The influenza virus is a rather dangerous infection that has become widespread in our country and throughout the world. As a rule, it manifests itself in autumn and winter. Despite all the efforts of scientists, the flu is modified and changed every year, so there is simply no universal cure for it.
The disease is characterized by ease of spread (airborne and contact routes) and severity of symptoms. Untreated flu can lead to serious complications.
At the moment, a huge number of pharmacological products have been developed to prevent the described disease. The most common are influenza vaccines. Today we will talk about two of them - Sovigripp and Grippol plus. Let's look at the composition of these vaccines, what their action is based on, and find out which is better tolerated - Sovigripp or Grippol Plus.
What is the difference between the composition of the vaccine Sovigripp and Grippol plus
Before considering how the compositions of the Sovigripp and Grippol Plus vaccines differ, it is necessary to give a brief description of each vaccine.
Sovigripp is a domestic drug that has been successfully used to vaccinate the population since 2013. The vaccine contains surfactants from different influenza strains. Every year the composition of Sovigripp undergoes changes due to mutation of the causative agent of the disease. This makes it possible to increase the effectiveness of the vaccine.
The main active and auxiliary components of the Sovigripp vaccine are:
- hemagglutinin of several influenza strains;
- thiomersal with ethyl mercury, which acts as a preservative;
- sovidon – as an adjuvant;
- a buffer solution containing potassium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium and potassium hydrogen phosphates, and purified water.
The drug is intended for injection into the muscle. Contrary to general belief, Sovigripp is not administered intranasally.
Grippol Plus is a Russian-made polymer-subunit liquid vaccine. The drug belongs to the third generation of vaccinations. This fact suggests that the active substance consists of surface influenza antigens that have been neutralized chemically. In this regard, they very rarely give allergic reactions.
Grippol Plus contains surface glycoproteins that were isolated from purified strains of influenza A and B. Azoximer bromide was added as an additional component. In addition, an auxiliary component of Grippol Plus is a phosphate-buffered saline solution.
The vaccine is a transparent yellow liquid. The drug can be administered either intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
Presence of preservatives
Preservatives are used for vaccines that are not only produced in large vials. Their addition avoids microbial contamination of the drug.
Thus, the Sovigripp vaccine uses thiomersal with ethyl mercury, and Grippol plus contains no preservatives at all.
Presence of an immunostimulant
Both vaccines belong to the third generation of immunobiological drugs. There is an opinion that their administration reduces immunity, so they add adjuvants, or substances that enhance the body's immunizing ability and increase the production of antibodies.
In Sovigripp, this component is represented by the compound sovidone, and in Grippol Plus - azokismer bromide, which has a wide spectrum of immunopharmacological effects.
The presence of an immunostimulant in the composition of vaccines makes it possible to protect cell membranes and more successfully build immunity to influenza strains. These compounds have an antioxidant effect, creating an artificial barrier to viruses.
Influenza virus antigen dose
As already mentioned, both vaccines are inactivated. Hemagglutinin and neurominidase, proteins present in the surface shell of the virus, were used as antigens in the preparations.
Let us consider the quantitative content of doses of antigens in each preparation.
Sovigripp in one dose (0.5 ml) contains:
- influenza type A strain (H1N1) – 5 mcg;
- hemagglutinin of influenza virus subtype A (H3N2) – 5 μg;
- influenza type B strain – 11 mcg.
The Grippol plus vaccine (recommended by domestic pediatricians for childhood influenza immunization) contains in a similar amount:
- influenza A viruses (H1N1) – 5 mcg;
- hemagglutinin of influenza virus subtype A (H3N2) – 5 μg;
- influenza type B antigens – 5 mcg.
As can be noted, the antigenic composition of the products in question is almost completely identical.
Everything you need to know about the FLU vaccination
What vaccines are used in the Republic of Belarus this season?
- "Grippol Plus" (country of origin - Russia);
- "Influvac" (country of origin - the Netherlands);
- "Vaxigrip" (country of origin - France);
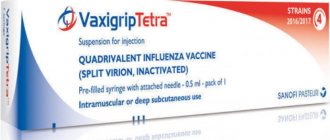
- "Vaxigrip Tetra" (country of origin - France);
- "Ultravac" (country of origin - Russia).
Which of these vaccines are used free of charge and which are paid for?
For immunization at the expense of budget funds, the Grippol Plus vaccine is used.
Grippol Plus, Influvac , Vaxigrip, Vaxigrip Tetra, and Ultravac are available for a fee
- All vaccines are registered on the territory of the Republic of Belarus, are comparable in effectiveness and have experience of use in our country and abroad.
- All vaccines are identical in the strain composition of influenza viruses.
- The vaccines used are highly effective and safe.
"Grippol Plus" , "Influvac", "Vaxigrip" - recommended for use in children from 6 months and in pregnant women.
"Vaxigrip Tetra" - recommended for use in children over 3 years of age and in pregnant women.
"Ultravac" - recommended for use in children over 3 years of age and not for use in pregnant women.
Is the Grippol Plus vaccine different from other vaccines?
It differs in that the Grippol Plus vaccine contains the immunomodulator polyoxidonium, which reduces the antigenic load (i.e. the vaccine contains 5 mcg of each strain of influenza virus). In all other vaccines, the amount of antigen is 15 μg of each strain.
A distinctive feature of the composition of the Grippol Plus vaccine is the presence of the immunomodulator Polyoxidonium, which has a wide spectrum of immunopharmacological effects, increases the immunogenicity of the vaccine and increases the immunological memory of the vaccinated person.
What are the contraindications to getting vaccinated against influenza?
- Temporary contraindications. Vaccination is temporarily postponed during an acute illness or exacerbation of a chronic disease. After the temperature has normalized (at the end of the acute illness) and the chronic disease has entered the remission stage, the vaccine can be administered.
- Absolute contraindications (i.e. vaccination is never carried out ). Allergic reaction to chicken egg whites. This allergy includes immediate swelling of the lower lip and throat when trying to eat a chicken egg in any form (boiled egg, scrambled egg, etc.). If there are no such reactions, and a person calmly and without consequences eats chicken eggs, then there is no allergy to chicken egg whites. An allergic reaction to previously administered influenza vaccines.
Is it possible to get the flu after vaccination and infect others?
You cannot get the flu if you are vaccinated with any vaccine. Since during the production process, vaccine viruses lose their ability to cause disease, but retain the ability to form protection.
When will immunity be formed?
Between the second and third weeks after vaccination, specific immunity develops, providing prevention of influenza for a period of up to 12 months.
What adverse reactions may occur after vaccination?
Out of 100 people vaccinated against influenza, 4-8 people may have local reactions in the form of redness, hardness or soreness at the site of vaccination, and 1-8 people out of 100 vaccinated may have general reactions in the form of a short-term increase in body temperature (up to 37.5 ° C ), general malaise. All these symptoms are short-lived and disappear spontaneously, usually after 1–2 days.
Does the flu shot guarantee 100% protection against the disease?
How reliable protection will be developed after vaccination depends on many factors, including. the patient’s age and health status, individual characteristics, etc. On average, out of 100 vaccinated people, 65-90 people will not get the flu. If a vaccinated person does get sick, his illness will be mild and without complications. Thus, vaccination guarantees protection against severe and complicated forms of influenza that end in unfavorable outcomes. The influenza vaccine has additional, to some extent immunomodulatory properties. Thanks to this, the immune system of approximately 15-20 people out of 100 vaccinated acquires additional protection from other respiratory viral infections.
Do I need to be vaccinated this year if I was vaccinated in the past?
Protective antibodies produced after vaccination are usually destroyed within 6-12 months after vaccination or their quantity becomes insufficient to protect against influenza in the new season. In addition, the variants of influenza viruses that are included in vaccines are updated annually. Therefore, it is necessary to be vaccinated annually.
Is there a difference in the effectiveness and duration of action of the drugs?
The effectiveness of the Sovigripp vaccine is no different from Grippol Plus.
If we talk about the effectiveness of the drugs, it can be noted that doctors are inclined to use the Sovigripp vaccine. In their opinion, it has a wider range of action and fewer side effects.
Clinical studies show that both vaccines meet the requirements of CPMP/EWP/1045/01, which apply to the immunogenic activity of influenza vaccinations, in terms of the level of seroprotection to all three vaccine strains.
The duration of action of both drugs is the same. The antiviral activity of vaccines develops on the 2nd...3rd days after vaccination and lasts from six months to a year.
Differences in the schedule and timing of vaccination
There are no differences in the administration of drugs. Immunization is carried out annually in the autumn-winter period, when epidemic instability is observed.
Vaccines are intended for intramuscular administration. Very rarely, Sovigripp can be injected subcutaneously. For the injection, choose the deltoid muscle or the anterolateral surface of the thigh.
The dose of the drug for children from six months to 3 years is 0.25 ml. Vaccination is carried out twice at an interval of 4 weeks. This immunization regimen is intended for previously unvaccinated children. If the child was vaccinated in the previous season, the dose of the drug is increased to 0.5 ml and administered once.
For children over three years of age and for adults, the dose of the drug is 0.5 ml once.
A special vaccination regimen is used for persons suffering from secondary immunodeficiency. The vaccine is administered twice with an interval of 4 weeks, 0.5 ml each.
Flu. Vaccinal prevention
The fundamental feature of influenza vaccine prevention is that the variability of the virus necessitates the need for annual vaccination .
In 1948, WHO created a special program aimed at combating influenza. Today, this program brings together four specialized international centers (in Atlanta, London, Melbourne and Tokyo) and more than 120 virology laboratories located around the world. Laboratories monitor the circulation of the virus and constantly exchange information with each other about which strains of the virus are found in the region where they are moving. All the results obtained flow to international centers. In February of each year, a WHO expert committee announces a forecast of which antigenic variants of the influenza virus will circulate in the coming season (The February forecast is focused on the Northern Hemisphere, and the forecast for the Southern Hemisphere is announced, as a rule, in August.) Over the past 15 years, the accuracy of the forecasts amounted to 92%. In March, WHO laboratories culture viruses and send the material to vaccine manufacturers. Each vaccine usually contains three types of viral antigens: two types A and one type B. From April to July, the production process takes place - growing, mixing, testing, trials. In August the vaccine is packaged, in September it goes to pharmacies, and vaccination is carried out in October-December.
Modern influenza vaccines are, in the vast majority of cases, well tolerated and have high preventive effectiveness.
Theoretically, flu vaccination is recommended for everyone who has a real chance of getting sick. And any city resident, any child attending a children's group, has plenty of chances to get sick.
In addition, there are categories of people for whom the flu vaccine is clearly indicated - indicated at any cost. These are people (adults, children - not important) for whom the flu is not just a dangerous disease, but a deadly one. We are talking about those who already have a certain disease that can worsen against the background of influenza: chronic diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, renal failure, diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiencies...
Risk groups for influenza include:
- children from 6 months to 15 years;
- elderly people (everyone over 65 years old);
- medical workers;
- everyone who works in trade, in catering establishments, in educational institutions, boarding schools and nursing homes.
Note!
Pregnant women are a particular risk group for influenza. They are the ones who are most likely to have a severe form of the disease with a fatal risk for both the fetus and the pregnant woman herself.
There are many influenza vaccines that are safe for use at any stage of pregnancy.
WHO strongly recommends that all countries consider pregnant women as a first-priority, highest-priority risk group subject to mandatory influenza vaccination!
Flu vaccination is not given to children under 6 months of age - to protect them, firstly, mothers are vaccinated during pregnancy, and secondly, they try to vaccinate as much as possible all those who come into contact with them.
If a flu vaccination is given for the first time in a child under 9 years of age who has not previously had the flu, then, as a rule, it is necessary to administer the vaccine twice with an interval of 4 weeks; for subsequent vaccinations (in other years and with other vaccine preparations), one administration will be sufficient.
A very important point is the timeliness of vaccination (before the onset of the flu epidemic). In this aspect, it should be taken into account that it takes from 7 to 20 days to develop immunity, depending on the type of vaccine.
For children under one year of age, vaccines are usually administered intramuscularly into the anterolateral thigh, and after one year of age - into the deltoid muscle.
Most manufacturers recommend using the pediatric (1/2 adult) dose of vaccine for children 6 to 35 months of age.
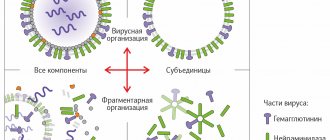
There are 5 options for influenza vaccines.
- Live vaccines containing live attenuated influenza virus.
- Inactivated whole-virion vaccines contain inactivated (dead) viruses. The word “whole virion” means that the virus is present entirely - it is not split or divided in any way.
- Split vaccines contain particles of the destroyed virus, its surface and internal proteins.
- Subunit vaccines contain only surface proteins, which, in fact, determine the antigenic version of the virus - hemagglutinin and neuraminidase.
- In addition to the immunogen, adjuvanted vaccines include a variety of adjuvants. A specific type of adjuvanted influenza vaccines are the so-called virosomal vaccines. The basis of virosomal vaccines are virosomes—particles consisting of fatty acids that are carriers of antigens.
Flu vaccines:
Agrippal S1 is a trivalent subunit purified inactivated influenza vaccine (Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics S.r.l., Italy; ROVI Contract Menufecchering S.L., Spain).
Vaxigrip is an inactivated split vaccine for the prevention of influenza (Sanofi Pasteur S.A., France; Pharmex Group LLC (packed from the in bulk form of the manufacturer Sanofi Pasteur S.A., France), Ukraine).
Influenza vaccine inactivated eluate-centrifuge liquid - influenza vaccine (FSUE NPO Microgen, Russia).
Grippovac is an inactivated liquid centrifugal influenza vaccine A(H1N1), A(H3N2) and B.
Flu-M is an inactivated trivalent vaccine for the prevention of influenza (Federal State Unitary Enterprise “St. Petersburg Research Institute of Vaccines and Serums and Enterprise for the Production of Bacterial Preparations” FMBA, Russia).
Grippol is a trivalent polymer-subunit liquid influenza vaccine (Petrovax Group of Companies, FSUE NPO Microgen, Russia).
Grippol Neo is a trivalent inactivated subunit adjuvant influenza vaccine (NPO Petrovax PHARM, Russia; LLC Pharma Life (packed in bulk from the company, Russia), Ukraine).
Grippol plus is a trivalent inactivated polymer-subunit influenza vaccine (NPO Petrovax PHARM, Russia; LLC Pharma Life (packed in bulk form from the company, Russia), Ukraine).
Grifor is an inactivated split influenza vaccine (FSUE NPO Microgen, Russia).
GC Flu is a vaccine for the prevention of influenza (split virion, inactivated) (Green Cross Corporation, Korea).
Intanza is an inactivated split vaccine for the prevention of influenza (Sanofi Pasteur SA, France).
Intanza 15 / Intanza 9 - inactivated liquid split vaccine for the prevention of influenza (for adults / for children) (Sanofi Pasteur S.A., France).
Inflexal V is a polyvalent inactivated liquid virosomal vaccine for the prevention of influenza (Berna Biotech Ltd., Crucell Switzerland LTD/SA, Switzerland).
Influvac is a vaccine for the prevention of influenza, surface antigen, inactivated (Abbott Biologicals BV, the Netherlands).
Influvir is a live monovalent influenza vaccine (FSUE NPO Microgen, Russia).
MonoGrippol is a monovalent inactivated subunit adjuvant influenza vaccine (NPO Petrovax PHARM, Russia).
MonoGrippol Neo is a monovalent inactivated subunit adjuvant influenza vaccine (NPO Petrovax PHARM, Russia; LLC Pharma Life (packed in bulk from the company, Russia), Ukraine).
MonoGrippol Plus is a monovalent inactivated subunit adjuvant influenza vaccine (NPO Petrovax PHARM, Russia).
Pandeflu is an inactivated subunit adsorbed monovalent influenza vaccine (FSUE NPO Microgen, Russia).
Panenza is an inactivated pandemic split vaccine for the prevention of influenza (Sanofi Pasteur S.A., France).
Sovigripp is an inactivated subunit influenza vaccine (FSUE NPO Microgen Russia).
Ultravac is a live allantoic influenza vaccine (FSUE NPO Microgen, Russia).
Ultrix is an inactivated split influenza vaccine (FSUE NPO Microgen, Russia).
Fluarix is an inactivated split vaccine (GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals, Branch of SmithKline Beecham Pharma GmbH & Co.KG, Germany).
Fluvaxin is an inactivated, purified, split influenza vaccine (Changchun Changsheng Life Sciences Ltd, China).
Fluvirin is a vaccine for the prevention of influenza, surface antigen, inactivated (Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics Limited, UK; Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics Limited, UK, packaged by Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics SRL, Italy).
published 10/10/2020 12:16 updated 23/07/2021 - Wiki of Dr. Komarovsky
Vaccine safety and side effects
Grippol plus and Sovigripp are recognized as one of the safest among Russian drugs. This effect is achieved by inactivating influenza viruses using chemical compounds.
However, despite being highly purified, influenza virus vaccines can cause a number of side effects. Let's look at the main ones.
Side effects of the Sovigripp vaccine:
- flu-like syndrome, which can be manifested by cough, runny nose and fever;
- headache;
- allergic reactions such as redness of the skin, rash. Very rarely, angioedema and anaphylactic shock may occur;
- compaction at the injection site and pain on palpation;
- dyspeptic symptoms (diarrhea, vomiting).
The Grippol Plus vaccine is characterized by similar side effects. The risk of an allergic reaction exists in both cases. Among the most dangerous symptoms is erythema nodosum, which occurs when fatty tissues are affected. In addition, rare neuralgia and paresthesia can be noted.
Contraindications and side effects are assessed in one block, so a few words must also be said about them.
Vaccination is not recommended:
- during periods of acute illness;
- if you are allergic to chicken protein, which is a component of any immunobiological drug;
- if undesirable symptoms occur during previous vaccination.
Let's summarize. Which is better - Grippol plus or Sovigripp
So which flu shot is best? Sovigripp or Grippol plus?
The difference, or differences, between the Grippol Plus and Sovigripp vaccines are insignificant.
Based on the above analytical information, it can be noted that the drugs have almost the same composition and the same type of side effects. Medicines are produced in Russia, have a high degree of purification and safety profile. The price of the drug Sovigripp is 200-250 rubles per dose. The cost of Grippol Plus is twice the price of a similar vaccine. The cost of one dose is 430 rubles.
If you evaluate the reviews of patients who prefer the Sovigripp vaccine, noting its greater effectiveness, then the choice will become obvious. In terms of price and quality, Grippol Plus is slightly inferior to the Sovigripp vaccine.
Grippol plus or Sovigripp. What will be better for children
Which flu vaccine is better: Grippol Plus or Sovigripp? Based on the safety profile of the medications presented, we can say that both drugs are completely identical. High quality and constant monitoring at the level of Roszdravnadzor allow us to say that both vaccines are perfectly suitable for use in children.
In comparison, Grippol Plus is inferior to the Sovigripp vaccine. However, individual opinions are not a reason to judge the effectiveness of the drug. Every year, the formulation of vaccines changes, which leads to an improvement in their quality and composition.
Both adults and children need to be vaccinated. As for pregnant women, anti-influenza drugs do not have embryotoxic or teratogenic effects, and therefore are not contraindicated during this period.
You can talk about the effectiveness of influenza vaccination for a long time, assessing its positive and negative aspects. We only note that the instructions for use of any vaccine contain a recommendation to administer it annually in order to avoid infection and complications during a flu epidemic.
Who needs a flu shot?
We recommend that all adults get a flu vaccine, especially those at risk:
- persons over 65 years of age, regardless of health status;
- patients of any age suffering from chronic diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- patients with diabetes mellitus, chronic renal failure, immunodeficiency conditions;
- women in the II–III trimesters of pregnancy and lactation;
- health workers;
- employees of educational institutions;
- personnel of service sector enterprises (shops, pharmacies, fitness centers, beauty salons).