Immunization is still considered the only reliable method of preventing dangerous infectious and viral pathologies. People who are poorly versed in medicine believe that vaccination and vaccine are synonymous. In fact, these are two different concepts. It is useful to know how a vaccination differs from a vaccine.
Inoculation and vaccine: what is the difference?
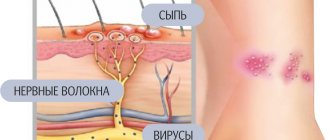
There is a significant difference between an inoculation and a vaccine. Vaccination is the process of introducing antigenic material into the body in order to develop specific immunity to certain diseases.
A synonym for this concept is vaccination. They instill protective powers against chickenpox, influenza, polio, rubella, diphtheria, plague, and tetanus.
A vaccine is an antigenic preparation that contains a live attenuated or killed pathogen intended for the prevention of certain infectious and viral pathologies. Examples of such a drug include DPT, Priorix, Tetrakok, Pentaxim.
Vaccine preparations are produced in the form of a lyophilisate or a ready-made suspension for injection. They can be polyvalent or single-component.
Main differences between vaccine and serum
The vaccine and serum have significant differences.
They include the composition, purpose, technology and manufacturing methods, the mechanism of influence on the body, rules of use, duration of action. A vaccine is a means that is used to prevent infection with dangerous infectious and viral diseases.
Serum is a drug that is developed and released for the treatment of already begun pathology.
The vaccine contains live or killed viruses, bacteria, their fragments, and toxoids. When these substances enter the blood, the body begins to produce protective elements - antibodies, which have the ability to destroy specific pathogens.
The serum already contains antibodies. When such a drug is introduced into the body, the fight against existing viruses and bacteria begins. The vaccine is used before pathogenic microorganisms enter or within a few days after possible infection.
The serum is used for already diagnosed infectious or viral diseases. After administration of the vaccine, antibodies are observed in sufficient quantities 2-4 weeks after injection.
The effect of immunization lasts for a long time - 5-20 years. The serum acts instantly, but does not last long - 1-2 months. The vaccine is obtained by cultivating bacteria and viruses, isolating their fragments, and neutralizing them.
To prepare the serum, the blood of immunized horses, humans, pigs, and rabbits is used. This drug helps to avoid the negative consequences of botulism, tetanus and other dangerous pathologies. If the vaccine is administered in a timely manner, a person will not become infected with the listed pathologies or will experience them in a milder form.
To experience the benefits of the vaccine, it must be administered a month before the epidemic or travel to a region with an increased incidence. To get results from using the serum, the product should be injected immediately after infection.
What is the difference between paid and free vaccinations?
All vaccinations are divided into paid and free. Much depends on where vaccination is carried out, with what drug, and during what period. In private clinics and public hospitals, within the framework of the schedule approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, they immunize with drugs free of charge.
Measles vaccine
For example, against measles and mumps in clinics at your place of residence, you can be vaccinated with Russian drugs LIV and ZHPV. And to protect against tetanus, whooping cough and diphtheria, the therapist will suggest the use of DTP. In case of emergency prevention of a viral or infectious pathology, vaccination is required to be given free of charge.
If a person wants to undergo an unscheduled vaccination, he will have to allocate a certain amount of money for this procedure. If there is a desire to perform immunoprophylaxis with an imported vaccine, then doctors will provide such a service for a fee. Then, instead of ZHV and ZHPV, Priorix will be injected, and DTP will be replaced with Infanrix or Pentaxim.
Paid vaccinations are given in private medical institutions. These institutions usually use foreign vaccine preparations. The cost of the procedure includes the price of the drug and the medical staff’s services for examining, examining the patient and administering the injection.
Preference for paid vaccinations with foreign vaccines is given for the following reasons:
- domestic drugs may be less well tolerated in sensitive individuals (this is especially true for DTP immunization). They contain merthiolate, Tween-80, which is dangerous to the body. Although these substances are present in the drug in microdoses that are safe for humans, foreign pharmaceutical companies no longer use such components. Therefore, imported products are considered safer;
- The choice of free vaccines is limited. Some people have intolerance to certain components. In this case, you have to look for an analogue drug;
- With the help of imported vaccinations, you can protect yourself from several diseases with one injection. The domestic product prevents the development of 1-3 pathologies;
- To get immunized at a local clinic, you often have to wait in a long line. In private medical centers, the client is vaccinated by prior appointment at a time convenient for him.
You can't refuse to get vaccinated
In connection with the unfavorable epidemiological situation in the capital, the chief state sanitary doctor for the city of Moscow, Elena Andreeva, issued a decree on June 15 “On carrying out preventive vaccinations for certain groups of citizens for epidemic indications.” The resolution is about ensuring vaccination against COVID-19 for categories of citizens who are subject to it without fail. Such workers must be vaccinated with the first component before July 15, and with the second before August 15. The vaccination must be done with a drug that has passed state registration in the Russian Federation.
Related article:
The capital's Department of Health reported details about the fight against Covid in Moscow
Related article:
“We are now registering the so-called Indian strain”
The resolution states that the intensity of the increase in incidence has increased since June 6, 2021, when it was 11% per day, and in subsequent days up to 20%. The situation with the new coronavirus infection in Moscow is worsening; analysis shows that people of working age from 18 to 60 years old are more likely to get sick - 60% of those sick. The resolution also provides the social composition of patients: working population - 73%, children - 13%, pensioners - 14%.
The decree applies to beauty salons, enterprises and trade establishments, sports and recreation, consumer services and public catering, banking and postal sectors, public transport, education and healthcare, culture and art and a number of others.
However, we are not talking about any forced vaccination, so this vaccination cannot be called mandatory, explains Alexey Khoruzhenko, managing partner of the Moscow Legal law office.
“The employee has no obligation to get vaccinated,” the lawyer emphasizes. — According to the Constitution of the Russian Federation, a person has the right to manage his health as he wants. Taking care of his health is his personal matter. It is the employer who faces penalties for failure to comply with the standard of vaccinating 60% of employees, but how the employer will solve this problem is another question.”
The responsibility for complying with the regulation truly lies with the employer. In accordance with Articles 6.3 of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation and 3.18 of the Moscow Administrative Code, individual entrepreneurs can be fined from 30 thousand to 50 thousand rubles, legal entities - from 100 thousand to 300 thousand rubles. Larger fines are provided for in case of repeated violation: an official can be fined in the amount of 300 thousand to 500 thousand rubles, an individual entrepreneur or legal entity - from 500 thousand to 1 million rubles, or his work can be suspended for up to 90 days.
The law also provides for fines for individuals, but this does not apply to refusal to vaccinate, Khoruzhenko reassures. By law, an employer cannot force an employee to get vaccinated; he can only motivate the employee in some way to get vaccinated (for example, in some companies an employee is given an additional day off).
“The law does not provide for consequences if an employee refuses to be vaccinated,” the lawyer emphasizes. “But the employer can take some internal measures, use unofficial levers of pressure. The employer must independently motivate 60% of employees to get vaccinated. That is, this is a semi-compulsory-voluntary story, and not mandatory vaccination.”
Khoruzhenko admits that in the future some article may be introduced into the Labor Code of the Russian Federation that will enable the employer to impose sanctions on an employee who does not want to be vaccinated, but at the moment this is not provided for by law.
It should be noted that many organizations and institutions had already begun a vaccination campaign long before the decree was issued.
In particular, the press service of the Higher School of Economics reports that from the moment vaccines against COVID-19 became available, the university has been constantly doing everything possible to motivate employees and students to get vaccinated. The second vaccination campaign is currently underway at the HSE; The demand for vaccination is high, and the university vaccinates everyone, including foreign citizens and even relatives of students and employees. For this purpose, the HSE operates a medical center that provides vaccinations with two drugs that have passed state registration in the Russian Federation.
Video on the topic
Should you get vaccinated? The immunologist answers:
It is difficult for a person who does not have a medical education to understand all the terminology that doctors use. Many people think that vaccination and vaccine are the same thing. In fact, these are two completely different concepts.
Vaccination is a process that involves introducing antigenic material into the body in order to protect against infectious and viral pathologies. A vaccine is a drug used to develop protection against specific diseases. These two concepts are interconnected and cannot exist separately.
What is the difference between all COVID-19 vaccines and what should you know when getting vaccinated? Category "Antivirus"
Vaccination is the most reliable way to protect yourself and your loved ones from severe COVID-19, doctors repeat. There is no more reliable evidence of safety than the mass vaccination that is actively underway around the world. Each drug has its own protection mechanisms, but the rules of vaccination are general.
Pfizer, Moderna, Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca, Sputnik V, Sinopharm – the names of the vaccines are well-known, but the differences are not.
There is a lot of information about drugs against COVID-19 on the Internet, and it’s not easy to understand. Taking into account the fact that scientists continue to develop potential vaccines against coronavirus. But all of them (current and future) are designed to teach the body's immune system to safely recognize and block the virus that causes COVID-19.
But the difference between the drugs is in the approach to development. There are three main ones, depending on what is used for immunization: a whole virus or bacterium, fragments of a microorganism (causing an immune response) or just genetic material.
Most coronavirus vaccines are given in two injections, one after the other after a certain period of time. Between the first and second injection, our body may be weakened. Are you sick? It is recommended to postpone the second stage of vaccination. A break is possible for up to two months - without any damage to the effectiveness of the vaccination.
For the first time after vaccination, it is recommended to be under medical supervision. In case of a possible allergic reaction. It is better not to wet or rub the injection site for one or two days. For a couple of days, give up physical (and, if possible, emotional) stress. And now – about side reactions.
Most people tolerate the vaccine without any special symptoms: mild weakness, pain, redness or swelling at the injection site, mild muscle discomfort, and sometimes fever are possible. Much less often - mild chills, nausea.
All these are absolutely normal reactions during the formation of immunity, experts say. It is advised not to lower the temperature to 38 degrees. If it gets higher, you can take an antipyretic that you usually use for a cold.
Vaccinated means protected, doctors repeat. The greater the proportion of those in a society who have been vaccinated, the higher the collective immunity, which means the lower the risk of a surge in diseases.
The main thing that every vaccinated person should be aware of is that the vaccine does not protect against infection, but against a severe course of the disease, in order to reduce the likelihood of such a development of events.
So, even after vaccination, you should not neglect safety measures: it is still necessary to maintain distance and wear a mask in public places. A vaccinated person can carry the virus without knowing it.
Until the coronavirus is defeated, attention to health should be increased as much as possible. And by getting vaccinated, you protect both yourself and those around you.
Subscribe to us on Telegram