When should you take the Quantiferon test?
- Comprehensive diagnosis of tuberculosis infection in combination with clinical and radiological data in children, people at risk (medical workers, people with immunodeficiency or people who have been in contact with a TB patient);
- Investigation of a questionable result of the intradermal Mantoux test (especially in patients vaccinated with BCG);
- If there are contraindications for skin tests (skin diseases, exacerbation of allergic or infectious pathologies).
Carrying out Mantoux and Diaskintest compatibility
Mantoux and Diaskintest are placed in the forearm. This “button” is known to many children from early childhood. A special thin needle is used to inject the solution. The drug is injected directly under the skin. Dosage – 0.2 ml. If the nurse inserts the needle carelessly and injures the blood vessels, a bruise may appear at the injection site. This cannot be considered a positive reaction to manta rays.
We recommend reading! Follow the link: Clinical observation groups
Diaskintest is placed in the right forearm for right-handers, and in the left for left-handers. Just like for the Mantoux test, a special thin needle is used and the drug is also injected under the skin. Dosage – 0.1 ml. Usually Diaskintest is given after a positive Mantoux reaction, but both drugs can be given at the same time. The main condition: you need to inject tuberculin into one hand, and do Diaskintest into the other.
Detailed description of the study
Tuberculosis (TB, Tb) is a chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis, MBT). MTB can affect all organs and tissues, but most often tuberculosis infection affects the lungs. Tuberculosis can affect both adults and children.
The difficulty of diagnosing tuberculosis is based on the various variants of the course of the infection. There are active tuberculosis (with clinical manifestations) and latent, or latent, tuberculosis infection (LTBI). LTBI is characterized by the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the body, which can be detected using special laboratory tests, but the presence of MBT in the body is not accompanied by clinical and radiological signs of TB infection.
The goal of LTBI detection is to prevent progression of asymptomatic TB infection to active TB and to initiate treatment early. The most common method for detecting LTBI is the tuberculin skin test (TST) or Mantoux test. Thanks to this test, MTB infection is determined, risk groups for TB infection are formed, and individuals are selected for vaccination or revaccination against tuberculosis. This test is also used to diagnose TB in children. However, the Mantoux test has a number of disadvantages, which include:
- Subjectivity when interpreting results;
- Lack of differentiation between active TB and LTBI;
- Insufficient diagnostic sensitivity in immunocompromised patients;
- The likelihood of false-positive results in patients who have been vaccinated with BCG (tuberculosis vaccine) or infected with mycobacteria that do not cause TB.
In this regard, an alternative diagnostic method was developed - QuantiFERON-TBtest (QFT), or quantiferon test. It is based on the determination of specific proteins in the blood - gamma interferons (γ-IFN), which are produced by T-lymphocytes in response to the entry of mycobacterium tuberculosis into the body. The advantages of QFT include:
- High specificity and sensitivity compared to TST;
- The result does not depend on previous BCG vaccination;
- Safety: unlike the Mantoux reaction, the study does not involve the introduction of any substances into the body.
This method, as an alternative to the Mantoux test, is approved by many authoritative medical societies, including the World Health Organization.
However, like the Mantoux test, the quantiferon test does not distinguish active tuberculosis from latent tuberculosis infection, so the result of this analysis must be compared with the clinical picture of the disease, X-ray diagnostic data and other studies.
Diaskintest or Mantu which is better
Many parents believe that the Mantoux test and Diaskintest are procedures that are no different from each other. They are really similar: in both cases, the medication is injected under the skin with a special thin needle, and the body’s reaction is checked after 72 hours (three days). However, there are still differences between Mantoux and Diaskintest. The difference lies in the composition of the drug administered.
In the early 1950s, the World Health Organization approved the tuberculin standard (PPD-S, tuberculin-Seibert). Since 1954, in our country, diagnosis of tuberculosis has been carried out using Lennikova purified tuberculin (PPD-L). The activity of tuberculins is indicated in TE - tuberculin units. This is an already diluted standard drug, and its use eliminates the human factor during testing, when medical personnel make mistakes when diluting the drug.
The drug used for the Mantoux test is supplied in the form of a solution to medical institutions and pharmacies. Dosage: in 0.1 ml - 2 TE PPD-L, but there are also higher values - 5 TE, 10 TE in 0.1. In simple terms, the testing solution is tuberculin, which is destroyed mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is recognized by the body as a potential threat. The immune system begins to defend itself and produces antibodies. Based on the body's reaction, it becomes clear whether the child is sick.
In 2009, doctors began doing Diaskintest. Its difference from Mantoux is that it is not tuberculin that is injected under the skin, but a tuberculosis recombinant (obtained through genetic engineering) allergen. And this solution, unlike PPD-L, makes it more likely to detect infection with Koch’s bacillus.
We recommend reading! Follow the link: The first signs of pulmonary tuberculosis in women at an early stage
Which test is more accurate?
Many years of observations have made it clear that the reliability of the Mantoux test result is no more than 70%. The body reacts equally to both Koch's bacillus, which causes tuberculosis, and to a recently received BCG vaccination. When the question arises whether the Mantoux test or Diaskintest is better, doctors are unanimous: Diaskintest shows the correct result in almost 100% of cases.
If the Mantoux reaction is positive, and Diaskintest indicates the absence of the disease, additional blood tests, urine tests, x-rays (for children) and fluorography (for adults), PCR analysis will not be required.
Doctors trust the proven method of detecting tuberculosis and recommend both tests, although, according to current legislation, they do not have the right to force parents to agree to this diagnostic method. Legal representatives and guardians have every right to prohibit a child from being tested if he does not have clinical symptoms of tuberculosis. In this case, your doctor may suggest another immunological test.
Which is safer?
Another question that worries parents is which is safer, Mantoux or Diaskintest. Adults often fear that the introduction of mycobacteria can cause tuberculosis infection, and for this reason they prohibit the Mantoux test from being performed on their child. In fact, the solution does not contain live and active mycobacteria, so there is no risk of infection.
Diaskintest is also safe because it contains no strains of bacteria, only protein isolated from them. However, it is the protein that can cause allergic reactions. After vaccination, you need to monitor the child’s well-being. Side effects, although rare, do occur.
References
- Guidelines for the management of patients with latent tuberculosis infection. World Health Organization, 2015. - 84 p.
- Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of latent tuberculosis infection in children. - M.: ROOI "Human Health", 2015. - 36 p.
- Clinical guidelines for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) in children, 2021. - 13 p.
- Materials from the reagent manufacturer. — URL: https://www.quantiferon.com/products/quantiferon-tb-gold/ (access date: 05/12/2021).
Decoding the results
Many parents are concerned about what is more harmful, the Mantoux test or the Diaskintest. In fact, both types of testing are absolutely safe for the child. The Mantoux test and the d-test can be performed on one-year-old children.
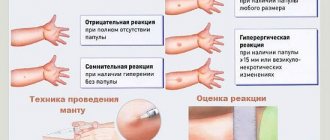
The results in both cases are assessed after 72 hours. The medical worker’s task is to check the injection mark, the presence or absence of infiltrate (red spot) and its size. We can talk about a negative reaction of the body when there is no redness or swelling at the injection site.
When performing a Mantoux test, a papule with a diameter of more than 1.7 cm should cause concern. This may be a direct indication of infection with tuberculosis. But, even in this case, it is too early to draw conclusions and make an accurate diagnosis. Usually, after a positive Mantoux reaction, Diaskintest is given.
If the Diaskintest result is positive, the child is prescribed additional diagnostic procedures.
If bubbles or ulcers appear near the injection site, this is a manifestation of an allergy, a hyperergic reaction. The child’s body reacted negatively to individual components of the drug, and in such a situation it cannot be stated or denied that there is a positive reaction to Mantoux or Diaskintest, an additional examination is prescribed.
When is replacement needed?
The Mantoux test is a diagnostic test that detects the presence in the body of mycobacteria that cause tuberculosis. A special drug called tuberculin is injected intradermally to assess the immune response. But this method has significant drawbacks, because the positive reaction is ambiguous.
It could mean:
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection;
- infection with other bacteria;
- recent BCG vaccination;
- allergic reaction.
A positive reaction to tuberculin administration after BCG vaccination makes the diagnosis of tuberculosis especially difficult. This is a preventive vaccination that is given to a child 2 hours after birth in the maternity hospital and revaccination is carried out at 6 years of age. The vaccine contains weakened mycobacterium bovine tuberculosis (Mycobacterium bovis). They contribute to the formation of the body's immune defense against possible infection. After vaccination, antibodies are produced to fight pathogenic microflora.
In addition to the BCG vaccine, the new BCG-M vaccine is used. It contains 2 times less antigens than a preventive vaccination. The BCG-M vaccine is given to premature, low-birth-weight babies. It is not used immediately after birth in the maternity hospital, but already in the hospital.
Tuberculin does not contain living microorganisms - only their metabolic products and particles of the cellular structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis. But this is enough for a reaction to tuberculin to appear after vaccination, which is considered a false positive. This effect is used to identify the need for revaccination, which is recommended in case of a negative reaction to the Mantoux test and the absence of a post-vaccination scar.
If it is necessary to check for the presence of acquired Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in recently vaccinated patients, the doctor prescribes Diaskintest instead of Mantoux.
In the absence of an active form of tuberculosis, DST gives a negative result.
Another disadvantage of Mantoux is the possibility of a positive reaction to tuberculin when infected with bacteria that do not cause tuberculosis. An allergic reaction to tuberculin tests can also contribute to obtaining a questionable result. For children with allergies, the Diaskin test is recommended instead of Mantoux.
Diaskintest can be done for adults and children over 1 year old. This diagnosis makes it possible to avoid prophylactic administration of anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy drugs, which are prescribed for a false-positive reaction to tuberculin.
Despite the fact that new tests are used in the diagnosis of tuberculosis, children need to have a Mantoux test done annually, but since this method gives false-positive and questionable results, if infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis is suspected and in a possible phase of the disease with active proliferation of mycobacteria, the Diaskin test is additionally performed .
It is not recommended to completely switch to using this method and abandon Mantoux, because Diaskin does not diagnose the early stages of infection. Determining the onset of the disease is especially important for effective treatment of children and prevention of the development of local forms of tuberculosis in the early period of infection.
T-spot and quantiferon test
As an alternative to the Mantoux reaction, scientists have developed a new method for the immunodiagnosis of tuberculosis: T-spot and quantiferon test, the results of which are not affected by previous BCG vaccination.
- The quantiferon test is based on a method for determining interferon gamma in the blood, which is produced by cells of the immune system (T-lymphocytes) when the tuberculosis bacillus enters the body.
- T-spot determines the number of T-lymphocytes themselves, sensitized by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
In terms of sensitivity and reliability, these methods are equivalent, the indications for the procedure are the same.
Blood test: interpretation of the result
There are 3 types of test results:
- Positive - antibodies found. The person was in contact with a patient with tuberculosis. A positive result may also indicate a latent form of tuberculosis. It is necessary to schedule an additional examination: x-ray of the lungs, computed tomography of the cell, sputum analysis, etc.
- Negative - no tuberculosis infection was detected in the body.
- Doubtful - this indicates that the immune response in the body has begun, but has not developed to its full potential. Therefore, the patient’s condition must be monitored and re-diagnosis (T-SPOT or Diaskintest) carried out after a few months. Also, the test can give a questionable result if the patient develops an immune response not to specific tuberculosis antigens, but to other infections. For example, in children it may be associated with the herpes virus. In case of a questionable result, some laboratories offer free re-testing.
After receiving the T-SPOT result, parents need to show the test to a TB doctor. The doctor will examine the child and write a report that can be shown in a child care institution, be it a kindergarten or school. However, the result of one test without a certificate from a TB doctor will not be considered valid. Do not forget that employees of children's institutions are not doctors and have no right to decipher the diagnostic results. It is recommended to make a decision on the specific choice of diagnostic method for your child, taking into account his health characteristics, together with a TB specialist.
Pros of T-SPOT
- research without intervention in the body. To diagnose tuberculosis, only a blood test is needed; — the study is suitable for children with allergic reactions and skin diseases; — early diagnosis of tuberculosis; - high specificity (specificity reaches 97%, this is the ability of the test not to give a false positive result in the absence of mycobacteria); - does not respond to the administration of the BCG vaccine. The Mantoux test can give a similar reaction; — no side effects or contraindications for the test; — the study is suitable for pregnant women who have been in contact with tuberculosis patients.
How to do it
Diaskintest and Mantoux test are done in the same way: a small amount of the drug is injected intradermally on the inside of the lower third of the forearm.
Carrying out a tuberculin test has its own characteristics:
- When mass tuberculin diagnostics is necessary, a needle-free injector is used. The cutaneous injection method is quick and painless.
- Considering that the immune reaction to tuberculin can become stronger only because it got into the site of the previous test, the place of administration of the drug changes: in an odd-numbered year, Mantoux is given in the left hand, in an even-numbered year - in the right.
- With the GST method (graduated skin test), tuberculin is applied to the forearm with decreasing concentration. Scarification is carried out in the opposite direction.
There are 6 types of reactions to GCT:
What do you think are the most important factors when choosing a medical institution?
- anergic (negative response from 0% to 100%);
- nonspecific (slight redness at 100%);
- normergic (moderate response from 25% to 100%, negative from 0% to 5%);
- hyperergic (increase in hyperemia from 0% to 100%);
- equalizing (positive answer from 0% to 100%);
- paradoxical.
In case of allergic reactions to the Mantoux vaccination, tuberculin test or Diaskin test, it is recommended to take a three-day course of antihistamines recommended by the doctor the day before. In case of individual intolerance to injection tests, the use of ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method) is considered.
How long after Mantoux can you do it?
Diaskintest and Manta can be done simultaneously in different hands or at any time interval.
This is due to the difference in the compositions of the drugs used during testing. Simultaneous testing on different hands was carried out in studies of the effectiveness of these diagnostic methods. The test groups were recruited from pre-examined people who, in one case, had a confirmed disease, and in the other, the subjects were reliably healthy. The results showed that none of the methods gives 100% results.
The standard period after Mantoux for the next tuberculin test is 6 months or 1 year. It is recommended to carry out tuberculin diagnostics at the same time of year, mainly in autumn.
The Mantoux test can be performed twice a year for the following children:
- with chronic nonspecific respiratory diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes mellitus;
- receiving hormonal, radiation and cytostatic therapy;
- HIV-infected people.