to put it mildly, questionable.
Science has found a correlation between vitamin D levels and the incidence of influenza, so taking it during the cold season makes sense if vitamin D levels in the blood are low.
Otherwise, the recommendations boil down to leading a healthy lifestyle - getting enough sleep, moving, breathing air, eating well, not smoking and washing your hands well with regular (non-bacterial) soap.
Not much, in the eyes of a concerned patient. Yes, and in the doctor’s opinion too. (Although, if you look closely, this is not at all small) But the “flu vaccine” sounds much more “scientific” and convincing than the banal advice to wash your hands.
Let us note an important fact. Increasingly, the voices of doctors and scientists are heard, who undoubtedly belong to the medical establishment and strongly support the idea of vaccination against infectious diseases, who at the same time propose to weaken the propaganda of immunization against influenza, as it is not supported by scientific data.
This is, for example, the editor of the very prestigious British Medical Journal (BMJ) Peter Doshi (his article), director of the US Center for Infectious Disease Research and professor at several universities Michael Osterholm (his statements), general practitioner from Glasgow Margaret McCartney (her article in BMJ) , pediatricians and faculty at the University of Rochester School of Medicine (New York State) Eric Biondi and Andrew Elaine (their article).
A number of scientists also draw attention to possible complications from influenza vaccines, of which the most alarming is that the immunity developed to one of the strains can worsen the body’s response to another strain of the virus, as a result of which the disease will be more severe.
Pediatrician Allan Cunningham expresses concern about this fact in his article published this winter in the BMJ.
What threatens those vaccinated against influenza?
There is also evidence from a 2012 Chinese study suggesting that influenza vaccination may increase susceptibility to other types of acute respiratory infections.
Vaccine effectiveness
The use of influenza vaccination reduces the incidence rate by 1.4-1.7 times, helps reduce the severity of the disease, and prevents the development of severe complications and deaths. The vaccine is effective in all age groups in approximately 70-90% of cases.
Immunization reduces hospitalizations for pneumonia by 40% in healthy adults and by 45 to 85% in older adults. In addition, the frequency of otitis media is reduced by 36-69%, exacerbations of chronic bronchitis by 20%, and the number of exacerbations of bronchial asthma is reduced by 60-70%. In organized groups of elderly people (nursing homes, boarding schools), mortality from influenza is reduced by 80%.
Immunity after administration of the vaccine is formed within 14 days and lasts throughout the season. Unfortunately, the immunity developed after vaccination is short-lived. This is largely due to the high variability of the circulating influenza virus, the emergence of a new or even the return of an old subtype of the virus. In this regard, the anti-influenza immunity developed in the previous year does not protect against the disease in the current year. Therefore, annual immunization is necessary using only the vaccine of the current year of production. Vaccinations with last year's vaccines are only 20-40% effective.
Flu forecasts 2018-2019
Scientists predict that several influenza viruses will be widespread in the Northern Hemisphere in 2019. Therefore, doctors predict an increase in the incidence and number of deaths from influenza.
Expected viruses:
- Michigan (H1N1) is a very aggressive and constantly mutating strain of influenza A. It is poorly tolerated, causing fatal complications.
- Hong Kong (H3N2) is a dangerous strain of A virus that affects people, birds and animals. It is very dangerous, as it disguises itself as an acute respiratory viral infection, and then causes severe complications from the bronchopulmonary and cardiovascular systems.
- Brisbane - group B influenza, proceeds like a moderate-severe acute respiratory viral infection, but rarely causes complications.
- Phuket is also classified as influenza B, which is not considered dangerous and rarely causes severe consequences.
The 2018-2019 influenza epidemic, provoked by several strains that are constantly mutating, is expected to be quite widespread. Doctors suggest that in 2018-2019. the flu will develop rapidly, be difficult to diagnose and cause deaths, statistically exceeding the average.
Post-vaccination reactions
Whole-virion influenza vaccinations are relatively highly reactogenic. Therefore, when using them, general reactions may develop in the form of increased body temperature, headache, weakness, as well as local reactions in the form of swelling, redness and pain at the injection site. Usually these reactions are mild and go away on their own.
Subunit, split, and virosomal vaccines are the least reactogenic of all flu vaccines. Only in 3% of cases are vaccinated people allowed to develop adverse reactions.
Patient reviews
Reviews from people who have been vaccinated against the flu and vaccinated their children, both positive and negative:
- “We used to vaccinate both ourselves and our son every year. But each time they were very sick, sometimes a few days after the vaccination, my son had a very high fever and all the symptoms of the flu appeared. Over the past few years, they refused vaccinations, began to harden themselves and take vitamins - since then they have not suffered from anything worse than a cold.”
- “Every year our whole family gets vaccinated against the flu, and we have never observed any side effects. But before vaccination, we undergo the necessary examinations and consult with a doctor.”
- “The only time I got myself a flu shot, in the evening I had to call an ambulance and go to the hospital. I won’t take any more risks.”
- “Several years ago, my husband was seriously ill with the flu, since then he gets vaccinated every fall and tolerates it very well. I would also follow his example, but I have contraindications.”
Feedback from patients makes you think and not neglect preparations for vaccination - eliminating contraindications for health reasons will allow you to avoid side effects and complications from vaccination.
Contraindications
For all influenza vaccines:
- hypersensitivity to chicken protein or any other component of the vaccine
- severe fever or allergic reactions after previous vaccination with influenza vaccines.
Influenza vaccination is postponed until the end of acute manifestations of the disease and exacerbation of chronic diseases. For mild ARVI, acute intestinal and other diseases, vaccination is carried out immediately after the patient has established a normal temperature.
The live vaccine is not used in children under 3 years of age, pregnant women and people with impaired immunity.
Recommended serums
The 2021 influenza vaccine should be given with trivalent or quadrivalent vaccines. Experts recommend abandoning live vaccines and choosing split-preparation subunit vaccines that have a high degree of purification.
Recommended domestic serums:
- Sovigrip.
- Flu.
- Grippol Plus.
Recommended imported serums:
- Vaxigrip
- Begrivak.
- Fluarix.
- Agrippal.
The listed drugs are the most effective against influenza A and B; they contain only antigens that promote the formation of immunity to viruses. It should be noted that vaccination against influenza in 2021 is mainly carried out with domestic vaccines, since imported drugs are not always available for purchase.
Types of drugs
At the moment, there are several drugs recommended for preventive administration that can either completely eliminate infection or significantly alleviate its course (on the principle of a mild form of acute respiratory infection or acute respiratory viral infection).
Classification
There are several options for classifying recommended and proven medications. By composition:
live vaccines; split inactivated; whole virion inactivated. By effect on strains:
trivalent - protect against three types of virus (two A and one B); quadrivalent - respectively protect against two types A and two B. In 2021, the first Russian-made quadrivalent vaccine will appear on the market. This will expand the list of recommended preventatives and help protect people from more strains at the same time.
When is the best time to get vaccinated?
The timing of vaccination is indicated by WHO recommendations. The vaccination campaign begins in September. This is due to the fact that the rise in influenza incidence begins in January-February. Within a few months, the vaccine should have time to begin producing protection. The optimal period is calculated based on the region, but it is not recommended to vaccinate later than the end of October, since there is a risk of getting sick at the very beginning of the epidemic season.
Why do they get vaccinated?
The influenza vaccine not only protects the body from developing the disease, but also reduces the risk of complications. Vaccination is considered the safest and easiest way to combat the annual flu epidemic. The active substance included in the drugs paralyzes the pathogenic cell, then destroys its membrane, preventing reproduction.
Important!
If a person’s immunity is not weakened, then vaccination will not harm health and will help cope with the next epidemic.
Vaccination is a voluntary event. Before vaccination, you should consult with a physician and, if necessary, take allergy tests for a certain type of drug in order to minimize the risk of complications.
Flu vaccine safety
In most cases, influenza vaccines are easily tolerated without side effects. The most common side effects:
- pain at the injection site;
- skin redness;
- slight increase in temperature;
- cough;
- joint pain;
- weakness.
All these symptoms are typical for all types of vaccines, but cold symptoms most often appear when using live vaccines with weakened strains of the virus. They are administered intranasally and are intended for people aged 2 to 50 years. Pregnant women and the elderly are given inactivated vaccines, which are given by injection.
The only contraindications to vaccination include an allergy to chicken egg white. Although many allergy sufferers are successfully vaccinated. If there was no reaction in previous cases, then annual vaccination is considered safe.
Timing of vaccination
The peak load of viral infection on people occurs in the winter season. Most often, the epidemic begins to develop in January or February. Until then, you should prepare in advance so as not to acquire swine, bird or other modifications of the flu. To do this, the drug should be introduced into the body in October or November of this year.
Free vaccinations are available at all clinics, public service centers and hospitals from September 4 to October 29, 2021. Within the designated time frame, an annual population vaccination program will be carried out, in which all cities of the Russian Federation participate. The noted medicine is allowed even for pregnant women, as it does not harm the development of the fetus.
Risk groups for influenza among children
Diseases in children that increase the chances of getting the flu:
— chronic lung diseases (bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis); - diabetes; - heart and blood diseases (anemia, hemodynamic disorders, treatment with immunosuppressants); - chronic kidney disease; - long-term treatment with aspirin (risk of developing Reye's syndrome with influenza); - metabolic diseases; - immunodeficiency (HIV infected).
It is also necessary to vaccinate all adults who are in contact with these children.