Progesterone is a hormone from the group of steroids. Its production in small quantities occurs in the adrenal glands. However, it is mainly produced during pregnancy. During pregnancy, progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum, which is a temporary gland. Progesterone is called the “pregnancy hormone” because it plays a key role in bearing a child and preparing the body for childbirth. This hormone is an essential element of a woman’s reproductive health, both during pregnancy and during its planning. Its decrease can lead to miscarriage, which requires appropriate correction with medications.
Functions of progesterone during pregnancy
In the body of both women and men, progesterone performs many beneficial functions. However, its main task is to prepare a woman for pregnancy and childbirth, as well as to ensure adequate breastfeeding. Progesterone during pregnancy promotes proper implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity, ensuring thickening of the endometrium. At the same time, this hormone reduces the mother’s immunity so that the fertilized egg can easily penetrate the uterus and not be rejected. In addition, progesterone also affects the nervous system, rebuilding it for future childbirth. The hormone promotes relaxation of the uterine muscles, which reduces the likelihood of spontaneous abortion. Against the background of progesterone, the mammary glands grow and increase in size, which prepares them for the lactation period. This steroid prepares the pelvic joints for future childbirth. Progesterone affects not only the mother’s body, but also the child’s fetus, improving the production of steroid hormones in the embryo’s body.
What is progesterone
Progesterone is a hormone. It is produced in both women and men. In the stronger sex, progesterone is produced by the adrenal cortex and testicular tissue. Progesterone is a precursor to many hormones, including testosterone.
Progesterone is often called the pregnancy hormone. And this is justified, since progesterone plays an important role in maintaining and prolonging pregnancy. In women, this hormone is mainly produced by the corpus luteum of the ovary. This is a temporary gland that forms in the ovarian tissue at the site of the ovulated follicle.
The corpus luteum of the ovary has a soft yellow color and is clearly visible on the surface of the ovary. Hence the name - corpus luteum of the ovary. In women, progesterone is also produced in the adrenal cortex, and as pregnancy progresses, by the placenta. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum fades away.
Progesterone when planning pregnancy
Progesterone is important not only during pregnancy, but also at the planning stage. It must be in a woman’s body in a certain concentration in order to improve the quality of the fertilized egg and create conditions favorable for conception in the uterus. In addition, progesterone prevents the appearance of cystic and fibrous formations in the genitals, improves the nutrition of adipose tissue, optimizes the functioning of the coagulation system and ensures normal glucose levels. Therefore, when planning a pregnancy, any girl should be tested for progesterone levels in the blood. If it is outside the normal range, then you need to try to normalize its level by taking progesterone drugs.
Changes in the body of a pregnant woman under the influence of progesterone
An increase in progesterone concentration begins in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. Under the influence of the hormone, the body begins to prepare for pregnancy - the mucous layer of the uterus thickens (according to ultrasound - an increase in the thickness of the endometrium), the mucous membrane becomes loose, its energy reserve increases, and blood vessels grow intensively. Progesterone reduces the contractile function of the uterus. When pregnancy occurs, the embryo will not experience difficulty in implantation due to contractions of the uterus.
When pregnancy occurs, the corpus luteum blossoms (it increases in size, and the production of progesterone also increases). Under the influence of progesterone, the contractile function of the smooth muscles of the body decreases. The lumen of the arteries increases and pregnant women experience a physiological decrease in blood pressure. This may lead to drowsiness, a feeling of slight fatigue, and a desire to lie down.
Progesterone has an immunosuppressive effect on a woman’s body. For the expectant mother, the fetus is genetically half foreign. The immune system must recognize the foreign material and reject it. That is, lead to a miscarriage. But, progesterone (like a number of other biologically active substances) reduces the activity of the immune system, suppressing it, thereby prolonging pregnancy. The immune system does not seem to notice the foreign part of the fetus.
It is important!
Progesterone also affects the central nervous system, forming the “pregnancy dominant”.
The future baby comes first. All other issues become secondary and unimportant. During pregnancy, it is important to maintain pregnancy dominance. Try to protect the pregnant woman from negative emotions and experiences. The dominant of pregnancy plays a significant role in the physiological gestation of pregnancy. An increase in glandular tissue of the mammary gland is also associated with the influence of progesterone. Already in the early stages of pregnancy, a woman notices engorgement and enlargement of the mammary glands. It is important at this moment to pay attention to your underwear. It should not put pressure on the mammary gland, but at the same time have good support.
Test for progesterone during pregnancy
Determining progesterone levels during pregnancy is an important analysis that is included in the range of mandatory examinations. If a pregnant woman is at risk of miscarriage, has a history of miscarriages or chronic diseases, then she needs to determine the level of progesterone at the very beginning of the first trimester. If the expectant mother does not have health problems, it is enough to take the test in the second and third trimesters. The level of this hormone during this period of pregnancy will show the functional state of the placental tissue and the embryo’s body. In addition, progesterone during pregnancy is released in case of post-term pregnancy. The analysis should be taken strictly on an empty stomach. It is advisable not to expose yourself to stressful situations or overexert yourself physically the day before the test.
Progesterone injections
Women, under no circumstances, should self-prescribe a course of Progesterone therapy. This is the mission of the doctor who will correctly calculate the dosage and duration of treatment.
Typically, their plan includes monitoring the patient’s condition by donating blood for the hormone and Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
How to give Progesterone injections
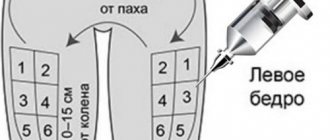
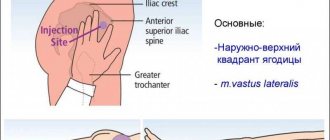
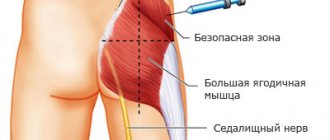
The drug is administered intramuscularly, but the instructions indicate that subcutaneous injections can also be given. Before manipulation, you need to warm the ampoule in your palm so that its contents reach a temperature of 40 degrees. After this, you need to wash your hands with soap and wipe them with alcohol.
The drug is drawn into a disposable syringe, the injection site is selected (in the buttocks or abdomen), and wiped with alcohol. The medicine must be administered slowly, despite the pain.
What is the dosage
The dose of the drug is selected by the doctor individually for each patient. In standard cases, the following treatment regimen can be used:
- To start menstruation (if delayed), progesterone is injected in the dosage prescribed by the doctor for seven days.
- To stop vaginal hemorrhages, the drug should be administered within a week, 0.50 ml-1.5 ml.
- For painful periods, 1.00% Progesterone is prescribed in an individually determined dosage for the patient 7 days before the start of the critical days.
Side effects of Progesterone injections
During the course of therapy, patients may experience side effects:
- jaundice develops;
- nausea;
- liver function is disrupted;
- swelling of tissues;
- blood pressure and cholesterol levels increase;
- sexual desire decreases;
- rapidly gaining weight;
- depression develops;
- headache;
- allergic manifestations;
- blood thickens, etc.
Important! If side effects are detected, the woman should consult a doctor who, if there is reason, will discontinue the drug or replace it with an analogue. In severe cases, symptomatic therapy can be carried out.
Effect of Progesterone injections
If the patient does the injections correctly, she will be able to achieve good results in the process of pregnancy planning and infertility treatment:
- the drug helps the embryo to take root;
- reduces the intensity of contractions of muscle tissue in the uterine cavity;
- stops menstruation during pregnancy.
At the same time, the drug begins to rapidly gain weight, and subcutaneous fat actively grows.
If a woman has benign tumors, polyps, cysts, etc., the medicine sometimes provokes their growth. After completion of therapy, patients restoring hormonal levels may be absent from menstrual periods for some time.
Low progesterone levels during pregnancy
There are many reasons why progesterone levels in the blood may decrease during pregnancy. As a rule, a reduced level of this hormone indicates an increased risk of spontaneous miscarriage, the development of an ectopic pregnancy, or intrauterine growth retardation. A decrease in progesterone concentration can be observed with insufficiency of the fetoplacental system, postterm pregnancy and gestosis. Reduced levels of progesterone during pregnancy are manifested by symptoms such as unstable mood, sleep disturbances, depression, pain during sexual intercourse due to vaginal dryness, decreased skin elasticity, constipation, flatulence, dizziness and fainting. An important criterion for reducing the level of this hormone is temperature fluctuations. As progesterone levels decrease, there is a decrease in numbers when measuring basal temperature.
Decreased progesterone, is it dangerous?
Both increases and decreases in progesterone levels require careful analysis. A decrease in hormone levels may indicate insufficient production of the hormone by the corpus luteum of the ovary, which can lead to termination of pregnancy. A decrease in hormone levels may also indicate feto-placental insufficiency, a burdened obstetric-gynecological history (history of miscarriage).
An increase in the level may indicate problems with its excretion, disruption of the placenta, somatic diseases of the mother, or multiple pregnancy. Therefore, a doctor examines each specific case. And, if necessary, recommends maintenance therapy.
Treatment of progesterone deficiency
If infertility is caused by an insufficient amount of progesterone in the body, then the level of the hormone must be increased by taking appropriate medications. They can be prescribed either in tablets for oral administration or in injection form. With a high risk of miscarriage and reduced progesterone levels, these drugs allow you to carry the fetus to term and prepare the body for childbirth. There is no single regimen for prescribing these hormonal drugs, so the doctor must select an individual regimen for each woman. Treatment for progesterone deficiency begins before 16 weeks of pregnancy.
To prevent miscarriage, progestins that do not have virilizing characteristics are used. The most common drugs for the treatment of progesterone deficiency during pregnancy are utrogestan, duphaston and 17-OPK. These are synthesized analogues of this hormone, which are considered effective in cases of high risk of miscarriage. Progesterone preparations can reduce the excitability of the uterus and improve the function of its mucous membrane. In general, treatment of progesterone deficiency allows, in most cases, to normalize the course of pregnancy and significantly reduce the risk of spontaneous abortion. In addition, synthesized progesterone analogues can also be used in women who are not pregnant. These drugs are indicated for pathology of the menstrual cycle and endometriosis. They should also be taken for frequent uterine bleeding of various origins.
Detecting progesterone deficiency before pregnancy
Clinically, progesterone deficiency may not manifest itself in any way. To diagnose this pathology, a comprehensive examination is necessary, including:
- measurement of basal temperature; in case of deficiency, the duration of the luteal phase will be less than 10 days;
- Ultrasound of the genital organs to visualize the corpus luteum and assess the thickness of the endometrium; the leading ultrasound signs of progesterone deficiency are: the absence of the characteristic heterogeneous internal echostructure of the corpus luteum and the thinning of its walls;
- Dopplerography and Doppler ultrasound (assessment of blood flow), which will reveal a depletion of the vascular pattern around the walls of the pathologically altered corpus luteum and a decrease in blood flow speed compared to the norm;
- study of hormonal profile: FSH, LH, prolactin, progesterone;
- endometrial biopsy (2-3 days before menstruation followed by histological examination of the biopsy), which can demonstrate a pronounced lag in the secretory reaction of the endometrium.
If the function of the corpus luteum decreases, pregnancy may not occur. This condition is manifested by progesterone deficiency and decreased endometrial secretion. All of these processes are the basis of infertility.
If there is a deficiency of progesterone synthesized by the placenta, the pregnancy may be terminated. After all, it is this hormone that supports the development of the fetus.