Causative agents of diphtheria, how does infection occur?
The causative agent of diphtheria is a microorganism from the genus Corynebacterium. When multiplying, it releases a toxin into the external environment. This potent substance determines the local reaction and systemic signs of diphtheria. However, not all diphtheria bacilli are capable of releasing toxin.
The microorganism persists on surrounding objects for up to 2 weeks, and survives boiling for less than 1 minute. The main routes of infection are airborne and household contact. Patients are the most contagious, but corynebacteria can also be released into the environment by apparently healthy carriers of microorganisms. It is the carriers who are now the main sources of infection, and most often these are children with chronic ENT diseases.
Symptoms of diphtheria depend on where the microbe enters the body. Most often these are the pharynx, trachea, nose, eyes, skin and mucous membrane of the external genitalia. After the pathogen enters, an incubation period begins, lasting from 2 to 12 days, at the end of which the patient becomes infectious.
Diphtheria symptoms
The most characteristic signs of diphtheria:
- film on the surface of fabrics, tightly welded to them;
- enlarged lymph nodes, increased temperature;
- mild pain when swallowing;
- headache, weakness, symptoms of intoxication;
- less often swelling and discharge from the nose and eyes.
Throat diphtheria is the most common form of the disease. It can have varying degrees of severity:
- Localized
It begins with an increase in temperature for 3 days and malaise. On the 2nd day, plaque appears on the tonsils and persists for a week. The submandibular nodes are slightly enlarged.
- Common
Diphtheria plaques spread to the uvula, palate, and oropharynx.
- Toxic
It develops quickly with an increase in temperature to 40˚C, sore throat, swelling of the subcutaneous tissue in the neck (a distinctive feature of this form). The films are dense, soaked in blood, have a sweetish odor, and spread throughout the nasopharynx.
- Lightning fast
Within a few hours, the temperature rises sharply, vomiting, convulsions appear, loss of consciousness occurs, blood pressure decreases, heart depression, and hemorrhages under the skin occur. Diphtheria films do not have time to form, since the death of the patient occurs in the next 2–3 days.
Symptoms of diphtheria in children under 5 years of age can manifest themselves in the form of croup - cough, increasing narrowing of the airways and suffocation. This is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Diphtheria in children can occur even against the background of immunity after vaccination, but the disease is milder:
- a localized form of the disease develops;
- croup does not occur;
- there are practically no complications;
- the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome is minimal.
Complications of diphtheria
A severe form of the disease has an extremely harmful effect on the cardiovascular system and can lead to heartbeat disturbances. Negative consequences also affect the nervous system, since damage to the peripheral or cranial nerve is not excluded, which can lead to paralysis, strabismus, and breathing problems.
The most dangerous complications of diphtheria include:
- problems with cerebral circulation;
- cerebral edema;
- kidney damage;
- hepatitis of diphtheria origin;
- toxic shock to the body;
- severe disorders of blood clotting processes;
- metabolic encephalopathy.
Symptoms and diagnosis of diphtheria
Signs of diphtheria in children and adults in the first days of the disease are nonspecific and resemble a sore throat, so when they appear, it is necessary to call a doctor at home. Pay attention to the following signs:
- a dense light film on the tonsils, difficult to remove with a spatula;
- the lesion is bilateral, but its size is unequal on the right and left;
- slight redness and sore throat;
- the temperature drops after 2–3 days, while plaque in the throat persists much longer;
- swelling of the neck is possible;
- after using anti-diphtheria serum, all symptoms quickly subside.
For any inflammation of the tonsils, a smear for diphtheria from the throat and nasal cavity is necessary.
To obtain a quick result, a diphtheria test is carried out using the PCR method, and a bacteriological examination of the obtained material is also used. Diphtheria diagnosis also includes the determination of antibodies to the bacterial toxin.
Insidious "film". What is diphtheria?
A disease such as diphtheria has been known since ancient times. Hippocrates and Homer also mention it in their works. The first clinical descriptions of the infection date back to the 1st–2nd centuries. ad.
Diphtheria is even reflected in fiction. The disease is described by A. Chekhov in “The Jumper” and M. Bulgakov in “Steel Throat”.
We talked about what diphtheria is, and whether we can say that these days this ancient disease is over forever, with Elena Gennadievna Koroleva, an infectious disease doctor at the Expert Clinic Tula.
- Elena Gennadievna, tell us what kind of disease this is - diphtheria? How often does it occur today?
— Diphtheria affects only people, i.e. it is an anthroponotic disease. Animals don’t get sick from it, and we can’t get infected from them.
Diphtheria is a bacterial infection (not viral), which is characterized by high intoxication and fibrinous inflammation at the site of entry of the pathogen. What is fibrinous inflammation? This is inflammation, the external manifestations of which are characterized by the presence of films.
The entrance gates of infection have different localizations. Diphtheria occurs in the eyes, nose, and genitals (mainly in girls in the first or second grade of school). It could even be diphtheria of the umbilical remnant of a newborn. A rare case, but nevertheless it occurs. And, of course, the main localization of the pathogen is the oropharynx and palatine tonsils.
I want to say that diphtheria has been known since ancient times. Homer and Hippocrates mentioned this disease in their works. Over the centuries, the name of the disease has changed several times. In historical works one can find, for example, the following: fatal pharyngeal ulcer, hangman's noose, malignant tonsillitis, croup. Despite the fact that the disease is very ancient, it has not lost its relevance today. Unfortunately, cases of diphtheria are still being identified in different regions of the world.
In the 90s, when the Soviet Union collapsed, I witnessed a very severe outbreak of diphtheria in Central Asia. The number of sick people was in the hundreds. There was a high mortality rate among both children and adults. During these same years, a high percentage of cases were registered in all post-Union republics and Russia. Then serious measures were taken to universally vaccinate the entire population. We went door to door and vaccinated everyone - both old people and children.
According to the literature, every twenty to twenty-five years an outbreak of diphtheria is possible as a result of a decrease in the “immune layer” of the population. If you do not remember about this disease, you can miss a case of diphtheria (under the guise of a sore throat) in a child or adult, which threatens the spread of infection and is dangerous for the life of the patient.
Look, from the time of Hippocrates to the present day, diphtheria remains a formidable and still epidemiologically significant disease, outbreaks of which are recorded in many parts of the world, including Russia, although diphtheria is considered a controlled infection. In fact, a person vaccinated against diphtheria according to all the rules (in accordance with the vaccination calendar) should not get sick when encountering a pathogenic bacterium, or can suffer a mild form of the disease. It all depends on the formation of protective immunity in each individual person.
According to the literature, every twenty to twenty-five years an outbreak of diphtheria is possible as a result of a decrease in the “immune layer” of the population
— Why does diphtheria develop and how is it transmitted?
— In diphtheria, the source of the disease is a sick person. But the most dangerous thing is healthy bacteria carriers. That is, a person is not sick, but is a source, a releaser of Loeffler’s bacteria (Corynebacterium diphtheria) into the external environment, and can infect others.
Diphtheria is transmitted through household contact or airborne droplets (sneezing, talking). Remember when we had soda fountains? So, after the diphtheria outbreak, all reusable glasses were removed. This bacterium can survive in saliva from a glass for two weeks. It stays on clothes and in dust for a very long time. Let's say a bacteria carrier spits on the street. In the dust that contains his saliva, the bacteria survive for up to six months. Therefore, this disease will not lose its relevance for a long time.
— What are the symptoms of diphtheria?
— Since diphtheria often affects the oropharynx and palatine tonsils, the main symptoms are similar to the manifestation of acute tonsillitis. As with a sore throat, there is a high temperature and sore throat.
With diphtheria, there is a specific smell from the mouth (the smell of rotten apples), a characteristic (very pale) appearance of the patient, the appearance of the throat, very severe intoxication (weakness, fever in the first days of the disease, headache, severe sore throat). With the development of a toxic form of diphtheria, edema spreads to the neck and anterior surface of the chest. The film that forms in the throat and on the tonsils is difficult to remove; in place of the removed film, a bleeding surface remains. The removed plaque from diphtheria cannot be rubbed with a spatula and sinks in water. With purulent sore throat there are no such manifestations.
Read materials on the topic:
We are looking for the causes of a constant sore throat. Take care of your throat! How to avoid “summer” sore throat?
— What examination is prescribed for suspected diphtheria?
— The main thing is the detection of corynebacteria (the causative agent of diphtheria), the so-called Loeffler’s bacterium. To do this, swabs are taken from the site of the entrance gate - where films were found (from the throat, nose, eyes, etc.). The analysis is called “throat swab for BL (Loeffler’s bacterium).” If there is bacteria at the site where the smear was taken, the test will definitely show it. General and biochemical blood tests will not show changes characteristic only of diphtheria.
Read more about general and biochemical blood tests in our articles:
How to properly take a general blood test? What does a biochemical blood test show?
— How to treat diphtheria? Is hospitalization required?
— If diphtheria is suspected, anti-diphtheria serum (toxoid) must be administered, which must be administered as early as possible (the serum inactivates the heavy toxin produced by the diphtheria bacillus). The less diphtheria toxin circulates in the blood, the sooner treatment is started, the more successful it is, and the lower the risk of complications.
Of course, this is done only in a hospital setting. Patients with suspected diphtheria should be hospitalized in one hundred percent of cases.
— Until what age are diphtheria vaccinations given?
— According to the sanitary and epidemiological rules that currently exist, up to 56 years of age. But there are so-called decreed groups of the population: kindergarten teachers, school teachers, medical workers. Since they communicate with a large number of people, it is advisable for them to be vaccinated at an older age.
Read materials on the topic:
Are unvaccinated children the healthiest? Vaccinations: where is the truth and where is the lie?
— Elena Gennadievna, how often should you be vaccinated against diphtheria?
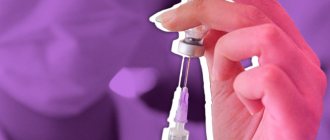
— We have a vaccination calendar, which was approved at the state level. The first vaccine against diphtheria is administered at three months, then at four and a half, at six months and the first revaccination a year. This is a DPT (adsorbed pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus) vaccine for young children. Older children and adults are no longer vaccinated against whooping cough. They are vaccinated with ADS, i.e. diphtheria, tetanus. Revaccination is carried out at 6 - 7 years, at 11 and then at 16 - 17 years. And then once every ten years. That is, throughout our lives we are vaccinated against diphtheria.
Interviewed by Marina Volovik
The editors recommend:
Childish suffering. Scarlet fever: recognize and treat The throat asks for help. How to treat chronic tonsillitis?
For reference
Koroleva Elena Gennadievna
Graduate of the pediatric faculty of the Kyrgyz State Medical Institute in 1992.
From 1992 to 1993, she completed an internship in pediatric infections.
In Frunze (Bishkek) she worked in the Republican Infectious Diseases Hospital as a children's infectious disease specialist. Then - a resuscitator in the intensive care unit for infectious patients.
In Tula, she worked at the regional children's hospital for 11 years. She headed the intensive care unit for 7 years.
Currently, he is an infectious disease doctor, anesthesiologist-resuscitator, and pediatric anesthesiologist-resuscitator at the Expert Clinic, Tula.
Treatment of diphtheria
The use of folk remedies for this disease is unacceptable. Treatment of diphtheria is carried out only in an infectious diseases hospital, in an isolated box. Delay in hospitalization can cause complications and unfavorable outcome of the disease.
Therapy uses anti-diphtheria serum, antibiotics, and restorative therapy.
Carriers of toxigenic strains (variants) of the pathogen identified during examinations are also subject to hospitalization. They are prescribed antibiotic therapy.
Clinical picture
With the development of laryngeal diphtheria, the picture of the occurrence of acute stenosis is clearly visible: the formation of fibrinous deposits, swelling of the laryngeal mucosa and spasm of the internal muscles of the larynx. With this disease, symptoms increase in a certain sequence and therefore the following stages can be distinguished:
- Dysphonic, sometimes called the stage of croupous cough;
- Stenotic;
- Asphyxial.
At the first stage of the disease, catarrhal changes develop: body temperature rises significantly, symptoms characteristic of general intoxication of the body appear. A cough appears, which gradually intensifies. Changes in the voice are observed - hoarseness up to aphonia (lack of a sonorous voice). This occurs because the vocal cords are covered with fibrinous plaque. The cough first becomes hoarse and then almost silent. The duration of this stage can be several hours or days.
When the second, stenotic phase of the disease occurs, manifestations such as aphonia and silent cough persist. They are accompanied by difficulty breathing, which occurs due to a decrease in the lumen in the larynx. This is caused by the presence of films, as well as a reflex spasm of the internal muscles of the larynx, which occurs due to the fact that the nerve endings are irritated by diphtheria toxin. Difficulty inhaling (inspiratory shortness of breath) is accompanied by a sharp retraction of the yielding areas of the chest (intercostal spaces, upper abdomen and the fossa located between the collarbones). As the edema increases, the degree of laryngeal stenosis also increases. In this case, the patient turns pale, and in some cases a cyanotic coloration of the skin appears (bluish color of the mucous membranes and skin). In addition, he rushes about and literally breaks out in cold sweat, his pulse becomes more frequent, and his breathing becomes noisy.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
The asphyxial stage lives up to its name. It is observed during the transition of laryngeal stenosis to the terminal stage. The patient becomes indifferent to what is happening around him, drowsy. The breathing rate increases and the pulse becomes thready. As a result, death occurs from suffocation.
Prevention
Creating artificial immunity against the disease is the most effective prevention of diphtheria. The first vaccination against diphtheria is carried out at the age of 3 months with the DPT or DPT vaccine. Then it is repeated at 4.5 months, six months, 1.5 years and 6 years. Diphtheria revaccination is carried out starting from the age of 16 once every 10 years. In addition to domestic drugs, an imported diphtheria vaccine is available - an analogue of DTP Infanrix or ADS - T.D. Vax.
Additional preventive measures:
- examination of nasopharyngeal swabs from all those in contact with the sick person;
- medical observation of contacted people for a week;
- disinfection of the premises after hospitalization of the patient.
Features of diphtheria
Diphtheria is a disease that directly depends on the level of vaccination of the population. Today, periodic increases in incidence are recorded, which occur with poor levels of vaccine prevention. Currently, the disease often shifts from childhood: diphtheria affects adults, especially those who, due to their profession, have to interact with a large number of people. As the epidemiological situation worsens, the disease occurs in people in a more severe form and the number of deaths increases. However, in people who have previously received diphtheria vaccinations, the disease is mild and is not accompanied by complications.
Treatment at the Mama Papa Ya clinic
The network of family clinics “Mama Papa Ya” offers vaccination services for children and adults, identification of pathogen carriers, and consultations with doctors of various specialties. Our advantages:
- an extensive network of branches in Moscow and other cities;
- affordable prices for medical services;
- full consultation on vaccination issues, assistance with choosing a drug, including allergic reactions;
- restorative treatment of corynebacterium carriers;
- examinations and consultations with specialists (cardiologist, neurologist) in the event of the development of complications of the disease.
If you have any questions about this topic, please make an appointment with the clinic by phone or on our website.
Reviews
Marina Petrovna
The doctor carefully examined my husband, prescribed an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis. She gave recommendations on our situation and ordered additional examination. No comments so far. Financial agreements have been met.
Roakh Efim Borisovich
I am simply delighted with the doctor and the clinic. I haven't had fun in clinics for a long time. Everything went perfectly from a logistics point of view, strictly on time. I also received aesthetic pleasure both as a patient and as a person. I could communicate and this communication gave me great pleasure. My deepest bow to the ultrasound doctor.
Luzina Sofya Khamitovna
I really liked Dr. Vlasova. Pleasant and sweet woman, a good specialist. I received an answer to all my questions, the doctor gave me a lot of good advice. I was more than satisfied with the visit.
Evgeniya
We visited the “Mama Papa Ya” Clinic with our child. A consultation with a pediatric cardiologist was needed. I liked the clinic. Good service, doctors. There was no queue, everything was the same price.
Olga
I really liked the clinic. Helpful staff. I had an appointment with gynecologist E.A. Mikhailova. I was satisfied, there are more such doctors. Thank you!!!
Anonymous user
I removed a lump from Alina Sergeevna, the operation was great! Many thanks to her for her sensitive attention and approach to every detail.
Anonymous user
Today I was treated at the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and attention. Many thanks to them and continued prosperity.
Iratyev V.V.
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Belova E.M.
Today I had a mole removed on my face from dermatologist I.A. Kodareva. The doctor is very neat! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Yulia Borshchevskaya is friendly and accurately fulfills her duties.
Anonymous user
I would like to express my gratitude to the staff of the clinic: Mom, Dad, and me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, a very friendly and cheerful team and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish your clinic prosperity.
Christina
I liked the first visit. They examined me carefully, prescribed additional examinations, and gave me good recommendations. I will continue treatment further; I liked the conditions at the clinic.
Anna
Good clinic, good doctor! Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and clearly explain what the problem is. If something is wrong, she speaks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don’t regret that I ended up with her.