In the middle of this year, new Sanitary and Epidemiological Rules “Conditions for the transportation and storage of immunobiological preparations” (SanPiN 3.3.2.3332–16) came into force. They were approved by Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated February 17, 2016 No. 19
. The topic of the rules for storing immunobiological drugs deserves special attention, since we are talking about drugs that require not just special, but, so to speak, “super-special” handling, and errors in working with them can result in significant problems for consumers-patients, and impressive administrative sanctions for pharmaceutical and medical organizations.
What is ILP?
The topic of immunobiological drugs (hereinafter also referred to as IL drugs)
or ILP) is more than relevant at the beginning of autumn. The transition from warmth to cold, from sun to cloudiness and rain, from rest to hard work is a risky period for the immune system. Summer bliss gives way to autumn colds, to which weakened organisms are especially susceptible.
First, let’s answer the question, what is ILP and what drugs are classified as immunobiological? This is far from an idle question, because pharmaceutical specialists working in the pharmacy and distribution segments often ask how to determine whether a particular drug belongs to the IMP.
According to clause 7 of the conceptual art. 4 of the Federal Law “On the Circulation of Medicines” (No. 61-FZ dated April 12, 2010), this concept refers to drugs intended for the formation of active or passive immunity or for diagnosing the presence of immunity or diagnosing a specific acquired change in the immunological response to allergenic substances . Accordingly, they are used for therapeutic, preventive and diagnostic purposes.
According to the mentioned paragraph of Law No. 61FZ, the list of immunological drugs includes vaccines, toxoids, toxins, serums, immunoglobulins and allergens. In this matter, there is a contradiction between the Law “On the Circulation of Medicines” and the General Pharmacopoeial Article “Immunological Medicinal Products” (OFS.1.8.1.0002.15). The latter also includes other biological drugs in the list of medical immunobiological drugs: bacteriophages, probiotics, cytokines, including interferons, microbial enzymes, etc., as well as drugs produced through biotechnological processes, including using genetic engineering.
So which of these legal acts should we follow? Here, pharmaceutical specialists can be recommended to adhere to the primacy of Law No. 61-FZ, since other regulatory legal acts, including the State Pharmacopoeia, are developed and adopted to implement its norms. Therefore, the requirements imposed by law for the conditions of storage and transportation of medical immunobiological drugs - they will be discussed below - do not apply to probiotics, bacteriophages, cytokines, including interferons, and microbial enzymes.
Surely the Ministry of Health is working to bring the norms and terms of various regulatory legal acts into compliance with the provisions of Federal Law No. 61FZ. But if we move from the dry language of jurisprudence to the living human language... In an amicable way, it would be easier for pharmaceutical practitioners if each package of IMP were marked with some identifying sign or at least the abbreviation “IMP”, indicating that it belongs to to the list of immunobiological drugs.
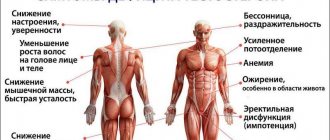
ILPs are available in different dosage forms: tablets, capsules, granules, powders, lyophilisates, solutions, suspensions, suppositories, ointments. IL drugs are very labile, so it is difficult and responsible to work with them. For example, violation of the rules and conditions for storing vaccines is one of the main reasons for the development of post-vaccination complications. This alone speaks to the importance of the topic of proper handling of this group of drugs at all production and logistics stages, as well as during the storage of biological products in medical and pharmacy institutions.
Experts call difficulties in transporting COVID vaccines in Russia
From December 7, Russia will begin mass vaccination of almost 2 million doses of coronavirus vaccine. However, transporting such volumes may face problems. RBC asked experts to name them and describe solutions
Photo: Sergey Bobylev / TASS
When mass vaccination against coronavirus begins in Russia, the key problem will be maintaining the required temperature of thousands of doses of the vaccine, doctors and companies interviewed told RBC. According to them, increasing the temperature inside a car or plane by even half a degree for half an hour will lead to the fact that the “thawed” batch of vaccine will have to be thrown out. Representatives of the authorities of various regions told RBC that the transportation conditions have been thought out for a long time.
Video
Mass vaccination against coronavirus will begin in the second week of December. This was announced by President Vladimir Putin, saying that Russia has already produced about 2 million doses of the vaccine for these purposes. Departments have exactly a week to develop rules for transporting the vaccine to hospitals - this is exactly the deadline Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin gave on Thursday, December 3.
Mishustin gave a week to develop rules for the delivery of the COVID-19 vaccine Society
Problems with undemanding vaccines
Russian vaccines against coronavirus infection are less demanding on storage conditions than vaccines developed in the USA and Germany.
Vector vaccine “Sputnik V”, developed at the Center named after. N.F. Gamaleya, exists in two forms: frozen (liquid “Gam-COVID-Vac”, storage temperature - no higher than minus 18 ° C) and lyophilized form (powder “Gam-COVID-Vac-Lio”, temperature storage from plus 2 to plus 8 °C). The peptide vaccine EpiVacCorona, developed in Novosibirsk, can be stored at temperatures from plus 2 to plus 8 °C. For comparison, the American Moderna vaccine and the drug developed by Pfizer and BioNTech require much lower storage temperatures - minus 70-80 ° C.
Read on RBC Pro
The Great Dismissal: Why Russia is Expecting a Mass Exodus of Employees
Get out of here: why top managers in Russia can’t find work
What is important to know about the unfolding energy crisis in Europe
Will the collapse of China's largest developer be the beginning of a global crisis?
However, when transporting domestic drugs, problems may still arise related to the need to strictly observe the temperature regime, doctors, laboratory and logistics employees told RBC, - Alexander Chepurnov, a researcher at the Federal Research Center for Basic and Translational Medicine, professor of virology, told RBC. This problem, according to him, becomes especially relevant when it comes to the supply of large volumes of the drug.
The so-called cold chain, that is, adherence to a strictly defined temperature for the storage and transportation of medical drugs from the moment of production to its intended use, is necessary not only for vaccines against COVID-19, and therefore has long been built by the Ministry of Health, the head of the laboratory of vaccine prevention and immunotherapy of allergic diseases told RBC Federal State Budgetary Institution "Research Institute of Vaccines and Serums named after. I. I. Mechnikov" Mikhail Kostinov.
In Moscow, they named the number of people who got sick during COVID vaccine trials Society
According to the expert, most vaccines used in Russia are stored at temperatures from plus 2 to plus 8 ° C, and if the drug requires storage at lower temperatures, then it cannot be used in rooms where there is no special equipment.
“There are refrigerators at minus 20 °C [in hospitals], they were intended for immunobiological preparations: serums, which must be stored frozen, biomaterials. Vaccines require special equipment. There should be additional generators that should turn on in case of a power outage,” he said.
Trucks against the epidemic
Immunobiological drugs are delivered to the end consumer in several ways: by car, by air delivery, or by combining these methods (multimodal transportation). For all these types, violation of the storage temperature of coronavirus vaccines remains the main risk, experts from transport companies specializing in the transportation of pharmaceuticals told RBC.
Currently, the transportation of vaccines in Russia is regulated by the requirements of SanPiN “Conditions for the transportation and storage of immunobiological medicinal products,” according to which drugs delivered in violation of the cold chain cannot be used, Stanislav Bulygin, responsible for the quality of transportation, told RBC.
Manturov personally delivered samples of the Russian COVID vaccine to Uzbekistan Society
“Literally this means the following: for example, if the temperature regime is violated by one minute and by 0.5 ° C, the product cannot be used. That is, it must be destroyed,” Bulygin explained.
This problem, according to him, is now being successfully solved with the help of thermal boxes (thermoboxes), the technology for using which is provided for by SanPiN. According to the expert, it has been well developed by participants in the circulation of medicines.
The use of thermal boxes, that is, tightly closed containers filled with cold elements, allows for good control of bottlenecks in transportation and reliably stops other possible risks: physical damage, getting wet, penetration of dust, dirt, etc.
According to Bulygin, Russian logistics companies now have enough transport capacity to deliver the required volume of vaccine: large thermal boxes (so-called pallets) can hold about 10 thousand doses of the vaccine. The truck can accommodate 30 such boxes, that is, one vehicle is capable of delivering 300 thousand doses of the vaccine, which is comparable to the population of an average city.
Bulygin believes that difficulties associated with a lack of knowledge and experience may arise if it is necessary to deliver a version of the vaccine that requires storage at a temperature of minus 18 ° C. “The entire process of storing and transporting a vaccine with a regime below minus 18 ° C on a national scale is a new process. And we know that everything new requires more attention, configuration, debugging, and, if necessary, correction,” he said.
“The market is more adapted to working with temperatures of plus 2 and plus 8 ° C, since the largest number of immunobiological drugs require this temperature. The equipment will be sufficient for targeted air delivery of cargo,” agrees Oleg Baykov, Deputy General Director of Biocard Logistics.
We agree that Russia is ready for large-scale vaccination from the point of view of transport infrastructure, and in the group, which is also involved in air transportation of pharmaceutical products. The company said that the main problem that has arisen in connection with the delivery of the vaccine at many airports around the world is the bottleneck effect due to the insufficient equipment of airports and warehouses for storing vaccines at a given temperature.
However, it can be overcome through careful planning. Thus, during air deliveries, maintaining the temperature regime is ensured using special containers capable of strictly maintaining a given temperature in the range from minus 20 to plus 20 °C for several days (RAP and RKN circuit containers). And warehouse storage can be avoided by reloading vaccines from a transport aircraft directly into refrigerated vehicles designed to transport temperature-sensitive cargo.
How coronavirus Halloween was celebrated in different countries. Photo report Photo gallery
A problem with vaccine delivery may arise at a time when large volumes of cargo need to be delivered by road over long distances, says Oleg Baykov, Deputy General Director of Biocard Logistics. According to him, transportation in thermal boxes has a significant drawback - the increased weight and volume of cargo due to packaging, which inevitably leads to an increase in delivery costs.
“DHL is already talking about 15,000 flights and 200,000 pallet spaces that will need to be moved under strict temperature control just to meet the basic vaccination needs of the global population. If we repackage products in thermal containers, we will need three times more shipping containers,” Baikov quotes estimates from a foreign company.
At the same time, according to him, despite all its shortcomings, thermal packaging is “the only complete way to maintain a truly stable cold chain.” “[Without thermal boxes] it will simply be impossible to avoid temperature issues when delivering unstable frozen forms of vaccines during loading and unloading; it will simply be impossible to deliver products to remote areas of our country,” he believes.
At the same time, he draws attention to the fact that refrigerators without thermal boxes are not suitable for the delivery of vaccines that require great precision in observing the temperature regime: inside the vans the temperature can “walk” in the range of plus 5 ° C, which is unacceptable. You cannot transport drugs that need to be stored at temperatures below minus 20 °C in vans without thermal boxes. “There are only a few such refrigerators that would cool to temperatures below minus 20 °C,” he explains.
Baikov calls transportation in thermal containers that can maintain a given temperature for three to four days the optimal way to transport the vaccine; for greater reliability, they can be loaded into refrigerators.
EIU economist doubts availability of vaccine before end of 2021 Society
How the vaccine is delivered to the regions
St. Petersburg Health Committee reported that the first two batches of the Sputnik V vaccine, intended for doctors, arrived in the city in the fall (442 doses). The third batch - 1,600 doses - arrived on December 3. The drug arrives in a liquid state, it must be stored at a temperature no higher than minus 18 ° C, the department reported to RBC St. Petersburg.
The Ministry of Health of the Nizhny Novgorod region reported that they expect to receive 2,772 doses of the GAM-COVID-Vac vaccine. According to the department’s statement, the storage and transportation of the vaccine is ensured “in accordance with the requirements of sanitary legislation SP 3.3.2.3332-16 “Conditions for transportation and storage of immunobiological preparations.” In total, conditions for vaccination have been created in nine medical organizations; letters have been sent to their heads “about the need to purchase refrigeration equipment to ensure storage conditions for the vaccine at a temperature of minus 18 ° C,” according to a message from the Ministry of Health received by RBC Nizhny Novgorod.
The Ministry of Health of Bashkiria reported that the first batch of vaccine in the region is expected on December 4-5. According to representatives of the department, two months ago, in anticipation of the first delivery, storage and transportation conditions were thought out. Minister of Health of the Republic Maxim Zabelin previously said that 1 thousand doses of the vaccine would arrive in the region by the end of the week.
“We are expecting the drug “Gam-COVID-Vac” (trademark “Sputnik V”). Federal services will deliver it to, which is provided with the necessary equipment for storing and transporting the vaccine,” Sofya Aleshina, press secretary of the regional Ministry of Health, told RBC Bashkortostan. According to her, this state-owned enterprise also has portable bags that maintain the required temperature conditions.
The choice of medical institutions for vaccination will depend on the volume of drugs. An option is currently being considered in which the vaccination campaign will be carried out in one or two clinics. Thus, vaccination of volunteers as part of post-registration trials of the vaccine in the region took place at polyclinic No. 52 in the city of Ufa. According to Aleshina, all 42 volunteers who were vaccinated from the first batch feel well, and there were no cases of coronavirus infection among them. There are “enough” people willing to get vaccinated in the region, she said.
More than 50 countries have submitted applications for the purchase of the Sputnik V vaccine Society
In the Perm region, they are waiting for the first batch of vaccine, designed for a two-time administration to 2,249 patients, reported the head of the region, Dmitry Makhonin, without specifying which drug will arrive in the region. According to him, medical workers will be vaccinated first, the vaccine will go to medical institutions in Perm, Berezniki and Tchaikovsky, where it is possible to provide the necessary storage conditions for the drug, and doctors will be brought there from departments repurposed for the treatment of patients with coronavirus.
In Moscow, vaccination points as part of the mass vaccination campaign will start operating on December 5, said the mayor of the capital, Sergei Sobyanin. Education workers, healthcare workers and city social service workers will be able to sign up for vaccination. According to him, the entire technological and organizational chain of vaccination has been created in the capital, warehouses, refrigerators and refrigerated containers have been prepared for the delivery of the vaccine. Vaccination points are already equipped with medical refrigerators, and staff have received special training.
According to Moscow Deputy Mayor for Social Development Anastasia Rakova, the capital was able to create the necessary logistics chains for storing and transporting the vaccine “at a temperature not exceeding minus 18 ° C in a place protected from light,” Rakova said. “To do this, we had to work out in detail the observance of the cold chain, which involves the delivery of the vaccine in special vehicles, in special thermal containers and subsequent storage at the institutional level, at the level of vaccination points in special medical freezers,” she added. At the same time, in Moscow they equipped “a special freezer that allows us to store large quantities of the vaccine - more than a million -,” Rakova said.
In Tatarstan, vaccination will begin next week, 3,700 doses of the Sputnik V drug will arrive. Vaccinations will be given in 40 medical institutions in the region, Liliya Galimova, head of the press service of the President of the Republic, told RBC Tatarstan. In addition, post-registration trials of the EpiVacCorona vaccine (developed by Vector) will begin in the republic, the press service of the regional Rospotrebnadzor told RBC, 500 doses of the drug have already arrived in the region. The EpiVacCorona vaccine is delivered to the republic using specialized transport, but it is not specified whether it will be by land or air. The temperature regime specified by the storage requirements was observed, the department assured.
According to the Deputy Minister of Health of Tatarstan Vladimir Zhavoronkov, places for storing the vaccine have now been worked out in the medical institutions of the republic. “The design of the study is entirely up to Rospotrebnadzor. All freezers and refrigerators are prepared,” he noted.
In addition to Tatarstan, pilot studies of EpiVacCorona will take place in four more regions: Moscow , as well as the Moscow , Tyumen and Kaliningrad regions.
Four levels of cold
Let's start with where these very requirements for immunobiological drugs are prescribed. In the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated August 23, 2010 No. 706n “On approval of rules for storing medicines,” they are not mentioned even once. Clause 32 of this regulatory act contains only a general indication that thermolabile medicines must be stored in accordance with the temperature conditions indicated on the primary and secondary packaging. ILPs, of course, belong to this group of drugs, but even among heat-labile drugs they form a special group, so this instruction is clearly not enough to organize their proper storage.
More comprehensive and detailed standards governing the storage conditions of immunobiological preparations can be found, in particular, in the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation. Let us highlight from GPM.1.1.0010.15 “Storage of Medicines” what concerns the topic under consideration. This pharmacopoeial monograph first of all notes that the proper quality of IMP, the safety and effectiveness of their use is ensured by the “cold chain” system
in a complex, that is, at all four of its levels. Their listing is contained in Section II of the above-mentioned Sanitary and Epidemiological Rules (hereinafter referred to as the Rules).
The first level of the “cold chain” is the delivery of individual products from the manufacturer to the wholesaler, including the customs clearance stage. The second is the storage of drugs of this group by drug wholesalers and their delivery to pharmacies and medical organizations (including individual entrepreneurs with a license for pharmaceutical or medical activities), as well as to other pharmaceutical distributors. The third level is storage of medical products by these same pharmacies, medical organizations and entrepreneurs, their retail sale, as well as delivery to other medical organizations or their separate divisions (local hospitals, clinics, outpatient clinics, maternity hospitals). Accordingly, the fourth level is the storage of immunobiological preparations and the organization of a cold chain in pharmacies and medical institutions.
From two to eight... Celsius
From OFS.1.1.0010.15 and OFS.1.8.1.0002.15, as well as from paragraphs. 3.2 and 3.5 of SanPiN it follows that ILP must be stored at a temperature from +2 °C to +8 °C, unless otherwise specified in the instructions for use or other regulatory documentation. That is, we are talking about ensuring a storage regime, which is called a “cold place” in the Global Fund. As for the transportation of immunobiological medicinal products, GPM.1.8.1.0002.15 emphasizes that its temperature and other conditions should not differ from those for storing IMP. Thus, the conditions for transportation and storage of immunobiological drugs are the same.
The rooms in which refrigerators are located for storing ILP should not overheat above +27 °C. GPM.1.1.0010.15 also specifies that access to cooled air must be provided to each package of ILP in the refrigerator. Let us recall in this regard that modern pharmaceutical refrigerators are equipped with appropriate air flow circulation systems. In addition, to comply with this standard, the packaging of IL-drugs should not be piled on top of each other.
It should also be borne in mind that OFS.1.1.0010.15 and clause 6.19 of the Rules do not allow storing ILP on the door panel of the refrigerator
. The logic of this ban is clear - the air temperature in this part of the refrigeration device is higher than in its other parts, and accordingly, the risk of going beyond +8 °C is higher. However, this standard is of little relevance for those who use pharmaceutical refrigerators rather than ordinary ones.
Correct connection of the refrigerator
When connecting, you need to take into account a number of nuances:
- compliance with the location where the equipment is located;
- distance to the walls of the room and nearby furnishings;
- state of the socket, the refrigeration unit will be connected;
- availability of thermometers.
When choosing a place for a refrigerator, you should be guided by the main goal - to strictly follow a number of rules. From this point of view, the most preferable is a separate room equipped with a modern ventilation system. It is also necessary that heating devices and any heat sources are located at a sufficient distance from these chambers.
The placement of the refrigerator is considered to comply with cold chain standards if it is placed on a level surface. Therefore, when installing it, use a building level. The unit is placed at a distance of 10 cm from the walls, which will ensure normal air circulation.
Before you start using the refrigerator, you need to make sure that the outlet is working properly and eliminate the possibility of accidentally disconnecting the unit from the power grid.
The readings make it possible to determine the boundaries of the permissible temperature range for the MIBP, so this device is the most important element of the control system. One thermometer should be installed in the refrigerator compartment, the second in the freezer.
Principles for storing MIBP in the refrigerator:
- according to SP 3.3.2.1120-02, boxes with vaccines sorted by type are placed in the main compartment on the middle and top shelves, and separately from each other (at a distance of 3-4 cm), a layer of cooled air is maintained between them;
- liquid vaccines such as Infanrix are stored exclusively on the bottom shelf; oral polio vaccine and lyophilized MIBP should be on top, but not very close to the evaporator;
- it is prohibited to place on door shelves, since the temperature there is not low enough;
- any others (Infanrix, DPT, Pentaxim, etc.) are recommended to be stored in the refrigerator for only three calendar months;
- expired MIBP should be disposed of rather than kept inside;
- if it is necessary to save them for observation, they are marked and moved to another refrigerator;
- to maintain a constant temperature, spare cold cells or plastic vessels with water are placed in the chamber;
- freezing of cold elements (or ice cubes) is carried out in the chamber itself;
- It is strictly forbidden to keep food and drinks together with the MIBP;
- You are allowed to open the door no more than 2-3 times a day, without breaking the rules.
They let in the fog
The following pharmacopoeial standard OFS.1.1.0010.15 must be quoted verbatim: “joint storage of immunobiological medicinal products in the refrigerator with other medicinal products is not allowed.” This norm is almost echoed by a similar instruction in clause 8.12.1 of SanPiN regarding the storage of immunobiological preparations: “combined storage of vaccines in the refrigerator with other medicines is not allowed.”
As you know, our legislation contains many vague rules that can be interpreted this way or that way. Even lawyers sometimes find it difficult to explain them. And inspectors can take advantage of this ambiguity. If you do this, they will say that you should have done it this way; Well, if you do it this way, it turns out that it should have been this way.
The 2021 SanPiN norm for immunobiological drugs “it is not allowed to store vaccines together in the refrigerator...”, which we have just outlined, seems to be attributable to such “Andromeda nebulae.” This requirement for the storage of vaccines and immunobiological drugs is perceived differently, some understand it as follows: IMPs and other heat-labile drugs must be stored on different shelves of the refrigerator. But some people draw attention to another possible interpretation of this norm: a separate pharmacy refrigerator should be allocated for storing IL-drugs.
There are signals from pharmacy workers that inspectors, during individual control activities, adhered to the second point of view. Therefore, we can recommend that pharmacists follow it for greater reliability.
The problem here is that in many, if not most pharmacies, IL drugs make up a very small proportion of the assortment (after all, we have not developed the tradition of pharmacy participation in immunoprophylactic processes). Sometimes it’s just a few or even two or three items. After all, there are no ILPs in the mandatory “minimum assortment”. It is very expensive to purchase and maintain a separate expensive pharmacy refrigerator for several assortment items - usually not among the top sellers. It’s easier to refuse to purchase these “troublesome” assortment items altogether. Simpler, but not better. It would be better if our regulators clarified this rule.
Traveling in a container
All the details of the optimal temperature regime for storing vaccines and IL drugs are set out in the new SanPiN rules for immunobiological drugs for 2021, to which we repeatedly refer. There are many of them, and such a large volume of norms cannot be covered within the framework of one article. Therefore, we can recommend that pharmaceutical specialists separately carefully study all the conditions for transportation and storage of medical immunobiological drugs.
Sections IV–VII of the new SanPiN contain requirements for refrigeration (freezing) equipment used to ensure the cold chain during transportation of industrial products, as well as for temperature control equipment. In order to properly transport immunobiological preparations, refrigerated trucks, thermal containers - including ultra-small (up to 10 dm3) and small (from 10 to 30 dm3, including medical cooler bags) - as well as cold packs should be used.
Hence the recommendation to pharmacy workers receiving goods from a representative of the carrier company not to take drugs from this group if they were delivered in a common box with other drugs (especially those requiring a different temperature regime) or if there are reasonable doubts that during transportation the temperature limits specified in the Global Fund and the Rules were violated.
"Cold chain"
In order to preserve the quality of vaccines and eliminate the risk of loss of their characteristics, a whole range of measures is provided that are aimed at creating optimal conditions for their transportation and storage as they arrive from the manufacturer to consumers. This complex is called the “cold chain”.
The cold chain is a key condition in the circulation of vaccines, which consists of several levels. If storage rules are violated at least at one level, all subsequent efforts lose their meaning.
Pharmacy organizations, as can be seen from the diagram, are located at the third level of the chain. Their management is responsible for organizing and complying with cold chain requirements.
The head of the pharmacy must approve the order appointing responsible persons. The employee who registers the receipt and transfer of vaccines must undergo preliminary training, during which he is explained the rules for transporting and storing medical supplies, and the features of working with measuring instruments and refrigeration equipment. A note about the briefing must be made in the briefing log. In the future, responsible employees must undergo annual job training.